Isoxsuprine
- Introduction
- Uses of Isoxsuprine
- How Isoxsuprine Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition
- Side Effects
- Interaction with Other Medicines
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- X. Special Populations
- XI. Overdosage
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XIII. Conclusion
Introduction
A Brief Explanation of Isoxsuprine Isoxsuprine is a medication known for its ability to widen blood vessels. This unique characteristic is particularly beneficial in cases where blood circulation is compromised. Significance in Modern Medicine In today's field, Isoxsuprine plays a crucial role. Its effectiveness in improving blood flow makes it essential for treating various conditions. Moreover, it has applications both officially approved and off-label. Purpose of the Article This article aims to provide an understanding of Isoxsuprine, its uses, how it works in the body, and potential interactions with other medications. By gaining insights, into this drug, healthcare professionals and patients can make informed decisions.
Uses of Isoxsuprine
Approved Uses
Isoxsuprine is a vasodilator that is commonly used to treat vascular disease, a condition that affects blood flow to the extremities1. By improving blood circulation through its vasodilatory properties, Isoxsuprine helps address circulatory issues at its source1. Here is a reference to support this information:
Off-label Uses
Isoxsuprine is a beta-adrenergic agonist used in the symptomatic treatment of cerebrovascular insufficiency, peripheral vascular disease of arteriosclerosis obliterans, thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger’s disease) and Raynaud’s disease1. While Isoxsuprine has its uses, the medicine goes beyond its approved indications. It has been suggested that Isoxsuprine may help to prevent contractions in cases of preterm labor but it is important to use it cautiously for this purpose1. In addition, Isoxsuprine’s circulatory benefits may provide relief for Raynaud’s Phenomenon, a condition characterized by decreased blood flow in the extremities1. Moreover, Isoxsuprine is sometimes used for circulatory conditions not explicitly mentioned in its approved labeling thanks to its inherent properties1. Here is a reference to support this information:
How Isoxsuprine Works
Isoxsuprine functions as a beta-agonist, targeting and stimulating specific receptors to induce the relaxation of vascular smooth muscles. In addition to its effect, Isoxsuprine plays a role in optimizing blood flow to peripheral regions by dilating arterioles. It is well absorbed when taken orally and efficiently metabolized by the liver, allowing for its distribution and therapeutic benefits throughout the body.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage for adults is generally between 10 and 20 mg taken 3 to 4 times, per day. On the other hand, when it comes to children dosing needs to be more cautious and adjusted based on their weight and particular medical condition.
Routes of Administration
Tablets: These are commonly used and can be taken with a glass of water. Injectable forms: In situations, injections may be recommended as a more direct method of administration.
Dose Adjustments
Patients with accompanying conditions may require adjustments to the dosage of Isoxsuprine. If a patient has insufficiency, it might be necessary to reduce the dose in order to prevent potential toxic effects. Similarly, for patients, with liver dysfunctions, it is essential to consider adjustments as it can affect the metabolism of Isoxsuprine.
Composition
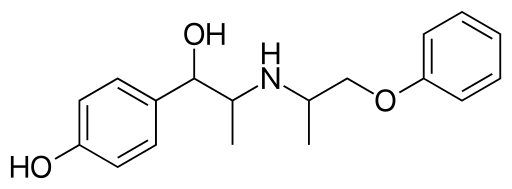
Isoxsuprine contains a combination of inactive ingredients, which work together to ensure the effectiveness and stability of the drug. The main component, Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride, is responsible for its effects. In addition, there are supporting ingredients, such as binders and fillers, that help maintain the structure and longevity of the drug. Isoxsuprine is available in formulations like immediate-release tablets and injectables to meet various clinical requirements.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Dizziness: After taking the medication, you might feel a sensation of lightheadedness. Palpitations: some patients may become more aware of their heartbeat. Nausea: You may experience gastrointestinal discomfort as a side effect.
Less Common Side Effects
Low blood pressure may occasionally occur as a side effect. An increased heart rate, although uncommon, should be monitored closely. Skin rashes could be an individual reaction in some cases.
Interaction with Other Medicines
Interactions between pharmaceuticals can be quite intricate. Isoxsuprine is undoubtedly no exception. When used alongside blood pressure medications, it could potentially increase the effects. If combined with anticoagulants, there may be a need for monitoring due to enhancements in anticoagulation. Additionally, when taken with vasodilators, there might be a synergistic vasodilation effect that requires adjustments to the dosage.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
Warnings
There is a warning to consider when using Isoxsuprine as it can increase the risk of bleeding especially when taken together with anticoagulant medications. It is crucial to monitor for any signs of excessive bleeding. Additionally, due to its ability to widen blood vessels, there is a possibility of experiencing a sudden drop in blood pressure, requiring careful observation and attention.
Contraindications
Tending Isoxsuprine or any of its additional ingredients is an apparent reason to avoid using it. It's important to note that, in cases of coronary artery disease, using Isoxsuprine may be ineffective and harmful, so it should not be used in such situations.
IX. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Parameters
Blood pressure: Regular monitoring can help prevent episodes of low blood pressure. Heart rate: Any irregularities in the rhythm of the heartbeat, such as a heart rate, should be identified and addressed promptly.
Lifestyle Considerations
Following a diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and low-sodium options can strengthen the therapeutic effects of Isoxsuprine. Additionally, moderate physical exercise can provide synergistic benefits while improving vascular conditions.
X. Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
Adjusting the dosage may be necessary for individuals with age-related kidney or liver issues. This is done to ensure that the treatment is optimized for the results. Monitoring these individuals is crucial due to their increased susceptibility to side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The FDA categorizes Isoxsuprine as Pregnancy Category C indicating that there is research on its safety for pregnant women. The information regarding the excretion of Isoxsuprine in breast milk is uncertain. Therefore,, medical professionals should determine the safety of using it during lactation on a case-by-case basis.
Administration to Children
The safety and effectiveness of Isoxsuprine in use are still uncertain due to a lack of substantial data. When determining the dosage for children, it is crucial to consider their weight and clinical condition.
XI. Overdosage
Signs of overdose may include,. These are not limited to a significant drop in blood pressure and an increased heart rate. Taking action usually involves gastric lavage (stomach pumping), providing symptomatic relief, and considering the use of vasopressor medications to counteract the effects of low blood pressure.

XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
It is recommended to store Isoxsuprine in a dry place away from direct sunlight at temperatures ideally between 15 and 30°C (59 86°F). It is crucial to be aware of the expiration date and responsibly dispose of any expired medications.
XIII. Conclusion
Key Takeaways: Isoxsuprine is a medication used to treat various vascular conditions, and it is vital to be aware of its uses and precautions. Why Consultation with a Healthcare Provider is Crucial: Due to the complexities involved in its usage and the potential for interactions, it is essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional for effective treatment.