Ivermectin/ Pyrantel Pamoate
- Introduction
- Composition and Mechanism of Action
- Approved Uses and On-Label Indications
- Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects and Common Adverse Reactions
- Contraindications, Warnings, and Important Precautions
- Special Considerations for Vulnerable Populations
- Overdosage: Recognition, Management, and Emergency Protocols
- Storage, Handling Precautions, and Drug Interactions
Introduction
Overview of Ivermectin/Pyrantel Pamoate
Ivermectin and Pyrantel Pamoate constitute an advanced therapeutic duo renowned for their potent antiparasitic properties. This combination is meticulously engineered to target a wide spectrum of parasitic infections, particularly those afflicting the gastrointestinal tract. The integration of these agents into modern therapeutic regimens reflects a commitment to precision medicine and optimized patient outcomes.
- Targeted antiparasitic efficacy
- Optimized pharmacokinetic profiles
- Enhanced patient compliance
Historical Background and Rationale for Combined Therapy
The historical evolution of these agents is as compelling as it is innovative. Ivermectin emerged from rigorous research on neglected tropical diseases, while Pyrantel Pamoate has been a stalwart in deworming protocols for decades. Their convergence was driven by a desire to harness complementary mechanisms, thereby amplifying antiparasitic efficacy and reducing individual limitations.
- Decades of clinical evolution
- Complementary pharmacological actions
- Strategic minimization of drug resistance
Significance in the Treatment of Parasitic Infections
The combined therapy holds substantial significance in contemporary parasitology. By addressing multiple facets of parasitic life cycles, this regimen offers a robust solution to the challenges posed by complex infestations. Its employment in clinical practice signifies a paradigm shift towards more holistic and effective management strategies. p>
- Comprehensive eradication of parasitic entities
- Enhanced treatment durability
- Reduced recurrence rates
Composition and Mechanism of Action
Chemical Composition and Formulation Details
Ivermectin is a macrocyclic lactone, while Pyrantel Pamoate is a tetrahydropyrimidine derivative; both are formulated with precision to ensure optimal bioavailability. Their formulation incorporates specialized excipients that stabilize pharmacokinetics and facilitate consistent therapeutic plasma concentrations.
- High-purity active compounds
- Stabilizing excipient blend
- Enhanced solubility and absorption

How Ivermectin Works: Pharmacodynamics and Target Pathways
Ivermectin exerts its antiparasitic action by binding to glutamate-gated chloride channels predominantly found in parasite neural and muscle cells. This binding induces hyperpolarization, resulting in rapid paralysis and subsequent parasite death. Short, incisive bouts of activity are complemented by sustained pharmacodynamic effects.
- Hyperpolarization of parasite cells
- Disruption of neuromuscular transmission
- Rapid onset of antiparasitic activity
How Pyrantel Pamoate Works: Mechanism and Efficacy
Pyrantel Pamoate functions as a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. Its mechanism induces spastic paralysis in helminths, thereby facilitating the expulsion of parasites from the host's system. This precise interference with parasite neuromuscular function is both rapid and efficient.
