Lercanidipine HCL
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Lercanidipine
- III. Uses of Lercanidipine
- IV. How Lercanidipine Works
- V. Dosage and Administration of Lercanidipine
- VI. Careful Administration of Lercanidipine
- VII. Important Precautions with Lercanidipine
- VIII. Lercanidipine in Special Populations
- IX. Side Effects of Lercanidipine
- X. Contraindications of Lercanidipine
- XI. Overdose of Lercanidipine
- XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Lercanidipine
- XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Brief Overview of Lercanidipine
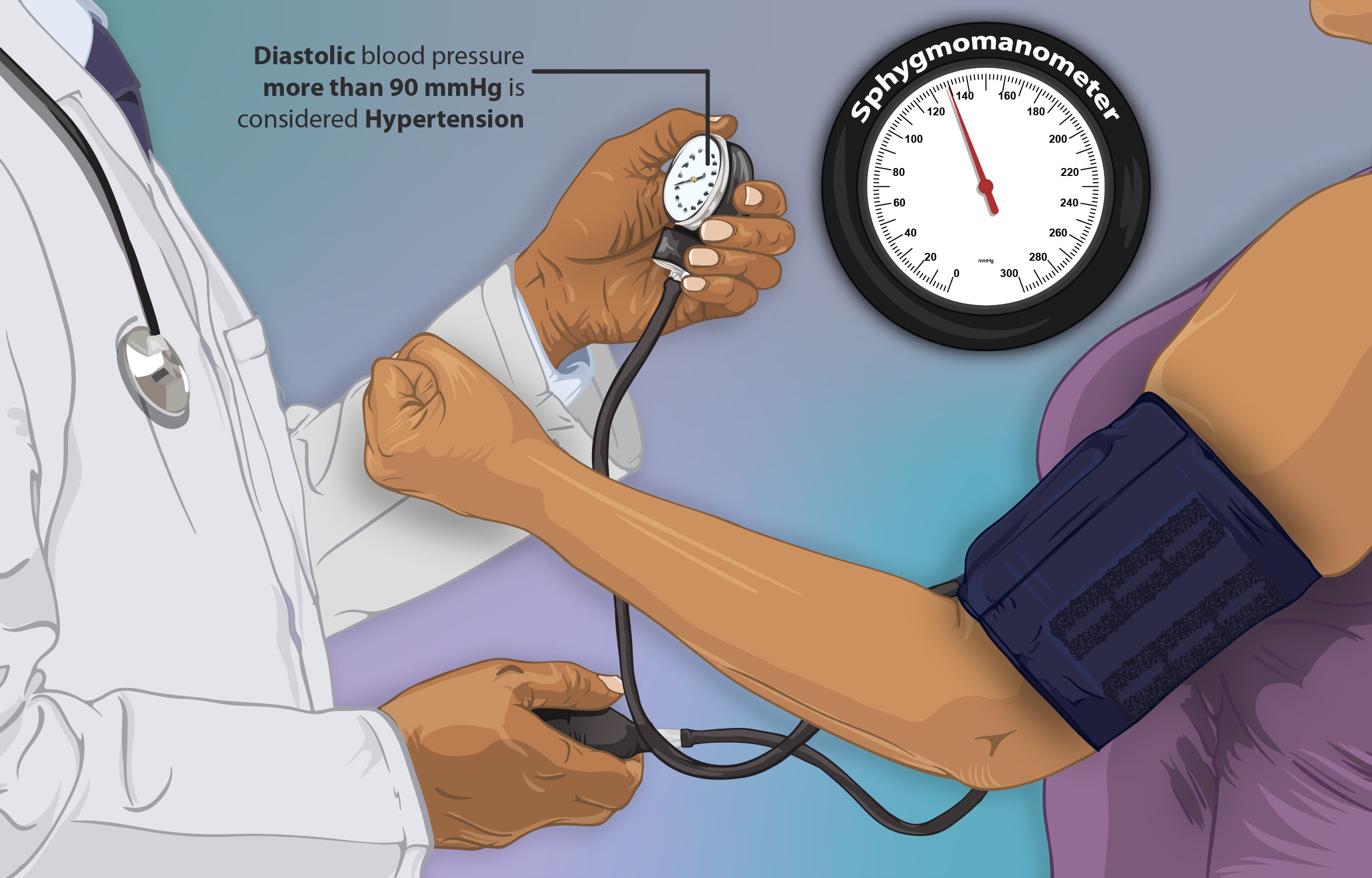
Lercanidipine, which belongs to the generation of calcium channel blockers and is known for its potency, is mainly prescribed for treating hypertension. It works by blocking the entry of calcium ions into cell membranes, widening blood vessels and ultimately lowering diastolic blood pressure. Its lipophilic property sets it apart from calcium antagonists, allowing for steady and controlled management of blood pressure while minimizing the risk of reflex tachycardia.
