Glibenclamide
- I. Introduction to Glibenclamide
- II. Composition and Chemical Structure of Glibenclamide
- III. How Glibenclamide Works
- IV. Uses and Applications of Glibenclamide
- V. Off-Label Uses of Glibenclamide
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Glibenclamide
- VII. Glibenclamide and its Interactions
- VIII. Side Effects of Glibenclamide
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications of Glibenclamide Use
- X. Overdose and Handling Precautions for Glibenclamide
- XI. Glibenclamide Administration: Careful Consideration for Special Populations
- XII. Important Precautions When Using Glibenclamide
- XIII. Conclusion: Glibenclamide in Modern Medicine
I. Introduction to Glibenclamide
A. Overview and Purpose of Glibenclamide
Glibenclamide, or glyburide in the United States, is a medication used to treat Type 2 Diabetes. It is classified under the sulfonylurea class of antidiabetic drugs. The primary function of Glibenclamide is to promote insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. Thereby decreasing blood glucose levels; this oral hypoglycemic agent is usually prescribed when dietary changes and physical activity do not adequately control blood sugar levels.
B. Brief History and Development of Glibenclamide
The introduction of Glibenclamide can be attributed to developments in the 1950s, which saw significant advancements in utilizing sulfonylureas for managing elevated blood sugar levels and serving as a second-generation sulfonylurea drug. Glibenclamide demonstrates superior effectiveness and fewer undesirable effects compared to earlier versions. Through the years, it has cemented itself as an indispensable tool in battling Type 2 Diabetes due to its efficacy and economical nature.
II. Composition and Chemical Structure of Glibenclamide
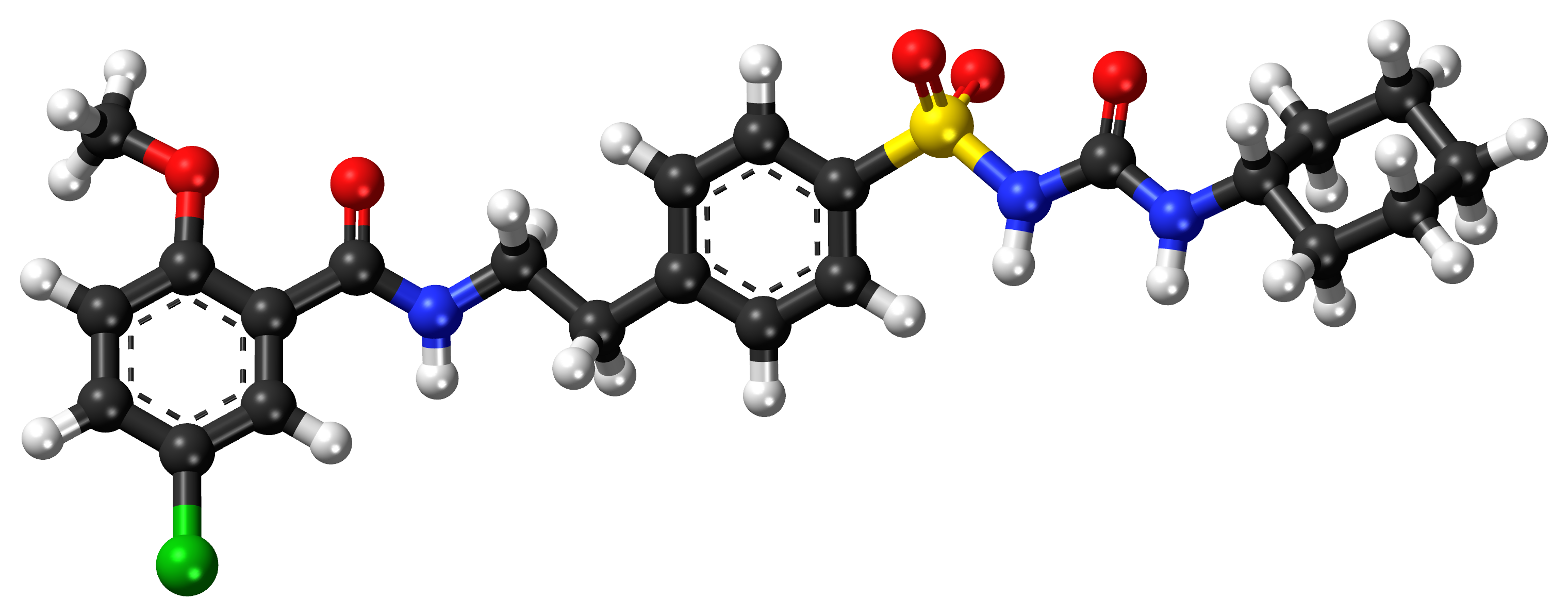
A. Active Ingredients in Glibenclamide
The compound known as Glibenclamide is the active ingredient in this medication. As a sulfonylurea derivative. Glibenclamide has the ability to lower blood sugar levels by causing the pancreas' beta cells to release insulin, regardless of its brand. Each tablet of Glibenclamide primarily consists of this active ingredient, along with other inactive substances that help with the delivery and absorption of the drug.