- Immediate neuromuscular blockade
- Acceleration of parasitic clearance
- Effective against a broad spectrum of helminths
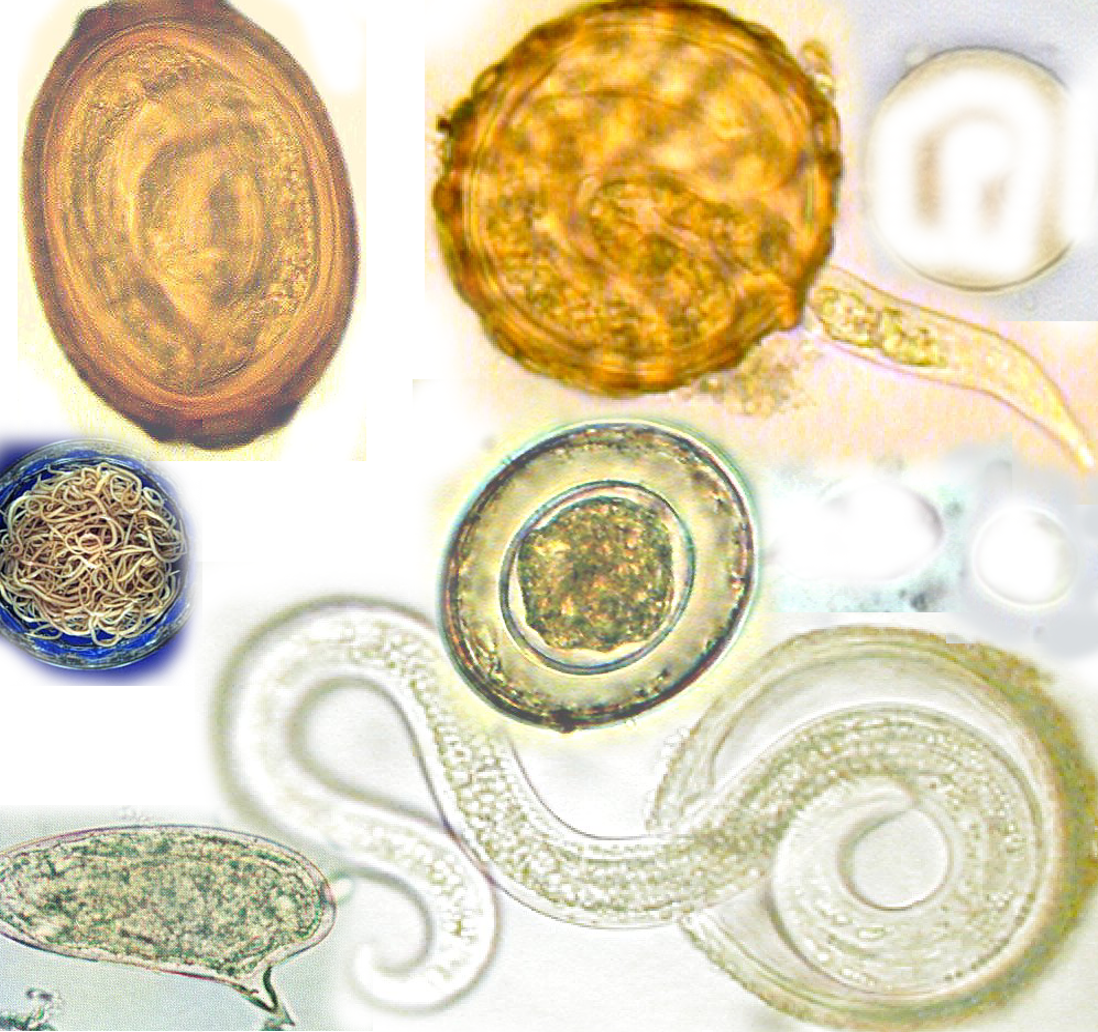
Synergistic Effects in Dual Therapy
When administered in tandem, Ivermectin and Pyrantel Pamoate exhibit synergistic properties that potentiate their individual therapeutic actions. The complementary interplay between these agents not only enhances overall efficacy but also diminishes the risk of developing drug resistance. This dual-action mechanism integrates brisk intervention with enduring therapeutic effects.
- Augmented antiparasitic potency
- Minimized resistance development
- Comprehensive coverage of parasitic life cycles
Ivermectin fenbendazole
Fenbendazole on its own or in combination with ivermectin was found to be more efficacious than the use of ivermectin alone in the control of Trichuris spp. Ivermectin has a longer persistence and thus may be efficacious against some degree of reinfection from parasites overwintering on the pasture. There is no residual effect of fenbendazole and it could be that fenbendazole is less effective because of this difference.
Approved Uses and On-Label Indications
Primary Uses in Treating Intestinal Parasites
The principal indication for Ivermectin/Pyrantel Pamoate is the treatment of intestinal parasitic infestations. Its efficacy in combating roundworms, hookworms, and pinworms is well-documented, providing a rapid and effective solution for gastrointestinal parasitism.
- Treatment of Enterobius vermicularis
- Management of Ascaris lumbricoides
- Reduction of Ancylostoma burdens
Ivermectin for human
Beyond its gastrointestinal applications, Ivermectin has secured approval for specific dermatological conditions such as scabies and ivermectin for rosacea The adjunctive use of Pyrantel Pamoate in these instances further reinforces the therapeutic scope, providing both systemic and localized relief.
