Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- I. Introduction to Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- II. Understanding How Gentamicin Works
- III. Comprehensive Guide to Gentamicin Usage
- IV. Dosage and Administration Details
- V. The Composition of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- VI. Storage Information for Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- VII. Potential Interactions with Gentamicin
- VIII. Important Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Careful Administration of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- X. Special Considerations for Gentamicin Use
- XI. Understanding Gentamicin Overdosage
- XII. Side Effects of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
- XIII. Important Precautions When Using Gentamicin
- XIV. Conclusion: Making the Most of Gentamicin Treatment
I. Introduction to Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
A. Brief History of Gentamicin
Gentamicin, a recognized antibiotic, originated in the 1960s when scientists discovered it in the bacterium Micromonospora. Since then, it has been extensively used in environments due to its strong ability to kill bacteria and effectively combat various bacterial infections3.
B. Commonly Treated Conditions
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops have long been used to treat eye and ear infections. They are effective against a range of conditions, including:
- Conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva)
- Otitis media (middle ear infection or inflammation)
- Otitis externa (also known as swimmers ear, an inflammation of the external ear canal)
The acting nature and broad spectrum of Gentamicin make it a trusted choice for addressing these ailments.
II. Understanding How Gentamicin Works
A. The Mechanism of Action
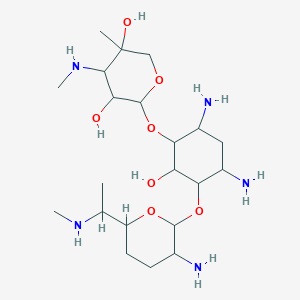
Gentamicin is classified as an aminoglycoside known for its distinct way of working. When Gentamicin is given, it enters cells and attaches to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. This attachment disrupts the process of protein synthesis leading to the creation of proteins that harm bacterial survival. This mechanism gives Gentamicin its ability to kill bacteria effectively, working against both gram-negative strains.
B. Role in Infection Treatment
Gentamicin plays a role in fighting infections. It can stop the growth and multiplication of bacteria by blocking protein synthesis within their cells1. This helps to control the condition. When used as eye or ear drops, it can provide medication levels directly at the site of infection, leading to faster symptom relief and recovery.

III. Comprehensive Guide to Gentamicin Usage
A. Standard Usage for Eye/Ear Infections
Healthcare professionals usually prescribe Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops based on the seriousness of the infection. The usual dosage typically involves putting one or two drops into the eye or ear every 4 to 6 hours. The length of treatment can vary depending on how severe the infection's how well the patient responds to the medication. It's essential to follow the dosage and not stop treatment early, even if symptoms seem to improve.
B. Off-label Uses and Their Effectiveness
Although Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops are primarily prescribed for treating eye and ear infections, they can sometimes be used off-label for other purposes. One example is the application to treat certain skin infections. Additionally, these drops may also be utilized to combat diseases in animals. However, it is crucial to note that any off-label use should only be undertaken under the supervision and guidance of a healthcare professional. It's important to understand that while Gentamicin may effectively serve these off-label uses, its efficacy and safety might not be extensively established as its primary indication for eye and ear infections.
IV. Dosage and Administration Details
A. Determining the Correct Dosage
Determining the amount of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops is essential in its practical use for treatment. The specific dosage depends on the seriousness of the infection and the patient's overall health condition2. Typically for adults with illnesses, it is recommended to use one to two drops every four hours. However, it is essential to follow the guidance provided by healthcare professionals as they better understand each patient's unique requirements.

