Levamisole
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Levamisole
- III. Uses of Levamisole
- IV. Off-label Use of Levamisole
- V. How Levamisole Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Levamisole
- VII. Side Effects of Levamisole
- VIII. Interactions and Contraindications of Levamisole
- IX. Special Precautions and Warnings with Levamisole
- X. Administration of Levamisole to Specific Populations
- XI. Overdosage of Levamisole
- XII. Storage and Handling Precactions for Levamisole
- XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Brief Overview of Levamisole
Levamisole is a medication used to treat infections caused by parasitic worms. Its immune-modulating abilities make it useful for more than getting rid of parasites. This drug, which belongs to the imidazothiazoles family, addresses public health challenges associated with parasitic diseases.
B. Historical Background and Development
Levamisole was first introduced in the 1960s to treat worm infections in animals. However, its potential as an agent for human use was soon realized. Over time researchers also discovered that the drug has properties which widened its range of medical applications.
II. Composition of Levamisole
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
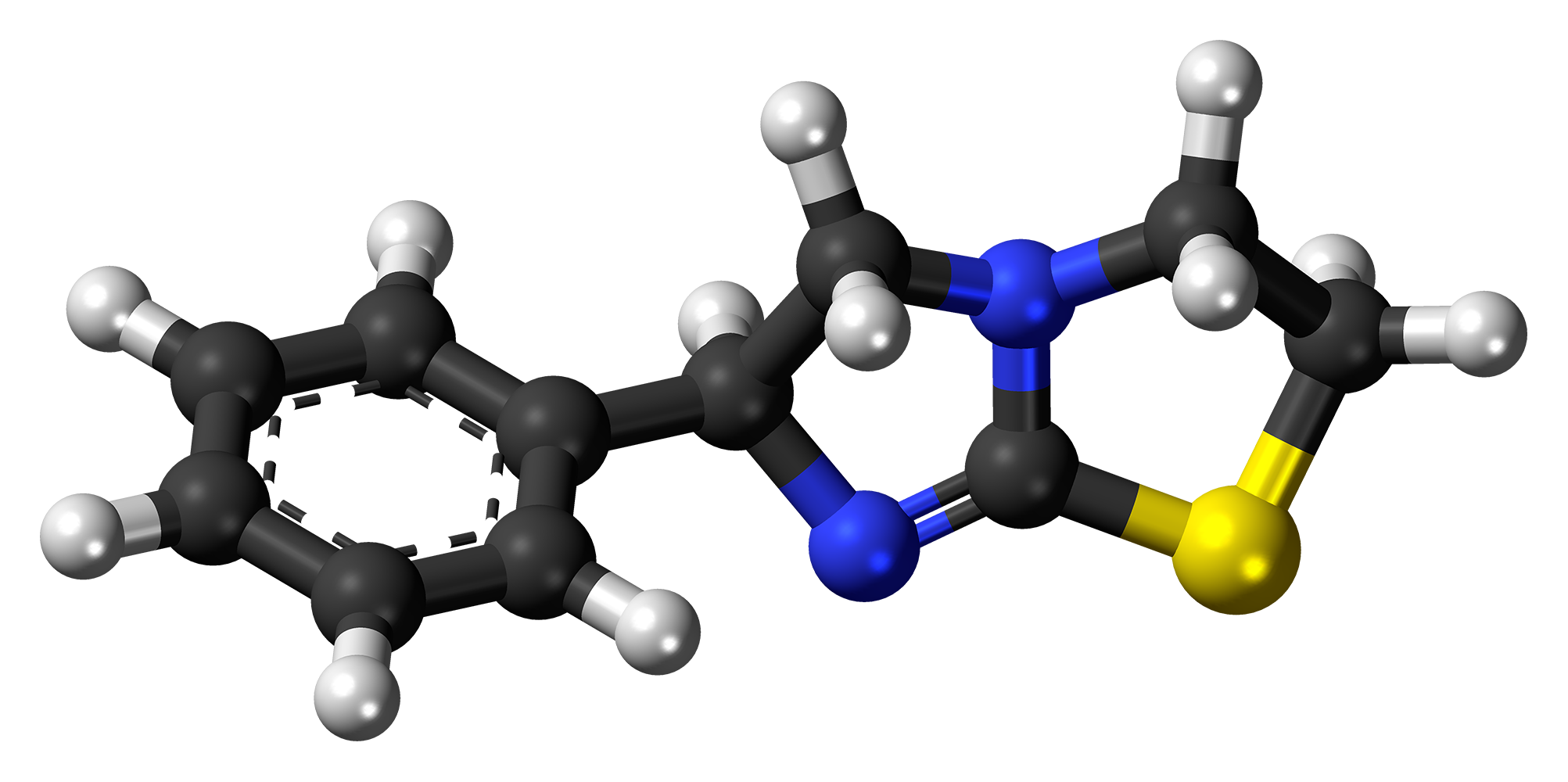
Levamisole has a formula of C11H12N2S and is known for its imidazothiazole ring. It is a compound that can easily be absorbed from the gut due to its nature. Because of its ability to bind strongly to proteins and its lipophilicity, it can effectively penetrate tissues and have a wide range of effects.
B. Different Formulations and Brand Names
Levamisole is sold under brand names globally, such as Ergamisol and Ketrax. It is predominantly available in tablet form. It can also be obtained as a liquid for oral consumption or as an injectable version making it versatile for different medical and veterinary applications.
III. Uses of Levamisole
A. Approved Medical Uses
Levamisole is an anthelmintic medication used to treat parasitic worm infections such as ascariasis and hookworm infections1. It works as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that causes continued stimulation of the parasitic worm muscles, leading to paralysis1. Levamisole has also been used alongside fluorouracil as an adjuvant treatment for colon cancer in some patients23. However, its application in cancer therapy has declined because of adverse reactions2.
2: Levamisole: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
3: Levamisole and 5-fluorouracil therapy for resected colon cancer: A new …
B. Veterinary Uses
Levamisole is an anthelmintic drug widely used in veterinary medicine to treat nematode infections in animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs, goats, poultry, and pets. It is effective against both mature and developing stages of nematodes12. Levamisole is commonly administered orally or subcutaneously1.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
- MSD Veterinary Manual - Imidazothiazoles
