Zidovudine
- I. Introduction to Zidovudine
- II. Composition of Zidovudine
- III. How Zidovudine Works
- IV. Primary Uses of Zidovudine
- A. Zidovudine in HIV/AIDS Treatment
- B. Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
- V. Off-label Uses of Zidovudine
- A. Potential Therapeutic Applications
- B. Current Research and Findings
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Zidovudine
- VII. Administration to Specific Populations
- A. Administration to Elderly Patients
- B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- C. Administration to Children
- VIII. Interaction of Zidovudine with Other Medications
- IX. Common Side Effects of Zidovudine
- X. Important Precautions When Using Zidovudine
- A. Contraindications for Zidovudine
- B. Careful Administration and Monitoring
- XI. Zidovudine Overdose: Causes, Symptoms, and Interventions
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Zidovudine
- A. Appropriate Storage Conditions
- B. Safe Handling and Disposal Measures
- XIII. Warnings about Zidovudine Use
- XIV. Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Zidovudine
I. Introduction to Zidovudine
A. Brief Overview of Zidovudine
Amongst antiretroviral medications designed for addressing cases involving Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), one widely known option is Zidovudine - or AZT. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) form the main classification of this drug. Although it was first developed in the 1960s, medical professionals turned to it to address HIV during the 1980s. Since then, Zidovudine has remained a critical aspect for doctors to consider when constructing antiretroviral therapy plans for tackling HIV infections. source.
B. Medical Context and Importance
In addressing HIV infection, Zidovudine is essential in halting disease advancement and effectively mitigating related manifestations. Given its remarkable impact on reducing mortality and morbidity linked to this condition, those living with HIV can enjoy a better quality of life by using this option. Global health organizations have duly recognized its importance by recognizing it among their critical drugs arsenal designated for such conditions, thus emphasizing its worldwide clinical significance.
II. Composition of Zidovudine
A. Main Components
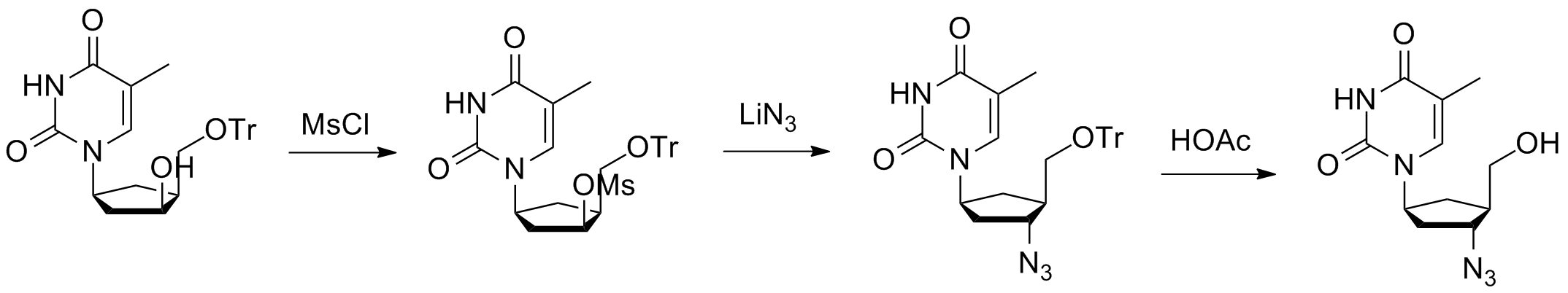
Zidovudine, also known as azidothymidine (AZT) is an artificial nucleoside built on thymidines' foundations using triphosphate phosphorylation technology. AZT competes with endogenous thymidine for cellular kinases' attention but lacks hydroxyl groups required for further chain elongation after incorporation into DNA or RNA sequences; thus ends complementary strand elongation upon binding at reverse transcriptases' allosteric site, apart from AZT active chemical component. It might also include biologically inert substances like microcrystalline cellulose or sodium starch glycolate during formulation practices source.
B. Pharmacological Class
Regarding pharmacology, Zidovudine is classified as a member of Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs). The function of these drugs is to hinder HIV reproduction by obstructing the reverse transcriptase enzyme that is crucial for viral replication. Such action ensures that HIV proliferation is halted source effectively.
