Ferriprox Syrup
- Introduction to Ferriprox Syrup
- Composition and Deferiprone mechanism of action
- Approved Uses of Ferriprox Syrup
- Off-Label Uses of Ferriprox Syrup
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects of Ferriprox Syrup
- Common Side Effects of Ferriprox Syrup
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Ferriprox Syrup
- Drug Interactions with Ferriprox Syrup
- Administration in Special Populations
- Storage and Handling of Ferriprox Syrup
- Overdosage of Ferriprox Syrup
- Important Handling Precautions
Introduction to Ferriprox Syrup
Overview of Ferriprox Syrup
Ferriprox Syrup is a medication created to treat iron overload levels in the body that often occur in individuals who receive regular blood transfusions. The syrup is recognized for its ability to remove iron from the body and prevent health issues.
Purpose and Significance in Medical Treatment
Excessive iron levels in the body can harm organs like the heart and liver, as well as the endocrine system. Ferriprox Syrup is crucial in reducing these risks by attaching to surplus iron and facilitating its elimination from the body, thus greatly enhancing the well-being of patients.
Regulatory Approvals and Clinical Use
Ferriprox Syrup has been authorized by governing bodies such as the FDA and EMA to validate its safety and effectiveness as a therapy for thalassemia and similar transfusion-dependent illnesses.
Composition and Deferiprone mechanism of action
Active Ingredients in Ferriprox Syrup
Ferriprox Syrup contains deferiprone as its component—a potent iron chelator that specifically attaches to unbound iron ions and creates complexes that are eliminated from the body.
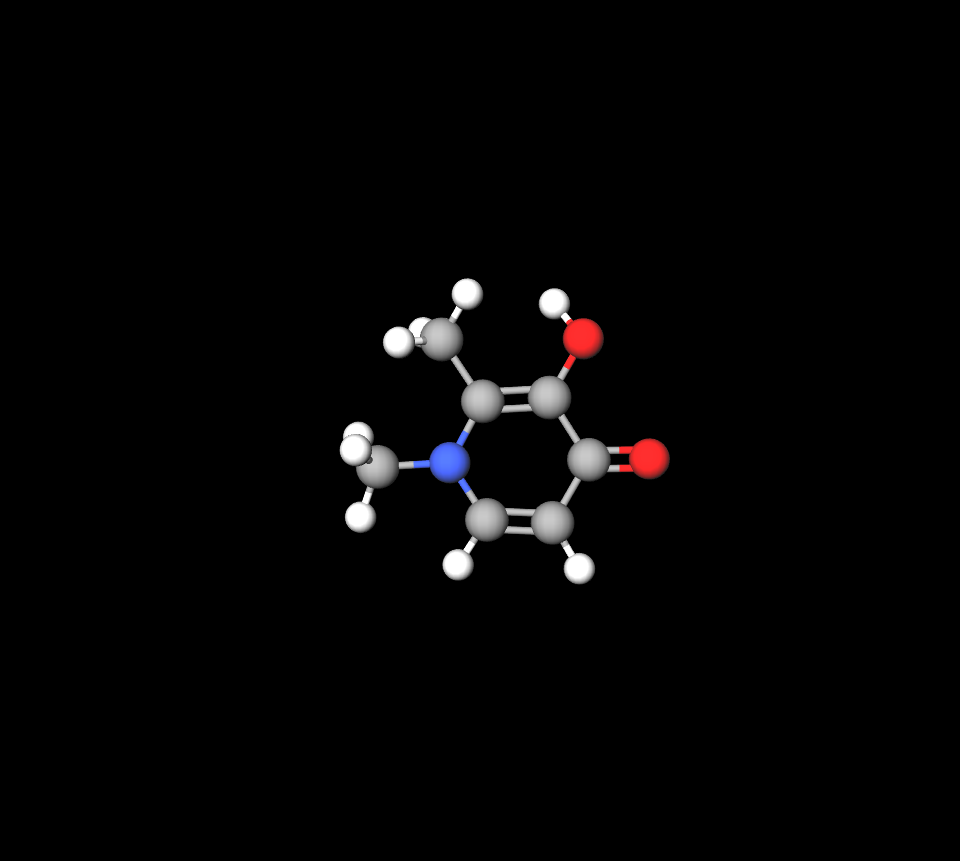
How Ferriprox Syrup Works in the Body
Upon consumption and absorption of Ferriprox Syrup, circulation occurs in the system within the blood vessels, where it focuses on iron ions to assist in their removal through urine and decrease the build-up of toxic iron levels.
