Lactic Acid/ Salicylic Acid
- Introduction
- Composition and Mechanism of Action
- Uses of Lactic Acid and Salicylic Acid
- Dosage and Administration
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Side Effects
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Interaction with Other Medications and Products
- Careful Administration Guidelines
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Overdosage and What to Do
- Important Precautions
- Handling Precautions
- Conclusion
Introduction
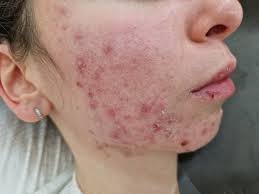
Lactic acid and salicylic acid are pivotal in dermatology and renowned for their transformative effects on skin health. Lactic acid, an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA), excels in exfoliation and hydration, while salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA), is celebrated for its ability to unclog pores and reduce acne.
Historically, these acids have been used in skincare treatments for centuries. From ancient Egyptian milk baths rich in lactic acid to modern acne therapies leveraging salicylic acid, their contributions are profound and enduring.
Their key differences lie in their solubility and function: lactic acid is water-soluble and primarily hydrates, while salicylic acid is oil-soluble and penetrates deeper into oily layers of the skin.
Composition and Mechanism of Action
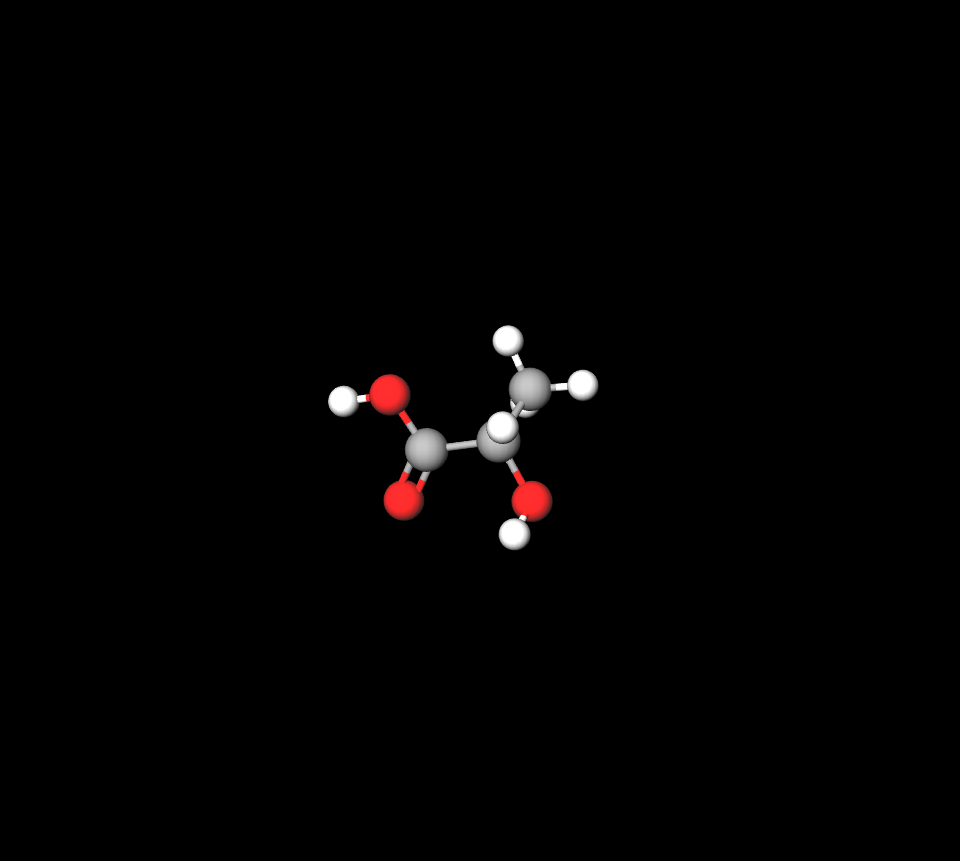
Chemical Structure of Lactic Acid
Containing a hydroxyl group next to a carboxyl acid component gives acid its properties as an exfoliant and moisturizer.