- Topical and systemic applications
- Adjunctive treatment in inflammatory dermatoses
- Enhanced skin condition management
Role in Managing Specific Parasitic Infections
The combined formulation plays an indispensable role in managing a myriad of parasitic infections. Its targeted action is pivotal in both common and esoteric cases of parasitism, rendering it a versatile tool in the clinician's armamentarium.
- Broad-spectrum antiparasitic activity
- Effective in multi-parasite infestations
- Robust action against resistant strains
Ivermectin for dogs

Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
Exploration of Off-Label Use in Viral and Inflammatory Conditions
Emerging studies have begun to explore the off-label potential of Ivermectin in modulating viral replication and attenuating inflammatory responses. These pioneering investigations open the door to novel applications that transcend traditional antiparasitic boundaries.
- Investigation in viral load reduction
- Potential in mitigating cytokine storms
- Exploratory anti-inflammatory applications
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing Regimens for Ivermectin
Standard dosing regimens for Ivermectin are meticulously calibrated to the severity of the parasitic load and patient-specific variables. A typical protocol involves a single, weight-adjusted dose, succeeded by periodic reassessment to confirm therapeutic success.
- Weight-based dosing adjustments
- Standardized therapeutic intervals
- Follow-up assessments for efficacy
Ivermectin dosage for dogs by weight
Ivermectin is approved for use in dogs at oral doses up to 0.024 milligrams per kilogram, whereas most dogs can tolerate doses of up to 2.5 milligrams per
Standard Dosing Regimens for Pyrantel Pamoate
Pyrantel Pamoate dosing adheres to established anthelmintic guidelines. Precise dosage determination is critical to optimize parasite expulsion while minimizing the potential for adverse effects.
- Conformance to clinical dosing charts
- Emphasis on accurate therapeutic titration
- Routine re-evaluation of treatment response
Administration Methods: Oral and Alternative Routes
The primary route of administration is oral, a method that guarantees consistent bioavailability and patient convenience. In select clinical scenarios, alternative delivery systems may be employed to further enhance therapeutic outcomes.
- Oral ingestion as the conventional method
- Exploration of adjunctive delivery systems
- Adaptation to patient-specific requirements
Dosage Adjustments Based on Patient Weight and Severity
Tailoring the dosage regimen is imperative, particularly when confronting significant variations in patient weight or severe parasitic infestations. Clinicians must exercise judicious clinical acumen to individualize treatment protocols, thereby ensuring maximal therapeutic benefit.
- Individualized dosing strategies
- Dynamic adjustments aligned with clinical progression
- Consideration of patient-specific variables
Side Effects and Common Adverse Reactions
Overview of Side Effects Associated with Ivermectin/Pyrantel Pamoate
The side effect profile of Ivermectin/Pyrantel Pamoate spans a continuum from mild, transient disturbances to more pronounced adverse reactions. Vigilant patient monitoring is imperative to preempt and manage any untoward effects.
- Mild gastrointestinal disturbances
- Occasional neurological manifestations
- Rare hypersensitivity events
Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal and Neurological Manifestations
Patients may experience transient gastrointestinal upset including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Concurrently, neurological symptoms such as dizziness and headache may occur; however, these are typically self-limiting and resolve without intervention.
- Short-lived gastrointestinal discomfort
- Transient neurological effects
- Self-resolving adverse symptoms
Management Strategies for Minimizing Side Effects
Proactive management strategies are vital to mitigate side effects. Comprehensive patient education, meticulous dose modulation, and rigorous follow-up are the cornerstones of minimizing adverse reactions. These measures ensure that any side effects are promptly addressed and managed.
- Preemptive patient counseling
- Implementation of dose adjustment protocols
- Continuous clinical monitoring
Contraindications, Warnings, and Important Precautions
Contraindications for Combined Therapy
Not all patients are suitable candidates for Ivermectin/Pyrantel Pamoate therapy. Contraindications include documented hypersensitivity to the constituent compounds, concurrent severe systemic infections, and specific comorbid conditions that may exacerbate adverse outcomes.
- Known allergies to macrocyclic lactones or tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives
- Severe immunocompromised states
- Incompatibility with certain systemic conditions
Warning Labels and FDA/EMA Guidelines
Strict adherence to warning labels and regulatory directives is essential. Healthcare providers are urged to remain vigilant and updated on the latest guidelines issued by the FDA and EMA to ensure the therapy is administered safely and effectively.
