Hydroxyurea
- Why is Hydroxyurea Prescribed?
- Understanding the Mechanism of Action
- Proper Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- How Long Can You Take Hydroxyurea?
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Hydroxyurea for Thrombocytosis
- Is There a Substitute for Hydroxyurea?
- Monitoring Treatment Progress
- Buy Hydroxyurea: A Comprehensive Guide for Patients
Hydroxyurea, also known as hydroxycarbamide, is a medication classified under agents. Its molecular structure includes hydroxyl and carbamoyl groups connected to a nitrogen atom. By interfering with activities, hydroxyurea proves to be an essential treatment option for various blood-related disorders.
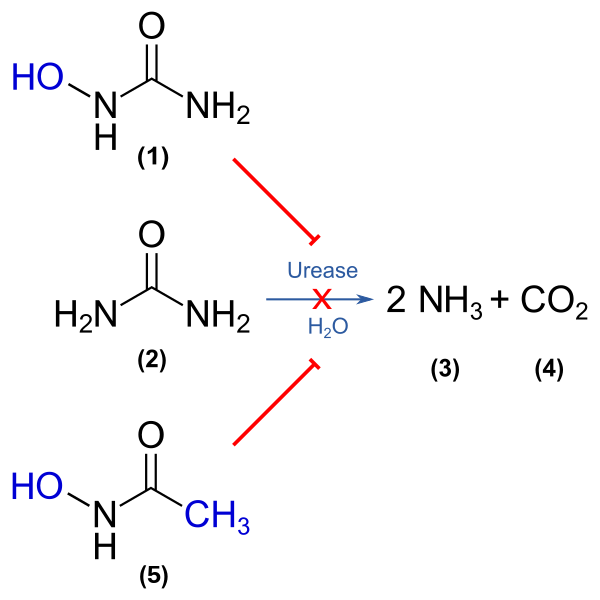
Definition and Chemical Structure
"Hydroxyurea" is a term used to describe a compound called N N' carbamimidoyl hydrazide, which has the chemical formula CH4N2O2. Its chemical structure consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (known as a carbonyl group) and single-bonded to another oxygen atom (known as a hydroxyl group). The hydroxyl group is connected to the compound through a nitrogen nitrogen bond (the hydrazine moiety). There is also an amide functional group ( CONH ) present.
Medical Applications
- Hydroxyurea is commonly prescribed to manage the symptoms of sickle cell disease as it helps increase the production of hemoglobin reduces inflammation and prevents red blood cells from becoming misshapen or "sickled." If you want to learn more about how this medication aids patients with this condition you can find information here.
- For individuals diagnosed with polycythemia vera, a type of blood cancer characterized by excessive production of red blood cells, hydroxyurea plays a crucial role in controlling the disease by slowing down cell division. If you're interested in understanding how it contributes to managing polycythemia vera further details are available.
- In addition to its applications in sickle cell anemia and polycythemia vera hydroxyurea is also utilized for treating thrombocythemia. This condition involves an overproduction of platelets, increasing the risk of blood clots and bleeding. By inhibiting DNA synthesis in dividing cells hydroxyurea effectively reduces platelet count and minimizes complications associated with this disorder. Please check out the provided resource to gain insights into its use for essential thrombocythemia treatment.
It's worth noting that hydroxyurea has been studied for its applications in addressing other medical issues, such as HIV and certain cancers. Understanding why your physician has specifically prescribed this medication for your situation is essential. To summarize, hydroxyurea (hydroxycarbamide) is a medication that interferes with cellular processes. It is utilized for treating blood disorders and is vital in managing these conditions effectively. It is often recommended for treating sickle cell disease polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia because it can help increase hemoglobin production, slow down cell division, and lower platelet count, respectively.
Why is Hydroxyurea Prescribed?
Hydroxyurea is a medication that has proven effective in treating blood disorders. It is frequently prescribed to manage conditions like sickle cell anemia and polycythemia vera, reducing complications linked to thrombocythemia. Now, let's explore these applications thoroughly.
