Lidocaine Ointment
- 1. Introduction to Lidocaine Ointment
- 2. Uses of Lidocaine Ointment
- 3. Off-Label Uses of Lidocaine Ointment
- 4. How Lidocaine Ointment Works
- 5. Dosage and Administration
- 6. Composition of Lidocaine Ointment
- 7. Storage and Handling of Lidocaine Ointment
- 8. Side Effects of Lidocaine Ointment
- 9. Common Side Effects of Lidocaine Ointment
- 10. Warnings and Precautions
- 11. Interactions with Other Medications
- 12. Contraindications for Lidocaine Ointment Use
- 13. Careful Administration Guidelines
- 14. Administration to Elderly Patients
- 15. Administration to Pregnant and Nursing Women
- 16. Administration to Children
- 17. Overdose and Toxicity
- 18. Handling Precautions
1. Introduction to Lidocaine Ointment
Overview of Lidocaine Ointment
The use of Lidocaine ointment is quite common as an anesthetic that works by numbing the skin or mucous membranes to ease localized pain and discomfort from issues such as minor skin irritations or dental treatments due to its quick action and effectiveness in modern healthcare practices.
History and Development of Lidocaine-Based Products
In 1943, Nils Löfgren, a chemist, introduced lidocaine,a groundbreaking advancement in anesthesia. It was developed to address safety concerns and enhance effectiveness compared to substances such as cocaine. Due to refinements,such as the development of ointments and gels, lidocaine has become an option for various medical purposes since its inception.
FDA Approval and Regulatory Status
Since 1948, Lidocaine has been approved by the FDA, and its safety has been consistently monitored. It is currently considered a prescription drug. Some over-the-counter versions are available for issues. Regulatory agencies in nations have identified it as an option, for managing acute and chronic pain.
2. Uses of Lidocaine Ointment
Primary Medical Uses of Lidocaine Ointment
Applying Lidocaine ointment is mainly for the purpose of:
- Relief from pain in an area.
- Numbing sensation for minor medical procedures.
- Soothing skin irritation and discomfort
Topical Pain Relief for Minor Skin Irritations
When dealing with cuts and insect bites or skin irritations, like reactions and dermatitis that cause pain and discomfort, applying lidocaine ointment topically on the skin surface area can help lessen the pain by numbing the affected region effectively.
Relief from Burns, Insect Bites, and Sunburns
Applying Lidocaine cream can help soothe burns and sunburn by cooling the skin and decreasing inflammation.It is also effective, in alleviating the discomfort caused by insect bites through numbing the nerve endings.
Dental Applications
Use in Minor Surgical Procedures
During procedures, like removing moles or conducting skin biopsies, Licensed Lidocaine ointment is frequently applied to numb the area and provides local anesthesia for a painless experience.
Pain Management in Hemorrhoids and Anorectal Conditions
Role in Dermatological Conditions Such as Itching and Eczema
Patients with long-term skin conditions such as eczema can find relief from itching by using lidocaine ointment as a part of their treatment strategy to effectively control symptoms.

3. Off-Label Uses of Lidocaine Ointment
Lidocaine in Tattoo Removal Aftercare
Doctors often use Lidocaine ointment to help reduce discomfort following tattoo removal procedures that involve laser treatment.
Chronic Pain Management (Neuropathic Pain)
Lidocaine ointment can offer relief to people experiencing pain from conditions like diabetes or shingles by numbing the affected area and enhancing overall well-being.
Topical Treatment for Vulvodynia
Using Lidocaine ointment has shown results in managing vulvar pain associated with vulvar vestibulitis syndrome by desensitizing the tissues in the affected area.
Off-Label Use in Postherpetic Neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is an issue that may linger following a bout of shingles; some doctors use lidocaine cream to help ease the nerve pain that patients endure.
Use in Migraine Management (via Nasal Application)
Lidocaine nasal treatments for migraines are not very common. Have been studied as a way to offer targeted relief, to specific patients.
4. How Lidocaine Ointment Works
Mechanism of Action: Blocking Sodium Channels
When Lidocaine is used it hinders the sodium channels, in nerve cells to stop the start and spread of pain signals effectively numbing the area being treated.
