Gentamicin
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Gentamicin
- III. How Gentamicin Works
- IV. Composition of Gentamicin
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Common Side Effects
- VII. Serious Side Effects and Warnings
- VIII. Contraindications
- IX. Drug Interactions
- X. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XI. Overdose Management
- XII. Summary and Key Takeaways
I. Introduction
Brief Overview of Gentamicin
Gentamicin is a type of antibiotic called an aminoglycoside that is commonly used to treat infections. This medication works by disrupting the production of proteins in bacteria, which ultimately slows down their growth.
Historical Context: Discovery and Development
Gentamicin, an antibiotic with an established background, has been in use since the 1960s. It was first discovered in the fermentation broth of Micromonospora purpurea. It has since undergone refinement and incorporation into standard medical procedures over the years.
Scope of the Article: What Readers Can Expect to Learn
This article explores Gentamicin, including its various medical applications, contraindications, potential side effects and additional pertinent information. The goal is to offer a resource for healthcare professionals and individuals who are interested in the topic.
II. Uses of Gentamicin
A. Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is effective against most gram-negative bacteria and staphylococcus species of gram-positive bacteria 1. It is typically administered as intravenous or intramuscular injections for systemic severe infections and is also used as topical and ophthalmic formulations 1. Gentamicin was a breakthrough in treating gram-negative bacillary infections, including those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1.
Gram-Negative Bacteria Coverage
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Proteus species
- Escherichia coli
Eye Infections
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic effective against most gram-negative bacteria and staphylococcus species of gram-positive bacteria 1. It is typically administered as intravenous or intramuscular injections for systemic severe infections and used as topical and ophthalmic formulations 1. Gentamicin was a breakthrough in treating gram-negative bacillary infections, including those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1.
Gentamicin ophthalmic is an antibiotic that fights bacteria in the eyes. It comes as a solution (liquid) or an ointment. It is a mixture of the sulfate salts of gentamicin C 1, C 2, and C 1A, obtained from cultures of Micromonospora purpurea. It contains preservatives like methylparaben, propylparaben, or benzalkonium chloride. It treats certain eye infections by instilling or applying it to the eyes several times daily. It is available only with a doctor’s prescription 2.
The usual adult dose for bacterial conjunctivitis is 1 to 2 drops of gentamicin ophthalmic solution into the affected eye(s) every 4 hours. For severe infections, up to 2 drops may be instilled every hour. The usual duration of topical anti-infective treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis is 5–10 days; 5–7 days usually adequate for mild bacterial conjunctivitis 345.
1: MedicineNet 2: Drugs.com 3: Drugs.com 4: MedlinePlus 5: Drugs.com
B. Surgical Prophylaxis
Pre-operative Preparations
In surgical procedures, doctors may use Gentamicin to reduce the chances of bacterial infections that can occur after the surgery 1. Gentamicin is an antibiotic that belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, thereby preventing the growth and spread of bacteria 1.
Here are some references that provide more information on the use of Gentamicin in surgical procedures:
-
UpToDate: This website provides detailed information on antimicrobial prophylaxis to prevent surgical site infection in adults. It discusses the use of Gentamicin and other antibiotics in surgical procedures.
-
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Surgery: This website provides clinical practice guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis. It discusses the use of Gentamicin and other antibiotics in various surgical procedures.
-
Bacterial isolates and their antibiotic sensitivity pattern of surgical site infections among patients admitted at a tertiary hospital in Ethiopia: This research article provides information on bacterial isolates and their antibiotic sensitivity pattern of surgical site infections among patients admitted at a tertiary hospital in Ethiopia. It discusses the use of Gentamicin and other antibiotics in surgical procedures.
C. Off-Label Uses
Possible Treatments for Fungal Infections
While Gentamicin is primarily used as an antibiotic to treat bacterial infections, some medical professionals have employed it for the treatment of certain types of fungal infections 1. However, this use is not widely accepted or recommended by most medical authorities 2.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections in animals 1. It is mainly used as a solution for injection for pigs, cattle, and horses and as an oral solution for poultry 1. Gentamicin is also used in human medicine, usually as a solution for injection for intramuscular administration 1. It is currently included in the list of essential medicines for human use of the World Health Organization (WHO) 1.