III. How Zidovudine Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Zidovudine operates by hindering the HIV replication process through a specific mechanism. It competes with thymidine, a natural nucleoside, for assimilation into viral DNA. By integrating successfully into this genetic material, Zidovudine obstructs further progression in DNA chain elongation accurately due to its lack of the 3' hydroxyl group component necessary for establishing phosphodiester bonds essential to move forward with DNA replication as source.
B. Role in HIV Treatment
In the arena of treating individuals with HIV. Utilizing an approach called combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) has become commonplace. One significant component often incorporated into cART is a medication called Zidovudine. With its ability to significantly lower viral load levels in tandem with other antiretrovirals--this therapeutic approach can make a remarkable difference for those affected by AIDS-related illness by slowing the rate at which symptoms progress while enhancing overall well-being source.
IV. Primary Uses of Zidovudine

In managing HIV infection. Zidovudine has become indispensable due to its critical role in resolving several challenges associated with this illness. It serves as a reliable preventative measure against mother-to-child transmission at different stages throughout gestation and childbirth. Furthermore, its efficacy in post-exposure prophylaxis underscores its value as a key treatment solution for healthcare providers worldwide. source.
A. Zidovudine in HIV/AIDS Treatment
Respectfully speaking, Zidovudine evokes excellent appreciation due to its critical contribution towards maintaining wellness among individuals affected by HIV/AIDS. Working hand-in-hand with other antiretroviral drugs via combination therapy(cART), it focuses on decreasing viral activity within a patient's body - ultimately slowing down disease progression rates while increasing levels for improved longevity and thriving mode span source. Essential elements creating value within Zidovudine during AIDS treatment include its reversed transcriptase enzyme-inhibiting capabilities that can help reduce viral replication, minimize morbidity and mortality experiences connected to HIV, and enable avoidance of many opsonizing- and infection-related deterrents.
B. Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
When preventing infection or disease after exposure to a pathogen, Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is utilized as a preventative medical treatment option in the circumstances related to HIV. Zidovudine plays an integral role in reducing the risk of transmission by being part of PEP when provided following potential exposure. By using medication like this one. Situations such as needlestick injuries experienced by healthcare personnel or unprotected sexual encounters can be addressed along with other incidents involving contact with infectious bodily fluids from sources that are known carriers of HIV. For a PEP treatment course involving multiple antiretroviral drugs, including Zidovudine over 28 days, to be effective, initiating it at the earliest possible moment post-exposure within the first 72 hours remains essential.
V. Off-label Uses of Zidovudine
Though primarily known for treating HIV/AIDS and post-exposure prophylaxis purposes. Medical researchers have explored various unapproved applications for Zidovudine (off-label uses). Clinical observations or preliminary research suggest that these unapproved uses could have therapeutic benefits. Current studies indicate that Zidovudines application may benefit people with specific cancer types, such as adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma, by acting on the HTLV 1 virus' reverse transcriptase enzyme source. However, it is essential to note that this assessment depends on limited research and current clinical observations. Extensive research is necessary for a complete understanding of Zidovudines' potential for off-label applications. Healthcare professionals should only administer off-label use of Zidovudine under guidance and supervision.
A. Potential Therapeutic Applications
In addition to being widely used for managing HIV. Zidovudine has been investigated as a potential therapy option for several other medical conditions. Researchers examining this drug's mode of action have explored whether it can effectively treat various retroviral infections or particular forms of cancer such as Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Possible therapeutic applications that are being studied undoubtedly include exploiting Zidovudines' antiviral properties not just for HIV purposes only but also applying them against different kinds of retroviruses affecting humans source. Moreover, the compounds' ability to impact cell replication has generated interest in their use as a cancer treatment.
B. Current Research and Findings
The prospects for utilizing Zidovudine appear optimistic; however, their foundation lies primarily in preliminary studies and clinical evaluations. Consequently, conducting further exploration is essential to determine its full benefits and risks conclusively. Despite these reservations, the possibilities presented by Zidovudine as a treatment option across several therapeutic domains are fascinating and warrant continuing inquiry source.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Zidovudine
A. General Dosage Guidelines
Zidovudine dosage differs from one individual to another, depending mainly on their current body mass index (BMI), overall physical fitness level, and presence of any comorbidities. Conventionally speaking, though, for adults over eighteen years, a standard dose ranges from two hundred milligrams (mg) up to three hundred mg taken through the mouth after eight or twelve hours intervals, respectively. However, adjusting doses forms part of doctors' discretion during treatment after gauging how patients respond and tolerate this medication therapy modality. source.
