Leflunomide
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Leflunomide
- III. How Leflunomide Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Leflunomide
- V. Off-Label Uses of Leflunomide
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Interaction of Leflunomide with Other Medications
- VIII. Common and Severe Side Effects of Leflunomide
- IX. Contraindications and Warnings
- X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XI. Overdosage and Management
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Leflunomide
Leflunomide is a vital medication to combat autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. This drug, known as a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD), blocks specific immune system pathways, resulting in decreased inflammation and related symptoms. Through its use, Leflunomide has dramatically enhanced the well-being of numerous patients. It showcases modern medicine's remarkable advancements in addressing chronic inflammatory conditions.
B. Brief History and Development of Leflunomide
Leflunomide has its origins in the late 20th century. When it was first developed for treating rheumatoid arthritis, its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1998 marked a milestone. It has since gained global recognition for its ability to alleviate symptoms of different autoimmune disorders. The introduction of leflunomide represented a significant breakthrough in therapy, offering hope to patients facing the challenges of autoimmune diseases.
II. Composition of Leflunomide
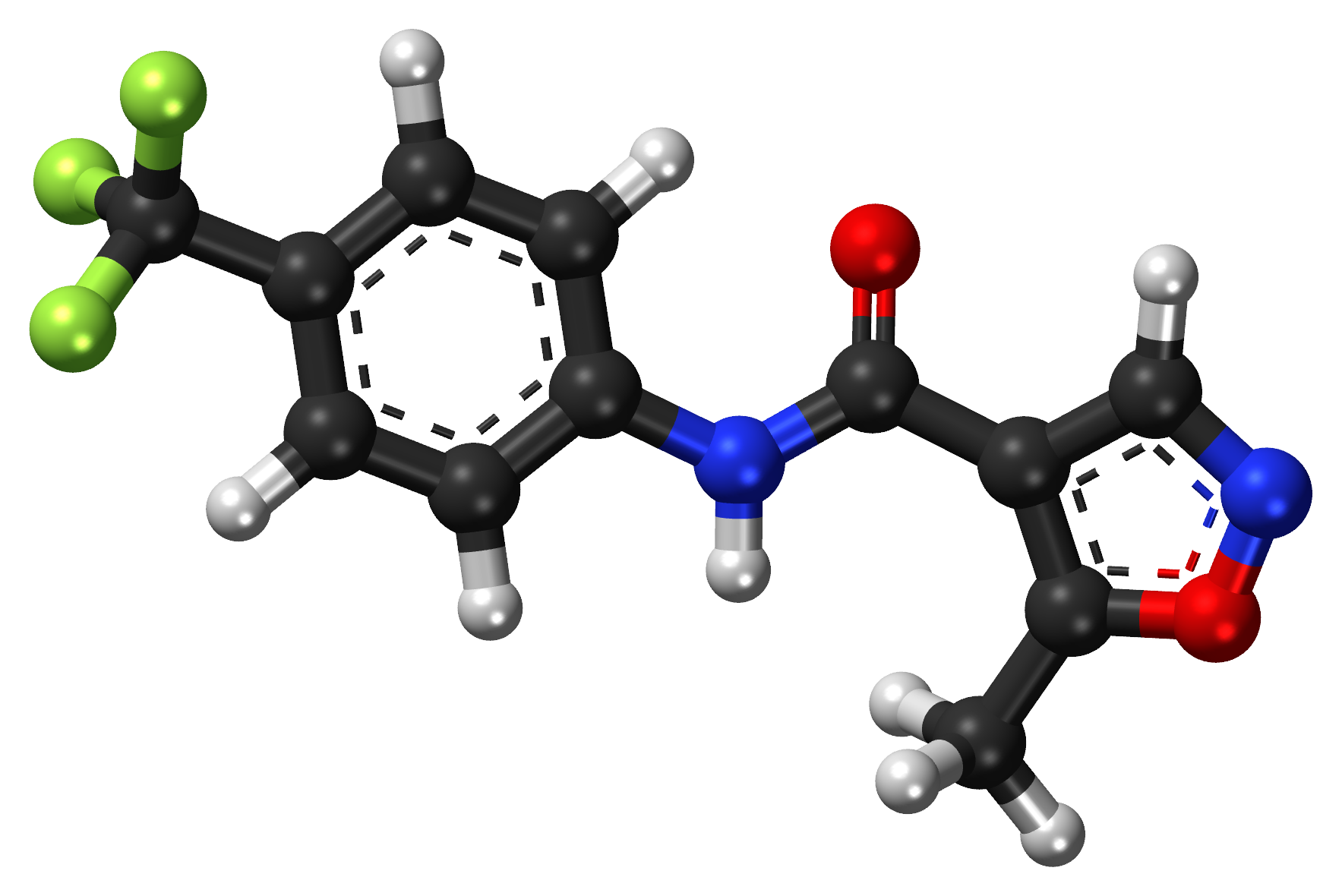
A. Chemical Composition and Structure
Containing a sophisticated chemical structure, leflunomide serves as an effective immunomodulatory agent. It comprises a five methylisoxazole ring attached to an α cyanoenol ether moiety upon administration. Leflunomide undergoes metabolic conversion into teriflunomide, which significantly impacts immune modulation.