Here are some references that provide more information on the use of Gentamicin in veterinary medicine:
-
European Medicines Agency: This website provides detailed information on Gentamicin, including its use in veterinary medicine. It discusses the indications and dosing regimens of Gentamicin-containing veterinary medicinal products.
-
MSD Veterinary Manual: This website provides information on using aminoglycosides, including Gentamicin, in animals. It discusses the pharmacology, indications, and dosing regimens of Gentamicin.
-
Reflection paper - Aminoglycosides: This research article provides a reflection paper on using aminoglycosides in animals. It discusses the development of resistance to aminoglycosides and their impact on human health.
III. How Gentamicin Works
Mechanism of Action
Gentamicin works by attaching to the subunits of bacteria, which hinders the production of proteins—a crucial process for the survival of bacteria.
Bacterial Resistance and Gentamicin
The increasing prevalence of strains resistant to Gentamicin is a significant issue that needs urgent attention. Some factors contribute to this resistance, such as incorrect dosages and failure to follow treatment plans consistently.
Comparison with Other Antibiotics
Gentamicin, when compared to penicillin or cephalosporins, has a limited range of action. However, it tends to be highly effective against Gram bacteria.
IV. Composition of Gentamicin
Active Ingredients
The main component of this medication is Gentamicin sulfate, obtained from strains of Micromonospora bacteria.
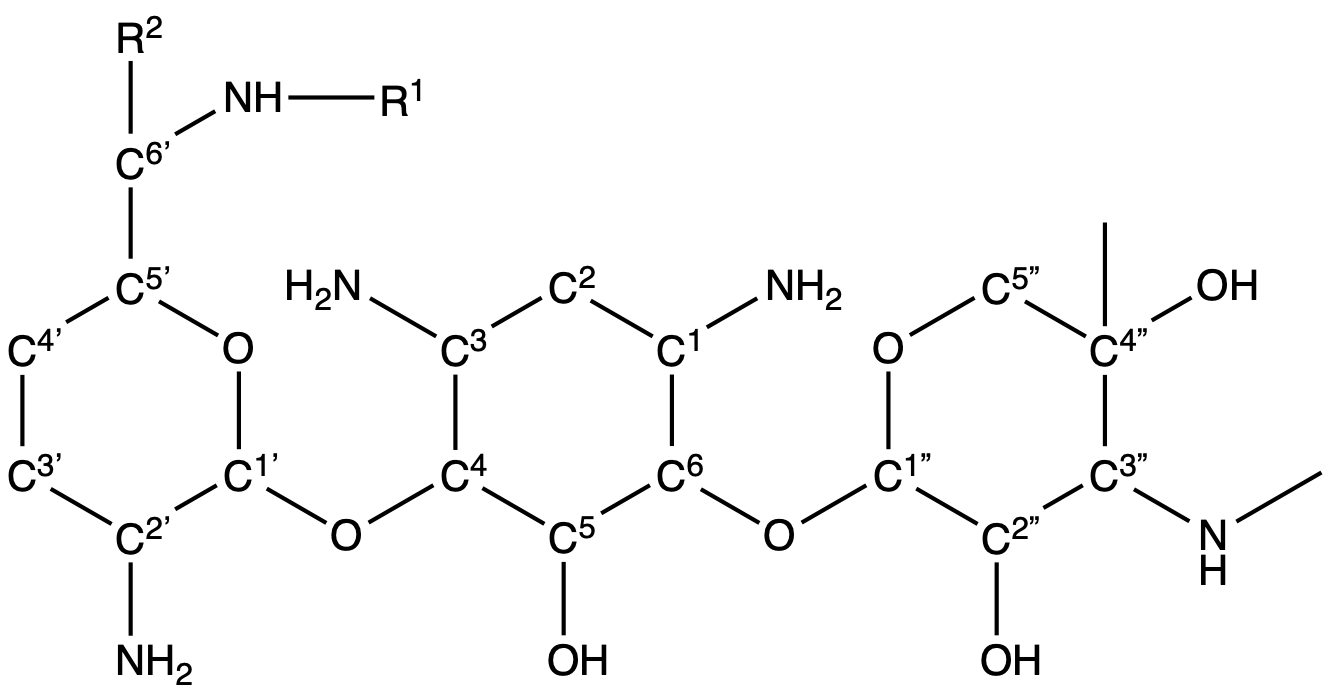
Additional Components
Depending on how it's being administered, additional substances such as saline or dextrose may be included.