Treating Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is characterized by red blood cells with a crescent shape, making it challenging for them to pass through small blood vessels. This can result in episodes of pain known as crises, as well as damage to organs and other severe health problems. Hydroxyurea is a medication that helps boost the production of hemoglobin (HbF), reducing sickle-shaped cell formation and improving overall symptoms in individuals with this condition. Hydroxyurea in treating sickle cell disease has demonstrated advantages, such as decreasing the frequency of pain crises and hospitalizations.
Managing Polycythemia Vera
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a condition that occurs when your bone marrow produces an excessive amount of red blood cells. This thickening of the blood can lead to health complications associated with PV. One potential treatment option for managing the symptoms and mitigating the risks is hydroxyurea. Hydroxyurea stops the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, thereby assisting in symptom management and reducing the likelihood of severe health issues related to PV (source).
Reducing Essential Thrombocythemia Complications
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a condition affecting the bone marrow characterized by an excess production of platelets. When high platelet counts can lead to blood clotting or bleeding events. For patients diagnosed with ET, doctors often prescribe hydroxyurea as the treatment option to reduce platelet levels and lower the risk of complications such as stroke or heart attack (source). The use of hydroxyurea effectively manages these conditions. Improves the quality of life for patients. It is essential to understand how hydroxyurea works to make an informed decision about its suitability for your specific situation.
Key Takeaway: Hydroxyurea is a medication used for blood disorders, including sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. Its mechanism involves increasing fetal hemoglobin production to reduce sickle-shaped cells in individuals with sickle cell anemia. Additionally, it slows down blood cell or platelet production to manage symptoms and minimize complications associated with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Hydroxyurea contributes significantly to improving patients' quality of life by managing these conditions.
Understanding the Mechanism of Action
To truly grasp the advantages, it is crucial to understand how Hydroxyurea operates within the body and its impact on processes.
How Hydroxyurea Works in the Body
Hydroxyureas central role is to hinder the activity of an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase. This particular enzyme plays a role in DNA replication, allowing cells to divide and grow. Hydroxyurea effectively slows down by blocking ribonucleotide reductase. Halts the replication process of fast-dividing cells, such as cancerous or abnormal blood cells. This action helps alleviate episodes in sickle cell anemia patients by boosting the production of fetal hemoglobin (HbF). HbF reduces the tendency of blood cells to become sickle-shaped and enhances oxygen delivery throughout the body. In cases of polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, slowing down cell division helps regulate the production of red blood cells or platelets that can lead to complications like clotting or bleeding. To delve deeper into how it functions at a molecular level, you can refer to this scientific article that discusses its mechanism of action.
Effects on Cellular Processes
- Hydroxyurea treatment has an impact on patients with sickle cell anemia. It leads to increased HbF levels, reducing episodes and hospitalizations caused by vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs). For information on managing sickle cell disease, you can refer to the resources provided by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
- In cases of polycythemia vera, hydroxyurea plays a role in controlling the production of red blood cells. This helps lower the risk of blood clots. It improves blood flow, thereby reducing the likelihood of complications like heart attacks or strokes. The Mayo Clinic offers information about polycythemia vera treatment.
- Hydroxyurea effectively lowers the risks associated with clotting events for patients with thrombocythemia by slowing down platelet production. This reduces clotting risks and alleviates symptoms such as headaches or dizziness. You can find an overview of thrombocythemia treatments on the Cancer.Net website.
Understanding how hydroxyurea works within the body is crucial for patients to grasp its benefits in treating blood disorders. Recent studies have shown that hydroxyurea therapy effectively manages these conditions with side effects compared to other treatments. If you are taking hydroxyurea, discussing any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider for use and safety is essential. To make sure of this, it's also necessary to have an understanding of the correct dosage and administration for optimal outcomes.
Key Takeaway: Hydroxyurea is a medication that works by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase. This action helps to slow down or halt the replication process of dividing cells. It has been proven effective in treating conditions such as sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. Compared to other treatments, hydroxyurea tends to have fewer side effects. If you are taking Hydroxyurea, discussing any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider is advisable.
