Ibandronic acid
- Introduction to Ibandronic Acid
- Uses of Ibandronic Acid
- How Ibandronic Acid Works
- Ibandronic acid dosage and Administration
- Composition of Ibandronic Acid
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Ibandronic acid interactions
- Ibandronic acid side effects
- Ibandronic acid warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Ibandronic Acid
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Overdosage and Emergency Management
- Important Precautions During Use
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Ibandronic Acid
Overview of Ibandronic Acid
Ibandronic acid is a type of bisphosphonate mainly utilized to support bone health by slowing down bone resorption processes and helping to manage conditions that impact strength effectively. It is well known for its role in decreasing fracture risks and preserving bone density.
Classification and Mechanism of Action
Ibandronic acid is categorized as a third-generation bisphosphonate that focuses on regulating function by binding to hydroxyapatite crystals in the bone structure and interfering with the resorption process to maintain bone strength and integrity in the run.
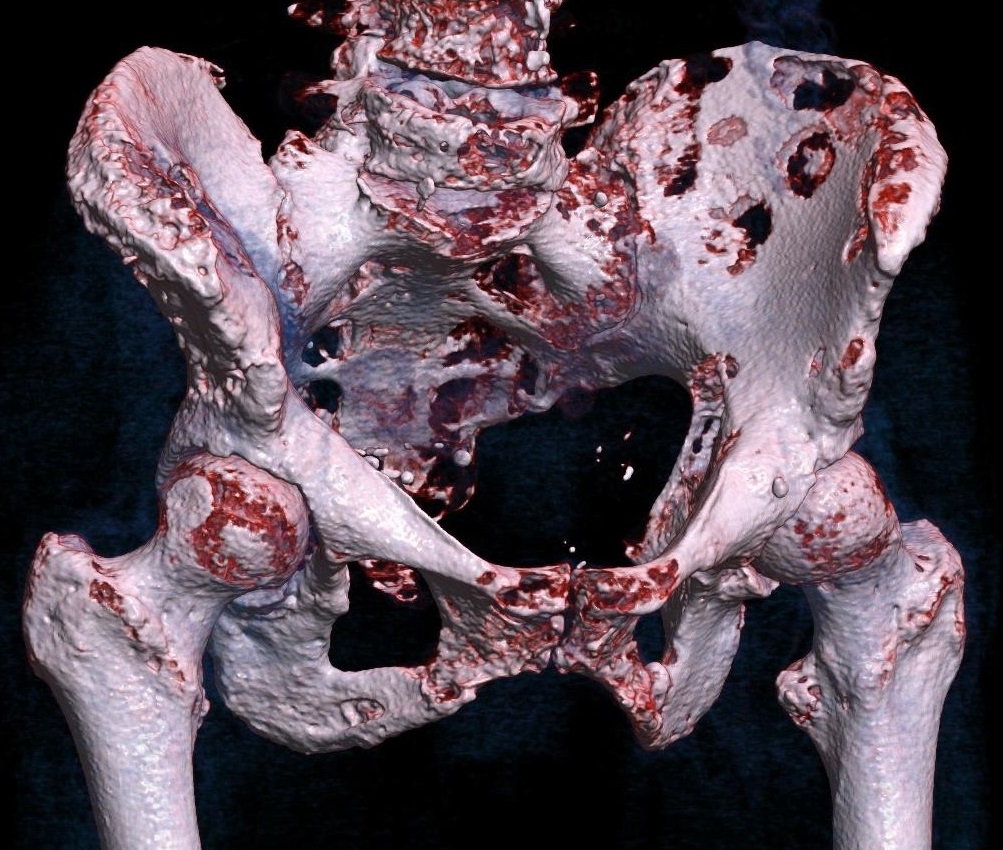
FDA-Approved and Global Uses
Ibandronic acid has received approval worldwide for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and cancer patients with bone metastases.
Importance in Treating Bone Health Conditions
Maintaining bones is essential for staying active and enjoying a quality of life in general. The use of ibandronic acid has changed how osteoporosis is treated by decreasing the likelihood of fractures and improving the stability of the skeletal system.
Uses of Ibandronic Acid
Primary Uses
Osteoporosis Treatment in Postmenopausal Women:
It works well to boost bone mineral density.
Prevention of Bone Fractures:
Decreases the likelihood of fractures in patients at risk of bone-related injuries.
Management of Bone Loss in Cancer Patients:
Prevents complications arising from metastases.