- Compliance with regulatory advisories
- Integration of current clinical guidelines
- Ongoing review of safety protocols
Careful Administration: Best Practices in Clinical Settings
Best practices in clinical settings dictate a thorough evaluation of the patient prior to therapy initiation. Rigorous monitoring, accurate dosing, and methodical post-administration surveillance are imperative to maximize efficacy while mitigating risks.
- Comprehensive patient assessments
- Systematic monitoring protocols
- Meticulous dosing and follow-up

Important Precautions for Patients with Preexisting Conditions
Patients with preexisting conditions require a heightened level of caution. A meticulous review of individual risk factors, coupled with customized therapeutic strategies, is paramount to avert potential complications. Enhanced surveillance and tailored interventions serve as critical measures in these scenarios.
- Individualized treatment plans based on comorbidities
- Rigorous risk-benefit analysis
- Continuous monitoring for adverse effects
Special Considerations for Vulnerable Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients: Dosing Adjustments and Monitoring
Elderly patients often present with intricate pharmacokinetic profiles necessitating bespoke dosing regimens. A judicious approach, coupled with rigorous monitoring, ensures optimal therapeutic efficacy. Short assessments combined with comprehensive geriatric evaluations guide adjustments. The regimen must accommodate diminished renal and hepatic functionalities.
- Customized dosage based on metabolic capacity
- Enhanced vigilance for adverse reactions
- Regular clinical reappraisals and laboratory evaluations
Safety and Administration for Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of expectant and lactating mothers mandates an austere appraisal of risk versus benefit. Protocols are meticulously curated to forestall fetal or neonatal exposure to potentially teratogenic compounds. Despite the rapidity of action, careful deliberation on the transplacental and excretory profiles is imperative.
- Stringent adherence to obstetric safety guidelines
- Continuous monitoring of maternal-fetal well-being
- Consultation with specialized perinatal care experts

Guidelines for Administration to Children: Age-Specific Considerations
Pediatric patients require formulations and dosing strategies that reflect their evolving physiology. Age-specific considerations underpin the necessity for tailored administration protocols. The pharmacodynamic response in younger patients may be erratic; thus, clinicians must implement calibrated dosing schedules.
- Weight- and age-adjusted dosages
- Frequent monitoring for pediatric-specific adverse events
- Utilization of child-friendly formulations
Recommendations for Patients with Comorbidities
Patients harboring concurrent pathologies necessitate an individualized approach. A confluence of comorbid conditions may potentiate drug interactions and modify pharmacokinetics. The therapeutic strategy must be sufficiently flexible to mitigate compounded risks while maximizing therapeutic gain.
- Comprehensive pre-treatment evaluation
- Integration of multidisciplinary consultations
- Ongoing surveillance for interaction-induced complications
Overdosage: Recognition, Management, and Emergency Protocols
Signs and Symptoms Indicative of Overdosage
Overdosage manifests through a spectrum of clinical indicators, ranging from subtle neurological aberrations to pronounced systemic disturbances. Early recognition is critical; symptoms may include acute disorientation, persistent tachycardia, and severe gastrointestinal disturbances. Immediate identification of these markers is paramount.
- Neurological anomalies such as confusion and tremors
- Cardiovascular irregularities including arrhythmias
- Gastrointestinal distress with pronounced emesis
Recommended Immediate Actions and Medical Interventions
Prompt intervention in suspected overdose scenarios can dramatically curtail the progression of toxic sequelae. Initial measures include cessation of drug administration and rapid stabilization of the patient. Both pharmacological and supportive therapies are deployed expeditiously to alleviate symptoms and restore homeostasis.
- Immediate discontinuation of the implicated medication
- Implementation of supportive care protocols
- Utilization of antidotal agents where applicable
Protocols for Emergency Care in Cases of Overdose
Structured emergency protocols are indispensable in managing overdose incidents. These protocols encompass advanced resuscitative measures and intensive monitoring in a controlled clinical environment. Coordination among emergency services and toxicology specialists is essential for a comprehensive response.
