IFOSFAMIDE + MESNA
- I. Introduction to Ifosfamide + Mesna
- II. Uses of Ifosfamide + Mesna
- III. How Ifosfamide + Mesna Works
- IV. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- V. Composition of Ifosfamide + Mesna
- VI. Contraindications and Warnings
- VII. Drug Interactions
- VIII. Careful Administration and Special Populations
- Administration to Elderly Patients
- Dose Adjustments and Increased Monitoring
- Higher Risk of Adverse Effects in the Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Teratogenic Effects and Contraindications During Pregnancy
- Risk of Excretion into Breast Milk
- Administration to Children
- Safety and Efficacy in Pediatric Oncology
- Dose Adjustments Based on Age and Weight
- IX. Overdose of Ifosfamide + Mesna
- X. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
- XI. Storage and Stability of Ifosfamide + Mesna
I. Introduction to Ifosfamide + Mesna
Overview of Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide is an alkylating drug that falls under the category of chemotherapy medications and is commonly utilized in treating cancer because of its capacity to harm the DNA of fast-growing cancer cells. It originates from the nitrogen mustard group and has demonstrated effectiveness in addressing various types of solid tumors.
Overview of Mesna
Mesna is a substance known as 2 mercaptoethanol sulfonate sodium that is created to help combat the harmful effects Ifosamide can have on the bladder by neutralizing toxic byproducts within it and ultimately ensuring that hemorrhagic cystitis, a prevalent and severe side effect often linked to Ifosamide therapy, is prevented effectively.
The Purpose of Combining Ifosfamide with Mesna
The use of Ifosamide and Mesna together is crucial in reducing the chances of urotoxicity issues occurring during treatment for cancer patients. Ifosamide medication's effects on cancer cells could potentially harm the bladder lining due to its metabolites. Mesna serves as an agent by attaching to these substances produced by the medication, thus averting bladder inflammation and bleeding concerns.
History and Approval of Ifosfamide + Mesna in Cancer Therapy
Since the 1980s, after receiving approval from bodies, Ifosafamide has been widely used in cancer treatment plans with success, thanks to the addition of Mesna as a protective agent that has significantly improved its safety and efficacy when used in therapy for various types of cancer.
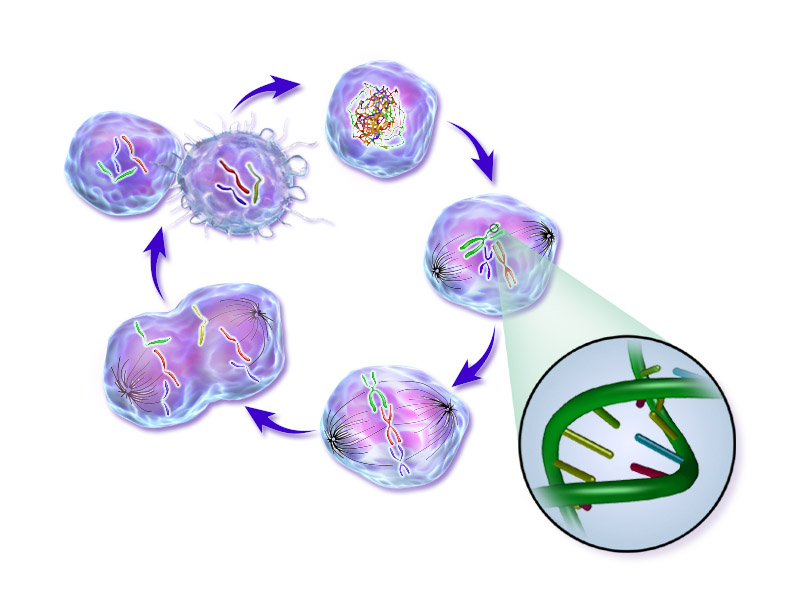
II. Uses of Ifosfamide + Mesna
Approved Uses in Cancer Treatment
Ifosfamide is widely utilized in treating several types of cancers. It is often prescribed for:
The drug's efficacy has been demonstrated across multiple cancer types, particularly where tumor burden is high and other treatments have failed.
Ifosfamide in the Treatment of Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Soft tissue sarcomas, a group of malignancies arising from connective tissues, are among the most responsive to Ifosfamide. It is used as part of multi-agent regimens to reduce tumor size or eliminate microscopic disease post-surgery.
Role in Treating Testicular Cancer
Ifosfamide is often combined with other agents, such as cisplatin and etoposide, in advanced or recurrent testicular cancer. Its potent cytotoxic effects make it an essential component in salvage chemotherapy regimens.
Use in Lymphoma Treatment
Both Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas have responded to Ifosfamide-containing protocols. Its inclusion in high-dose chemotherapy regimens has improved outcomes, particularly in relapsed or refractory cases.
