Jula Gel
- Introduction to Jula Gel
- Composition of Jula Gel
- How Jula Gel Works
- Approved Uses of Jula Gel
- Off-Label Uses of Jula Gel
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects of Jula Gel
- Important Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Jula Gel
- Careful Administration Guidelines
- Administration Considerations for Specific Populations
- Drug and Product Interactions
- Overdosage and Toxicity Risks
- Proper Storage and Handling of Jula Gel
- Handling Precautions and Safety Measures
Introduction to Jula Gel
Jula Gel is a topical formulation designed for targeted relief from pain, inflammation, and dermatological conditions. Its advanced composition allows for deep penetration into the skin, ensuring rapid and effective results. Primarily used for musculoskeletal discomfort and skin irritations, this gel is trusted by medical professionals for its efficacy and safety.
The key active ingredients in Jula Gel work synergistically to provide relief. These components exhibit anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and skin-healing properties. Understanding the mechanism behind the gel's action is essential for maximizing its therapeutic benefits.
Applying Jula Gel correctly is crucial to achieving optimal results. Proper usage prevents excessive absorption, reduces side effects, and enhances the gel's ability to provide sustained relief.
Composition of Jula Gel
The efficacy of Jula Gel stems from its scientifically formulated composition, which includes:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs): Aloe Juice, Natural Chlorophyll, Biowhite, Tulsi are the primary agents responsible for the therapeutic effect. They target inflammation, pain, or microbial infections, depending on the condition being treated.
- Inactive Ingredients: These components enhance texture, absorption, and stability. They include emulsifiers, penetration enhancers, and preservatives that ensure prolonged shelf life.
- Advanced Formulation: The gel is designed for optimal bioavailability, ensuring that the active compounds reach affected areas efficiently while minimizing systemic absorption.

How Jula Gel Works
Jula Gel operates through a pharmacological mechanism that enables targeted action at the site of application:
- Penetration into the Skin: The gel formulation facilitates deep absorption without leaving a greasy residue.
- Reduction of Inflammation: Anti-inflammatory agents suppress inflammatory pathways, decreasing redness, swelling, and pain.
- Accelerated Healing: Certain ingredients promote tissue repair and regeneration, expediting recovery from wounds or irritation.
- Duration of Action: Depending on the severity of the condition, relief can last for several hours, making it a reliable choice for sustained symptom management.
Approved Uses of Jula Gel
Jula Gel is prescribed for a range of medical conditions, including:
- Dermatological Conditions: It is effective in treating eczema, psoriasis, and allergic dermatitis.
- Pain Relief and Inflammation: Commonly used for muscle pain, joint inflammation, and post-traumatic swelling.
- Wound Healing and Scar Management: Promotes regeneration of damaged skin and minimizes scar formation.
- Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties: In some formulations, it helps combat bacterial and fungal skin infections.
- Other Official Indications: Used for conditions such as sunburn, minor burns, and insect bites.
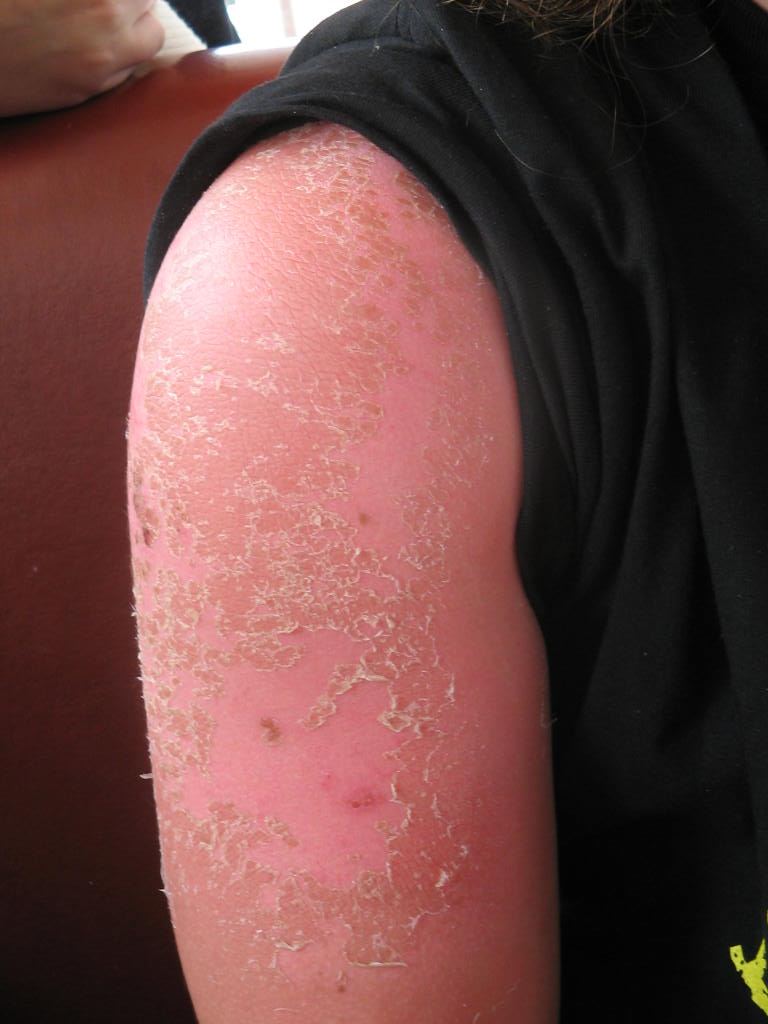
Off-Label Uses of Jula Gel
Beyond its approved indications, Jula Gel is sometimes utilized for alternative purposes:
- Unconventional Dermatological Applications: Anecdotal reports suggest effectiveness in reducing acne lesions and hyperpigmentation.