Hypertension
B. Historical Background and Development
The origins and progress of Lercanidipine can be traced back to the 1980s when researchers were striving to create safer and more efficient drugs. Recordati, a pharmaceutical company, played a crucial role in its development by conducting extensive clinical trials demonstrating its remarkable tolerability and effectiveness. After receiving approval in 1997, it has become essential in the fight against hypertension worldwide.
C. Role in Modern Medicine
Lercanidipine has become a medication in the field of medicine today. It is often prescribed as a treatment for high blood pressure, especially for individuals who may have difficulties with other initial treatments. In addition to its effectiveness in managing hypertension, Lercanidipine's ability to widen blood vessels proves advantageous in conditions with narrowing or rigidity, showing potential for unapproved uses as well.
II. Composition of Lercanidipine
A. Active Ingredients
Lercanidipine contains Lercanidipine hydrochloride as its active component. It belongs to a group of compounds called dihydropyridine derivatives, known for their ability to block calcium channels. When used in the body, Lercanidipine hydrochloride specifically. It inhibits L-type calcium channels found in the smooth muscles of blood vessels resulting in its therapeutic benefits.
B. Inactive Ingredients
Similar to pharmaceutical products, Lercanidipine also includes various inactive or excipient ingredients that are essential for ensuring the drug's stability, absorption, and administration. Although these ingredients may differ depending on the manufacturer, common excipients consist of lactose monohydrate microcrystalline cellulose and magnesium stearate. While these compounds do not directly contribute to the effectiveness of the drug, they play a role in its overall formulation.
C. Available Forms and Strengths
Lercanidipine is available in strengths to meet the specific needs of individual patients. Tablets are the standard form of this medication with 10mg and 20mg dosage options. The dosage prescribed by a healthcare professional considers factors such as age, kidney function, and other medications being taken. This personalized approach ensures that each patient receives the dose based on their specific medical situation.