- Wikipedia - Levamisole
- Parasites & Vectors - Anthelmintic efficacy of fenbendazole and levamisole in native fowl in …
C. Recent Research and Potential Future Applications
Levamisole is being investigated for its potential use in immunomodulation for HIV/AIDS and autoimmune diseases12. However, it is essential to note that these applications are still being experimented with and require research3.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
- SpringerLink - Kaleidoscope of autoimmune diseases in HIV infection
- African Journal of Biotechnology - The Role of Levamisole and HIV-1 Nef-p24 Fusion Protein in IL-4 Gene …
- Verywell Health - AIDS vs. Autoimmune Diseases
IV. Off-label Use of Levamisole
A. Off-label Uses in Medical Settings
Levamisole has been used off-label to treat conditions such as recurrent mouth ulcers and pediatric nephrotic syndrome12. However, it is important to highlight that these applications lack approval from regulatory authorities, and the decision to use Levamisole in such cases relies solely on the discretion of individual healthcare providers1.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
- Medicines For Children - Levamisole for nephrotic syndrome
- Springer - Update on the treatment of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome
- Springer - Levamisole and ANCA positivity in childhood nephrotic syndrome
B. Off-label Uses in Veterinary Medicine
Levamisole has been used in an unofficial capacity to address issues like parasitic skin infestations and certain immune-mediated diseases. However, it is essential to note that these applications are not officially endorsed and should be approached with care as they lack approval from regulatory authorities.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
C. Risks and Controversies Surrounding Off-label Use
Levamisole has been used off-label to treat conditions such as parasitic skin infestations and certain immune-mediated diseases12. However, it is important to highlight that these applications are not officially endorsed and should be approached carefully as they lack approval from regulatory authorities3. The side effects of Levamisole can be quite unpredictable and serious13. Therefore it’s crucial to approach off-label use cautiously and carefully consider the advantages versus the associated risks3.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
- Wikipedia - Levamisole
- DrugBank Online - Levamisole: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action
- Mayo Clinic Health System - Taking off-label medication
V. How Levamisole Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Levamisole functions as a ranging deworming agent by activating nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the parasite's body. This results in muscle contraction, paralysis, and, ultimately, the removal of the parasite. Additionally, Levamisole impacts the immune system, boosting both cellular and antibody-based immune responses. As a result, it improves the body's capacity to combat infections and diseases.