Off-Label Uses
Treatment of Hypercalcemia of Malignancy:
Restores calcium balance in cancer patients.
Paget's Disease
Off-label use for managing this chronic disorder.
Ibandronic acid breast cancer
It reduced bone loss in individuals with breast cancer that has spread to the bones, showing an effect similar to what's seen with intravenous zoledronic acid treatment.
How Ibandronic Acid Works
Inhibition of Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is carried out by osteoblasts, in the bodys bone maintenance process. Ibandronic acid works to limit their function. Helps maintain bone density even in abnormal situations.
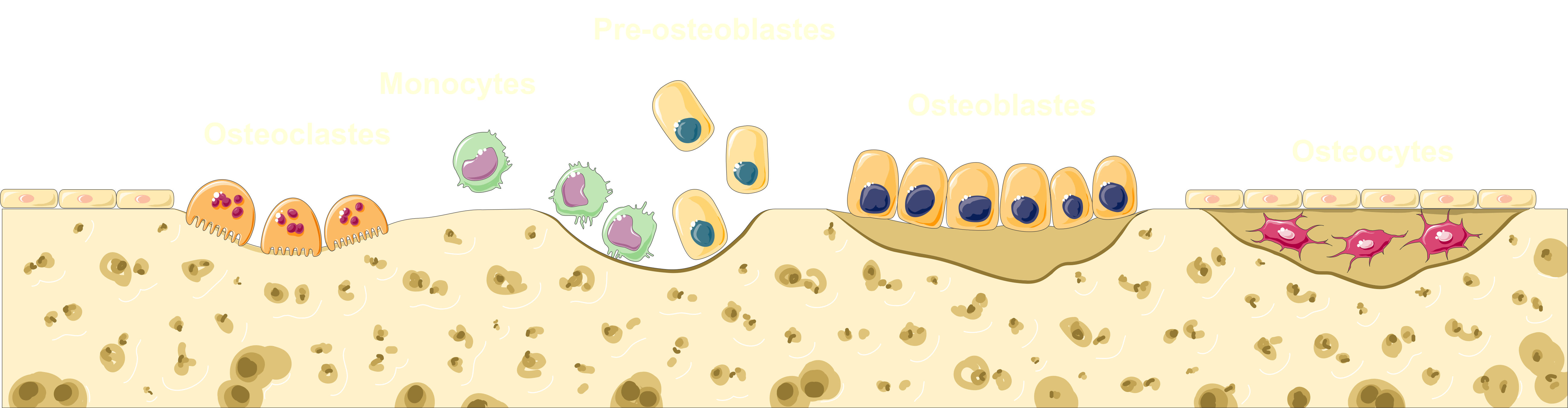
Interaction with Hydroxyapatite in Bone Matrix
It forms a connection with hydroxyapatite in bones, the mineralized part. This helps to keep the bone structure intact and prevent it from breaking down.
Long-Term Effects on Bone Density
Over time of using acid regularly helps increase bone density and provides lasting advantages, for people with ongoing conditions such, as osteoporosis.
Ibandronic acid dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Osteoporosis Prevention and Treatment
For postmenopausal osteoporosis, the usual dose is 150 mg taken by mouth monthly or 3 mg administered intravenously every three months; it's essential to stick to the dosing schedule for the treatment to work effectively.
Dosage Adjustments for Cancer-Related Bone Disorders
You might need doses at times to match your requirements depending on how seriously your bones are affected and your kidney function.
Administration Routes: Oral vs. Intravenous
Oral administration offers convenience but requires adherence to strict guidelines to avoid gastrointestinal issues. Intravenous routes are reserved for patients unable to tolerate oral formulations.
Tips for Optimal Absorption and Reduced Side Effects
- Remember to consume on an empty stomach and wash it down with a glass of water.
- Remember not to lie down for half an hour after taking the medication.
- Try not to take calcium or antacids right before you take your medication.
Composition of Ibandronic Acid
Active Ingredients
Ibandronic acid is the active ingredient in this medication. It belongs to a class of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates.