- Potential Musculoskeletal Benefits: Used for conditions like tendonitis and bursitis due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Emerging Research: Studies are exploring its role in treating neuropathic pain and inflammatory skin disorders.
- Risk vs. Benefit Analysis: Off-label use should always be discussed with a healthcare provider to weigh efficacy against potential side effects.
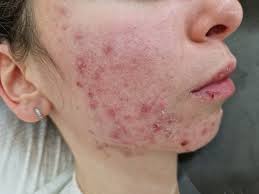
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
For optimal therapeutic results, Jula Gel should be applied according to the recommended guidelines:
- Standard Dosage: A thin layer is typically applied to the affected area two to three times daily.
- Method of Application: The gel should be gently massaged into the skin until fully absorbed.
- Frequency and Duration: The duration of treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition.
- Dosage Modifications: Adjustments may be necessary for elderly patients, children, or individuals with pre-existing conditions.

Side Effects of Jula Gel
While Jula Gel is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience adverse reactions. Several factors, including skin sensitivity and application frequency, influence the severity of these effects.
- Managing Side Effects: If irritation occurs, reducing frequency of use or switching to a milder formulation may be beneficial.
- Minimizing Risk: Conducting a patch test before widespread application can help prevent severe reactions.
Common Side Effects of Jula Gel
- Mild Skin Irritation: Redness or slight discomfort may occur, particularly in individuals with sensitive skin.
- Itching and Dryness: Some users report temporary dryness or peeling.
- Burning Sensation: A mild stinging sensation may be felt upon initial application.
- Other Reactions: Minor swelling or discoloration can sometimes develop.
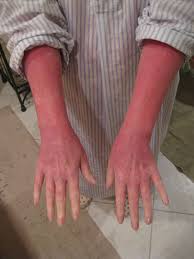
Severe or Rare Side Effects
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms such as hives, facial swelling, and difficulty breathing require immediate medical attention.
- Systemic Absorption-Related Complications: Rarely, prolonged use can lead to unintended absorption into the bloodstream, causing systemic effects.
- Photosensitivity Reactions: Some users may develop heightened sensitivity to sunlight, leading to sunburn-like symptoms.
- Emergency Situations: If severe irritation or anaphylactic symptoms appear, discontinuation and urgent medical care are essential.
Important Warnings and Precautions
Jula Gel, while highly effective, requires adherence to strict precautions to mitigate potential risks. Individuals must use the gel responsibly, following recommended guidelines to prevent adverse reactions and unintended systemic effects.
- Situations Where Caution is Required: Patients with pre-existing dermatological conditions, compromised immune systems, or hypersensitivity should consult a healthcare provider before using Jula Gel.
- Risk of Allergic Reactions: Sensitivity testing is advisable before full application. A patch test on a small skin area can help determine individual tolerance.
- Unintended Systemic Absorption: Excessive application, particularly over large body areas, may lead to systemic absorption, resulting in unwanted pharmacological effects.
- Prolonged Use and Excessive Application: Chronic or excessive use can lead to skin thinning, irritation, or tachyphylaxis, reducing the gel's efficacy over time.
Contraindications for Jula Gel
Jula Gel is contraindicated in several clinical scenarios, and its use must be strictly avoided in individuals meeting any of the following criteria:
- Absolute Contraindications: Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions or anaphylaxis to its active ingredients should avoid use.
- Hypersensitivity to Components: Those allergic to preservatives, excipients, or stabilizing agents in the formulation must refrain from application.
- Pre-Existing Skin Conditions: Individuals with conditions such as eczema, open wounds, or active infections may experience exacerbation of symptoms.
- Chronic Illness Considerations: Patients with systemic diseases, such as liver or kidney disorders, should consult a physician before incorporating Jula Gel into their treatment regimen.