B. Pharmaceutical Formulation and Appearance
Glibenclamide is commonly found in the form of oral tablets. These tablets come in various strengths ranging from 1.25 mg to 5 mg. The tablets may have different colors, sizes, and imprints depending on the manufacturer. Nevertheless, regardless of these physical attributes, every tablet is carefully crafted to guarantee efficient absorption and metabolism of the active ingredient Glibenclamide within the body.
III. How Glibenclamide Works
A. Understanding the Mechanism of Action
The mode of action of Glibenclamide is quite complex. This medication works by attaching itself to the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP) found on the membranes of pancreatic beta cells. When it binds to these channels, they close, causing the cells to depolarize and opening calcium channels. The entry of calcium ions then stimulates the release of insulin-containing granules. It is resulting in higher levels of insulin being released into the bloodstream. Consequently, this helps to lower blood glucose levels.
B. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glibenclamide
Once taken orally, Glibenclamide gets absorbed efficiently within our gastrointestinal tract. Thanks to its superior bioavailability rate. It enters our bloodstream rapidly and achieves peak concentrations approximately within 2 6 hours post-ingestionation (Lewis et al., n.d.). To a large extent, Glibenclamide binds itself to proteins present in plasma. Cytochrome P450 enzyme system, located in the liver. Plays a key role in metabolizing this drug (Lewis et al., n.d.). The primary route of excretion for these metabolites is through bile, while secondary elimination occurs through urine. When considering its pharmacodynamic aspects. Glibenclamides' main therapeutic function revolves around lowering blood glucose levels. It accomplishes this by enhancing insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells that are still fully functional (Koda Kimble et al., 2012). Furthermore, Glibenclamide may have the ability to bolster the sensitivity of peripheral tissues toward insulin which consequently enhances glucose uptake and utilization.
IV. Uses and Applications of Glibenclamide
A. FDA-approved Indications
Glibenclamide is a potent oral medication used to treat Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, a condition approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is primarily prescribed for individuals whose blood glucose levels cannot be effectively managed through diet and exercise alone and when insulin is not preferred or feasible.1
References
B. The Role of Glibenclamide in Diabetes Management
Glibenclamide is a crucial part of the treatment options for Type 2 Diabetes. Its primary function is to enhance insulin secretion, which helps restore the body's disrupted glucose balance. Specifically, Glibenclamide achieves this by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin, reducing hepatic glucose production, and improving the ability of peripheral tissues to respond to insulin and take up glucose. By effectively controlling blood sugar levels over time, Glibenclamide plays a vital role in preventing long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. As a result. It significantly improves the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
Here are some references that you can use:
1. The Inhibitory Effects of Insulin on Hepatic Glucose Production
2. Metformin Ameliorates Dysfunctional Traits of Glibenclamide
3. Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | SpringerLink
C. Other Medical Conditions Benefitting from Glibenclamide
In addition to diabetes, Glibenclamide has displayed potential in treating other medical conditions. A growing body of evidence indicates that Glibenclamide could be advantageous in managing hyperinsulinemia. A condition marked by an excess of insulin in the bloodstream. Moreover. Several studies propose that Glibenclamide may play a role in alleviating polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) by improving insulin resistance, which is commonly observed in individuals with this disorder.