Off-label Uses of Ifosfamide
Potential Use in Pediatric Cancers
Treatment for childhood cancers, such as rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma, often involves using Ifosamide in combination with therapies due to its effectiveness in reaching the brain and treating cancers that impact the nervous system.
Experimental Use in Certain Types of Leukemia
In types of leukemia that have come or are not responding to treatment as expected, ifosamide is being studied as part of new treatment plans to see if it can help patients better. Initial research results are positive. Further studies are required to confirm its effectiveness thoroughly.
Investigational Use in Metastatic Cancers
Ifosamide is being studied for its potential to treat cancers that have not responded to therapies, providing a possible ray of hope for individuals with advanced-stage illnesses.
III. How Ifosfamide + Mesna Works
Mechanism of Action of Ifosfamide
Ifosmide operates by a method called alkylation, where it creates connections with the DNA of cancer cells, disrupting their ability to reproduce and ultimately causing cell death. Its toxic effects are especially strong in cancer cells that divide rapidly.
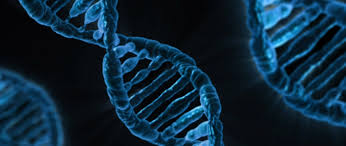
Alkylation and DNA Damage in Cancer Cells
By adding groups to the DNA molecules in the strands of DNA, Ifosmide is meant to create links and mismatched connections between the bases of the DNA, which leads to harm and eventually initiates apoptosis (cell death programmed by nature).
Immunomodulatory Effects
Ifosamide does not directly kill cells. It also influences the immune system by triggering immune responses against cancer cells that survive after causing tumor necrosis.
Role of Mesna in Preventing Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Hemorrhagic cystitis is a dangerous complication of Ifosfamide. Mesna neutralizes acrolein, a toxic byproduct of Ifosfamide metabolism, protecting the bladder lining from chemical damage.
Mesnaâs Mechanism of Protection
Mesna has sulfhydryls that interact with the substances created by Ifosfamide. Neutralize them to avoid building up in the urinary system.
Why Mesna Is Essential with Ifosfamide Administration
Using Mesna is crucial in decreasing the chances of bladder irritation and hemorrhagic cystitis when administering Ifosmamide in chemotherapy treatments.
IV. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing of Ifosfamide
When prescribing Ifos famide, doctors usually consider the patient's body surface area to determine the dosage, ensuring that each individual receives the amount of medication tailored to their needs. The standard dosage typically falls within the range of 1. ̶̶̶ ̶̶̶ ̅ 1. Ɛ, to Ƨ. ट grams, per meter of body surface area.
Based on Body Surface Area (BSA)
Calculating dosages using Body Surface Area (BSA) helps customize treatment to ensure that patients of varying body types receive the dosage for their needs.
Dose Adjustments Based on Renal Function
Patients with kidney issues may need to change their medication dosage to lower the chances of kidney damage. It's important to have tests to check kidney function during treatment.
Mesna Dosing and Timing
Intravenous vs Oral Administration of Mesna
Mesna can be given through a vein or by mouth, depending on what the patient prefers and the treatment needs in a setting or at home.
Timing of Mesna Doses in Relation to Ifosfamide
Mesna is usually administered prior to the use of Ifosmide and continued throughout and after its administration to safeguard the bladder consistently by neutralizing any harmful metabolites.
Administration Frequency and Cycles
Typically, in the course of treatment, ifosfamide for cancer patients involves alternating between treatment phases and periods of rest over a span of three to four weeks, per cycle based on the cancer type. The patient's response to treatment.
V. Composition of Ifosfamide + Mesna
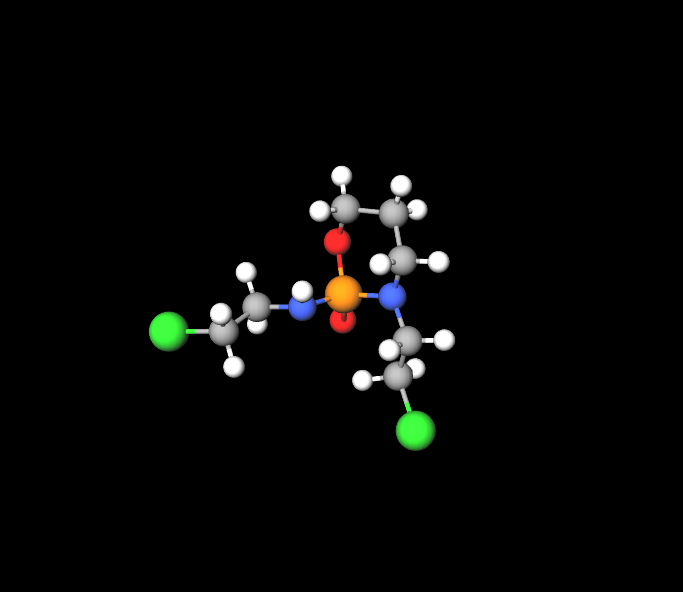
Chemical Structure of Ifosfamide
Ifosmide is a man-made version of cyclophosphamide. Its three-membered ring allows it to work as an alkylating agent.