Proper Dosage and Administration
Understanding the correct dosage and administration of Hydroxyurea is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment. The specific dosage may vary depending on the illness being treated and individual factors such as age, weight, and overall health.
Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions
Individuals with sickle cell anemia are expected to begin treatment with a dose of Hydroxyurea at around 15 mg per kilogram of body weight. This dosage can be modified based on how the patient responds to the medication and their ability to tolerate it. When prescribing Hydroxyurea to children, a healthcare professional must determine the dosage (source). In the case of polycythemia vera, patients typically start with a dose ranging from 15 to 25 mg per kilogram of body weight. Adjustments may be necessary depending on how each individual responds to the treatment. When treating thrombocythemia, a typical starting dose is 500 to 1000 mg daily. However, this dosage may vary depending on the needs and circumstances of each patient (source).
Tips for Safe and Effective Use
- Follow the instructions given by your doctor; take Hydroxyurea precisely as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not make any changes to the dosage. Stop taking the medication without consulting them beforehand.
- Stick to a schedule: To achieve optimal results, taking Hydroxyurea regularly and maintaining a consistent daily routine is important.
- Regularly monitor your blood counts; Your healthcare provider will likely ask you to undergo blood tests while undergoing Hydroxyurea therapy. This helps in monitoring its effectiveness and identifying any side effects early on.
- Prevent contact with skin and eyes: If the capsule's contents come into contact with your skin or eyes, wash thoroughly with soap and water immediately. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
In conclusion, it is crucial to understand the dosages for different conditions when taking Hydroxyurea. Recent studies have compared the effectiveness of Hydroxyurea therapy with treatments. Following these guidelines for administration, patients can increase their chances of successful treatment outcomes while minimizing potential side effects. Proper dosage and administration of Hydroxyurea are essential to ensure results with minimal side effects. Therefore, being aware of the risks of taking Hydroxyurea is crucial.
Key Takeaway: Understanding the dosage and administration is crucial for ensuring safe and effective treatment with Hydroxyurea. The recommended doses may differ based on the treated medical condition, such as sickle cell anemia or polycythemia vera. It is essential for patients to adhere to their doctor's instructions, maintain a schedule, and regularly monitor their blood counts.
Potential Side Effects
Like any medication, there can be side effects when using Hydroxyurea. That's why it's essential to be aware of the negative reactions and carefully monitor your health while taking this medication.
Common Side Effects
Patients who use Hydroxyurea may experience side effects such as:
- nausea, vomiting,
- diarrhea or constipation
- dizziness or headache
- hair loss (alopecia) and
- skin rash or itching (pruritus).
Usually, these symptoms are not severe. It can be managed effectively. However, if they continue or worsen over time, you must seek guidance from your healthcare provider on handling them.
Serious Side Effects and Warning Signs
Apart from the common side effects, there is a possibility of encountering serious complications when taking Hydroxyurea. These complications can be life-threatening in some cases. It is essential to remain alert for warning signs such as:
- Experiencing fever or chills, which may indicate an infection due to a weakened system—
- noticing symptoms of anemia like fatigue, shortness of breath or pale skin coloration.
- Observe that you bruise easily or experience excessive bleeding, even from minor injuries.
- You were having difficulty eating due to mouth sores.
If you encounter any of these symptoms while taking Hydroxyurea, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Your doctor will assess the situation. May need to adjust your dosage accordingly.
Tips for Minimizing Side Effects
To minimize the side effects of Hydroxyurea, there are a few strategies you can follow;
1. Stay hydrated by drinking an amount of water regularly.
2. Manage nausea and vomiting by eating frequent meals.
3. Protect your skin from direct sunlight or use protective clothing and sunscreen outdoors, as Hydroxyurea can make your skin more sensitive to UV rays.
Remember to communicate with your healthcare provider with any concerns or questions about the side effects. They can guide how to cope with these issues while taking Hydroxyurea. For information on managing side effects, you can refer to a helpful resource from the National Cancer Institute. It's essential to be aware of the reactions that may occur when taking hydroxyurea and understand how long it is safe to continue taking it to maximize its benefits while minimizing risks.