- Activation of emergency response systems
- Continuous monitoring in an intensive care unit
- Administration of counteractive therapies based on toxicological assessments
Storage, Handling Precautions, and Drug Interactions
Proper Storage Guidelines and Shelf-Life Management
The stability and efficacy of pharmacotherapeutics are contingent upon scrupulous storage conditions. Medications must be stored in environments that preclude exposure to deleterious factors such as humidity and extreme temperatures. Shelf-life management protocols are strictly adhered to in order to preserve medicinal integrity.
- Maintain temperature-controlled storage
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and moisture
- Regularly review expiration dates and product integrity
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Meticulous handling practices are imperative to avert contamination and degradation of pharmaceutical compounds. Both healthcare professionals and patients must observe rigorous protocols when dispensing and administering medications. The process is streamlined by adhering to standardized procedures designed to mitigate inadvertent exposure.
- Adherence to aseptic handling techniques
- Employment of personal protective equipment
- Training on proper medication administration protocols
Patient Guidance for Safe Storage and Handling
Empowering patients with robust guidance on the proper storage and handling of their medications is a pivotal aspect of therapeutic success. Clear, concise instructions, combined with pragmatic tips, ensure that the medication remains potent and efficacious until administration. This guidance is disseminated through both verbal consultation and printed literature.
- Store medications in a secure, cool, and dry location
- Adhere strictly to usage instructions as prescribed
- Dispose of expired or compromised medications safely
Ivermectin/ Pyrantel Pamoate FAQ
- What is pyrantel used for?
- How long does pyrantel take to deworm?
- Is pyrantel better than mebendazole?
- Is pyrantel a good dewormer?
- Which is better, pyrantel or albendazole?
- What worms does pyrantel not treat?
- How to use ivermectin for dogs?
- What is ivermectin used for?
- Can ivermectin paste be absorbed through the skin?
- Can I give my dog ivermectin paste?
- Can you give ivermectin to dogs without a vet?
- How much ivermectin to give a dog for mange?
- What kind of parasites does ivermectin cure?
- Is ivermectin a steroid or antibiotic?
- Is ivermectin antifungal?
- Does ivermectin stop itching in dogs?
- How much ivermectin paste can I give my cat?
- Is ivermectin harmful to dogs?
- What breed of dogs cannot take ivermectin?
- How to know if ivermectin is working?
- What plant is ivermectin made from?
- What infections does ivermectin treat?
- Is ivermectin safe for human skin?
- Can ivermectin cure mange?
- How long does it take for itching to stop after ivermectin?
- How many times should I give ivermectin to my dog?
- Can I put ivermectin on my cat for fleas?
- How long does it take for ivermectin to start killing parasites?
- Can you use ivermectin on dogs for fleas?
- Can I give ivermectin paste to my dog?
- Can I deworm my dog with ivermectin?
- Is ivermectin painful for dogs?
- What is the natural source of ivermectin?
- Can Ivermectin treat lice?
- Is ivermectin a steroid or antibiotic?
- Can ivermectin paste be absorbed through the skin?
- Does ivermectin stop itching in dogs?
- What parasites does ivermectin treat?
- How much ivermectin paste can I give my cat?
- Is ivermectin good for fleas and ticks?
- Can I give ivermectin paste to my dog?
- How quickly does ivermectin work for mange?
What is pyrantel used for?
This medication is often used to treat worm infections such as pinworms, roundworms, and hookworms. Pyrantel belongs to a class of drugs known as anthelmintics. It works by paralyzing the worms and allowing the body to expel them through bowel movements.
How long does pyrantel take to deworm?
1-2 hrs
Is pyrantel better than mebendazole?
Both drugs have proven to be effective in treating enterobiasis.
Is pyrantel a good dewormer?
Many people consider Pyrantel to be a cost remedy, for eliminating parasites since a dose is usually sufficient to treat the infection effectively.
Which is better, pyrantel or albendazole?
Albenzadole has a success rate of 72% while Pyrantel Pamoate boasts an efficacy rate of 32%.
What worms does pyrantel not treat?
Doctors frequently recommend Pyrantel pamoate for treating worm infestations such as hookworm and Ascaris infections but its effectiveness in treating trichuriasis may be limited.
How to use ivermectin for dogs?
You can choose to give Ivermection in forms, like tablets or chewable options or even use a liquid or paste instead if needed help is recommended for injections.
What is ivermectin used for?
Patients are frequently given Ivermetin to address ailments such, as river blindness, also known as onchocerciasis and infections from threadworms in the intestines called strongyloidiasis. It is a remedy for worm infestation issues.