B. Interaction with Other Drugs and Substances
Levamisole can interact with different drugs and substances like any other medication, which might change its effectiveness or cause adverse reactions. For example, if taken together with anticoagulants there could be a chance of bleeding due to Levamisole's potential to cause agranulocytosis. Similarly, when combined with medications processed by the liver, it could increase the amount of those drugs in the bloodstream, potentially leading to toxicity.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Levamisole
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
The recommended amount of Levamisole will differ depending on the treated condition. A typical dosage for parasitic infections in adults would be around 100 to 200 mg per day, for one or two consecutive days. If needed, this dosage can be repeated after a week.
B. Variations in Dosage for Specific Conditions
The treatment of hookworm and ascariasis often requires a dose of 150 mg, which is typically adequate. However, when used as part of cancer therapy, the dosage may need to be higher. In these cases, it can take up to 50 mg three times a day for three days, followed by rest. In practice, the dosage varies significantly depending on the species, age, and condition of the animal being treated.
C. Route of Administration
Levamisole is usually taken by mouth, although it can also be given through injections into the muscles or, under the skin in veterinary medicine.
VII. Side Effects of Levamisole
A. Common Side Effects and Their Management
Levamisole can sometimes lead to common effects like feeling nauseous, vomiting, having diarrhea experiencing abdominal pain and tiredness. Most of these symptoms can be handled with care and might not require stopping the medication. However, patients must be aware of these side effects before starting the treatment.

B. Serious or Rare Side Effects
Some patients might encounter significant side effects such as skin rashes, seizures, inflammation of the lungs, and agranulocytosis. A severe decrease in white blood cells can make one more susceptible to infections. If you notice any indications of these effects, it is essential to seek medical assistance.
C. Factors Influencing Side Effects
Various factors can influence the occurrence of side effects, such, as the patient's health, any existing conditions they may have other medications they are taking, and the dosage and duration of Levamisole therapy. For example, if someone has liver or kidney problems or is using drugs that could potentially harm these organs, they might experience more intense side effects. As a result, it may be necessary for these individuals to undergo monitoring and have their dosage adjusted accordingly.
VIII. Interactions and Contraindications of Levamisole
A. Potential Drug Interactions
Levamisole has the potential to interact with medications, which could affect how well they work or make their side effects more intense. It's important to note that when Levamisole is combined with anticoagulants, it may raise the risk of bleeding. Additionally, Levamisole can also interact with drugs metabolized by the liver, possibly increasing their levels in the bloodstream to an extent.
B. Known Contraindications
Levamisole should not be used if a patient has a known allergy to the drug. Additionally, it is not recommended for patients with liver or kidney problems due to the potential for increased toxicity. Furthermore, it is advised to avoid using Levamisole in situations where stimulating the system could be harmful such as in cases of autoimmune diseases.
C. Potential Food and Lifestyle Interactions
Although there are no food interactions, taking Levamisole with a meal is generally recommended to minimize any potential discomfort in the gastrointestinal system. It's important to consider lifestyle choices such as smoking and alcohol consumption as they can affect how the drug is metabolized, potentially resulting in heightened side effects. Therefore, reducing or abstaining from these substances while undergoing Levamisole treatment might be beneficial.