Effect on Nerve Signals and Pain Transmission
Lidocaine works by stopping sodium ions from entering nerve cells, which in turn interrupts the passing of signals that cause pain to reach the brain.
Duration of Action and Onset of Relief
The impact of Lidocaine usually starts shortly after it is applied. Provides relief that can last anywhere, from 30 minutes to a few hours, based on the strength of the solution and the treated region.
Pharmacokinetics of Topical Lidocaine
When lidocaine is used on the skin surface directly it gets absorbed into the layers of the skin with little entering the bloodstream. The way it moves through the body depends on how its applied and in what form.
5. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage for Various Conditions
The amount of lidocaine ointment you should use varies based on the issue you're addressing:
- For skin irritations, gently apply a thin layer up to three times a day.
- When dealing with hemorrhoids, apply the ointment following bowel movements.
- In applications, put an amount on the gums before the procedure.
Guidelines for Applying Lidocaine Ointment
Apply Lidocaine ointment thinly and evenly on the area to ensure coverage without excessive use, which could lead to absorption into the body system and should be avoided to maintain effectiveness.
Frequency and Duration of Use
The number of times you apply it depends on the situation but usually shouldn't exceed three to four times a day; it's advised not to use it for a period without consulting a healthcare professional.
Application Techniques for Different Areas of the Body
When dealing with membranes treatment or skin applications varied concentration levels are necessary Gloves should be used during application to avoid exposure.
Adjustments for Elderly, Children, and Special Populations
Older individuals might need reduced dosages because of their skin and enhanced absorption capabilities; on the other hand, it's important for youngsters to use lidocaine only under close supervision in accordance with guidelines specific to their age group.
6. Composition of Lidocaine Ointment
Active Ingredients: Lidocaine Concentration
The main component is lidocaine. It is usually found in strengths, between 2 and 5%, depending on the purpose of use. Higher strengths offer numbness but also come with increased dangers.

Inactive Ingredients and Their Roles
Typical components that are not active consist of emulsifiers and stabilizers along with water-based carriers that maintain their texture and storage durability while not interfering with their numbing effects.
Variations in Formulation (Cream, Gel, and Ointment Forms)
There are various types of Lidcaine. Creams and gels are absorbed quicker compared to ointments that have longer lasting effects because they form a barrier, on the skin.
Benzocaine vs lidocaine
Lidocaine is a stronger, yet equally effective, local anesthetic than Benzocaine, and its effects last for approximately 90 minutes. Benzocaine is considered to be less severe in nature, and its effects last for around ten minutes from the time of application.
Lidocaine hydrochloride
Lidocaine, in its hydrochloride salt form, is an aminoethylamide and a classic example of belonging to the amide class of drugs. Blocking the surge, in membrane permeability to Na+ lidocaine interacts with voltage gated Na + channels located in nerve cell membranes.
Novocaine vs lidocaine
Novocaine (also known as procaine), an older medication, may cause side effects like restlessness, convulsions, dizziness, and allergic reactions. While Lidocaine acts faster lasts longer. Carries a risk of side effects compared to novocaine.
Xylocaine vs lidocaine
Lidocaine and Xylocaine (also referred to as lignocaine) are essentially the medications used to alleviate pain during treatments, specifically known as Xylocaine Dental in the provided information brochure.
7. Storage and Handling of Lidocaine Ointment
Ideal Storage Conditions
Be sure to keep the Lidocaine ointment in a place at room temperature and shielded from sunlight and moisture to preserve its strength and performance.
Shelf Life and Expiration Information
The average duration that lidoderm ointment remains effective is usually 2 to 3 years; nonetheless, it's advisable to dispose of any expired ointments as their effectiveness may decrease with time.
Safe Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
Make sure to take steps to prevent accidentally swallowing or getting the product in your eyes. Always wash your hands thoroughly after use to avoid spreading any contaminants.
8. Side Effects of Lidocaine Ointment
Overview of Common Side Effects
While Lidocaine ointment is usually considered safe to use. It may lead to side effects, like skin irritation or redness, along with a burning sensation.