B. Adjustment Factors for Specific Populations
For individuals with renal or hepatic problems, it's vital to take note that their Zidovudine dosage may require adjustments due to decreased drug clearance rates. Close observation of patients is necessary in such cases to catch any adverse outcomes early on and tailor the dose accordingly a credible reference provided this information source.
VII. Administration to Specific Populations
The administration of Zidovudine requires careful attention among specific populations like pregnant women, nursing mothers, children, and the elderly. Safety and effectiveness considerations are necessary in these groups before prescribing this drug therapy. During childbirth, healthcare professionals often use Zidovudine to avert mother-to-child transmission of HIV; however, meticulous monitoring is needed because it can cause harmful impacts on infants' source. Changes in renal function can alter pharmacokinetics among older patients, which might impact adequate dosing requirements, leading to a vigilant assessment mechanism for safety measures that need timely adjustments. Pediatric doses depend on body weight for optimal outcomes with enhanced effectiveness ensuring maximum safety against any real or perceived health risks or side effects associated with its usage source.
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Treating elderly patients with Zidovudine necessitates careful consideration due to the physiological transformations that occur as one age, specifically related to kidney function and drug removal from body tissues. For this reason, adjusting dosage levels based on individual requirements becomes essential for healthcare providers working with geriatric patients treated with Zidovudine. Adding another layer of complexity to geriatric treatment plans is medication regimen intricacy since elderly individuals commonly take multiple medications regularly and frequently, leading to increased risk for medication interaction complications; both provider and patient benefit from close observation aimed at minimizing adverse events pertaining to medication use source.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Preventing the mother-to-child transfer of HIV is a critical objective that Zidovudine helps achieve significantly. This medication poses no significant harm during gestation and can considerably lessen the chances of an infant contracting HIV from its parent(s). However, keeping a watchful eye on both expectant moms taking Zidovudine and their progenies becomes necessary because side effects may sometimes arise. Given that nursing moms living with HIV are typically discouraged from breastfeeding their young ones as it can propagate the virus spread through breast milk - given that Zidovudine does get excreted via lactation - certain women may nonetheless decide otherwise... while keeping in mind what's at stake source.
C. Administration to Children
Lastly, it's noteworthy that zidovudine has applications in pediatric medicine too. Nevertheless, doctors determining an appropriate dose for children must consider their body weight before administering this medication. To effectively manage potential side effects and minimize risks centrally linked with medication experiences among young patients, closely monitor symptoms with frequent evaluations, which might result in modifying prescribed dosages based on how they respond to treatment courses guided by outlined recommendations from specified sources concerned about safety and effectiveness of medication treatments for young people receiving care such as described here-source used source.
VIII. Interaction of Zidovudine with Other Medications
A. Common Drug Interactions
It's crucial to understand that taking Zidovudine simultaneously with certain other medications may lead to diverse outcomes. One possible scenario is for these medicines' effects to get altered or for side effects to intensify unexpectedly. Notably, risky drugs include ganciclovir and interferon alfa because they could significantly increase the likelihood of hematological toxicity when combined with Zidovudine usage. However. On the positive side. Zidovudine can interact positively with other antiretroviral drugs like lamivudine to produce a potent synergistic effect. source.
B. Steps to Avoid Adverse Interactions
Maintaining caution against negative drug interactions requires patients to regularly inform their healthcare providers about all medicinal or supplemental inputs including prescription medications, OTC drugs and dietary supplements under use. Identification of potential conflicts would call for managed surveillance complemented by dose adaptations or replacement therapy when necessary.
IX. Common Side Effects of Zidovudine
A. Mild and Frequent Side Effects
As a commonly seen result of using Zidovudine, headache, nausea, vomiting and fatigue are considered mild side effects. Nonetheless. Patients should communicate any prolonged discomfort to their healthcare provider for appropriate management source.
B. Recognizing Serious Adverse Effects
Occasionally Zidovudine can result in significant adverse reactions like severe anemia or neutropenia, lactic acidosis, and hepatomegaly with steatosis. It's crucial to get quick, professional help at the first sign of any such symptoms. Henceforth it's important for patients to be informed about these potentially severe side effects through healthcare providers' advice so that they can pursue appropriate preventative measures without undue delay source.