III. Uses of Lercanidipine
A. Primary Uses
Lercanidipine is an effective calcium antagonist that is primarily used to treat hypertension(1), a widespread health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It works by relaxing the muscles in the arteries and reducing resistance, which helps lower high blood pressure and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease(2). One of its advantages is its ability to provide consistent blood pressure control for 24 hours without significantly affecting heart rate, making it an excellent choice for managing high blood pressure.(3)
1. PubMed Central - Lercanidipine in Hypertension
2. NCBI - Lercanidipine in the Management of Hypertension: An Update
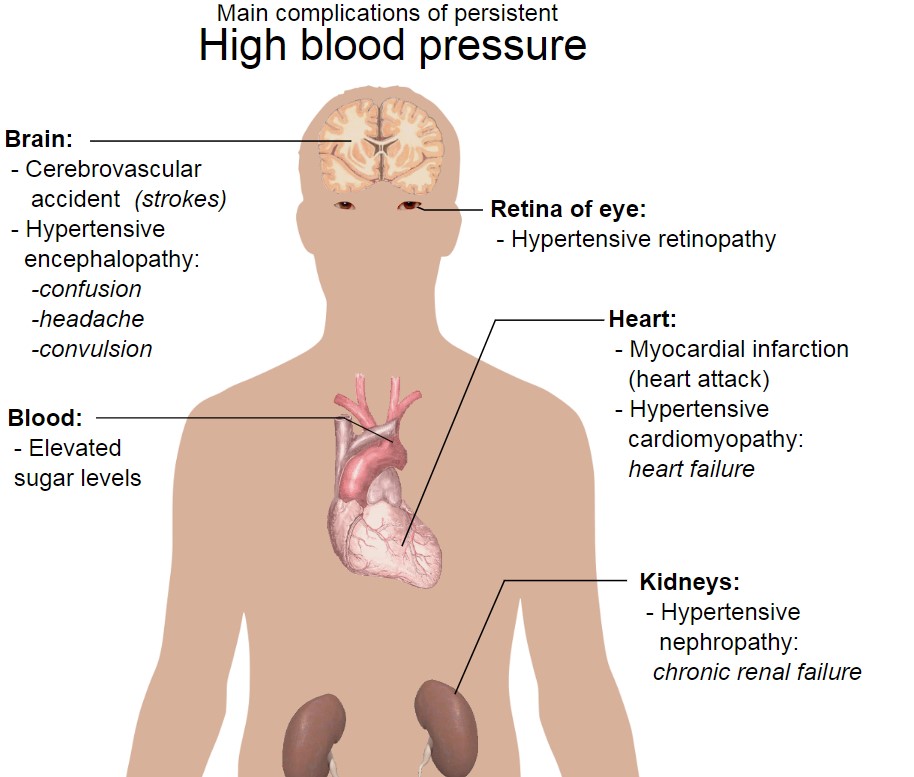
Hypertension Complications
B. Evidence-based Off-label Uses
Off-label use is when a medication's prescribed for a condition that regulatory bodies haven't officially approved. In the case of Lercanidipine, there have been some evidence-based discoveries regarding its off-label uses, which open up possibilities for therapy;
1. Chronic stable angina; Research suggests that Lercanidipine's strong vasodilatory effects may help manage angina.(1)
2. Raynaud Phenomenon; Preliminary evidence indicates that Lercanidipine might have a role in treating this condition characterized by the narrowing of peripheral arteries.(2)
However, it's crucial to emphasize that while off-label use can be beneficial, it should always be pursued with the guidance of a healthcare professional who considers the contraindications and potential side effects associated with the drug.
2. ESVM guidelines – the diagnosis and management of Raynaud’s phenomenon
C. Emerging Therapeutic Applications
The use of Lercanidipine in treatments is continuously evolving.
- Ongoing research suggests that it may affect protecting of the kidneys, especially for hypertensive patients with renal impairment.
- Additionally, some studies propose that Lercanidipine could potentially be used to treat arterial hypertension, a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the lung arteries.
However, it is essential to note that extensive clinical trials are required to definitively confirm the safety and effectiveness of these emerging applications.
IV. How Lercanidipine Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Lercanidipine is classified as a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist. It blocks the movement of calcium ions through the L-type calcium channels in the muscle cells of blood vessels. This blocking action causes the arteries to relax, resulting in decreased resistance in the vascular system and ultimately lowering blood pressure.
B. Pharmacokinetics
The way Lercanidipine behaves in the body is quite interesting.
When taken orally, it gets absorbed quickly. It reaches its highest levels in the blood after about 1.5 to 3 hours. However, because of how it's processed in the body only around 10% of it becomes available for systemic use.
It stays active for about 8 to 10 hours, which's why it has a lasting effect on blood pressure control throughout the day. All these factors together influence how and when the medication works, well as how it is prescribed and used for treating hypertension.
C. Effect on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Health
Lercanidipine works by widening blood vessels, which helps to lower blood pressure. This, in turn, reduces the strain on the heart. Lowers the risk of cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes. Moreover, its minimal effects on heart rate and conduction parameters highlight its safety for the system.