Careful Administration Guidelines
For certain populations and conditions, Jula Gel requires careful administration and ongoing medical supervision to prevent complications.
- Cases Requiring Medical Supervision: Individuals with chronic skin disorders, circulatory issues, or a history of hypersensitivity reactions must use Jula Gel under medical guidance.
- Pre-Existing Conditions: Patients with psoriasis or chronic dermatitis may require customized dosing or adjunctive therapies.
- Interaction with Other Medications: Topical steroids, retinoids, and systemic medications may interact with Jula Gel, necessitating a review of concurrent therapies.
- Recommended Monitoring: Regular dermatological evaluations are advised for long-term users to assess efficacy and potential side effects.
Administration Considerations for Specific Populations
Use in Elderly Patients
Age-related changes in skin integrity necessitate special considerations when prescribing Jula Gel to elderly patients.
- Dosage Adjustments: Reduced frequency or lower concentrations may be required due to thinner and more fragile skin.
- Risk of Skin Thinning: The aging dermis is more susceptible to atrophy, increasing the likelihood of irritation and delayed healing.
- Precautionary Measures: Elderly patients should use a moisturizing base alongside Jula Gel to minimize dehydration and irritation.

Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of Jula Gel in pregnant and lactating women requires careful assessment due to potential fetal and neonatal exposure.
- Pregnancy Safety Profile: Limited clinical data exist regarding fetal effects, making cautious use imperative.
- Fetal Risk Considerations: Certain active ingredients may cross the placental barrier, potentially affecting fetal development.
- Absorption and Breastfeeding: Small amounts may transfer into breast milk, warranting medical consultation before use.
- Medical Guidelines: Healthcare professionals typically recommend alternatives with well-established safety profiles.
Use in Children and Infants
Children's skin exhibits heightened sensitivity, necessitating age-specific precautions when applying Jula Gel.
- Age Restrictions: Pediatric use is generally contraindicated for infants unless explicitly prescribed.
- Safety Concerns: The risk of systemic absorption is higher due to the increased surface-area-to-body-weight ratio in children.
- Common Adverse Reactions: Skin irritation, redness, and increased sensitivity are frequently observed in pediatric patients.
- Dermatologist Recommendations: Pediatric dermatologists typically advocate for milder formulations in younger age groups.
Drug and Product Interactions
Jula Gel may interact with other topical and systemic treatments, potentially altering efficacy or causing adverse effects.
- Topical Treatment Interactions: Avoid simultaneous use with strong corticosteroids or exfoliating agents, as they may amplify irritation.
- Systemic Medication Considerations: Certain drugs, such as blood thinners, may have interactions requiring professional oversight.
- Skincare Product Avoidance: Harsh cleansers, alcohol-based toners, or abrasive scrubs can compromise skin integrity and exacerbate irritation.
- Managing Concurrent Use: A staggered application schedule is often recommended when combining multiple topical treatments.
Overdosage and Toxicity Risks
Excessive application of Jula Gel can lead to localized and systemic toxicity, necessitating prompt medical intervention.
- Overdose Symptoms: Severe irritation, redness, peeling, and swelling may indicate excessive use.
- Complications: Absorption beyond recommended thresholds can result in systemic side effects, such as dizziness, nausea, or dermatological inflammation.
- Emergency Management: Immediate discontinuation and symptomatic treatment are required in overdose cases.
- Medical Interventions: In severe cases, detoxification protocols or systemic corticosteroids may be required.
Proper Storage and Handling of Jula Gel
Maintaining optimal storage conditions ensures product efficacy and safety.
- Storage Conditions: Keep Jula Gel at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and humidity.
- Expiration Considerations: Expired products may lose potency or develop harmful degradation byproducts.
- Contamination Prevention: Avoid direct contact with the tube opening to minimize microbial contamination.
- Safe Disposal: Expired or unused gel should be disposed of in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste guidelines.
Handling Precautions and Safety Measures
Ensuring safe handling practices minimizes exposure risks and enhances application safety.
- Safe Application Techniques: Apply Jula Gel using clean hands or a sterile applicator to prevent contamination.
- Healthcare Provider Safety: Clinicians administering the gel should use gloves when treating patients with open wounds.
- Use in Individuals with Skin Barrier Defects: Those with compromised skin integrity must exercise caution to avoid systemic absorption.
- Accidental Ingestion or Exposure: If ingested, seek immediate medical attention; if exposed to the eyes, rinse thoroughly with water.
Jula Gel FAQ
What is Jula Gel?
Jula Gel is commonly utilized to heal burns and alleviate discomfort associated with issues, like herpes and psoriasis well as to aid in wound healing and other ailments.
What is Jula Gel used for?
Jula Gel is commonly applied to soothe burns and alleviate pain associated with ailments like herpes and psoriasis while also aiding in the healing of wounds and addressing medical issues.