IX. Special Precautions and Warnings with Levamisole
A. Important Precautions
It is important to exercise caution when administering Levamisole due to the possibility of side effects. Monitoring blood cell counts and liver function is recommended, especially when using higher doses or for an extended period. Patients should also be informed about reporting symptoms that may indicate agranulocytosis, such as fever or a sore throat.
B. Warning Signs of Adverse Reactions
It could be a sign of severe adverse reactions if you experience skin rashes, seizures, difficulty breathing, or signs of infection while taking Levamisole. You must seek medical attention if these symptoms occur during your treatment.
C. Careful Administration Guidelines
It is essential to use Levamisole to ensure it is safe and effective. This involves following the prescribed dosages, not missing any doses, and stopping the medication according to the instructions given by your doctor. If you happen to skip a dose, take it soon as you remember unless it's almost time for your next dose.
X. Administration of Levamisole to Specific Populations
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Older individuals might experience increased vulnerability to the side effects of Levamisole due to age-related decline in liver, kidney, or heart function. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage and closely monitor this group of patients to minimize any associated risks.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Considering the risks, it is advisable only to use Levamisole during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh any potential adverse effects. Similarly, caution should be exercised when using Levamisole while nursing as it may be excreted in breast milk and exposed to it.
C. Administration to Children
Levamisole is commonly prescribed to treat infections in children. However, adjusting the dosage according to their body weight is essential as this can affect the risk of side effects, like agranulocytosis. Therefore it is recommended to monitor children who are given Levamisole.
XI. Overdosage of Levamisole
A. Symptoms and Signs of Overdosage
Taking much Levamisole can lead to increased side effects, including intense nausea, frequent vomiting, diarrhea, and symptoms affecting the central nervous system, like dizziness and confusion. In some cases, there is a possibility of experiencing seizures. In instances, agranulocytosis and related infectious complications may develop.
B. Immediate Actions and Treatments
If someone is thought to have taken much of the medication, seeking immediate medical help is crucial. The usual course of treatment involves providing care for the symptoms and offering support. Sometimes activated charcoal might be given to lower the absorption of the drug if the person seeks attention within a few hours of taking it. It's important to note that there isn't a remedy for an overdose of Levamisole.
C. Long-term Consequences of Overdosage
The long-term effects of taking much Levamisole are mainly connected to its ability to cause agranulocytosis, a severe decrease in white blood cells. This condition can make a person more vulnerable to infections, which, if not treated promptly, could result in considerable illness and even death.
XII. Storage and Handling Precactions for Levamisole
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
Levamisole is best stored at room temperature, between 15°C and 30°C. It should be kept in a dry location shielded from direct sunlight and out of the reach of children and pets.
B. Guidelines for Safe Handling and Disposal
Handle Levamisole tablets with your hands and only remove them from the container when taking your medication. If you have any leftover or expired medication be sure to dispose of it by following the guidelines in your local area or consulting a healthcare professional or pharmacist.
C. What to Do in Case of Spillage or Exposure
If there is a spill, cleaning the area using a wet cloth is essential to minimize any potential exposure. If Levamisole comes into contact with your skin or eyes, rinse the area immediately with plenty of water. If you accidentally ingest or inhale it or experience any reactions, seek immediate medical assistance.
XIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points about Levamisole
Initially created to treat infections, Levamisole has gained recognition for its strong ability to modulate the immune system. While it is practical, its usage is restricted due to the possibility of adverse reactions and the requirement for precise dosage and administration.
B. Current and Potential Future Role of Levamisole in Medicine
Levamisole is still being utilized to treat infections and as a supplement in cancer treatment. However, ongoing research indicates it may have potential applications, such as addressing immunological disorders and infectious diseases. As we gain an understanding of its intricate workings and effectively manage any associated side effects, there is a possibility that Levamisole could find utility in medicine beyond its current uses leading to benefits for a broader range of patients.