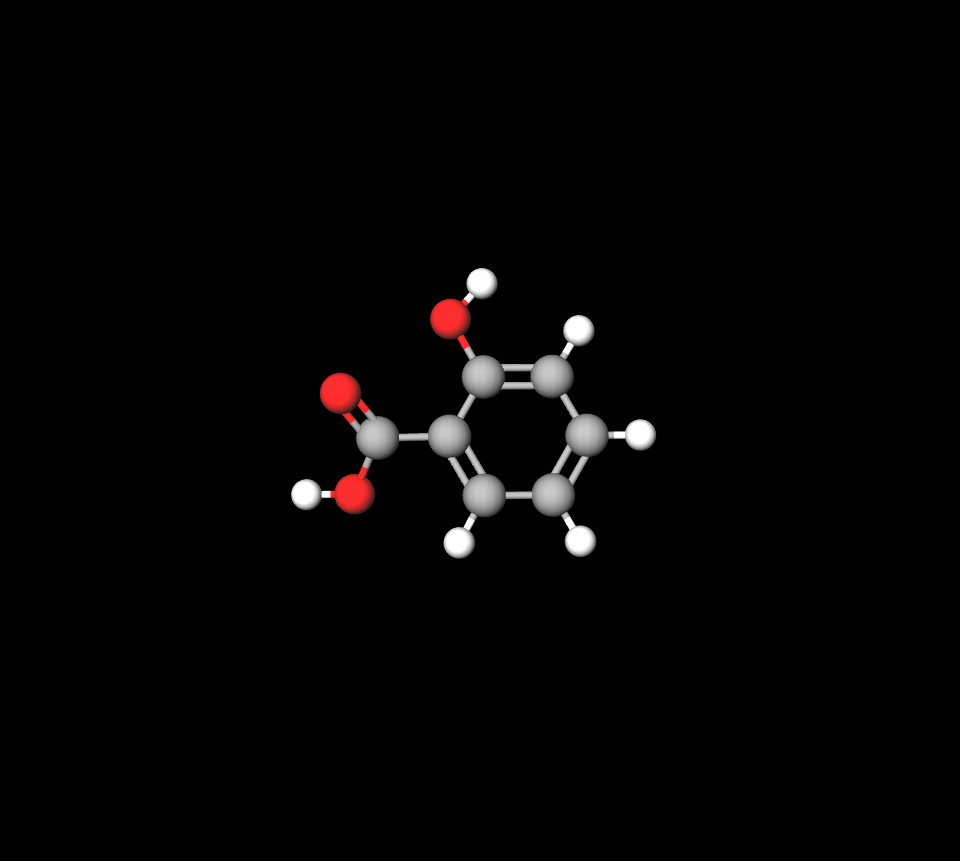
Chemical Structure of Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is well suited for breaking down skin debris and sebum due to its ring and hydroxyl group configuration.
How Lactic Acid Works in Exfoliation and Hydration
Gently exfoliating skin cells with acid unveils softer skin below and boosts hydration for those with dry or mature skin concerns.
How Salicylic Acid Works as a Keratolytic Agent
Salicylic acid goes into the pores to break down keratin plugs and unclog them effectively, which helps in reducing inflammation and preventing acne formation.
Lactic acid fermentation
During the absence of oxygen, in bacteria and animal cells, like muscle and red blood cells, lactic acid fermentation takes place, creating both energy known as ATP and lactic acid via a metabolic process.
Lactate vs lactic acid
The chemical structures of lactate and acid are quite similar. The key distinction lies in the presence of an additional hydrogen atom in lactic acid that is absent in lactate.
Lactic acid vs glycolic acid
The gentle lactic acid comes from milk and is ideal for those with skin due to its mild nature; on the other hand, the potent glycolic acid sourced from sugar cane goes deeper into the skin and is preferred for treating acne effectively. Lactic acid is often suggested for individuals with sensitive skin types, whereas glycolic acid is better suited for oily skin.
Glycolic vs salicylic acid
Both glycolic acid and salicylic acid are ingredients in skincare products known for their skin exfoliation and acne-fighting properties. The key distinction lies in their suitability for skin types; glycolic acid is preferred for dry skin types, whereas salicylic acid is more effective for oily or acne-prone skin.
Salicylic acid vs benzoyl peroxide
Salicylic acid functions by removing skin cells and excess oil from the skin to unclog pores effectively It is particularly effective in treating blackheads and whiteheads while also aiding in the prevention of future breakouts. Benzoyl peroxide operates by combating acne causing bacteria present on the skin It is most suitable for targeting red and inflamed acne as well as whiteheads and is Often recommended as an initial treatment, for mild to moderate acne conditions
Salicylic acid and niacinamide
Niacinamide is added to your skincare regimen since it offers distinct advantages for your skin and is typically safe to use together. Just keep in mind that if you have skin type it's crucial to handle them with care and be observant of any signs of irritation that may occur.
Lactic acid and retinol
Before you apply retinoids to your skin, using lactic acid can be beneficial as it helps in exfoliating and removing skin cells on the surface, allowing the retinoids to penetrate better and be more effective.
Lactic acid and vitamin c
Formulating lactic acid and vitamin C together enhances the effectiveness and absorption of vitamin C significantly—a combination for individuals with sun-damaged skin or persistent dark spots and pigmentation issues.
Uses of Lactic Acid and Salicylic Acid
Treatment of Acne
Management of Hyperpigmentation
Role in Keratosis Pilaris Treatment
Using acid helps to soften keratin deposits and lessen roughness typically linked with keratosis pilaris condition while salicycic acid aids, in smoothing skin by clearing buildup in hair follicles.