B. Unique Characteristics of its Composition
The distinct structure of leflunomide plays a pivotal role in its therapeutic benefits. Its active metabolite, teriflunomide, is of particular significance, which stays in the body for a prolonged period owing to its extended half-life. This characteristic enables consistent immunosuppressive effects and facilitates once-daily dosing, promoting patient adherence to the treatment regimen. Additionally, the molecule's relatively lipophilic properties improve its ability to penetrate inflamed tissues and effectively target the area requiring treatment.
III. How Leflunomide Works
A. Mechanism of Action
The functioning of Leflunomide is quite distinctive due to its unique mechanism of action. It hinders dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). An essential enzyme in creating pyrimidine ribonucleotide uridine monophosphate (rUMP). As a result, lymphocyte growth reduces, leading to decreased autoimmune activity and consequent inflammation.
B. Role in the Immune System and Anti-inflammatory Properties
Leflunomide acts as a DMARD, which is crucial in modulating the immune system. Its ability to inhibit lymphocyte proliferation helps temper the immune response. Thereby reducing the hyperactivity commonly linked with autoimmune diseases. Additionally, leflunomide possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties. This is achieved by decreasing the levels of inflammatory cytokines, ultimately minimizing tissue damage and relieving the clinical symptoms associated with inflammation, such as pain and swelling. Consequently, leflunomide emerges as a potent therapeutic agent for autoimmune pathologies.
IV. Approved Uses of Leflunomide
A. Leflunomide for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Leflunomide is commonly used to manage rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic systemic disease characterized by persistent joint inflammation that often leads to joint damage and disability. As a powerful disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), Leflunomide interrupts the inflammatory process contributing to joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Leflunomide's primary mechanism of action is inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a crucial enzyme in the pyrimidine synthesis pathway necessary for lymphocyte growth. Through this action, Leflunomide reduces the autoimmunity and inflammation associated with the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Consequently, it helps control disease activity, ease symptoms, and slow disease progression123.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Leflunomide:
B. Leflunomide for Psoriatic Arthritis
Leflunomide has proven to be beneficial in effectively managing both rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects individuals with psoriasis; it causes significant pain and can be disabling. In addition to affecting the joints, this illness also impacts the skin and nails. Leflunomide is critical in treating psoriatic arthritis by performing functions similar to those seen with rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Its ability to suppress lymphocyte proliferation reduces inflammation, reducing joint pain and swelling. The drug also aids in improving joint function while slowing down the progression of joint damage associated with this condition. Furthermore, certain patients have experienced positive outcomes concerning their skin-related psoriasis symptoms through Leflunomide1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Leflunomide:
V. Off-Label Uses of Leflunomide
A. In the Treatment of Lupus
Leflunomide has been found to have utility in treating systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a complicated autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation in multiple systems. The clinical effectiveness of Leflunomide in SLE is attributed to its ability to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. In particular, Leflunomide has shown promise in managing lupus nephritis, a severe kidney manifestation of SLE. Research indicates that when used alongside standard-of-care therapy, Leflunomide can enhance the response to treatment in lupus nephritis, making it a potential option for refractory cases.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Leflunomide:
B. Potential Use in Other Autoimmune Disorders
Due to its immunomodulatory capabilities, researchers are currently investigating the potential of Leflunomide in treating other autoimmune disorders. Conditions such as vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, and autoimmune hepatitis have been the focus of these studies, with some suggesting that Leflunomide may have positive effects. It is essential to acknowledge that although early results appear promising, further extensive and well-designed trials are needed to confirm the effectiveness of Leflunomide in treating these conditions. Nevertheless, these investigations highlight the potential of Leflunomide as a versatile therapeutic option for a range of autoimmune diseases.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Leflunomide:
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosing Guidelines
Proper dosing requires proper dosing to achieve the therapeutic benefits of Leflunomide while minimizing potential adverse effects. For adults with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis, the recommended initial dosage is generally 100 mg daily for three days, followed by a maintenance dosage of 10 to 20 mg daily. Whether it's taken with or without food, Leflunomide allows for flexibility in administration. Monitoring patients closely for therapeutic response and potential adverse effects is crucial, and adjusting the dosage as needed is essential. Always remember that Leflunomide should only be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional experienced in treating rheumatological diseases.
