Lidocaine
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Lidocaine
- III. How Lidocaine Works
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Lidocaine
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Lidocaine Products
- VII. Side Effects of Lidocaine
- VIII. Interactions with Other Drugs
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XI. Special Considerations for Administration
- XII. Overdosage and Its Implications
- XIII. Storage Recommendations for Lidocaine Products
- XIV. Handling Precautions for Lidocaine
I. Introduction
Brief History of Lidocaine
In the middle of the century, Lidocaine made its mark as an innovative breakthrough in the medical field. This remarkable medication was created in 1943 by Nils Löfgren, a chemist from Sweden. After it quickly became an essential component in numerous medical treatments playing a vital role in relieving pain and controlling irregularities related to the heart.
Overview of Its Medical Importance
From a standpoint, Lidocaine's medical importance is unmatched. It is widely used in medical situations and has proven effective in relieving and treating ailments. Its versatile role as an antiarrhythmic agent highlights its widespread use in clinical medicine.
II. Uses of Lidocaine
Local Anesthesia: Dental and Minor Surgeries
Lidocaine is commonly used as an anesthetic in dental procedures and minor surgeries. It provides relief by acting swiftly, ensuring a deep level of anesthesia for smooth procedures, and has a duration that minimizes the need for repeated applications.
References:
- 1Lidocaine: A Local Anesthetic, Its Adverse Effects and Management - MDPI
- 2Understanding Dental Anesthesia: Types, Side Effects & Risks - Healthline
- 3Medical Clearance for Common Dental Procedures | AAFP
Treatment of Irregular Heartbeats: Antiarrhythmic Agent
In health, Lidocaine is known for its ability to prevent irregular heart rhythms. Modulating ion channels helps stabilize the heart's activity, protecting it from any potential dangers.
References:
- 12018 American Heart Association Focused Update on Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Use of Antiarrhythmic Drugs During and Immediately After Cardiac Arrest An Update to the American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care - Circulation
- 2Can Lidocaine Be Used for Heart Arrhythmias? - Healthline
- 3ACLS and Lidocaine | ACLS-Algorithms.com
Relief of Postherpetic Neuralgia: Topical Patch
Lidocaine proves to be highly effective in reducing the discomfort caused by neuralgia. When applied as a patch on the area, it helps calm the irregular nerve signals, ultimately relieving the associated symptoms.
References:
- 1Postherpetic neuralgia - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
- 3Lidocaine transdermal patches reduced pain intensity in neuropathic …
- 2Lidocaine patches for back pain: Side effects, dosage, safety
Eczema and Itch Relief: Topical Applications
Lidocaine not provides relief from pain and helps with heart-related issues, but it also has a noticeable ability to alleviate itching. When applied topically, it offers a needed break from the relentless itch experienced by individuals with conditions like eczema, ultimately improving their overall quality of life.
Reference:
- Lidocaine - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Lidocaine Topical: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- Lidocaine Patches: Uses, Side Effects, and More - GoodRx
III. How Lidocaine Works
Mechanism of Action: Numbing Effect
The critical aspect of how Lidocaine works is its ability to block the sodium channels in nerve cells. Doing it interrupts the transmission of nerve signals and creates a numbing sensation in a specific area. This action is what makes Lidocaine effective as a pain reliever.
Impact on Cardiac Cells: Regulating Heart Rhythms
Regarding the heart, Lidocaine works by regulating ion channels, which helps maintain stability in the cell membrane of the heart muscle. This prevents any electrical activities and ensures that the heart beats in a coordinated and rhythmic manner.
IV. Off-Label Uses of Lidocaine
Chronic Pain Management
In addition to its uses, Lidocaine has also been used off-label to treat chronic pain. Its effectiveness in reducing nerve signals makes it a valuable tool in managing conditions such as neuropathic pain disorders.
References:
- Pharmacologic management of chronic non-cancer pain in adults - UpToDate
- INTRAVENOUS ANESTHETICS FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PAIN - AAPC
Migraine Prophylaxis
Lidocaine, a substance explored within the realm of neurology, has shown potential as a treatment for migraines. It works by regulating the excitability of neurons, reducing the frequency and intensity of episodes. However, it is essential to note that this effect has been observed in groups of individuals.