Use in Chemical Peels and Skin Rejuvenation
Applying chemical peels containing these acids helps eliminate damaged layers of skin to reveal a youthful look.

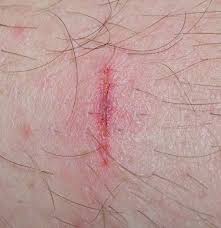
Off-Label Uses for Lactic Acid in Wound Healing
Off-Label Uses for Salicylic Acid in Wart Removal
Salicylic acid for scalp
Salicylic acid for razor bumps
Salicylic acid acts as a beta acid that helps pores by removing dead skin cells and reducing inflammation to aid in the healing of razor bumps.
Salicylic acid for hair
Using acid can assist in eliminating residue from products, like oils and sweat, that accumulate on your scalp and hair.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosages for Topical Application
In products, lactic acid is usually found in concentrations ranging from 7 to 11%, while salicylic acid is commonly present, in treatments at levels, between 1 and 1·8%.
Guidelines for Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peels may use acid concentrations ranging from 30% to 50% and salicylic acid concentrations, between 20% and 30%. It is advised to seek expert supervision during the process.
Recommended Frequency of Use for Daily Skincare Products
It's best not to use it more than twice a day to avoid irritation, and remember to apply the products after washing your face.
Adjustments for Sensitive Skin
Testing a patch is important for the skin. It's best to begin with lower concentrations and then slowly increase them as your skin can handle it.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions for Stability
Remember to keep the items in a dark area to avoid them from spoiling or losing their effectiveness due to exposure to sunlight.
Shelf Life and Expiration Details
Most formulations typically retain their effectiveness, for a period of 12 to 24 months when stored appropriately.
Proper Handling to Avoid Contamination
Remember to use hands or applicators when handling the product to avoid introducing any bacteria into it.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects of Lactic Acid
Common Side Effects of Salicylic Acid
Rare but Severe Side Effects and Symptoms to Monitor
Be alert for reactions such as swelling or ongoing irritation and stop using the product if any symptoms worsen to seek advice from a dermatologist.
Warnings and Contraindications
Conditions Where Lactic Acid Use is Contraindicated
It's best to steer when dealing with eczema or if the skin's natural barriers are damaged.
Conditions Where Salicylic Acid Use is Contraindicated
Not recommended for those with allergies to salicylates or severe dry skin issues.
Warning Signs of Allergic Reactions
Watch out for redness and blisters or if you're having trouble breathing. These could be signs of a bad reaction.
Lactic acid blood test
Measuring the level of acid in the blood through a blood test is a way to detect a condition known as lactic acidosis, where there is an excessive buildup of this acid in the bloodstream, which can pose serious risks to health, including heart issues and organ failure, if not addressed promptly.
Interaction with Other Medications and Products
Interaction with Retinoids and Other Acids
Using retinoids or strong acids together can lead to irritation. It's best to separate their application by a few hours.
Potential Reactions with Prescription Medications
It's advisable to seek advice from a doctor when using medications to prevent excessive exfoliation.
Guidelines for Combining with Moisturizers and Sunscreens
Remember to apply a non-comedogenic moisturizer and a broad spectrum sunscreen to safeguard your skin barrier.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Administration to Individuals with Sensitive Skin
People with sensitive skin need strategies when using lactic acid or salicylic acid since these active ingredients can lead to irritation if not used correctly. It is recommended to begin with lower concentration products and slowly increase how often you apply them to avoid any issues. Doing a patch test before fully applying the product can help identify any possible negative reactions.
Salicylic acid breastfeeding
Salicylic acid is typically deemed safe for use during breastfeeding as it's not expected to be absorbed or show up in breast milk; nonetheless, it is advisable to refrain from using it on areas of the body that could come into contact with the baby's skin.
Precautions for Individuals with Existing Dermatological Conditions
Those with conditions such as rosacea, eczema, or psoriasis should exercise caution. Consult a dermatologist before incorporating these acids into their regimen. The acids may exacerbate inflammation, especially if the skin barrier is already compromised.
Monitoring for Adverse Effects in Long-Term Use
Regularly monitoring the condition of your skin is important for prolonged use of the product as it can result in skin thinning or increased dryness. If used check-ups, with a dermatologist every few months can help maintain safe and beneficial results.
Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly
Adjustments for Aging Skin
As skin ages it often becomes thinner and more fragile in nature. For individuals it is advised to use amounts of lactic acid or salicylic acid. To prevent dryness when using these acids it is important to use hydrating products alongside them.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Lactic acid pregnancy
Pregnant women and nursing mothers should consult healthcare providers before using these acids. Current research suggests that low concentrations, particularly of lactic acid, are generally safe. However, high-concentration chemical peels or frequent applications are not advised during pregnancy.