Available Forms: Injection, Topical, etc.
- Injectable solutions
- Topical creams
- Eye drops
V. Dosage and Administration
A. General Guidelines
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The recommended infection dose usually falls between 3 to 5 mg per kilogram of body weight per day.
Route of Administration
- Intravenous
- Intramuscular
B. Administration to Special Populations
Elderly Patients
It is common to make changes when renal function decreases.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Only use it when absolutely necessary, as the medication can pass through the barrier and could potentially impact the development of the fetus.
Pediatric Use
Careful consideration should be given to the dosage for pediatric patients to prevent any potential harm to their kidneys or ears.
C. Careful Administration
Importance of Following Medical Advice
It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage instructions to minimize the chances of experiencing any adverse side effects.
Monitoring Drug Levels in the Blood
Regular blood tests are recommended to keep track of any signs of toxicity.
VI. Common Side Effects
Minor Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Mild skin rash
Frequency of Occurrence
A small number of patients experiences these symptoms and can usually be effectively managed.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
If you continue to experience side effects or if they become more severe, it is recommended that you seek immediate medical advice.
VII. Serious Side Effects and Warnings
A. Warning Signs
Kidney Damage
Some signs to watch out for are a reduction in urine production and swelling in the legs and feet.
Hearing Loss
In some cases although uncommon, there is a possibility of encountering an adverse effect where patients might suffer from tinnitus or potentially permanent hearing impairment.
B. Important Precautions
Avoiding Alcohol
Excessive drinking can worsen the effects of Gentamicin on the kidneys.
Pre-existing Conditions that May Increase Risk
If you have any existing kidney or hearing problems, please be cautious when starting Gentamicin therapy.
VIII. Contraindications
Known Allergies
Before administering Gentamicin or any other aminoglycosides, it is crucial to ensure that the patient does not have a documented allergy to these medications. Allergic reactions can present as hives, breathing difficulties, or a severe rash.
Patients with Certain Medical Conditions
Individuals with kidney problems hearing difficulties, or a condition called myasthenia gravis should avoid taking this medication unless specifically instructed to do so by a qualified healthcare provider.
Interaction with Other Medications
When Gentamicin is taken together with medications like diuretics or other drugs that can harm the kidneys there is a possibility that the toxicity could increase. It's essential to be cautious, in situations.
IX. Drug Interactions
Possible Interactions with Other Antibiotics
Combining Gentamicin with antibiotics such as cephalosporins can increase the risk of harmful effects on the kidneys or ears, making those effects worse.

Impact on Birth Control Effectiveness
While there is no proof, specific sources indicate that Gentamicin could potentially reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. It might be advisable to consider using birth control methods in such cases.
Consequences of Mixing with Alcohol
It is highly discouraged to consume Gentamicin and alcohol as it can enhance the harmful effects on the kidneys.
X. Storage and Handling Precautions
Ideal Storage Conditions
Store the medication at room temperature and ensure it is kept away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Shelf Life
Make sure you pay attention to the expiration date. After it expires, the effectiveness and safety of Gentamicin may change due to changes in its pharmacokinetics.
Disposal of Unused Medication
Following federal and state regulations is essential to properly dispose of expired Gentamicin. It should not be flushed down the toilet or sink.
XI. Overdose Management
Symptoms of Overdose
In situations where an excessive amount is taken, signs of overdose may include,. These are not limited to sudden kidney failure, difficulty breathing, and a temporary loss of muscle control.
Immediate Actions to Take
In case of an overdose, it is crucial to take action. Dial emergency. Provide necessary support until professional medical assistance arrives.
Long-term Consequences
Long-term consequences of taking Gentamicin include lasting harm to the kidneys and hearing, highlighting the importance of prompt intervention.
XII. Summary and Key Takeaways
Importance of Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Gentamicin should not be taken without consultation with a healthcare professional. It is crucial to seek their advice for both prescription and dosage decisions.
Responsible Use
By following the recommended instructions regarding usage interactions with other drugs and contraindications, you can significantly reduce the associated risks.
Recap of Potential Risks and Benefits
Gentamicin's antibiotic properties make it highly effective in combating many bacterial infections. However, its effectiveness comes with the potential for side effects and interactions, emphasizing the importance of using it judiciously. This concludes our overview, which aims to shed light on various aspects of Gentamicin, including its effectiveness and the precautions associated with its use.