Skin Redness and Irritation
Skin may become slightly red after use, which is normal, and usually goes away within hours of applying the product. If irritation continues it is advisable to stop using the product, for relief.
Burning Sensation at the Application Site
After you apply the product to your skin, you might feel a burning or tingling sensation right away if you have sensitive skin.
Temporary Numbness or Tingling
The expected numbness resulting from lidocaine might occasionally spread beyond the region. Leading to a temporary loss of feeling.
Uncommon but Serious Side Effects
- Allergic reactions - Severe skin reactions
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to lidocaine are uncommon. May manifest as hives or swelling in the face or throat and difficulty breathing; seek medical assistance if such symptoms occur.
Severe Skin Reactions
Sometimes, with extended use or heightened sensitivity, issues can arise, like dermatitis that affects the skin severely.
Lidocaine toxicity
Signs of lidocaine overdose consist of feeling lightheadedness and disorientation along with the possibility of experiencing seizures when an excessive quantity enters the blood circulation system.
9. Common Side Effects of Lidocaine Ointment
Localized Skin Reactions
The common side effects often involve skin reactions, in an area of the body and can appear as mild redness or itching sensations.
Numbness and Tingling
Prolonged sensations of numbness and tingling may arise in the area when using doses of lidocaine.
Sensitivity or Mild Allergic Reactions
Over time and with repeated use of lidocaine products, some people might experience a sensitivity to the substance that could lead to responses like a rash or itching.
Temporary Discomfort at the Application Site
Patients might feel an unease when they first apply the medication; however, this sensation usually fades away once the medicine starts working its magic.
10. Warnings and Precautions
Avoiding Use on Broken or Infected Skin
Avoid using Lidocaine on skin that is broken or infected because it can increase absorption into the bloodstream and raise the chances of experiencing side effects.
Caution in Individuals with Known Lidocaine Sensitivity
If a person has a sensitivity, to lidocaine or other anesthetics it is recommended to steer of using it and seek advice, from a healthcare professional beforehand.
Risk of Systemic Absorption with Excessive Use
Prolonged or excessive usage may cause the body to absorb the substance systemically and potentially result in lidocaine toxicity that can show up as problems with the system or cardiovascular system.
Importance of Adhering to Prescribed Dosages
It is essential to follow the recommended doses to prevent any reactions or harmful outcomes resulting from incorrect usage or excessive intake.
11. Interactions with Other Medications
Potential Interactions with Antiarrhythmic Drugs
When using lidocaine as an anesthetic, with qualities alongside other medications for irregular heartbeats like Class I antiarrhythmics such as procainamide or mexiletine, be cautious due to the potential combined impact on cardiac conductivity that could result in more severe side effects or heightened toxicity levels. It's advised that heart rhythm is monitored closely in such situations.
Interaction with Other Local Anesthetics
When lidocaine is combined with anesthetics, like bupivacaine or tetracaine, it can boost the effects of the anesthesia. It increases the chances of toxicity particularly when used over areas or, in high doses. Healthcare providers need to be cautious and limit the dosages to prevent outcomes.
Impact on Use with Topical Medications
When using lidocaine ointment in combination with treatments like corticosteroids or antifungals, absorption rates may change, which can impact how effective the medications are and the chances of experiencing side effects throughout the body. It is important for healthcare professionals to use their judgment when deciding to use topical agents together.
Use with Prescription and Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Products
Using lidocaine ointment alongside prescription or over-the-counter painkillers like NSAIDs or acetaminophen usually doesn't cause interactions between drugs in cases; however, it's important to be mindful of the overall effects when combining multiple pain relief medications for individuals with kidney or liver issues.
12. Contraindications for Lidocaine Ointment Use
Known Hypersensitivity to Lidocaine or Local Anesthetics
People who have had reactions to lidocaine or similar types of anesthetics should steer clear of using it to prevent severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis from occurring. Before using it on patients with sensitivities a patch test could be helpful, in assessing any reactions.
Contraindications in Patients with Heart Block
Patients with types of heart block should avoid using Lidocaine unless they have a pacemaker in place to address any issues that may arise due to its impact on conduction and potential worsening of arrhythmic conditions.