B. Instructions for Proper Administration
To speed up the healing process, it is essential to administer Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops. Make sure your hands are clean to avoid any contamination. When using eye drops, tilt your head back gently, pull down your eyelid, and carefully place the prescribed drops in the created space; for ear drops, tilt your head sideways. Gently insert the drops maintaining that position for a while to allow proper absorption. Remember not to touch the tip of the dropper with your hands or the affected area to prevent contamination.
C. Adjustments for Specific Conditions
Sometimes the dosage may need to be adjusted in cases. People with kidney issues, for instance, might need a dosage because the drug takes longer to leave their bodies. Likewise, if an infection is particularly severe, the healthcare provider might suggest a frequency of administration. The goal is always to ensure the drug works well while keeping any side effects as low as possible.
V. The Composition of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
A. Active Ingredients and Their Roles
In these eye/ear drops, the main ingredient is Gentamicin sulfate, an antibiotic belonging to the aminoglycoside family. Its mechanism of action involves blocking protein synthesis, ultimately causing the death of bacteria and controlling infections.
B. Inactive Ingredients and Their Functions
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops also contain additional components. These components can include substances that help maintain the pH of the solution, additives that prolong the shelf life, and solvents that assist in dissolving the ingredients. Although these components are considered inactive, they have a role in improving the medication's effectiveness, stability, and overall usability.
VI. Storage Information for Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
To ensure that Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops remain effective, it's essential to store them. Keep them at room temperature, away from light and excessive heat. Avoid freezing the drops, as this may compromise their potency.
B. Shelf Life and Expiration Details
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops usually have a shelf life of around two years from the manufacturing date. However, it is advisable to use the drops within one month after opening the container to avoid contamination. Remember not to use the drops after the expiration date mentioned on the packaging.
VII. Potential Interactions with Gentamicin
A. Drug Interactions to Be Aware Of
Although Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops are generally considered safe, it's essential to be aware that they can interact with medications, which may impact their effectiveness or cause unwanted side effects. It is particularly worth noting that taking them alongside diuretics such as furosemide can potentially increase the risk of experiencing ototoxicity4. Therefore it's crucial to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you currently use, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, and dietary supplements.
B. Impact on Concurrent Medical Conditions
Patients with existing conditions, especially kidney disease, should be careful when using Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops as it may worsen their renal function impairment. Likewise, individuals with disorders such as myasthenia gravis might be more susceptible to experiencing additional muscle weakness. A comprehensive medical history is crucial for healthcare providers to adjust the dosage or consider treatments to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the therapy.
VIII. Important Warnings and Contraindications
A. Situations to Avoid Gentamicin Use
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops should be avoided in situations even though they are effective. If you have a known sensitivity, to Gentamicin or any other aminoglycosides it is best to steer of using them. Similarly if you have an eye/ear infection caused by a virus or fungus using these drops may not be ineffective but could potentially make the condition worse.
B. Potential Risks and Adverse Reactions
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops have possible risks and side effects like any other medication. These can vary from irritation, itching, or redness to more severe reactions like damage to the ear (ototoxicity) damage, to the kidneys (nephrotoxicity), or severe allergic reactions. Patients must be aware of any symptoms and report them promptly to their healthcare provider.
IX. Careful Administration of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
A. Precautions for Safe Administration
To ensure the administration's safety, washing your hands before handling the drop is essential. This will help prevent the introduction of any harmful substances. It is also crucial to avoid any contact between the dropper tip and surfaces including your eyes or ears as this could lead to contamination. If you wear contact lenses, remember to remove them before applying the drops and wait at least 15 minutes before putting them back in.
B. Response to Adverse Reactions
If you notice any effects such as ongoing discomfort, inflammation, or redness or more severe indications like changes in vision, loss of hearing, or signs of an allergic response, discontinue the use of the drops right away and seek medical assistance. It is crucial to address any adverse reactions to prevent any potential complications.
X. Special Considerations for Gentamicin Use
A. Administration to the Elderly
Elderly individuals could potentially face increased risks of experiencing effects, particularly those associated with kidney function. As a result, it is crucial to administer the effective dosage and consistently monitor renal function. It is always advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional for instructions on dosage and administration.

B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Since Gentamicin can pass through the placenta and has been found in breast milk, it is advisable to consider using it during pregnancy or breastfeeding only if the advantages outweigh any risks. It is crucial to have a conversation with your healthcare provider so they can assess the risks and benefits and make an informed decision on what would be the most suitable approach.

C. Administration to Children
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops can be safely used in children. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper guidance. The dosage may require adjustments depending on the child's age, weight, and the seriousness of the infection.

XI. Understanding Gentamicin Overdosage
A. Symptoms of Overdosage
Using amounts of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops can increase the likelihood of experiencing adverse side effects5. Suppose you notice irritation, intense redness, swelling, dizziness, difficulty hearing, or breathing problems due to a severe allergic reaction. In that case, promptly informing a healthcare provider about these symptoms is essential.

B. Emergency Measures and Treatment
If someone takes many drops, they must stop using them and get medical help immediately. Treating an overdose of Gentamicin usually involves providing support for the symptoms. If someone swallows it by mistake, they may need to induce vomiting or wash out their stomach. It's crucial to act to prevent any lasting effects.
XII. Side Effects of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops
A. Most Common Side Effects
The typical side effects of Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops are usually temporary include:
- Minor irritation
- Redness
- Mild discomfort
In some cases, these symptoms go away on their own without needing to stop the treatment. However, if any of these symptoms persist or worsen, you must inform your healthcare provider.
B. Rare But Serious Side Effects
Although it is uncommon, there are instances where patients may encounter adverse effects from using Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops. These can include allergic reactions, hearing loss due to ototoxicity, or kidney damage caused by nephrotoxicity. If you experience symptoms like hearing difficulties, problems with balance, unexplained swelling, or alterations in urination patterns, it's essential to seek prompt medical attention.
XIII. Important Precautions When Using Gentamicin
A. Handling Precautions
Handling Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops is crucial to ensure effective treatment. Make sure to wash your hands after administering the drops. To avoid contamination, avoid touching the dropper tip, and remember to put the cap on after each use. If you notice any changes in color or cloudiness of the solution, it's best not to use it and seek advice from your healthcare provider.
B. Medical Follow-up and Regular Monitoring
It is essential to have check-ins and keep a close eye on your treatment progress while using Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops. This way, healthcare professionals can evaluate how the infection responds, make any needed changes to the dosage and watch out for any side effects. MingMaintaining consistent communication with your healthcare provider throughout the treatment period is always helpful.
XIV. Conclusion: Making the Most of Gentamicin Treatment
A. Summary of Key Points
Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops are a used and effective antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class commonly prescribed to treat bacterial infections in the eyes and ears. This medication works by stopping the synthesis of proteins in bacteria, which helps to control and reduce the disease. It is essential to store it administer it carefully, and follow the prescribed dosage for optimal therapeutic results. Being aware of side effects and seeking timely medical advice if any adverse reactions occur can further ensure the safety of using this medication.
B. Encouragement for Patient Involvement in Care
Patients can significantly improve their treatment outcomes by participating in their care. This involves adhering to all instructions regarding medication administration, monitoring for any potential side effects attending all scheduled follow-up appointments,, and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals. By staying well-informed and actively engaged, patients can play a role in ensuring the success of their Gentamicin treatment.