References:
Treatment of Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders
Lidocaine is known for its ability to be used in ways including treating gastrointestinal issues. Its ability to relax muscles has proven effective in relieving symptoms such as cramps and spasms associated with certain motility disorders.
References:
V. Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms: Gel, Injection, Patch, etc.
Lidocaine comes in forms to suit different needs. There are gels and creams that can be applied on the skin, injectable solutions used for anesthesia and patches designed for long-lasting release. Having these different options allows for delivery, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment.
Recommended Dosing for Different Conditions
The amount of Lidocaine needed varies depending on the condition being treated. For example, dental procedures may require more than treating a cardiac arrhythmia. Therefore healthcare professionals must determine the dosage carefully.
Proper Administration Techniques
It is essential to follow the administration guidelines to ensure Lidocaine is used correctly. This involves using techniques for injections and preparing the skin correctly for topical applications. By doing this, we can maximize the effectiveness of the treatment while minimizing any problems or side effects.
VI. Composition of Lidocaine Products
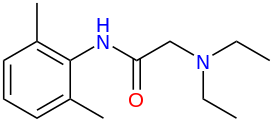
Main Ingredient: Lidocaine Hydrochloride
The core component of Lidocaine products is Lidocaine Hydrochloride, a compound with both solubility and pharmacological potency. This chemical substance forms the basis for the qualities of the drug.
Common Additives and Preservatives
The main ingredient is enhanced with additives and preservatives. These components, which include stabilizers and antioxidants, are responsible for maintaining the product's freshness and effectiveness over time.
Variations by Product Type
Lidocaine can come in formulations, each with its specific additives. For example, gels may include emollients to provide a texture, while injectables might contain isotonic agents to meet their particular needs. These differences are designed to cater to the requirements of each formulation.
VII. Side Effects of Lidocaine
Most Common Side Effects: Nausea, Dizziness, Burning at Application Site
Similar to any medication, Lidocaine can have side effects. Some patients may experience nausea, moments of dizziness, or a slight burning sensation in the area where it is applied topically. However, these effects are typically harmless. Usually go away on their own.
Serious Side Effects: Breathing Difficulties, Seizures, Low Blood Pressure
Sometimes cases more severe difficulties may arise. These can involve problems with breathing, sudden seizures, or a sudden decrease in blood pressure. When these things happen, it's essential to seek medical help.
Factors Influencing Side Effects: Dosage, Duration, Health Status
The likelihood of experiencing side effects depends on factors such as the amount of medication taken, how long it is taken, and the individual's overall health condition. The risks may increase for individuals with existing health conditions. When accidentally taking too much medication.
VIII. Interactions with Other Drugs
Drugs That Increase Lidocaine Levels: Beta-blockers, Cimetidine
Certain medications, such as Beta blockers or Cimetidine, have the potential to increase the levels of Lidocaine in the bloodstream. This interaction in how the body processes the medication can raise the chances of experiencing effects, so adjusting the dosage carefully is essential.
Drugs That Decrease Effectiveness: Phenytoin, Phenobarbital
On the hand, medications such as Phenytoin or Phenobarbital, which are used to treat epilepsy, can reduce the effectiveness of Lidocaine. These medications speed up how Lidocaine is broken down in the body, potentially weakening its benefits.
Combining Lidocaine with Blood Pressure Medications
Lidocaine's impact on the heart could potentially interact with medications. When these are used together, there is a possibility of a combined effect leading to blood pressure. Therefore it is essential to monitor the situation and consider adjusting the dosage if necessary.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
Individuals with Heart Conditions
Individuals who have been diagnosed with cardiovascular conditions need to exercise extreme caution when it comes to the use of Lidocaine. This is because the drug's natural effects on the heart could unintentionally worsen existing heart conditions leading to complications. Cardiologists and anesthetists must work together closely to ensure that Lidocaine is used judiciously in these situations.
Allergic Reactions to Local Anesthetics
Many people may have an extreme sensitivity to local anesthetics like Lidocaine. This can result in symptoms such as red rashes, swelling, and even severe allergic reactions like anaphylactic shock. Because of these sensitivities, it becomes necessary to explore anesthesia methods.