Avoidance in Patients with Severe Liver Disease
Liver damage can have an impact on how the body processes lidocaine cream since it can build up and cause effects in people with liver problems.
Special Contraindications in Individuals with Certain Skin Conditions
People suffering from skin issues, like eczena or psoriasis should steer clear of using lidocaine ointment on their skin if their skin barrier is already damaged due to conditions like burns or others similar, to it as it could increase the risk of toxic effects by boosting the amount absorbed into the body.
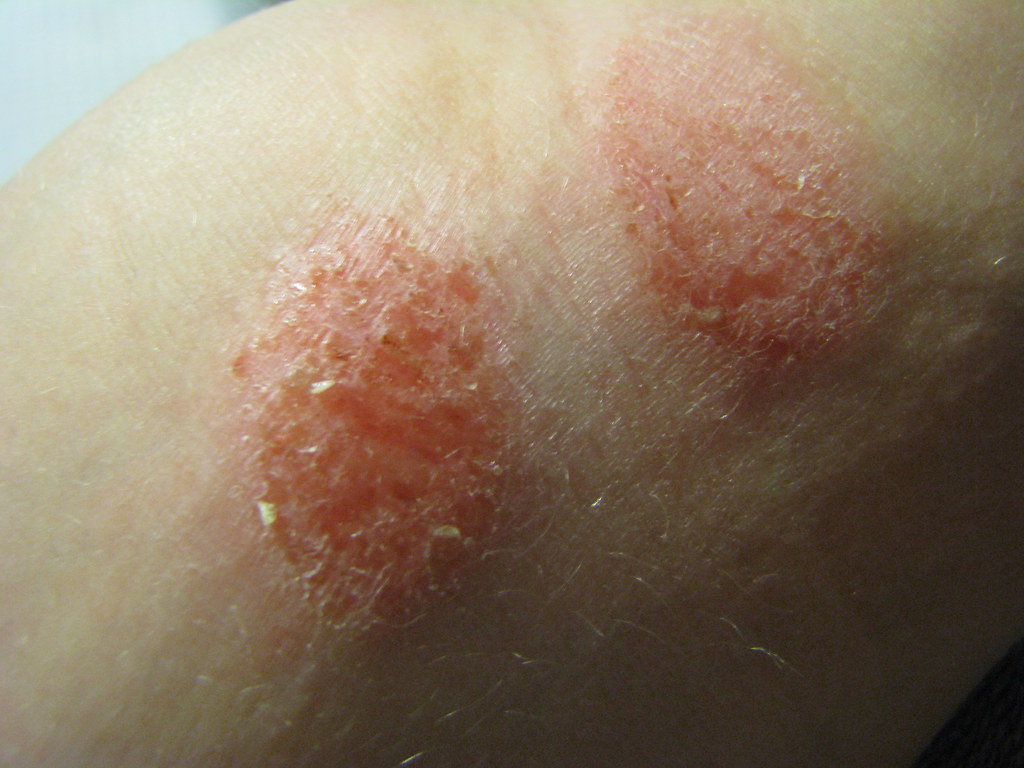
13. Careful Administration Guidelines
Monitoring for Signs of Systemic Toxicity
When lidocaine is applied on the skin surface, topical use can still allow for absorption into the body system, especially when used excessively or on damaged skin areas. Systemic toxicity signs may include feelings of up thoughts and sudden muscle contractions.It's crucial to keep a watch on its use during periods or when taken in high amounts to avoid any possible issues arising.
Reducing Dosage in Patients with Compromised Liver Function
Patients suffering from liver insufficiency struggle to process lidocaine effectively, which raises the likelihood of drug buildup and potential harm to the body. This calls for an approach, in adjusting the dosage and restricting the usage duration to guarantee safety for these individuals.
Avoiding Prolonged or Excessive Application in High-Risk Groups
Individuals, at risk groups like adults or those with existing heart conditions need careful supervision when using lidocaine ointment on their skin to prevent any negative effects, like irregular heartbeats or overall toxicity that could arise from prolonged or excessive application.