X. Important Precautions When Using Zidovudine
Monitoring blood counts regularly is crucial to using Zidovudine since hematological toxicity can potentially occur in patients. Signs of anemia or neutropenia require prompt intervention, including dose adjustments or therapy cessation. Those with existing liver conditions should be extra vigilant about potential lactic acidosis and hepatotoxicity symptoms development source. Patients must remember that Zidovudine can aid in managing HIV symptoms and lowering viral load. It does not eliminate infection nor stop virus transmission.
A. Contraindications for Zidovudine
In some cases administering Zidovudine may not be permissible due to specific contraindications for specific medical conditions. For example, patients with a known allergy or hypersensitivity toward this drug and its ingredients must avoid taking it altogether; additionally, individuals grappling with significantly decreased bone marrow function should not take Zidovudine because doing so poses a risk of developing hematological toxicity that negatively impacts their blood cell counts and hemoglobin levels source.
B. Careful Administration and Monitoring
When medicating patients with Zidovudine, due diligence during administration promotes safety against serious adverse reactions or ineffective drug interactions that may occur during therapy sessions. With these facts in mind, an attentive approach ensuring accurate dosages supplemented by regular monitoring regimes using blood-based testing allowing analysis of hematological toxicity alongside evaluation for hepatotoxicity utilizing liver function screening methods is mandatory to ensure optimal patient care management. Moreover, educating patients about early identification and notification regarding unfamiliar or unusual symptoms promptly assists medical professionals in making necessary adjustments and interventions on their treatment plan source.
XI. Zidovudine Overdose: Causes, Symptoms, and Interventions
A. Recognizing Overdose
Recognizing the warning signals regarding Zidovudine overdose is important since, although uncommon, sometimes, fatalities occur. The signs are fatigue and manifestations such as headache, vomiting, and, importantly, significant hematological abnormalities, including severe anemia or neutropenia. In certain exceptional situations, individuals might suffer lactic acidosis- a medical emergency that pushes the limits between life and death source.
B. Immediate Actions and Long-Term Management
In case of an overdosing event concerning Zidovudine, obtaining urgent medical attention is critical for optimal outcomes. Medical professionals prioritize providing support alongside symptom management while diligently observing hematological and metabolic factors during treatment. Consequently, attending frequent follow-up appointments aids in ensuring complete healing and watching out for any permanent repercussions arising from the initial overdose episode. source.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Zidovudine
It's crucial to maintain the quality of Zidovudine by storing it appropriately—namely. In a cool dark place that doesn't expose it to moisture or direct light. To prevent unintentional consumption of this medication by minors or pets in your home surroundings or workplace area. Ensure you keep the medicine out of sight and out of reach immediately after usage. Its also essential only to use this drug before its expiry date lapses since consuming expired drugs has significant health implications on users' welfare source.
A. Appropriate Storage Conditions
Zidovudine needs careful handling before use when preserving its effectiveness. To prevent irreversible damage caused by exposure of drug molecules within the solution, ambient lighting protects Zidovudine within its initial package. The medication requires suitable conditions for storage, with ambient temperature maintained at a range of 15-25 degrees Celsius while avoiding high humidity or extreme heat. It's important to note that storing this medication in bathrooms is not ideal as it increases the risk of moisture exposure. To gain further clarification on proper drug upkeep and storage recommendations, refer to the enclosed leaflet or positively engage with an approved pharmacist source.
B. Safe Handling and Disposal Measures
Proper handling of Zidovudine involves being mindful of hygiene and keeping it inaccessible to children and animals alike. Any outdated or surplus medicine should never be disposed of via household waste or wastewater but instead returned to a pharmacy for safe disposal. This practice is an environmentally friendly option while reducing any chances for accidental exposure.
XIII. Warnings about Zidovudine Use
A. Potential Health Risks
Zidovudine is a powerful medical intervention and has produced many positive outcomes; however. It poses some health risk factors that you should consider before choosing this treatment option. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms like a headache or feeling unwell while others could encounter serious cases such as liver damage or abnormalities in the blood cells. It's paramount for people susceptible to hypersensitivity reactions due to allergic tendencies towards Zidovudine or any of its elements to proceed with utmost caution source.