Severe Liver Disease Patients
The liver, which is responsible for metabolizing Lidocaine, plays a role in how this drug is processed in the body. When people have liver problems, it can affect the clearance of Lidocaine and lead to increased levels of the drug in the bloodstream. This could potentially result in neurotoxicity or cardiotoxicity.
X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
When administering Lidocaine it is crucial to monitor vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure particularly when using higher doses. This helps detect and address any changes, in the body's cardiovascular system at an early stage.
Ensuring Sterile Techniques with Injections
Administering Lidocaine injections, whether under the skin or through a vein, requires attention to maintaining sterile conditions. This process guarantees the prevention of infections, promotes the possible treatment results, and reduces potential adverse reactions in the surrounding tissues.
Importance of Disclosing All Medical Conditions
Considering all the conditions a person may have and having a complete clinical history can help ensure the safety of using Lidocaine. This thorough disclosure allows for treatment plans considering possible interactions with other medications and individual susceptibilities.
XI. Special Considerations for Administration
Elderly: Adjusted Dosing and Monitoring
The elderly population often shows changes in how their bodies process and respond to medications. Because of this, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage of Lidocaine when administering it to these individuals. Additionally, it is wise to monitor them due to their increased susceptibility to experiencing adverse effects from the medication.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Benefits vs Risks
When it comes to nursing women, it's essential to carefully consider the pros and cons of using Lidocaine. While Lidocaine is not known to cause birth defects, its ability to pass through the placenta and into breast milk should be cautiously approached. The main goal is to prioritize the mother's and baby's health.

Children: Age-specific Dosages and Precautions
Pediatric patients, due to their developmental characteristics, need to be prescribed specific doses of Lidocaine based on their age. Additionally, extra caution is taken with these recipients to prevent any potential risks. Pediatricians and anesthetists work together to determine the treatment plans for them.
XII. Overdosage and Its Implications
Symptoms of Lidocaine Overdose
Accidentally taking Lidocaine can lead to a range of symptoms. These may include issues like tremors, seizures, or even coma. It can also cause problems such as a slow heart rate (bradycardia), low blood pressure (hypotension), or irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). In addition, there may be difficulties, like slowing down or stopping breathing. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms for proper and timely treatment.
Immediate Interventions and Treatments
When dealing with a suspected overdose, it is essential to take action. This involves stopping Lidocaine providing care, and using specific antidotal treatments. Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy is one such treatment that shows promise in combating toxicity.
Long-term Health Impacts
Although prompt interventions can help lessen the consequences of an overdose, some people may face long-term effects, especially if there was significant damage to the nervous system or heart.
XIII. Storage Recommendations for Lidocaine Products
Ideal Temperatures and Conditions
Lidocaine products are usually stored at room temperatures that are carefully controlled, typically ranging from 20°C to 25°C. Any variations outside of this range could potentially affect the effectiveness of the medication.
Safeguarding Against Contamination
Handling products in multi-dose vials or topical preparations with caution is essential to prevent microbial contamination. Every time you use them, follow hygiene practices and maintain a sterile environment.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Like any other medication, Lidocaine products have a specific period in which they can be safely used; once this time has passed, there may be doubts about their effectiveness and safety. That's why it's essential to check the inventory and dispose of any expired stocks promptly.
XIV. Handling Precautions for Lidocaine
Protecting Skin and Eyes
It is essential to be cautious when coming into contact with Lidocaine solutions as they can irritate. Therefore, it is advisable to wear gloves and eye shields, particularly in clinical or laboratory environments.
Proper Disposal of Unused or Expired Products
Considering the properties of Lidocaine, it is important not to dispose of it casually. Using pharmaceutical disposal methods, we can protect the environment and prevent unintended exposure.
Reporting Adverse Reactions and Incidents
Pharmacovigilance continues to be an aspect of ensuring drug safety. Therefore, reporting any unexpected reactions or incidents related to Lidocaine to the appropriate authorities is crucial. The information gathered from these reports plays a role in shaping future guidelines and improving patient safety.