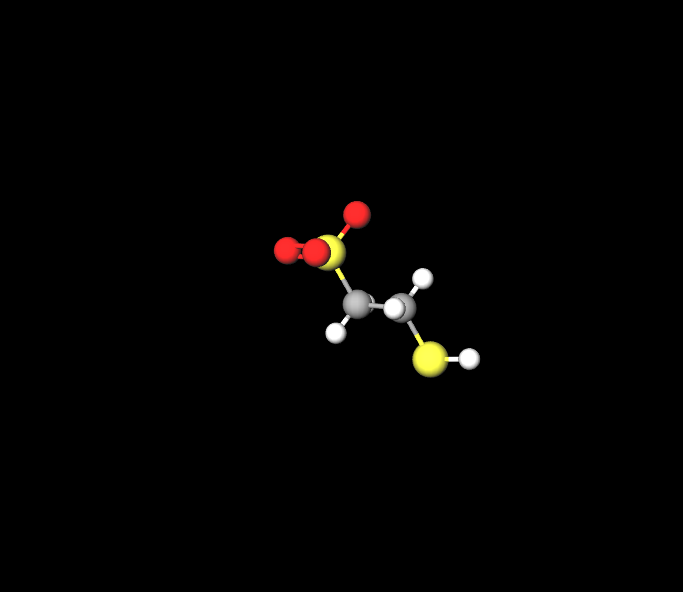
Chemical Structure of Mesna
The molecular structure of Mesna contains a thiol group that plays a role in its detoxifying function.It is a compound that dissolves in water and can be quickly broken down and eliminated from the body.
Available Formulations
Ifosfamide and Mesna are available in several formulations to suit different treatment protocols.
- Powder for injection
- Premixed solutions
Doxorubicin and ifosfamide
Chemotherapy drugs, like Doxorubicin and Ifosafamide are commonly used together to treat tissue sarcomas alongside relevant information regarding your cancer diagnosis and general chemotherapy guidelines should be considered while reading this information.
VI. Contraindications and Warnings
Known Hypersensitivity to Ifosfamide or Mesna
Patients who have a documented allergy to Ifosmide or Mesna should steer clear of using these medications due to the potential for reactions ranging from skin irritations to severe anaphylactic reactions; thus, it's crucial to thoroughly review a patient's medical history prior to treatment initiation.
Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Ifosfamide is primarily excreted through the kidneys, making it unsuitable for patients with significant renal impairment. In such cases, toxic metabolites may accumulate, leading to heightened nephrotoxicity. Caution and close monitoring are required in patients with renal dysfunction.
Patients with Active Infections
If a patient has an infection and takes Ifosmide for treatment, which weakens the body's ability to fight off germs during chemotherapy, there's a higher chance of developing serious infections that could be life-threatening.
Hepatic Dysfunction and Drug Metabolism
Ifosfamide undergoes hepatic metabolism, and patients with liver dysfunction may have altered drug processing, resulting in either reduced efficacy or increased toxicity. Regular liver function tests are recommended before and during treatment.
Use in Patients with a History of Urinary Tract Disorders
Individuals with existing tract conditions might be vulnerable to hemorrhagic cystitis caused by Ifosamides' side effects. Mesna helps reduce this risk; however, those with bladder or kidney issues should exercise added caution.
Ifosfamide toxicity
A significant portion of ifosfamide's effects stem from its byproducts in the body's metabolism process—especially acrolein—which play a crucial role in causing severe kidney and bladder-related health issues as these metabolites pass through the kidneys and produce damaging compounds, like ROS and nitrogen, that harm renal and urothelial cells.
VII. Drug Interactions
Potential Interactions with Other Chemotherapy Drugs
It is a practice to combine ifosfamide with chemotherapy drugs as this can impact its effectiveness or potential side effects. It is essential to choose accompanying medications to prevent any interactions or heightened toxicity levels.
Interactions with Anticoagulants and Blood Thinners
Patients taking anticoagulants or blood thinners need monitoring when prescribed Ifosamide, as it may increase the chances of bleeding complications in individuals prone to hemorrhage due to existing health issues.
Risk of Drug Interactions with Nephrotoxic Agents
Ifosfamide has the potential to harm the kidneys. When combined with medications that can also affect kidney function, like antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the chances of kidney damage rise substantially. The regular monitoring of function during treatment is essential for care.