Key Takeaway: Hydroxyurea may have side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, dizziness or headache, hair loss (alopecia), skin rash, or itching. There's also a possibility of complications like fever or chills indicating an infection due to a weakened immune system, as well as excessive bleeding after minor injuries. However, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help reduce these side effects.
How Long Can You Take Hydroxyurea?
Hydroxyurea is a medication for treating different blood disorders, including sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. However, patients often have concerns regarding the length of time hydroxyurea should be taken and its safety for use.
Safety of Long-Term Use
Studies have shown that hydroxyurea can be safely used for a period in many cases. For example, research conducted on sickle cell anemia patients taking hydroxyurea for more than ten years has shown significant improvements in their health without any severe side effects or complications (source). However, it is important to remember that every patient's situation differs. It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before making any decisions about long-term usage.
Risks Associated with Prolonged Treatment
- Possible health risks; While it is uncommon there have been some reports of kidney and liver damage linked to long-term use of hydroxyurea. To ensure detection of any potential abnormalities regular blood tests are recommended (according to the Mayo Clinic).
- Potential for developing cancers: Certain studies indicate a potentially elevated risk of developing leukemia or other types of cancer after prolonged exposure to this medication. However, further research is necessary to verify these findings.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Your healthcare provider will develop a treatment strategy tailored to your condition and requirements. This strategy might involve checkups, blood tests, and adjustments to your dosage or medication. You must closely adhere to your doctors guidance and promptly communicate any concerns or side effects you encounter throughout the treatment process.
Alternatives to Hydroxyurea
If hydroxyurea is not suitable for long-term use in your case, treatment options may be available depending on your specific medical condition.
- For instance, individuals with sickle cell anemia can explore alternatives like L glutamine therapy, which the FDA has approved.
- Similarly, patients with polycythemia vera might find medications such as ruxolitinib, according to the American Cancer Society.
In summary, while hydroxyurea is generally considered safe for prolonged periods in patients, it is crucial to consult closely with your healthcare provider when considering its long-term usage or exploring alternative treatments. It's essential to understand any drug interactions before taking this medication and consider how hydroxyurea may interact with other medications you are currently using.
In summary, Hydroxyurea is a medication that can be used safely for periods to treat blood disorders like sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. However, it's important to be aware of risks associated with long-term usage, such as kidney or liver damage and an increased risk of developing leukemia or other cancers. Collaborating closely with your healthcare provider will help guide you through decisions regarding long-term usage or alternative treatments.
Interactions with Other Medications
When using Hydroxyurea, it is essential to be mindful of interactions with other medications. Certain drugs can have effects when combined with Hydroxyurea, causing heightened side effects or diminished efficacy of either medication. To safeguard your well-being and ensure the effectiveness of your treatment regimen, please adhere to the following guidelines;
Drugs that May Interact with Hydroxyurea
- Certain antiviral medications, such as didanosine (Videx) and stavudine (Zerit), have been known to increase the risk of pancreatitis when taken together with Hydroxyurea.
- If you are undergoing cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy, it is essential to note that using these treatments concurrently with Hydroxyurea may potentially amplify the side effects of both therapies.
- Because Hydroxyurea weakens the system,, so consult your healthcare provider before receiving any live vaccines during your treatment.
- It's worth mentioning that combining Hydroxyurea with medications like allopurinol might impact the effectiveness of these drugs in treating gout.
Steps to Avoid Negative Interactions
- Maintaining communication with your doctor and providing them with a comprehensive list of all the medications you are currently taking, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, supplements, and herbal products, is essential. This information will help your healthcare provider make informed decisions regarding potential interactions between these medications.
- To minimize the risk of drug interactions, it is crucial to follow your doctor's instructions precisely when taking Hydroxyurea. Avoid adjusting dosages or discontinuing any medications without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Stay vigilant while using Hydroxyurea and other drugs. Promptly inform your doctor if you experience any unusual side effects or notice worsening symptoms. Your doctor may need to adjust dosages or consider treatments accordingly.