Mechanism of Action in Iron Chelation Therapy
Deferiprone operates by chelating non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI), which is harmful to tissues. This process minimizes oxidative stress and prevents cellular damage, offering long-term protection for vital organs.
Deferasirox vs deferiprone
Deferiprone was more effective than deferoxamine and deferasirox in reducing iron levels and emerged as a promising treatment choice. Safety results indicated that deferasirox is associated with a likelihood of adverse effects than deferiprone, highlighting its safety advantages.
Approved Uses of Ferriprox Syrup
Primary Treatment for Iron Overload in Thalassemia Patients
Use in Sickle Cell Disease and Other Transfusion-Dependent Conditions
Beyond thalassemia, Ferriprox Syrup is effective in managing iron overload in patients with sickle cell anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, ensuring a better quality of life.
Role in Managing Iron-Related Complications in Chronic Anemia
Off-Label Uses of Ferriprox Syrup
Potential Use in Non-Transfusion-Dependent Iron Overload
Investigational Applications in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Other Conditions Under Research
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosage Based on Age and Body Weight
The usual dose is determined based on the individual's body weight range of 25 to 33 mg per kilogram. It is split into two or three doses per day to achieve the best treatment results.
Administration Instructions for Maximum Efficacy
It is advisable to consume Ferriprox Syrup either with or without food as instructed by a healthcare professional to ensure hydration throughout the treatment period.
Guidelines for Missed Doses or Overdose
In case of a missed dose, patients should take it as soon as remembered, unless it is close to the next dose. Overdose requires immediate medical attention due to potential toxicity.
Side Effects of Ferriprox Syrup
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Although Ferriprox Syrup is usually well tolerated by individuals, higher doses or prolonged usage may lead to some negative impacts, which can be effectively managed with appropriate medical supervision.
Short-Term Versus Long-Term Side Effects
Rare but Serious Adverse Reactions
Rare but serious reactions, like agranulocytosis, require monitoring of blood counts during treatment.
Common Side Effects of Ferriprox Syrup
Nausea and Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Frequent complaints include queasiness and stomach discomfort that often subside with usage.
Urine Discoloration and Its Implications
Patients frequently observe a color in their urine due to iron being expelled from the body, which is generally considered a harmless indication that the medication works effectively.
Fatigue and Mild Headaches
Sometimes, you might feel a bit tired or get a headache temporarily; however, these issues are usually not severe and pass quickly.

Warnings and Precautions
Important Warnings Associated with Ferriprox Use
Patients need to be mindful of the possibility of agranulocytosis. They should promptly notify healthcare providers if they experience symptoms such as fever or a sore throat, emphasizing the importance of blood tests for monitoring purposes.
Precautions for Patients with Pre-Existing Conditions
Patients with liver or kidney issues may need doses of medication and extra monitoring during treatment.
Monitoring Requirements During Therapy
Regular blood tests are essential to ensure that the treatment is safe and works well; they check things like liver function and serum ferritin levels.
Contraindications for Ferriprox Syrup
Absolute Contraindications
Not everyone can use Ferriprox Syrup, as it may not be safe for some individuals. Individuals with known allergies to deferiprone components should avoid it to lower any risks of infections caused by neutropenia.
Conditions Requiring Caution Before Prescribing
Before recommending Ferriprox Syrup, it's important to assess conditions such as;
- Regular monitoring of liver enzymes is needed for individuals, with existing liver issues.
- Kidney issues: Changes in dosage might be necessary.
- Bone Marrow Suppression in History: It leads to a vulnerability to blood-related issues.
Risk Factors Associated with Non-Compliance
Failure to adhere to prescribed monitoring schedules can lead to undetected complications. Irregular dosing may reduce efficacy and exacerbate iron overload, potentially causing organ damage.
Drug Interactions with Ferriprox Syrup
Known Interactions with Other Medications
Avoid using Ferriprox Syrup with drugs that lower bone marrow activity, like clozapine or immunosuppressants; combining it with iron chelators risky due to potential increased toxicity.
Foods and Substances to Avoid
Iron supplements or foods rich in iron may disrupt the chelation process, so it's recommended that patients steer clear of these items while undergoing treatment to maximize effectiveness.
Effects on Efficacy and Safety
Using antacids with aluminum or magnesium at the same time as Ferriprox Syrup might lessen its absorption capabilities. It's advisable to limit alcohol intake to avoid extra strain on the liver.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Dosage Considerations for Geriatric Patients
Older patients experience decreased metabolic and kidney function, necessitating dosage modifications according to body weight, and diligent monitoring of treatment efficacy is vital.