Children
Guidelines for Safe Use in Pediatric Populations
Salicylic acid is commonly employed to treat children's ailments such as warts. It should only be applied in areas under medical guidance. Lactic acid can be utilized cautiously for particular skin issues, like keratoses pilaris by choosing formulations.
Overdosage and What to Do
Signs and Symptoms of Overuse or Overdose
Using much of these acids may result in redness, peeling, or a sensation of burning on the skin. In instances excessive use of acid may cause salicylism, which is characterized by feelings of nausea, dizziness or a ringing sensation, in the ears.
Steps to Take in Case of Accidental Ingestion or Skin Damage
Immediate medical attention is necessary if you ingest these acids orally; rinse your mouth thoroughly and do not induce vomiting unless instructed by a healthcare provider. In case of skin damage, from exposure to the acids, wash the area with water and apply a calming emollient. If symptoms persist despite these measures,seek guidance promptly.
Important Precautions
Avoiding Sun Exposure Post-Application
Both lactic acid and salicylic acid increase photosensitivity. Sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection and SPF 30 or higher is essential after application to prevent UV-induced damage.
Proper Rinsing Techniques to Prevent Buildup
Make sure to rinse your skin after using products that contain acid to prevent irritation – this step becomes particularly important, with wash-off items such as cleansers and masks.
Testing for Sensitivity Before Use
Before trying a product, on your skin in larger areas like behind the ear or on the forearm, it can help you avoid potential allergic reactions or irritation by doing a small patch test first.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling During Chemical Peels
For high-quality chemical peels to be effective and safe to use gloves and apply them without overlapping layers to prevent overexposure.
Avoiding Contact with Eyes and Mucous Membranes
Disposal Methods for Expired or Unused Products
Make sure to follow the waste management rules in your area when getting rid of items that have passed their expiration date, and refrain from pouring liquids into the drain to protect the environment.
Conclusion
Summary of the Benefits and Applications
Both lactic acid and salicylic acid provide advantages such as exfoliation and moisturization along with treating acne and managing pigmentation issues in skincare routines. A reason why they are commonly used in both cosmetic products.
Importance of Professional Guidance in Use
Monitoring skin care is crucial to guarantee the efficient use of these products, allowing experts to suggest suitable strengths and compositions customized for each person's requirements.
Encouragement for Patch Testing and Adherence to Guidelines
Following guidelines for patch testing. Using skincare acids as recommended can help reduce risks and improve outcomes for maintaining healthy and glowing skin.
Lactic Acid/ Salicylic Acid FAQ
- Can I use lactic acid with salicylic acid?
- What can you not mix lactic acid with?
- Which is better for acne scars, lactic acid or salicylic acid?
- What are the side effects of lactic acid and salicylic acid?
- What to use after salicylic acid?
- Can I leave lactic acid on overnight?
- Can I use salicylic acid every day?
- Who should avoid salicylic acid?
- Does salicylic acid lighten skin?
- Does lactic acid remove dark spots?
- What happens if I stop using salicylic acid?
- How long to leave salicylic acid on face?
Can I use lactic acid with salicylic acid?
Yes
What can you not mix lactic acid with?
Retinol, enzymes, benzoyl peroxide, along with AHAs and BHAs, are commonly used in skincare products for their benefits on the skin.
Which is better for acne scars, lactic acid or salicylic acid?
If your skin is sensitive, you should begin with an acid such as acid or mandelic acid, which are good options. Opting for acid to address acne scars would be a choice.
What are the side effects of lactic acid and salicylic acid?
Feeling a sensation of burning or itching accompanied by redness or irritation.
What to use after salicylic acid?
After using acid on your skin, remember to moisturize it as it may cause dryness.
Can I leave lactic acid on overnight?
If the level of acid is low and properly balanced in your product or formulae solution application, you can opt to leave it on your face overnight for better results.
Can I use salicylic acid every day?
It's safe to use your cleanser every day if it contains acid as an ingredient.
Who should avoid salicylic acid?
Avoid taking this medication if you have diabetes or suffer from blood circulation. Additionally, refrain from using this treatment for warts that have hair growing out of them or are located on the face or in the areas inside the nose or mouth. Moreover do not apply it to moles or birthmarks as it could lead to irritation.
Does salicylic acid lighten skin?
It aids in diminishing the visibility of spots and blemishes while reducing hyperpigmentation on the skin.
Does lactic acid remove dark spots?
Yes
What happens if I stop using salicylic acid?
If you stop the treatment for acne early, the problems might return.
How long to leave salicylic acid on face?
Please keep it on for 5 minutes initially. If you don't feel any discomfort, you can extend the duration to up to 15 minutes.