Here are some references that you can use:
1. Resistance to the Insulin and Elevated Level of Androgen
2. Insulin Resistance and the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Mechanism
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Insulin: Our Understanding in the Past
V. Off-Label Uses of Glibenclamide
A. Potential Therapeutic Areas for Glibenclamide
Although Glibenclamide primarily controls Type 2 Diabetes, researchers are investigating its potential applications in other therapeutic areas. One of the off-label uses that show promise is neuroprotection, specifically in mitigating the severity of ischemic stroke. Additionally, Glibenclamide has been found to have potential in cardiovascular disease by limiting infarct size in myocardial ischemia. It can also effectively reduce the frequency of acute gout attacks by lowering serum uric acid levels.
Here are some references that you can use:
1. Neuroprotection in Acute Ischemic Stroke
2. Initial assessment and management of acute stroke
3. Guidelines for Management of Stroke - WHO/OMS Extranet Systems
B. Current Research and Evidence for Off-Label Use
Extensive research is currently being conducted to validate the off-label uses of Glibenclamide. Some clinical trials have found evidence of its neuroprotective properties. Suggesting that it may help reduce cerebral edema in stroke patients. Likewise, studies on myocardial infarction models have shown a potential cardioprotective effect. Despite these promising findings, it is imperative to conduct more large-scale and rigorous clinical trials to conclusively determine the safety and efficacy of Glibenclamide for these off-label purposes.
Here is a reference that you can use:
1. Neuroprotection in Acute Ischemic Stroke
VI. Dosage and Administration of Glibenclamide
A. Recommended Dosage for Different Age Groups
The dosage of Glibenclamide is tailored to each patient's needs, and it is usually initiated at a low level. The dose is then gradually increased until the desired response is achieved. The initial daily dose typically falls between 2.5 mg and 5 mg in adults. However, for elderly patients, starting with a lower amount of 1.25 mg is advisable to reduce the chances of hypoglycemia. It should be noted that Glibenclamide is not commonly prescribed to children except in particular cases where strict medical oversight is present.
B. Instructions for Safe and Effective Use
Glibenclamide is typically taken orally. Once or twice a day. With the first main meal. To ensure safe and effective use, it is important not to split, crush or chew the tablet. Instead, swallow it whole.
Furthermore, taking Glibenclamide at approximately the same time every day is advisable. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next scheduled dose. It is crucial not to double up on doses under any circumstances. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to evaluate the medication's effectiveness and make necessary dosage adjustments if needed.
C. Adjustments in Dosage and Considerations
Dosage adjustments may be needed depending on the patient's medical condition. Response to treatment. And results from blood glucose monitoring. For patients with kidney or liver problems. It is important to carefully adjust the dosage due to a longer half-life and the potential for low blood sugar. It is crucial to have regular checkups with a healthcare provider to ensure the correct dosage is being given and to watch out for any possible side effects.
VII. Glibenclamide and its Interactions
A. Drug-Drug Interactions with Glibenclamide
Glibenclamide has the potential to interact with many other medications, which could impact its effectiveness and safety. It is important to note that certain drugs, such as Beta blockers, Warfarin, and specific antifungal agents, may increase the hypoglycemic effect of Glibenclamide. On the other hand, and Oral contraceptives may reduce its hypoglycemic action. It is advisable to always consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new medication while using Glibenclamide.