V. Dosage and Administration of Lercanidipine
A. Standard Dosage
The recommended dosage of Lercanidipine for treating blood pressure in adults is 10 mg per day. However, depending on how each patient responds and tolerates the medication, the dosage can be increased to 20 mg daily. It's best to take the drug in the morning without food or shortly after a meal, as it helps with absorption.
B. Dosage Adjustments in Specific Populations
It is essential to customize the dosage of Lercanidipine according to patient characteristics.
- When dealing with elderly patients, starting with a lower dose might be advisable due to the changes in how their bodies process the medication.
- In cases where patients have liver or kidney problems, monitoring them and potentially adjusting the dosage is crucial since their ability to clear the drug might be affected.
C. Steps for Safe Administration
To ensure the administration of Lercanidipine, it is important to check if the patient has any allergies to Lercanidipine or its ingredients.
Additionally, make sure that the patient is not consuming grapefruit juice or any grapefruit-based products, as these can interact with Lercanidipine and lead to levels of it in the bloodstream.
VI. Careful Administration of Lercanidipine
A. Considerations Before Starting Treatment
Before starting treatment with Lercanidipine, it is important to perform a health evaluation to ensure that no medical conditions or factors would make this medication unsuitable. It is also essential to gather information about the patient's medications to identify and avoid any possible adverse reactions or interactions.
B. Managing Missed Doses and Dose Timing
If you accidentally forget to take a dose, make sure to take it soon as you remember unless it's almost time for your next dose. In that case, it's better to skip the missed dose to avoid any risk of taking too much medication.
C. Tips for Maximizing Treatment Effectiveness
To ensure the results from your treatment, it is crucial to adhere to the prescribed plan. Missing doses can impede the effectiveness of the therapy. It is essential to monitor your blood pressure as this can provide valuable insights into how well the treatment is working and allow for timely adjustments if needed. Alongside medication, it is essential to focus on making lifestyle changes, for control of blood pressure. Remember that a holistic approach combining both medication and healthy habits yields the outcomes.
VII. Important Precautions with Lercanidipine
A. Interactions with Other Medications
When administering Lercanidipine it is important to consider the possibility of drug-drug interactions.
- Taking Lercanidipine with CYP3A4 inhibitors (such as ketoconazole or erythromycin) may increase the levels of Lercanidipine, in the body, which can raise the risk of experiencing negative effects.
- If you are using beta blockers at the time be cautious as it could potentially enhance the antihypertensive effect.
- Additionally combining Lercanidipine with antihypertensive medications can lead to an additive effect possibly resulting in excessive reduction of blood pressure.
B. Precautions for People with Certain Health Conditions
Health conditions have the potential to impact how Lercanidipine behaves in our bodies, which's why it's important to take certain precautions. For individuals with liver or kidney problems, close monitoring and potential dosage adjustments may be necessary. It's advised to use Lercanidipine if someone has heart conditions, like sick sinus syndrome, uncontrolled heart failure, or a recent heart attack.
C. Lifestyle Considerations (Diet, Alcohol, Exercise)
The way you live your life greatly impacts how effective and safe Lercanidipine treatment is. Here are a few lifestyle factors to keep in mind;
- Diet; It's important to avoid consuming Lercanidipine with a high-fat meal or grapefruit juice as these can interfere with its absorption.
- Alcohol; Be cautious about alcohol consumption as it can amplify the blood pressure lowering effect of Lercanidipine potentially leading to low blood pressure (hypotension).
- Exercise; While regular exercise is recommended for managing hypertension it's advisable to avoid intense physical exertion as it may cause a spike, in blood pressure.
Remember these lifestyle considerations can help optimize the effectiveness and safety of your Lercanidipine treatment.