Monitoring Requirements in Older Adults
It's crucial to check liver and kidney function and also monitor blood counts in this group of people to reduce the chances of any harmful effects.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
Ferriprox Syrup falls into Pregnancy Category D, which suggests there may be risks to the fetus if used during pregnancy; it is advisable to use it only if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Risks to Nursing Infants
Deferiprone is released in breast milk, so nursing mothers are recommended to stop breastfeeding during the treatment to prevent any harm to the baby.
Children and Adolescents
Dosage Adjustments for Pediatric Patients
For children and adolescents, the dosage must be carefully calculated based on body weight to minimize side effects and optimize outcomes.

Safety and Efficacy Studies in Younger Populations
Studies have shown that Ferriprox Syrup is successful, in controlling iron levels in children according to clinical trials findings. However it's crucial to keep track of growth and development as a measure.
Storage and Handling of Ferriprox Syrup
Optimal Storage Conditions for Stability
Ferriprox Syrup should be stored at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep the bottle tightly closed to maintain stability.
Guidelines for Proper Handling and Disposal
Unused medication should be disposed of according to local regulations. Avoid flushing the syrup down the drain to prevent environmental contamination.
Tips for Maintaining Medication Integrity
- Store in its original container.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Do not use beyond the expiration date.
Overdosage of Ferriprox Syrup
Symptoms of Overdose and Their Severity
Symptoms of overdose include:
- Severe nausea and vomiting.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Neurological symptoms such as dizziness or confusion.
Emergency Management and Treatment Protocols
In situations of overdose, it is advised to administer stomach pumping as a step and then provide necessary care. It is crucial to reach out to poison control centers promptly for expert advice and assistance.
Long-Term Effects of Overdose
Extended exposure to an overdose can lead to liver or kidney harm, making it essential to monitor and follow up regularly to avoid long-term consequences.
Important Handling Precautions
Proper Handling to Avoid Contamination
Remember to use measuring instruments when giving the syrup and avoid touching the liquid directly to keep it sterile.
Guidelines for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to ensure medications are stored correctly, educate patients on how to handle them, and regularly check that patients are following the prescribed treatment.
Patient Education on Safe Usage
Patients need to be educated on how crucial it is to follow the recommended medication dosages and keep track of their monitoring appointments while being alert to any initial indications of negative responses.
Ferriprox Syrup FAQ
- What is Ferriprox used for?
- Is Ferriprox approved by the FDA?
- When is the best time to take deferiprone?
- What is the age limit for deferiprone?
- What is the half life of Ferriprox?
- How much iron does deferiprone remove?
- What are the side effects of deferiprone?
- What is deferiprone?
- What does deferiprone do?
- What is deferiprone used for?
- How does deferiprone work?
- Deferiprone how to take?
- How deferiprone works?
What is Ferriprox used for?
Ferriprox, also known as deferiprone is a medication prescribed for managing iron overload resulting from blood transfusions, in individuals diagnosed with thalassemia syndromes, sickle cell disease or other types of anemias.
Is Ferriprox approved by the FDA?
Yes
When is the best time to take deferiprone?
Try having a meal when you take this medicine to reduce stomach discomfort. Carry out your doses in the morning, around noon, or later, in the evening.
What is the age limit for deferiprone?
Ferriprox Tablets are recommended for adults and children aged 9 years and above, while Ferriprox Oral Solution is suitable for individuals aged three years and older.
What is the half life of Ferriprox?
1.9 hours
How much iron does deferiprone remove?
18.6% reduction
What are the side effects of deferiprone?
nausea, vomiting, stomach pain; infections; joint pain; or. abnormal liver function tests
What is deferiprone?
Deferiprone is prescribed to eliminate iron from the system in individuals with thalassemia or sickle cell disease who undergo blood transfusions or have anemia.
What does deferiprone do?
Deferiprone is prescribed to eliminate iron from the system in individuals, including adults and children aged 3 years and above who are affected by thalassemia. This disorder results in a reduced count of red blood cells.
What is deferiprone used for?
Deferiprone is prescribed to eliminate iron from the system of individuals, both adults and children aged 3 years and above, who are afflicted with thalassemia, a disorder leading to reduced red blood cell count.
How does deferiprone work?
Deferiprone is a substance that helps remove iron from the body by binding to ions and creating a stable complex in a ratio of 3 parts deferiprone to one part iron, which is then excreted through urine.
Deferiprone how to take?
two or three times daily.
How deferiprone works?
Deferiprone belongs to a group of medicines known as iron-chelating agents, which function by binding to iron in the body to facilitate its elimination from the system.