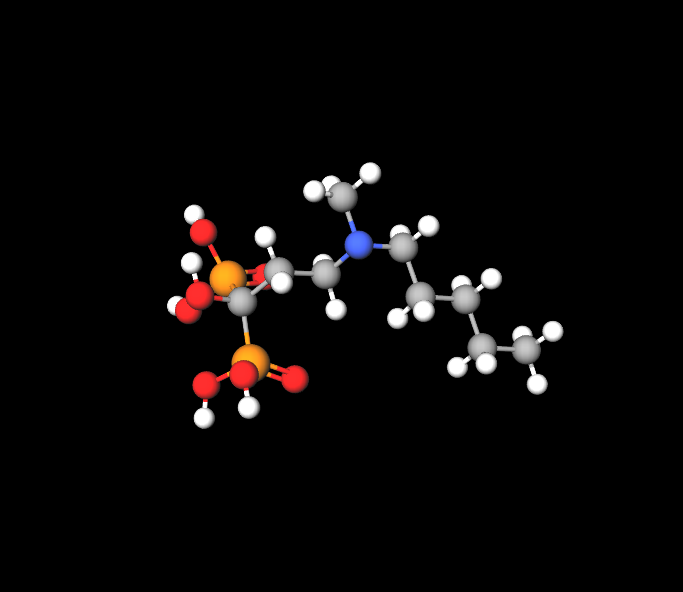
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
The tablet formulation and stability are maintained by incorporating lactose microcrystalline cellulose along, with stabilizers, in the ingredients.
Available Formulations: Tablets and Injections
Two main options exist for acid delivery. Oral tablets or quarterly intravenous injections.
Ibandronic acid vs alendronic acid
Both ibandronic acid and alendronic acid are types of bisphosphonates commonly prescribed for osteoporosis treatment. Ibandronic acid, when administered at lower dosages, has been noted to have negative effects compared to alendronic acid, especially in the upper digestive system.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Ideal Storage Conditions for Tablets and Injectable Forms
Please store the item in a place away, from direct sunlight and moisture at temperatures ranging from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Make sure to follow the expiration date, as improper storage could affect its effectiveness.
Safe Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
Make sure to discard it using the specified pharmaceutical waste disposal services to prevent environmental harm.
Ibandronic acid interactions
Common Drug Interactions
- Antacids and calcium supplements may hinder absorption in the body.
- NSAIDs and Corticosteroids can potentially lead to risks of irritation.
Potential Impact on Laboratory Test Results
Careful consideration is required when interpreting laboratory tests due to the impact acid can have on calcium and phosphate levels.
Food and Beverage Interactions
It's best to take it with water for absorption rather than have it with other food or drinks.
Ibandronic acid side effects
Common Side Effects
- Digestive issues, like feeling sick and having discomfort in the stomach area.
- Experiencing flu-like symptoms
Less Common but Severe Side Effects
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ): Associated with long-term use.
- Atypical Femoral Fractures: Rare but serious adverse events.
How to Recognize and Manage Side Effects
It's important for patients to quickly report any pain or swelling and keep up with check ups to watch out for any rare complications.
Ibandronic acid warnings and Precautions
Situations Requiring Careful Monitoring
It's important to closely monitor patients taking ibandronic acid to ensure their safety and well-being. Patients with existing kidney problems or gastrointestinal issues should be carefully evaluated before starting treatment. Regular monitoring of kidney function and calcium levels is essential to prevent any complications.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
While uncommon, some patients may experience reactions like skin rashes, itchiness, or even anaphylaxis. Individuals aware of their allergies to bisphosphonates or additives should avoid using the medication. It is important to have emergency procedures to address any allergic symptoms that may arise.
Contraindications for Ibandronic Acid
Absolute Contraindications
- Patients with kidney problems, defined as having a creatinine clearance of more than 30 mL/min, are advised to steer clear of ibandronic acid to prevent potential harm to their kidneys.
- Conditions like narrowing of the esophagus or difficulty swallowing can worsen irritation in the esophagus, raising the chances of experiencing consequences.
Relative Contraindications
- Untreated low levels of calcium in the blood, known as hypocalcemia, should be addressed before starting any treatment regimen.
- Ensuring that you have vitamin D levels is vital for maximizing the medication's effectiveness and minimizing issues.
Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
As people age, they may need to adjust their medication doses because their kidney function tends to decline with age. It's essential to check how well the kidneys are working and follow the guidelines to improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce any effects.
Administration to Pregnant and Nursing Mothers
- The use of ibandronic acid is advised against during pregnancy because studies on animals have shown harmful effects on fetal and neonatal development.
- Safety precautions for breastfeeding mothers should be taken into account when considering acid use since it is uncertain whether this medication is passed into breast milk; exploring treatments may also be recommended to ensure the well-being of the infant.