14. Administration to Elderly Patients
Adjusting Dosage for Age-Related Changes in Skin and Absorption
As people get older, their skin changes, such as becoming thinner and having blood flow, which can affect how medications work in the body by increasing absorption and making their effects last longer, so doctors need to adjust doses for elderly patients to prevent too much build-up in the body.
Special Considerations for Elderly with Comorbid Conditions
Senior patients frequently have health issues such as heart problems and liver issues when they seek medical care, whereas using lidocaine may trigger negative responses due to these health conditions in older individuals.It is crucial for healthcare providers to thoroughly assess patients before recommending lidocaine cream by considering their well-being.
Monitoring for Increased Sensitivity to Side Effects
The older demographic might face increased vulnerability to the reactions of lidocaine, such as feeling lightheadedness and confusion or experiencing post-administration, especially if there is absorption into the system; it is recommended to conduct routine checks for maintaining safety and effectiveness throughout the treatment process.
15. Administration to Pregnant and Nursing Women
Safety of Lidocaine Ointment During Pregnancy
During pregnancy usage, the classification of Lidocaine falls under Category B, which suggests no harm based on animal studies but lacks controlled research on pregnant women's outcomes yet indicates its overall safety during pregnancy, with application caution advised when benefits exceed risks, especially in the initial three months of gestation.
Transfer of Lidocaine to Breast Milk: Risk Assessment
Although Lidocaine can transfer into breast milk in quantities according to studies conducted so far, its topical usage is not expected to pose a risk to a breastfeeding baby in most cases; nevertheless, it is recommended to be cautious about excessive application or prolonged use of the ointment while breastfeeding.
Recommended Alternatives for Pain Relief in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
For pregnant and nursing women looking for options, lidocaine can explore drug choices like using cold compresses or trying physical therapies for pain relief during their journey to motherhood and the breastfeeding period. Acetaminophen continues to be the choice, for managing pain in these groups.
16. Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosage Guidelines
Children should use lidocaine ointment with care. Adjust the dosage according to their age and weight well as the condition being treated specifically. For kids than two years old, it's best to apply a concentrated form of lidocaine sparingly and avoid applying it too often.
Safe Applications for Minor Injuries and Pain Relief
In children's groups of people or individuals under the age of 18 years old, using lidocaine cream may be useful for addressing wounds, like cuts or scrapes and insect stings, by offering comfort and ease. It's important for caregivers to adhere closely to the advised amount guidelines to prevent use.
Avoiding Lidocaine Ointment in Infants and Toddlers: Risks and Precautions
It is usually advised against using Lidocaine ointment on infants than two years because their skin is thinner and their liver is not fully developed yet, which puts them at higher risk of absorbing the medication into their system and experiencing harmful effects, like seizures and breathing difficulties.
17. Overdose and Toxicity
Signs and Symptoms of Lidocaine Toxicity
Using Lidocaine ointment can cause toxicity when applied excessively to injured skin or large areas of the body. Initial signs of overdose may include fatigue and confusion, such as blurred vision. Severe toxicity may result in symptoms like seizures or difficulty breathing, leading to a coma.
Central Nervous System Effects (Seizures, Dizziness, Confusion)
When the levels of lidocaine rise in the blood system, it mainly affects the nervous system, causing symptoms like confusion and tremors or even seizures that need urgent medical attention.
Cardiovascular Symptoms (Arrhythmia, Hypotension)
In instances of toxicity, lidocaine has the potential to impact heart function by causing heart rhythms or substantial decreases in blood pressure, which could result in life-threatening situations and require immediate medical intervention.
Emergency Management and Treatment for Overdose
Managing an overdose of lidocaine requires providing care and closely monitoring signs, for any changes or concerns. Severe cases of toxicity may be treated using lipid emulsion therapy. In situations involving collapse due to an overdose, it is important to start cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols promptly to address the situation effectively.
Long-Term Effects of Lidocaine Toxicity
Long-term consequences of lidocaine toxicity are infrequent. It can include lasting issues, like memory loss or difficulties, with motor skills if the overdose is severe or treatment is delayed.