B. Necessity of Regular Monitoring and Follow-ups
Zidovudine treatment poses potential health risks that should not be overlooked. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are necessary to mitigate these risks. This entails conducting blood tests, liver function checks, and general assessments of patient well-being at suitable intervals. Additionally, patients must be vigilant in reporting any new or deteriorating symptoms immediately to their healthcare provider for prompt attention source.
XIV. Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Zidovudine
A. Recap of Zidovudine Features
In combating HIV/AIDS, Zidovudine assumes a critical role by diminishing viral load and slowing down disease progression. At the same time, this medication provides considerable benefits to patients. Potential health hazards must be approached carefully and managed properly source.
B. Empowering Patient Decision-Making
The effective management of Zidovudine necessitates patients' understanding of its potential risks alongside the beneficial factors underpinning it. Accordingly, adequate information should be made available to empower patients to make knowledgeable health decisions aligned with their preferences source. In this regard, they must grasp why following medication dosages is critical, recognize side effects signaling possible complications, and engage in consistent health screening authorized by reputable sources collaboratively with healthcare providers as appropriate for best outcomes.
Zidovudine FAQ
- What is Lamivudine Abacavir?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What are Lamivudine side effects?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Abacavir?
- What is the drug class of Lamivudine?
- What is the mechanism of action of Lamivudine?
- What class is Lamivudine in?
- What is Lamivudine 3TC?
- What are the side effects of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Efavirenz?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Zidovudine?
- What are the uses of Lamivudine?
- What is Abacavir and Lamivudine?
- What is Zidovudine and Lamivudine?
- What is the cost of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the role of Lamivudine in Hepatitis B?
- How is Lamivudine used in Hepatitis B treatment?
- What is Lamivudine?
- What is the structure of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What does the Lamivudine package insert include?
- What is Lamivudine Emtricitabine?
- What is Lamivudine and Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine Dolutegravir?
- What is a Lamivudine tablet?
- What is the generic name for Lamivudine?
- What are the warnings associated with Lamivudine?
- What is the renal dosing for Lamivudine?
- What are the interactions of Lamivudine?
- What are the contraindications of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine HBV?
- What is Lamivudine and Emtricitabine?
- What is Lamivudine solution?
- What does Lamivudine NRTI mean?
- What are the adverse effects of Lamivudine?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine-Zidovudine tab 150-300 mg?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Dolutegravir?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate?
- What is the indication of Lamivudine?
- Is there copay assistance for Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine oral solution?
- What is Lamivudine resistance in Hepatitis B treatment?
- Can Lamivudine cure Hepatitis B?
- Why is Lamivudine called 3TC?
- Can Lamivudine be used as PEP?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine used for?
- What is Lamivudine tablet used for?
- What is Lamivudine used to treat?
- What is Lamivudine used for?
- Is Lamivudine a protease inhibitor?
- Is Lamivudine used for HIV?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine used for?
- What is the role of Lamivudine in Hepatitis B treatment?
- How is Lamivudine used in the treatment of Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine?
- What is the structure of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What information can be found in the Lamivudine package insert?
- What is the relationship between Lamivudine and Emtricitabine?
- What is the combination of Lamivudine and Tenofovir used for?
- What is Lamivudine Dolutegravir?
- What is a Lamivudine tablet?
- What is the generic name of Lamivudine?
- What are the warnings associated with Lamivudine?
- How is Lamivudine dosed in patients with renal impairment?
- What are the potential interactions of Lamivudine?
- What are the contraindications for Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine's role in treating HBV?
- How do you pronounce Lamivudine?
- What is the combination of Lamivudine and Emtricitabine used for?
- What is Lamivudine solution?
- Is Lamivudine an NRTI?
- What are the adverse effects of Lamivudine?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What does a Lamivudine-Zidovudine 150-300 mg tab entail?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Dolutegravir?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate?
- What is the indication for Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine copay assistance?
- What is Lamivudine oral solution?
- How does resistance occur in Hepatitis B treatment with Lamivudine?
- Can Lamivudine cure Hepatitis B?
- Why is Lamivudine called 3TC?
- Can Lamivudine be used as PEP?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine used for?
- What is Lamivudine tablet used for?
- What is Lamivudine used to treat?