Administration to Pediatric Patients
Ibandronic acid is not approved for use in children because there is not enough data to support its safety and effectiveness in this age group, according to the available research studies.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Ibandronic Acid Overdose
Symptoms of an overdose could present as levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body, along with issues like nausea and inflammation of the esophagus in the upper gastrointestinal tract area. Severe instances may result in kidney problems or disruptions in electrolyte levels.
Immediate Steps for Management
In cases of overdose, discontinue the medication immediately. Administer milk or antacids to bind the drug and reduce absorption. Gastric lavage may be considered if ingestion is recent, particularly for oral formulations.
Long-Term Monitoring for Overdose Effects
It is important to check kidney function and electrolyte levels and ensure bone health in patients receiving treatment. Supportive measures, such as taking calcium and vitamin D supplements, may be needed to prevent any negative effects.
Important Precautions During Use
Regular Bone Density and Renal Function Monitoring
Regular bone density screenings and kidney function evaluations are crucial, for monitoring the effectiveness and safety of treatments. These tests play a role in detecting complications early and facilitating prompt intervention when needed.
Guidelines for Dental Procedures and ONJ Prevention
Prior to starting acid treatment, it is essential to conduct assessments, especially for individuals with cancer or those who are about to undergo dental procedures. Adequate oral care and refraining from tooth extractions can greatly lower the chances of developing ONJ.
Importance of Adequate Calcium and Vitamin D Intake
Optimal calcium and vitamin D levels enhance the therapeutic effects of ibandronic acid. Patients should be advised on dietary sources and supplementation as needed to maintain bone health.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Safety Measures for Preparing and Administering Injectable Formulations
Healthcare providers need to wear gloves and suitable protective gear when administering acid to safeguard against contamination and uphold patient safety through meticulous adherence to airtight procedures.
Minimizing Exposure During Handling
It is crucial to dispose of used vials and needles to prevent exposure to harmful substances like cytotoxic medications in healthcare settings following facility guidelines.
Ibandronic acid FAQ
- When to take ibandronic acid?
- What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
- What is ibandronic acid?
- What is ibandronic acid used for?
- How long should i take ibandronic acid?
- How does ibandronic acid work?
- How to use ibandronic acid?
- How to take ibandronic acid tablet?
- How to take ibandronic acid injection?
- How ibandronic acid works?
- Can ibandronic acid cause joint pain?
- What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
- How to give ibandronic acid?
- How to administer ibandronic acid?
When to take ibandronic acid?
Be sure to take it in the morning before eating anything, drinking coffee, or taking any medications.
What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
Ibandronate is often prescribed to treat osteoporosis by improving bone strength and reducing the risk of fractures.
What is ibandronic acid?
Bisphosphonate, known as acid, is commonly used to prevent bone fractures in individuals with bone-related cancers.
What is ibandronic acid used for?
It is practical, in addressing elevated calcium levels in the bloodstream resulting from cancer metastasizing to the bones (secondary bone cancer) as bone fragility or discomfort stemming from breast cancer spreading to the bones.
How long should i take ibandronic acid?
You typically have to use acid for a minimum of 6 months to see its impact on your bones before continuing as long as it remains effective.
How does ibandronic acid work?
Acid decreases the activity of osteoclasts, which can alleviate pain and enhance bone strength by lowering the loss of calcium from the bones, leading to a restoration of calcium levels in the blood.
How to use ibandronic acid?
You should always remember to have your acid tablets in the morning, along with a glass of water.
How to take ibandronic acid tablet?
In the morning, make sure to take your acid tablets with a glass of water.
How to take ibandronic acid injection?
Administer Ibandronic acid concentrate for infusion in the form of a solution over a period of 2 hours.
How ibandronic acid works?
Ibandronate functions by slowing the activity of bone-resorbing cells, thereby aiding in restoring equilibrium and enhancing the strength of your bones.
Can ibandronic acid cause joint pain?
Symptoms of the illness might include chills or shakes, headaches, and pains in the muscles or bones.
What are ibandronic acid tablets for?
A medication called ibandronate treats osteoporosis by enhancing bone strength and reducing the risk of fractures.
How to give ibandronic acid?
Remember to take the tablet in the morning on a stomach without sucking or crushing it; swallow it whole with a full glass of water while sitting or standing upright.
How to administer ibandronic acid?
Administer Ibandronic acid concentrate for the solution, and administer an infusion via a drip lasting 2 hours.