Ketoconazole
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Ketoconazole
- III. Off-label Uses of Ketoconazole
- IV. How Ketoconazole Works
- V. Composition of Ketoconazole
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Ketoconazole
- VIII. Warnings and Precautions
- IX. Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration
- XI. Interactions with Other Drugs
- XII. Overdosage
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XIV. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A Brief History of Ketoconazole: Ketoconazole was first approved by the FDA in the 1980s and has since been crucial in treating fungal infections. Its effectiveness in addressing types of fungal infections has made it an invaluable asset in pharmaceuticals. Overview of its Medical Importance: Ketoconazole uses have expanded beyond treating fungal infections. It is now utilized for conditions and even specific hormonal imbalances. This medication has proven to be a tool in bridging gaps in modern medical treatments. Scope of the Article: This comprehensive article explores the applications, potential side effects, and necessary precautions associated with Ketoconazole.
II. Uses of Ketoconazole
a. Antifungal Applications
b. Dermatological Uses
Seborrheic Dermatitis: People with this condition may experience flaky skin, usually on their scalp. Using Ketoconazole shampoos can often help improve these symptoms. Tinea Versicolor: Patches of skin identify this condition and can also be treated effectively with Ketoconazole, which has excellent antifungal properties.
The content is correct and accurate, as ketoconazole is a topical antifungal medication that can treat various skin infections caused by fungi, such as seborrheic dermatitis and tinea versicolor12345. Ketoconazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of a fungal component called ergosterol, which disrupts the fungal cell membrane and prevents its growth2. Ketoconazole can be applied as a cream, gel, foam, or shampoo to the affected areas, usually once or twice a day for two to four weeks depending on the condition and the strength of the product1345. Ketoconazole can cause some side effects such as skin irritation, dryness, itching, burning, or hair loss34. Ketoconazole should not be used by people who are allergic to it or have liver problems34.
1: Ketoconazole cream vs. clotrimazole cream - MedicineNet 2: Selenium Sulfide vs Ketoconazole: Which is Better? - Life Pathdoc 3: Ketoconazole Cream - Uses, Side Effects, and More - WebMD 4: Ketoconazole : an antifungal medicine used to treat skin infections - NHS 5: Ketoconazole (Topical Route) Proper Use - Mayo Clinic
c. Additional Therapeutic Uses
Cushing's Syndrome, an endocrine disorder, is another condition where Ketoconazole has demonstrated promising outcomes by inhibiting the synthesis of corticosteroids. For prostate cancer early studies indicate that Ketoconazole can help manage hormone prostate cancer by reducing testosterone production.
Ketoconazole has been used in high doses for the treatment of Cushing’s syndrome and advanced prostate cancer, but it has not been approved by the FDA for these indications and it may cause serious side effects such as liver damage123. Ketoconazole can inhibit the enzyme CYP17A1, which is involved in the biosynthesis of corticosteroids and androgens, thus reducing the levels of these hormones in the body45. Ketoconazole may be a useful option for patients with Cushing’s syndrome who have failed other treatments or are awaiting surgery4. Ketoconazole may also have some activity against prostate cancer cells that are resistant to castration or other hormonal therapies5. However, ketoconazole is not a first-line treatment for these conditions and should be used with caution and under close monitoring by a doctor123.
1: Ketoconazole: MedlinePlus Drug Information 2: Ketoconazole Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com 3: Ketoconazole Tablets: Package Insert - Drugs.com 4: Ketoconazole in Cushing’s syndrome: a profile of its use 5: The role of ketoconazole in current prostate cancer care - Nature
III. Off-label Uses of Ketoconazole
Hair Loss Treatment: While it hasn’t received FDA approval for this purpose, some people use Ketoconazole shampoo alongside treatments for alopecia. When it comes to Androgenic Alopecia, it is specifically used to combat the impact of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on the scalp. Furthermore, investigations are into other off-label uses, particularly in treating certain dermatological conditions.
The content is mostly correct and accurate, as ketoconazole shampoo is a topical antifungal medication that can also treat hair loss caused by fungal infections or androgenic alopecia123. Ketoconazole shampoo can inhibit the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT, a hormone that can shrink hair follicles and cause hair loss123. Ketoconazole shampoo can also reduce inflammation and improve scalp health, which may promote hair growth13. However, ketoconazole shampoo is not approved by the FDA for hair loss treatment and it should be used as an adjunct or complementary therapy along with other products such as minoxidil or finasteride124. Ketoconazole shampoo may also cause some side effects such as dryness, oiliness, itching, burning, or irritation of the scalp or hair245. Ketoconazole shampoo should not be used by people who are allergic to it or have liver problems45.
1: Should You Use Ketoconazole Shampoo for Hair Loss? 2: Ketoconazole for Hair Loss: What You Need to Know - GoodRx 3: How To Use Ketoconazole Shampoo For Hair Loss Prevention - Stylecraze 4: Ketoconazole Shampoo For Hair Loss: Types, Side Effects, and More 5: Ketoconazole Shampoo: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and More - Healthline
IV. How Ketoconazole Works
How Ketoconazole Works Against Fungi: Ketoconazole hinders the production of ergosterol, an element in the cell membranes of fungi. This interference causes the membranes to become more permeable, leading to the death of cells. How it is Processed in the Body: When taken orally, the drug is absorbed through the tract and then metabolized by the liver. Effects on Hormonal Pathways: Ketoconazole can inhibit enzymes responsible for synthesizing steroids, which can impact hormonal pathways.