In conclusion, understanding potential medication interactions is vital for successful Hydroxyurea therapy. Recent studies have compared Hydroxyurea to cancer treatments and found it effective with fewer side effects. By maintaining communication with your healthcare team and closely following their guidance, you can minimize risks and maximize the benefits of this powerful medication. Remember that it is critical to remain aware of interactions between hydroxyurea and other drugs to ensure their potency. With the importance of understanding drug interactions in mind, let us now explore the use of hydroxyurea for thrombocytosis. Key Takeaway: When using Hydroxyurea, it is essential to be mindful of interactions with other medications. Some medications, such as antivirals and drugs for gout, can potentially have effects or decrease the effectiveness of Hydroxyurea. To prevent any interactions, it is essential to have open communication, with your healthcare team and carefully adhere to their guidelines.
Hydroxyurea for Thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis or essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a blood condition with excessive platelet production in the bone marrow. This can result in a chance of blood clots, which can lead to complications like stroke or heart attack. One effective way to manage thrombocytosis is through hydroxyurea, a medication that helps control production and lowers the risk of clotting.
Treating Essential Thrombocythemia with Hydroxyurea
Research has demonstrated that hydroxyurea successfully reduces platelet counts in patients with ET, consequently decreasing their risk of developing complications. This medication functions by inhibiting an enzyme called ribonucleotide reductase, which plays a role in cell DNA synthesis. By disrupting this process, hydroxyurea slows down the production of platelets and promotes normal blood flow.
- Dosage: Typically, adults with ET begin with a recommended dose of 15 mg/kg/day taken once daily. Your doctor will closely monitor your response to the treatment. Make adjustments to the dosage as necessary.
- Duration: The length of treatment varies depending on patient requirements and response to therapy. Some patients may require long-term use, while others only need short-term treatment.
- Effectiveness: Hydroxyurea has been proven effective in managing symptoms associated with platelet counts, such as fatigue, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, or bleeding episodes.
Monitoring and Side Effects
When you're taking hydroxyurea for thrombocytosis, it's essential to visit your healthcare provider for checkups. They will conduct blood tests to monitor your platelet count and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. Hydroxyurea may have side effects, including nausea or vomiting loss of appetite, mouth sores or ulcers, hair thinning or loss (alopecia), and skin rash or itching. If you experience side effects like fever, chills, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, swelling in the face/lips/tongue/throat, or signs of an allergic reaction such as hives, contact your doctor immediately.
Alternatives to Hydroxyurea for Thrombocytosis Treatment
In situations when patients experience difficulties with hydroxyurea due to its side effects or contraindications, like pregnancy or breastfeeding, they may consider alternative treatments. These alternatives can include medications like anagrelide (Agastron/Thromboreductin/Xagrid), interferon-alpha therapy (Rofact/Pegasys/Roferon A), and dose aspirin under medical supervision. It is essential to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of hydroxyurea before opting for this medication as a viable option for thrombocytosis. Therefore, patients should explore treatment options such as making lifestyle changes or trying different medications before deciding on hydroxyurea. In the following discussion, we will explore whether any substitutes for hydroxyurea might be more suitable for specific individuals.
Key Takeaway: Hydroxyurea is a medication used to manage thrombocytosis, a rare blood disorder characterized by excessive platelet production in the bone marrow. It helps regulate production and reduces the risk of clotting by inhibiting the ribonucleotide reductase enzyme involved in cell DNA synthesis. Regular checkups with healthcare providers are essential while taking hydroxyurea since it may lead to side effects such as nausea or vomiting, hair thinning or loss (alopecia), skin rash, or itching.
Is There a Substitute for Hydroxyurea?
If you're thinking about hydroxyurea therapy, it's important to explore options that might be available. While hydroxyurea is effective for conditions like sickle cell anemia polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, some patients may struggle with the drug. I prefer alternative treatments for personal reasons. Luckily some substitutes can be considered in consultation with your healthcare provider. Some of these alternatives include;
- L glutamine; This amino acid supplement has been approved by the FDA as a treatment option for cell disease. It helps reduce stress on red blood cells and can effectively decrease pain crises associated with the condition.