Can ivermectin paste be absorbed through the skin?
When Ivermetin is applied to the skin surface only a small amount enters the bloodstream where P glycoprotein acts as a safeguard for the blood brain barrier to prevent accumulation of Ivermetin in brain tissue.
Can I give my dog ivermectin paste?
You can also utilize it in medications that aid in ward off heartworm in dogs.
Can you give ivermectin to dogs without a vet?
Most dogs can handle Ivermectin well without any problems. Its important to follow your veterinarians instructions when administering it to them.
How much ivermectin to give a dog for mange?
Administer a dosage of 200 micrograms of Ivermection, per kilogram subcutaneously for 2 to 5 sessions separated by a two week interval has shown efficacy. Often leads to positive outcomes in terms of recuperation.
What kind of parasites does ivermectin cure?
Ivermection treatment has shown outcomes, in combating parasites such as strongyloidiasis and ascariasis and addressing skin problems like scabies and larva migrans well as certain infections, like filariasis and onchocerciasis.
Is ivermectin a steroid or antibiotic?
Iverctin isn't classified as a steroid or an antibiotic
Is ivermectin antifungal?
No
Does ivermectin stop itching in dogs?
Yes
How much ivermectin paste can I give my cat?
A common suggestion is to administer an amount of 24 micrograms for every kilogram of a cats weight.
Is ivermectin harmful to dogs?
When provided in doses and, under the guidance of a professional ivermection is typically considered safe for dogs and has proven to be highly effective in combating various parasites.
What breed of dogs cannot take ivermectin?
Some types of dogs such as collies and sheepdogs or their mixed breeds tend to exhibit a heightened sensitivity to ivermectin when compared to breeds.
How to know if ivermectin is working?
Once you begin using Ivermectin medication, its effects will gradually become noticeable, although it may take some time before you start experiencing relief from your symptoms.
What plant is ivermectin made from?
Streptomyces avermitilis
What infections does ivermectin treat?
People often depend on Ivermection to treat cases of river blindness caused by threadworms and other worm infections because of its effectiveness.
Is ivermectin safe for human skin?
Yes
Can ivermectin cure mange?
Yes
How long does it take for itching to stop after ivermectin?
After getting rid of the mites with medication treatment itching may persist for weeks.
How many times should I give ivermectin to my dog?
Monthly
Can I put ivermectin on my cat for fleas?
Yes
How long does it take for ivermectin to start killing parasites?
Right away after it's applied
Can you use ivermectin on dogs for fleas?
While fleas and ticks may not bear any resemblance to worms outwardly, certain treatments, from choices, can effectively eliminate fleas and ticks along with ear mites.
Can I give ivermectin paste to my dog?
Ivermection is an used medication, in the field of animal care and veterinary medicine to treat parasites in a variety of animals such, as dogs and is also utilized in preventing heartworm infections.
Can I deworm my dog with ivermectin?
Sometimes people consider ivermectin as a medication used to deworm dogs.
Is ivermectin painful for dogs?
When administered properly to dogs Ivermection is usually considered safe. Errors in dosage may lead to reactions.
What is the natural source of ivermectin?
S.avermictilils is known as the source of Ivermectin found so far.
Can Ivermectin treat lice?
Yes
Is ivermectin a steroid or antibiotic?
When it comes to categorizing medications Ivermeсtin is not classified as a steroid or an antibiotic; instead it falls under the category of drugs utilized to manage infections.
Can ivermectin paste be absorbed through the skin?
When ivermectin is applied to the skin it is absorbed into the bodys system through use indicating that P glycoprotein (PGp plays a role, in safeguardng the blood brain barrier and preventing the buildup of ivermectin in brain tissues.
Does ivermectin stop itching in dogs?
Yes
What parasites does ivermectin treat?
It is commonly utilized for addressing worm infections, like Onchocerciasis and Ascariasis well as for combating issues such, as Pediculosis (lice infestation) and scabies (mite infestation).
How much ivermectin paste can I give my cat?
24 µg/kg of body weight
Is ivermectin good for fleas and ticks?
Not as efficient as other medications.
Can I give ivermectin paste to my dog?
One could also utilize it in medications to safeguard dogs against heartworm infections.
How quickly does ivermectin work for mange?
3 weeks