B. Adjustments for Specific Patient Populations
Additional precautions must be considered when administering Leflunomide to specific patient populations. For example, it is essential to closely monitor older adults as they may face a higher risk of experiencing adverse effects. Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment should exercise caution due to potential changes in Leflunomide metabolism. Moreover, it is not advised to use Leflunomide in children or adolescents under 18 due to a lack of sufficient data on its safety and effectiveness. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also avoid Leflunomide as it can cause significant harm to both the developing fetus and the nursing infant.
VII. Interaction of Leflunomide with Other Medications
A. Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
Leflunomide has the potential to interact with various other medications. It is potentially affecting its effectiveness or increasing the likelihood of adverse effects. For example, combining it with methotrexate or other immunosuppressive drugs may raise the risk of pancytopenia. Additionally, drugs that are metabolized by the CYP450 2C9 pathway, like warfarin, may interact with Leflunomide. It requires careful monitoring. It is essential to be mindful of all possible drug interactions before initiating Leflunomide therapy and to conduct regular check-ups once treatment has begun.
B. Impact of Food and Alcohol on Leflunomide Absorption
Food does not usually affect how the body absorbs Leflunomide so patients can take the medication with or without a meal. However, it is essential to avoid alcohol when using Leflunomide because it can worsen the harmful effects on the liver. To lower the chance of liver toxicity. It is advised for patients to stay away from alcohol while taking Leflunomide and for some time after stopping the treatment.
VIII. Common and Severe Side Effects of Leflunomide
A. Commonly Reported Side Effects
Although Leflunomide commonly offers good tolerance among patients, it is worth noting that there might be instances where specific individuals experience side effects. The frequently reported ones include diarrhea, nausea, rash, and mild elevations in liver enzymes. Other side effects such as alopecia, weight loss, and hypertension are also possible. Patients need to be aware and promptly communicate any encountered side effects to their healthcare provider to ensure appropriate management.
B. Rare but Serious Side Effects
While rare occurrences are associated with it, caution must be exercised when using Leflunomide due to its potential to induce substantial adverse reactions requiring immediate medical attention. Noteworthy among these reactions are indicators pointing towards serious infections, including symptoms like fever or sore throat; evidence hinting at liver dysfunction, which may include yellow discoloration affecting both eye and skin; and severe respiratory complications typified by shortness of breath. It should be recognized that a minor proportion of the patient population may also encounter pancytopenia—an alarming drop in blood cell levels. Consequently, it becomes increasingly imperative for healthcare professionals to monitor patients under Leflunomide treatment diligently. It is considering the gravity of these severe side effects.
IX. Contraindications and Warnings

A. Individuals who Should not Take Leflunomide
Leflunomide should not be taken in certain circumstances as it can have adverse effects. Individuals with severe liver problems should avoid Leflunomide because it can increase the risk of liver damage. People with significant immune deficiencies, such as those with AIDS are also advised against taking Leflunomide due to the higher risk of developing infections. In addition, Leflunomide should not be used by anyone who has shown allergy or hypersensitivity to the medication or its components. This could result in severe allergic reactions. Moreover, due to its potential to harm a developing fetus, pregnant women and women of childbearing age who are not using reliable contraception should avoid Leflunomide.