B. Glibenclamide and Food Interactions
Drinking alcohol can enhance the hypoglycemic effect of Glibenclamide, which can cause a sudden decrease in blood sugar levels. Moreover, consuming excessive amounts of grapefruit juice might elevate the levels of Glibenclamide in the blood, increasing the likelihood of experiencing hypoglycemia. Consequently, it is recommended to limit alcohol consumption and consult a medical professional about dietary habits.
C. How Other Medical Conditions May Impact Glibenclamide's Efficacy
Particular medical conditions can impact the effectiveness and safety of Glibenclamide. An instance of this lies in individuals with liver or kidney diseases who might experience changes in drug metabolism and elimination processes. These alterations increase the potential for developing hypoglycemia. Furthermore, vigilance is necessary when prescribing Glibenclamide to patients with thyroid disease, adrenal or pituitary insufficiency issues, and severe cardiovascular ailments.
VIII. Side Effects of Glibenclamide
A. Common Side Effects and Their Management
Glibenclamide is known to cause a few side effects, including mild hypoglycemia, nausea, heartburn, and weight gain. If any of these effects persist or worsen. It is advisable to seek immediate medical attention. To better handle these side effects. It is recommended to monitor blood glucose levels regularly. Make dietary adjustments. And optimize the dosage.
B. Rare but Serious Side Effects
C. Identifying and Reporting Adverse Reactions
Promptly report any unexpected or severe symptoms after ingesting Glibenclamide to a healthcare professional to ensure proper medical attention. It is crucial to identify signs indicating severe adverse reactions such as dizziness, confusion, rapid heartbeat, and yellowing of the eyes or skin. And unusual bleeding or bruising. By informing healthcare professionals about these reactions. They can learn about this medication's safety profile and effectively handle its usage.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications of Glibenclamide Use

A. Understanding the Risks: Glibenclamide Contraindications
Glibenclamide should not be used in certain conditions because it can have adverse effects or may not work effectively. These conditions include Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis, and severe renal or hepatic dysfunction. It is also not recommended for patients with hypersensitivity to sulfonylureas, including Glibenclamide. Awareness of these contraindications is essential to avoid unnecessary risks or complications.
B. Specific Patient Populations: Precautions in Elderly, Pregnant Women, Nursing Mothers, and Children
When administering Glibenclamide to specific patient populations, such as the elderly. Pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children. It is essential to take special consideration. In the case of elderly patients, it may be advisable to start with a lower dose due to potential decreased renal function. Pregnant women and nursing mothers should only use Glibenclamide if the potential benefits are determined to outweigh the risks. As for children, Glibenclamide must be administered under strict healthcare provider supervision since its safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been extensively studied.
X. Overdose and Handling Precautions for Glibenclamide
A. Recognizing and Managing Glibenclamide Overdose
Taking an excessive amount of Glibenclamide can lead to a condition called hypoglycemia. Symptoms like shakiness, nervousness, rapid heartbeat, and sweating characterize hypoglycemia. When there is suspicion of hypoglycemia, it is imperative to ingest a readily available source of sugar, such as fruit juice or glucose gel. In severe cases, immediate medical intervention is necessary.
B. Proper Storage and Disposal of Glibenclamide
Maintaining appropriate storage conditions for Glibenclamide requires storing it at room temperature and protecting it from exposure to light and moisture. Preserving the environment entails entirely refraining from disposing of medicines through wastewater or household waste channels. Instead, please consider utilizing established collection systems accessible within your vicinity. By embracing such responsible measures, we can actively contribute to Environmental preservation efforts.
C. Guidelines for Safe Handling of Glibenclamide
It is essential to handle Glibenclamide tablets with clean and dry hands. Furthermore, it is essential to keep the bottle tightly closed when the tablets are not being used. Patients should be kindly reminded not to share their medication with others and to use it solely as prescribed by their healthcare provider.