VIII. Lercanidipine in Special Populations
A. Administration to the Elderly
Older people might undergo changes in how their bodies process and eliminate drugs. As a result, it may be worth considering starting with doses of Lercanidipine and keeping a close eye, on blood pressure throughout the treatment.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Lercanidipine should only be taken during pregnancy if the advantages outweigh the risks. The safety of using Lercanidipine during pregnancy has not been confirmed. We are unsure if Lercanidipine is passed into breast milk, so it's advised to exercise caution when considering its use for nursing mothers.
C. Administration to Children
Lercanidipine has not been proven to be safe and effective for children. Therefore it is currently not recommended to use it in children.
D. Administration in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Patients who have liver or kidney problems may experience changes, in how their bodies process and eliminate Lercanidipine medication. It is important to adjust the dosage and closely monitor their blood pressure and any possible side effects to ensure their safety.
IX. Side Effects of Lercanidipine
A. Overview of Potential Side Effects
Although Lercanidipine is usually well tolerated, like any medication, it may have some side effects. These can vary from temporary effects to more serious ones that could potentially be life-threatening.
B. Common Side Effects
Some of the side effects of taking Lercanidipine may include ;
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Flushing
- Swelling in the extremities
These side effects are generally mild. Tend to go away as your body gets used to the medication.
C. Serious Side Effects and Warning Signs
In some cases Lercanidipine might lead to side effects, such as;
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Unusual fatigue
- Weakness
- Severe dizziness
- Fainting
If you experience any of these symptoms or notice any other concerning changes in your mental well being it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. It's important to note that this list doesn't cover all side effects, so if you have any unexpected changes, its best to discuss them with a healthcare professional.

Chest Pain
X. Contraindications of Lercanidipine
A. Absolute Contraindications
Lercanidipine should not be given under the following conditions;
- Patients with a known sensitivity or allergy to Lercanidipine or any of the ingredients in the product.
- Patients with angina or those who have experienced a heart attack within the past month.
- Patients with liver problems.
B. Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications warrant caution than a complete cessation of treatment. In cases of hepatic or renal impairment, it is crucial to closely monitor the effects on Lercanidipine metabolism and excretion. When using Lercanidipine alongside medications such, as CYP3A4 inhibitors or other antihypertensive, it is important to exercise caution monitor carefully, and potentially adjust the dosage accordingly.
XI. Overdose of Lercanidipine
A. Symptoms of Overdose
Taking an amount of Lercanidipine could lead to some potential effects, such as a significant drop, in blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and even a possible loss of consciousness.
B. Immediate Steps to Take in Case of Overdose
If someone experiences an overdose it is crucial to contact a healthcare professional or reach out to the poison control center immediately. In case the person is unconscious, it's important to position them on their side in what is known as the recovery position.
C. Long-Term Management of Overdose
Long-term management can include the following;
1. Providing care by ensuring proper airway, breathing and circulation.
2. Administering symptom-based treatments tailored to the patients condition. This may involve fluids if the patient is experiencing low blood pressure.
XII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Lercanidipine
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
Lercanidipine needs to be stored in an dry location away, from direct sunlight and kept out of the reach of children.
B. Safe Handling and Disposal
It is important to avoid using Lercanidipine after the expiration date indicated on the package. Additionally, it is recommended to consult with a pharmacist or local waste disposal company for safe disposal methods rather than disposing of it in regular waste.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
This thorough conversation provides an overview of Lercanidipine, including its composition, uses, how it works, recommended dosage instructions, contraindications, possible side effects, what to do in case of an overdose, and safe storage practices.
B. Role of Lercanidipine in the Broader Landscape of Antihypertensives
Lercanidipine is a medication in the world of antihypertensives. As a calcium channel blocker, it offers benefits such as long-lasting effects and its ability to target blood vessels selectively. These qualities make it a valuable choice for treating blood pressure.
C. Importance of Patient Education and Adherence to Treatment
Education for patients plays a role in effectively managing hypertension. It is important for individuals to have knowledge about their medications, potential side effects, and proper methods of administration. This understanding can greatly enhance adherence to treatment resulting in improved control of hypertension and better overall health outcomes.