B. Warnings and Precautions before Starting Leflunomide
Before embarking on Leflunomide therapy, certain precautions should be considered to prioritize patient safety. Assessing liver function before initiating treatment is highly recommended, as this medication has a perceived risk of hepatotoxicity. Moreover, continuous monitoring of liver function throughout the treatment duration should be carried out diligently. The need for regular blood cell counts as a preventive measure against potential blood dyscrasias is equally significant by adhering to these routine tests. Healthcare professionals can identify any abnormalities promptly and take necessary actions accordingly. Furthermore, screening patients for latent tuberculosis before commencing Leflunomide therapy is essential to ensure patient well-being in cases where tuberculosis has been diagnosed. Timely initiation of suitable treatment becomes imperative before beginning Leflunomide. Lastly, patients must be informed about this medication's inherent risks of severe infections. Patients should receive proper counseling and be encouraged to proactively report any concerning signs or symptoms they may experience without delay. This collaborative effort between healthcare providers and patients enables prompt intervention when required.
X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
A. Leflunomide Administration in Elderly Patients
Prudence is advised when prescribing Leflunomide to elderly individuals. Owing to age-associated physiological changes characterized by declining hepatic and renal function, their response toward the medication may differ significantly, along with an increased likelihood of encountering undesirable side effects. Thus, it is essential to exercise careful discretion while determining dosages and implementing rigorous monitoring protocols to safeguard their well-being effectively within this specific patient subset.
B. Leflunomide Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pregnant women should not use leflunomide because it can cause harm to the developing baby. Women capable of becoming pregnant must use effective birth control while taking Leflunomide and for a certain amount after stopping the treatment. If a woman becomes pregnant while using Leflunomide, she should be informed about the potential risks to her unborn child and offered a procedure to remove the drug from her body. It is not known whether Leflunomide metabolites pass into breast milk, so nursing mothers are advised not to use this medication. However, the decision to stop breastfeeding or cease taking the drug should consider how important the drug is for the mother's health.
C. Considerations for Leflunomide Administration in Children
Leflunomide is not advised in individuals below 18, specifically children and adolescents. This recommendation arises from a shortage of safety and effectiveness data in this age group. It is imperative to acknowledge that the therapeutic advantages and risks associated with Leflunomide have not been extensively examined in pediatric patients, which restricts its application in this population.
XI. Overdosage and Management
A. Symptoms of Leflunomide Overdose
Even though Leflunomide overdosage is rare, its implications on an individual's health cannot be undermined. The associated signs and symptoms often mirror the drug's adverse effects consisting of gastrointestinal troubles such as diarrhea and nausea. Hair loss (alopecia), Skin rashes, and increased liver enzyme levels. As situations worsen, there might be observed hematological changes like leucopenia and pancytopenia alongside the potential for liver damage (hepatotoxicity).
B. Emergency Management and Treatment Options
Suppose a Leflunomide overdose is suspected. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. The first step in managing the overdose is to provide general support by closely monitoring the patient's vital signs and clinical condition. An effective strategy for dealing with Leflunomide overdose is to expedite the removal of the drug from the body. This can be achieved by administering cholestyramine or activated charcoal, which disrupts enterohepatic recirculation and speeds up elimination. It is also essential to regularly monitor complete blood counts and liver function tests until the patient's condition stabilizes.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Optimal Storage Conditions for Leflunomide
To ensure Leflunomide's quality and effectiveness, storing it at room temperature is recommended. It is advisable to keep it away from direct light and moisture as these factors may impact its stability. The optimal temperature range for storing Leflunomide is typically between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius. To further safeguard its integrity. Please refrain from storing it in areas with high humidity, such as the bathroom, additionally, for the safety of children and pets. Kindly ensure Leflunomide is kept out of their reach to prevent accidental ingestion.
B. Safe Handling Guidelines for Leflunomide
To ensure the effectiveness of Leflunomide and minimize any possible risks. It is crucial to handle it safely. It is essential not to break or crush the tablets. And if a tablet becomes damaged. It should not be handled by pregnant women or those planning to become pregnant due to the potential risk to the developing fetus. Washing hands after handling Leflunomide tablets is also recommended, even if they are undamaged. To avoid any potential exposure. When it comes to unused or expired Leflunomide tablets, they should be disposed of properly. Flushing them down the toilet or pouring them into the drain is not advised unless specifically instructed. Patients are encouraged to contact their pharmacist or local waste disposal company for more information on safe disposal methods for Leflunomide.