- Ruxolitinib; Primarily used to treat myelofibrosis (bone marrow scarring), ruxolitinib has also shown promise in managing symptoms of polycythemia vera. However, it should only be considered if other initial therapies have not been successful.
- Anagrelide; Specifically designed to treat thrombocythemia by reducing platelet production, anagrelide can be an option for patients who cannot tolerate hydroxyurea or are not responding well to the treatment.
In addition to medication options, nonmedicinal approaches may also be beneficial in managing thrombocythemia symptoms. For instance, let's consider the use of blood transfusions.
- Regular blood transfusions effectively relieve anemia and reduce complications associated with sickle cell disease.
- Another standard procedure is phlebotomy, which involves the removal of blood from the body using a needle. This method is commonly used to treat polycythemia vera by reducing the count of blood cells.
- Making lifestyle changes can also be crucial in managing symptoms related to these conditions. This includes maintaining a lifestyle with regular exercise, proper hydration, and a well-balanced nutrition plan.
Recent studies have shown that hydroxyurea compares favorably to treatments for sickle cell anemia polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. However, it is important to note that taking hydroxyurea may lead to side effects, and not all patients respond well to this medication. Therefore, discussing alternatives or substitutes for hydroxyurea with your healthcare provider is highly recommended before making any changes to your treatment plan. They can guide you on the options based on your specific condition and medical history. While there may not be a substitute for hydroxyurea, closely monitoring your treatment progress is vital for achieving optimal outcomes. By tracking your progress during therapy, any necessary adjustments can be made. Implemented as needed.
Key Takeaway: If you are considering hydroxyurea therapy, you must understand that options are available. You may want to discuss with your healthcare provider the possibility of using L glutamine, ruxolitinib, and anagrelide to manage conditions like sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. Moreover, pharmacological options are available, such as blood transfusions, phlebotomy, and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
When you are prescribed Hydroxyurea, it is vital to monitor your progress during the treatment. This can be accomplished by scheduling checkups and blood tests. It is also essential to evaluate the effectiveness of the medication and make adjustments to the dosage as needed.

Regular Check-Ups and Blood Tests
Your healthcare provider will arrange appointments to evaluate how your body responds to Hydroxyurea therapy. During these visits, they will conduct an examination, discuss any side effects or concerns you may have, and order blood tests. These tests are necessary for monitoring your health while taking this medication as they can detect any changes in blood cell counts that might indicate potential problems or complications. Monitoring hemoglobin levels helps assess how effectively Hydroxyurea is managing the symptoms of sickle cell anemia. Regularly checking blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets ensure these values remain within safe ranges throughout the treatment. Periodic liver function assessments are conducted to ensure that Hydroxyurea does not affect liver health over time.
Assessing Effectiveness and Adjusting Dosages
Your doctor will thoroughly review the results of your checkups and blood tests to determine if any changes in dosage or frequency of administration are needed. It's crucial for patients receiving Hydroxyurea to maintain clear communication with their healthcare providers because your feedback plays a significant role in optimizing the outcomes of your treatment. If you encounter any side effects or feel the medication is insufficient relief, you should consult your doctor about adjusting the dosage or exploring other potential treatment options. If necessary, they might suggest modifying the dosage or considering treatments. Remember that patience is vital when taking Hydroxyurea so make sure to follow your physician's guidance and continue with the course; it may take some time to observe its full effect. Patients taking Hydroxyurea can ensure they maximize its benefits while minimizing risks associated with this potent medication by closely monitoring their treatment progress through regular checkups and blood tests.
Key Takeaway: When using Hydroxyurea, monitoring your treatment progress through checkups and blood tests is essential. This helps evaluate the medication's effectiveness and allows for dosage adjustments as needed. To optimize treatment outcomes and minimize risks associated with this powerful medication, patients should maintain open lines of communication with their healthcare providers.