Lidocaine allergy
Allergic reactions can vary from symptoms like hives and redness with intense itching to more severe reactions such as swelling and breathing difficulties. Severe life-threatening responses could include difficulty breathing (apnea), blood pressure (hypotension), and passing out (loss of consciousness).
18. Handling Precautions
Safe Application Tips for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare workers need to adhere to guidelines when using lidocaine cream to prevent accidental overexposure. They should wear gloves when applying the cream and avoid covering areas without considering the potential for absorption into the body.
Avoiding Contamination of the Ointment
To avoid any risk of contamination, make sure to seal the lid of the ointment container every time you use it. If you suspect contamination it's best to dispose of the ointment and get an one to keep patients safe.
Proper Disposal Methods for Expired or Unused Ointment
Please make sure to follow your guidelines when disposing of expired or unused lidocaine ointment by using a medication take-back program for disposal instead of flushing it down the drain or throwing it in the household trash to prevent environmental contamination.
Lidocaine Ointment FAQ
- How long does lidocaine last?
- What is the strongest prescription lidocaine patch?
- What is 5% lidocaine ointment used for?
- Why are lidocaine patches removed after 12 hours?
- What is the first sign of lidocaine toxicity?
- Who should not use lidocaine patch?
- How long do lidocaine patches last?
- How long do lidocaine injection side effects last?
- How long does it take for lidocaine to wear off?
- How much lidocaine to mix with rocephin?
How long does lidocaine last?
The numbing sensation from Lidocaine can persist for an average of half an hour to three hours; however, in some cases, it may extend up to two days before fading away naturally. Should the effects linger beyond an hour without subsiding as expected, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider. Overdosing on Lidocaine can result in seizures, irregular heart rhythms, and, in some instances, distress.
What is the strongest prescription lidocaine patch?
There are three variations of Lidocaine patches sold, with strengths of 5%, 4%, and 1%. Depending on the manufacturer, the directions and age restrictions for these patches may vary.
What is 5% lidocaine ointment used for?
5 % Lidocaine ointment is used to numb the membranes in the mouth and throat for anesthesia purposes, as a lubricant during intubation procedures, and to provide pain relief for burns, such as sunburns, cuts on the skin, and insect bites.
Why are lidocaine patches removed after 12 hours?
The suggestion to wear each plaster for 12 hours is because there is a chance of experiencing skin reactions, like rashes or itching, if worn for periods.
What is the first sign of lidocaine toxicity?
At the stages of this condition's onset, restlessness and disorientation are followed by lightheadedness and sleepiness. Well, feelings of unease and altered hearing perception, along with ringing in the ears and tingling around the mouth coupled with a metallic flavor in the mouth, and difficulty speaking clearly, are also present.If not addressed promptly, these initial indicators may develop into convulsions, cessation of breathing, or unconsciousness.
Who should not use lidocaine patch?
Patients who have a known sensitivity, to anesthetics of the amide type or any other component of the product should not use the LIDOCAINE PATCH 5%.
How long do lidocaine patches last?
The pain relief provided by lidocaine patches typically lasts between 8 and 12 hours, depending on the patch being used. To minimize risks and side effects associated with the use of these patches, follow the instructions provided on your prescription label or the over-the-counter packaging.
How long do lidocaine injection side effects last?
Sometimes, you might experience side effects that typically do not require attention, but these effects may diminish as your body gets used to the medication during the treatment process.
How long does it take for lidocaine to wear off?
Different types of anesthetics have varying durations of effectiveness, in wearing off administered into the body system. For example; The effects of lidocaine usually wear off within one, to two hours whereas lidocaine combined with epinephrine (which acts as a vasoconstrictor) can prolong the numbing sensation for two to four hours.
How much lidocaine to mix with rocephin?
For an injection using Rocephin 250 mg or 500 mg dosage strength, it is mixed with 2 ml of a 1% lidocaine hydrochloride solution and administered into a sizeable muscle mass in the body. Similarly, for Rocephin 1 g dose, it is mixed with 3. 5 Ml of the solution and injected into the muscle. It is advisable not to exceed a dosage of 1 g at an injection site.