XI. Glibenclamide Administration: Careful Consideration for Special Populations
A. Administration to the Elderly: Dosage, Side Effects, and Precautions
In older adults. Renal function may be compromised, potentially resulting in the buildup of Glibenclamide and an increased likelihood of experiencing hypoglycemia. Therefore, initiating treatment with a smaller dose and adjusting gradually while closely monitoring blood glucose levels is advisable. Furthermore, it is important to monitor for any other adverse reactions such as gastrointestinal disturbances, dizziness, or confusion.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Recommendations
Pregnant women and nursing mothers should consider using Glibenclamide only if the potential benefits outweigh the associated risks. It should be noted that there is limited data on the use of Glibenclamide in pregnant women. Therefore if Glibenclamide is chosen as a treatment during pregnancy, close monitoring of patients should be undertaken throughout the pregnancy without proper medical advice. It is not recommended for breastfeeding women to use Glibenclamide.
C. Administration to Children: Efficacy, Side Effects, and Dosage Adjustments
The safety and effectiveness of Glibenclamide in children have not been entirely determined. However. In certain situations. It could be considered for use with careful medical oversight. It is essential to closely monitor the dosage and potential side effects to prevent adverse reactions like low blood sugar levels. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for maintaining proper control and minimizing the likelihood of side effects.
XII. Important Precautions When Using Glibenclamide
A. Recognizing Signs of Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Patients using Glibenclamide should remain alert for indications of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, the main dangers tied to its use. Hypoglycemia is characterized by symptoms like perspiration. Shaking, moodiness, disorientation, or rarely unconsciousness can occur. In contrast, hyperglycemia might manifest as a frequent need to urinate, excessive thirstiness, fatigue, and vision problems. Timely identification of these signs can significantly enhance patient prognoses.
B. Regular Monitoring and Check-ups During Glibenclamide Therapy
Regular monitoring is of utmost importance during Glibenclamide therapy. Patients must be adequately educated on the significance of conducting routine blood glucose checks at home and ensuring regular medical checkups to keep track of their HbA1c levels, which provide a long-term assessment of blood glucose control. Additionally, physicians should periodically monitor liver and kidney function as Glibenclamide undergoes hepatic metabolism and renal excretion.
C. Lifestyle Adjustments for Optimal Results with Glibenclamide
Patients should understand that taking Glibenclamide alone is insufficient to manage diabetes effectively. It is essential to incorporate lifestyle modifications alongside medication for optimal outcomes. These modifications consist of several factors: First. Maintaining a consistent and balanced diet plays a crucial role. This involves limiting the consumption of sugars and saturated fats while including whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables in one's meals. Secondly, regular physical activity is essential. Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week can significantly contribute to managing blood glucose levels effectively. Moreover, individuals should strive to maintain a healthy weight. Even a modest weight loss can positively affect blood glucose control if one is overweight. Establishing a regular sleep schedule is also integral in managing insulin and glucose levels. Adequate sleep contributes to maintaining balance in these aspects. Finally, patients should avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake moderately. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact blood glucose control and should be avoided altogether. By incorporating these lifestyle changes alongside taking Glibenclamide, patients can enhance their diabetes management plan and improve their overall health outcomes considerably.
XIII. Conclusion: Glibenclamide in Modern Medicine
A. The Evolving Role of Glibenclamide in Therapeutics
Over the years. Glibenclamide has been an essential tool in the fight against Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Despite the introduction of newer therapies, Glibenclamide plays a crucial role in managing diabetes by stimulating insulin production and lowering blood glucose levels in addition to its established uses. This medicine has also shown promise in treating neonatal diabetes and certain types of stroke. It is expanding its potential applications in therapeutics.
B. Current Research and Future Directions for Glibenclamide Use
Ongoing studies are contributing towards enhancing our understanding of the numerous potential applications of Glibenclamide outside the realm of diabetes treatment. Notably, evidence reveals promising benefits in specific neurological conditions due to Glibenclamide's capacity to inhibit SUR1—a critical subunit found within ATP-sensitive potassium channels—which ultimately aids in averting brain swelling during acute brain injuries. As we progress further and uncover the extensive network through which Glibenclamide interacts within our biological system. Its role within contemporary medicine is poised for evolution and will likely unveil new prospects for therapeutic interventions.