Buy Hydroxyurea: A Comprehensive Guide for Patients
Hydroxyurea, a medication commonly prescribed for treating cancer and sickle cell anemia functions by impeding the proliferation of cells. Its mechanism involves slowing down or halting the growth of cells within the body. When consuming Hydroxyurea, adhering to dosage and administration guidelines is crucial while remaining vigilant about any potential side effects. Patients should communicate openly with their healthcare provider regarding any medications they may be taking to prevent possible drug interactions. If you want to purchase Hydroxyurea online, we urge you to visit Buy Pharma for priced options and dependable service.
Hydroxyurea FAQ
- Is there a substitute for Hydroxyurea?
- How long can you take Hydroxyurea?
- Hydroxyurea for sickle cell?
- Hydroxyurea polycythemia vera?
- Hydroxyurea for thrombocytosis?
- Hydroxyurea side effects?
- Hydroxyurea in sickle cell?
- Hydroxyurea uses?
- Hydroxyurea mechanism of action?
- Hydroxyurea 500 mg?
- Hydroxyurea MOA?
- Hydroxyurea for polycythemia vera?
- What is Hydroxyurea?
- Hydroxyurea mechanism?
- Hydroxyurea drug class?
- Hydroxyurea dosage?
- Hydroxyurea dose?
- Hydroxyurea cost?
- What happens if you stop taking Hydroxyurea?
- Is Hydroxyurea chemotherapy?
- Hydroxyurea interactions?
- Hydroxyurea brand name?
- Hydroxyurea package insert?
- Hydroxyurea maximum dose?
- Hydroxyurea warnings?
- Hydroxyurea fatigue?
- Hydroxyurea and sickle cell?
- Hydroxyurea for sickle cell anemia?
- Hydroxyurea contraindications?
- Hydroxyurea generic name?
- Hydroxyurea indications?
- Hydroxyurea pronunciation?
- Hydroxyurea drug?
- Hydroxyurea wiki?
- Hydroxyurea class?
- Hydroxyurea classification?
- Hydroxyurea toxicity?
- Hydroxyurea thrombocytosis?
- Hydroxyurea medication?
- Hydroxyurea sickle cell disease?
- Hydroxyurea price?
- Hydroxyurea for high platelets?
- Is Hydroxyurea a chemotherapy drug?
- Is Hydroxyurea a chemo drug?
- Hydroxyurea chemotherapy?
- Hydroxyurea chemo?
- Hydroxyurea adverse effects?
- Hydroxyurea dose for polycythemia vera?
- Hydroxyurea capsules?
- Hydroxyurea immunosuppression?
- Hydroxyurea nursing considerations?
- Hydroxyurea off-label uses?
- Hydroxyurea macrocytosis?
- Hydroxyurea MOA sickle cell?
- Hydroxyurea use in sickle cell disease?
- Hydroxyurea for sickle cell side effects?
- How does Hydroxyurea help sickle cell?
- What does Hydroxyurea do for sickle cell?
- Is Hydroxyurea an immunosuppressant?
- Hydroxyurea sickle cell mechanism?
- Hydroxyurea skin side effects?
- Hydroxyurea suspension?
- Hydroxyurea side effects sickle cell?
- Hydroxyurea essential thrombocythemia?
- Hydroxyurea ulcers?
- Hydroxyurea therapy?
- Hydroxyurea treats sickle cell disease by?
- Hydroxyurea anemia?
- Hydroxyurea pregnancy?
- Hydroxyurea platelet?
- Hydroxyurea pills?
- Hydroxyurea long term side effects?
- Hydroxyurea reviews?
- Hydroxyurea monitoring?
- Hydroxyurea hair loss?
- What is Hydroxyurea used for in sickle cell?
- What does Hydroxyurea do for sickle cell patients?
- Hydroxyurea and alcohol?
- Hydroxyurea generic?
- Hydroxyurea treatment?
- Hydroxyurea tablets?
- Hydroxyurea AML?
- Hydroxyurea liquid?
- Hydroxyurea leukemia?
- Hydroxyurea rash?
- Hydroxyurea myelosuppression?
- Hydroxyurea fetal hemoglobin?
- Hydroxyurea drug interactions?
- Hydroxyurea definition?
- Hydroxyurea prescribing information?
- Hydroxyurea and polycythemia vera?