Effects on Metabolism of Other Drugs
Ifosamide has the potential to change how other medications are metabolized in the body and can affect drugs processed by the liver, leading to lower-than-needed levels or increased toxicity of these medications. Therefore, it requires dosage modifications and frequent monitoring to ensure proper therapeutic levels are maintained.
VIII. Careful Administration and Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Older patients are frequently at risk for experiencing the effects of chemotherapy because their organs may not function as well due to aging processes. It is crucial to make changes, to the dosage and closely monitor any responses to guarantee both safety and effectiveness in this specific group of individuals.
Dose Adjustments and Increased Monitoring
Elderly patients often need their doses adjusted due to health conditions, like kidney or liver issues, that they may have alongside illnesses they might be dealing with like diabetes or high blood pressure.
Higher Risk of Adverse Effects in the Elderly
The elderly are more prone, to experiencing outcomes like bone marrow suppression and issues with the system and heart health. So it's important to be especially watchful, in handling these side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Teratogenic Effects and Contraindications During Pregnancy
It's not recommended to use Ifosamamide during pregnancy because it can cause birth defects in the baby if exposed to it while in the womb; hence, it's best to avoid this drug for women bearing children unless essential and reliable contraception is in place.
Risk of Excretion into Breast Milk
Ifosamide might be passed into breast milk and could harm a nursing baby; therefore, women receiving this treatment should avoid breastfeeding until the medication is out of their system post-chemotherapy.
Administration to Children
Ifosamide has been commonly utilized in treating childhood cancers like rhabdomyosarcoma within the field of oncology; however, its proper use involves dosage and close monitoring owing to the distinct pharmacokinetics observed in children.
Safety and Efficacy in Pediatric Oncology
The safety record of Ifosmamide in children has been confirmed for types of cancer; however, it's important to watch out for side effects like nerve damage and kidney problems that might be more severe in younger patients.
Dose Adjustments Based on Age and Weight
In medicine, doctors usually determine the dosage according to the child's body size or weight to provide a treatment that is effective and safe for each individual child. In this regard, careful monitoring is essential throughout the treatment process for children.
IX. Overdose of Ifosfamide + Mesna
Symptoms of Ifosfamide Overdose
Taking Ifosafamide can lead to serious problems, like feeling confused or dizzy or having seizures and severe blood cell suppression issues, which need urgent medical attention to avoid life-threatening situations.
Management of Overdose
Managing an overdose typically includes addressing symptoms through hydration and balancing electrolytes while closely monitoring kidney and liver functions for any changes or complications that may arise. In instances of overdose cases where necessary treatment may not be sufficient to address the situation, hemodialysis might be considered as a potential option to eliminate the drug from the body's circulation system.
Supportive Care and Symptomatic Treatment
Patients who experience bone marrow suppression due to an overdose of Ifosamide often need treatments like blood transfusions and growth factor administration to manage the condition. In a hospital setting, intensive monitoring plays a role, in aiding recovery.
The Role of Mesna in Overdose Situations
Mesna does not reverse Ifosfamide's systemic toxicity but plays a crucial role in preventing bladder toxicity even in overdose scenarios. Administering higher doses of Mesna may be necessary to counteract the increased production of urotoxic metabolites.
X. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Safe Preparation and Administration of Ifosfamide + Mesna
Healthcare professionals need to adhere to guidelines when dealing with Ifosamide and Mesna. These medications are categorized as substances that demand specific safety measures during their preparation and use to prevent potential exposure risks.
Guidelines for Handling Hazardous Chemotherapy Agents
To reduce the risk of exposure, chemotherapy agents like Ifosfamide should be handled in a controlled environment, such as a biological safety cabinet. Personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn at all times during preparation and administration.
Protective Measures for Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers administering chemotherapy should wear gloves, gowns, and eye protection to prevent accidental exposure. In case of accidental skin contact or inhalation, immediate decontamination procedures should be followed.
XI. Storage and Stability of Ifosfamide + Mesna
Proper Storage Conditions for Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide should be stored at room temperature, away from direct light and moisture. Once reconstituted, the solution is stable for a limited period and must be used within the manufacturerâs specified timeframe.
Storage Recommendations for Mesna
Store Mesna in a dry place just like you would store Ifosamife. The stability of Mesna can differ depending on whether it is in powder form or already mixed up in a solution; the manufacturer usually gives storage instructions for it.
Shelf Life and Stability Considerations
The shelf life of Ifosfamide and Mesna is limited, and both drugs must be used before their expiration date to ensure safety and efficacy. Reconstituted solutions have a much shorter window for administration, typically requiring use within 24 hours.
Handling After Reconstitution
Once reconstituted, Ifosfamide must be handled with care. Following aseptic techniques during preparation is crucial to prevent contamination, and the solution should be used promptly to maintain its potency.