V. Composition of Ketoconazole
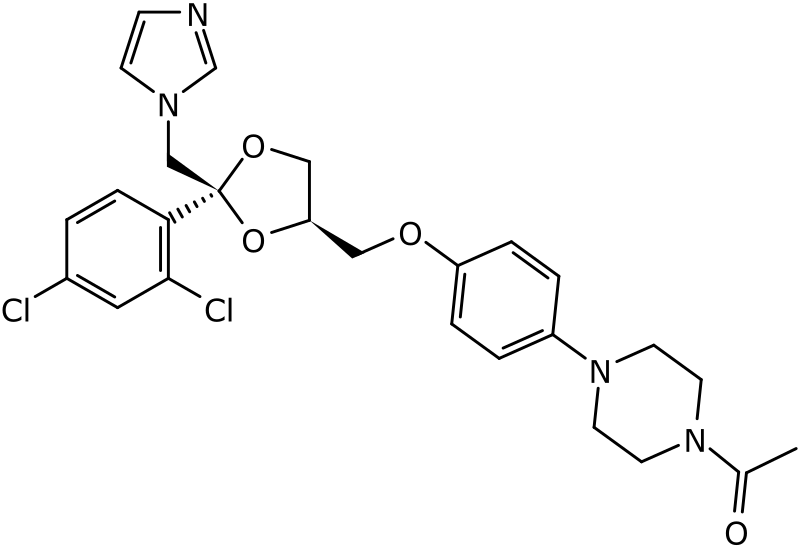
The main component of the formulation is Ketoconazole itself. Additional ingredients such as binders and preservatives may be included depending on the form of the medication. Ketoconazole is offered in states, including tablets, creams, and shampoos.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Dosage Recommendations: The recommended dosages may differ depending on the ailment being treated. When treating Candidiasis, an approach would be taking one 200 mg oral tablet daily. How the medication is administered will depend on its form and the specific indications with options, including application or oral ingestion.
VII. Side Effects of Ketoconazole
Common Side Effects; Feeling Experiencing vomiting. Serious Side Effects; Potential liver damage; It is crucial to be aware of the possibility of hepatic toxicity. Allergic reactions; This may manifest as symptoms, like hives or anaphylaxis.
VIII. Warnings and Precautions
It is recommended to get liver function tests while undergoing long-term treatment. Before starting the treatment, it may be necessary to conduct an allergy test to check for any hypersensitivity to azole antifungals. It's important to note that consuming alcohol can worsen the liver damage risks linked with Ketoconazole.
IX. Contraindications
Liver Disease: It is not recommended to administer Ketoconazole to patients who already have liver diseases due to the harm it can cause to the liver. People in this group risk experiencing adverse effects on their liver. Allergy to Azole Antifungals; If someone has reacted to Azole antifungals in the past, they should avoid using Ketoconazole and consider alternative treatment options. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Ketoconazole can pass through the barrier and be present in breast milk. Therefore, pregnant and breastfeeding women should not use it unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks.
X. Careful Administration
Necessary Precautions: It is important to monitor liver function and observe signs of adrenal insufficiency. When administering this medication to patients, it is crucial to exercise caution as they may be more susceptible to adverse effects. In some cases, lower initial dosages are often recommended. The use of this medication in women and nursing mothers should be discouraged unless necessary. If it is deemed necessary both maternal and fetal health should be closely monitored. When prescribing this medication to children, strict medical supervision is essential to minimize the risks associated with imbalances and liver function.
XI. Interactions with Other Drugs
When taking blood thinners like Warfarin, it is essential to be cautious when using Ketoconazole at the time. This combination can increase the anticoagulation effects of the blood thinners. May lead to excessive bleeding. If you also take antacids, separate the intake of Ketoconazole and antacids to ensure absorption of the medication. Additionally, certain antibiotics, like Erythromycin, can enhance the activity of Ketoconazole. Increase the risk of adverse effects when taken together. So, it's crucial to be mindful of interactions between these medications.
XII. Overdosage
Overdosing may lead to symptoms such as intense nausea, vomiting, and liver problems. It is crucial to seek medical attention in such cases. Urgent interventions, like lavage and administering fluids intravenously, should be initiated promptly. Chronic overdosing could potentially cause severe liver damage, adrenal insufficiency, and other irreversible consequences.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions
For results, it is recommended to store Ketoconazole at room temperature, away from moisture or direct sunlight. The specific storage requirements might vary depending on the form of the medication. It's advisable to refer to the package insert for accurate instructions. If there is a spillage, it should be immediately dealt with using personal protective gear. Contaminated products should be disposed of following waste protocols.
XIV. Conclusion
Key Points Summary: Ketoconazole is an antifungal medication with many uses, including treating fungal infections, skin conditions, and hormonal imbalances. However, taking precautions and being aware of interactions with other drugs is essential. It's crucial to have medical supervision. Final Recommendations for Effective Use: Consult a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Follow the recommended dosage instructions. Be mindful of possible side effects and situations where this medication should not be used to ensure safe and effective results.