Lignocaine
- I. Introduction to Lignocaine Gel
- II. Composition of Lignocaine Gel
- III. Understanding How Lignocaine Gel Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Lignocaine Gel
- V. Off-label Uses of Lignocaine Gel
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Lignocaine Gel
- VII. Warnings and Contraindications of Lignocaine Gel
- VIII. Administration of Lignocaine Gel: Special Populations
- IX. Side Effects and Managing Overdose of Lignocaine Gel
- X. Storage, Interaction, and Handling Precautions for Lignocaine Gel
- XI. Essential Precautions When Using Lignocaine Gel
- XII. Conclusion: Key Takeaways on Lignocaine Gel
I. Introduction to Lignocaine Gel
A. Definition and Key Properties
Lignocaine Gel, also known as Lidocaine in some places, is a type of numbing cream used primarily to alleviate pain and discomfort. It works by numbing the skin and surrounding tissues making it helpful for reducing pain caused by skin conditions or procedures involving the skin. It acts as a remedy against the sensory response of the nervous system, to harmful stimuli. Its unique ability to dissolve in lipids enables it to penetrate mucosal surfaces making it widely used in minor surgical procedures.
B. Historical Development and Medical Relevance
Lignocaine, originally developed in 1943 by the Swedish chemist Nils Löfgren was a result of the search for a more efficient local anesthetic than cocaine, which was widely used back then. The introduction of Lignocaine brought advancements to various areas of medicine such as dentistry, dermatology, and minor surgeries, thanks, to its improved safety record and effectiveness.
II. Composition of Lignocaine Gel
A. Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main ingredient in Lignocaine Gel is lignocaine hydrochloride, which's responsible for its therapeutic effects. Typically the concentration of this ingredient falls between 2% and 5%; in addition to that, the gel also contains ingredients known as "inactive" ones. These inactive ingredients act as carriers or vehicles for the ingredient and may include hydroxyethylcellulose, sodium hydroxide purified water, and more. Apart from their role, carrying these inactive ingredients also contributes to the texture of the gel, making it easy to apply and providing a longer shelf life.
B. Differentiating Brands and Formulations
Even though the main active ingredient stays the same in brands, there can be differences in the "inactive" ingredients that can affect how users experience them. These variations can show up in things like how thick or thin the gel's, how quickly it gets absorbed its scent, and more. Additionally, some brands might add ingredients, like antiseptics or vasoconstrictor, to improve the effectiveness of the gel or broaden its range of applications.
III. Understanding How Lignocaine Gel Works
A. The Science Behind Lignocaine
Lignocaine, a type of medication that helps with heart rhythms, works by stopping the flow of ions needed to start and carry electrical signals. Its main action is to block sodium channels in the membranes of nerve cells, which slows down the process of depolarization and reduces the frequency of impulses. This action prevents pain signals from being transmitted to the brain resulting in a numbing or pain-relieving effect.
B. Application and Absorption Process
Applying the gel penetrates your skin, and the lignocaine in it works by blocking the nerve pathways. This happens because it reduces the ability of the nerve covering to allow sodium ions to pass through. As a result, it prevents nerve impulses from starting and traveling. However, remember that the gel's effects are mostly limited to an area and temporary. Normal sensation usually returns once the drug is broken down and eliminated from your system. To get the most out of this gel while minimizing any risks or side effects, make sure to use it as instructed by a healthcare professional or according to the product's guidelines.
IV. Approved Uses of Lignocaine Gel
A. In Dentistry
Notably, one of the applications of Lignocaine Gel, also known as Lidocaine Gel, is dentistry(1). This anesthesia compound helps in numbing or temporarily reducing sensations in the treated area, making it a valuable tool for procedures. For use; Primarily, Lignocaine Gel is used as a topical anesthetic for various procedures inside the mouth(2). This includes anesthesia for dental fillings, extractions, or cleaning treatments. Creating a sensation helps alleviate discomfort and provides a more manageable experience for the patient. Gum treatment; Lignocaine Gel is also beneficial in treating inflamed or diseased gums, expanding its usefulness in dentistry. It can be applied to the area to relieve pain and facilitate more effective treatment methods.(3)
1. MayoClinic - Lidocaine And Prilocaine (Gingival Route)
2. CleavelandClinic -Lidocaine; Prilocaine Peridontal Gel
3. Decisions in Dentistry - Update on Dental Topical Anesthetics
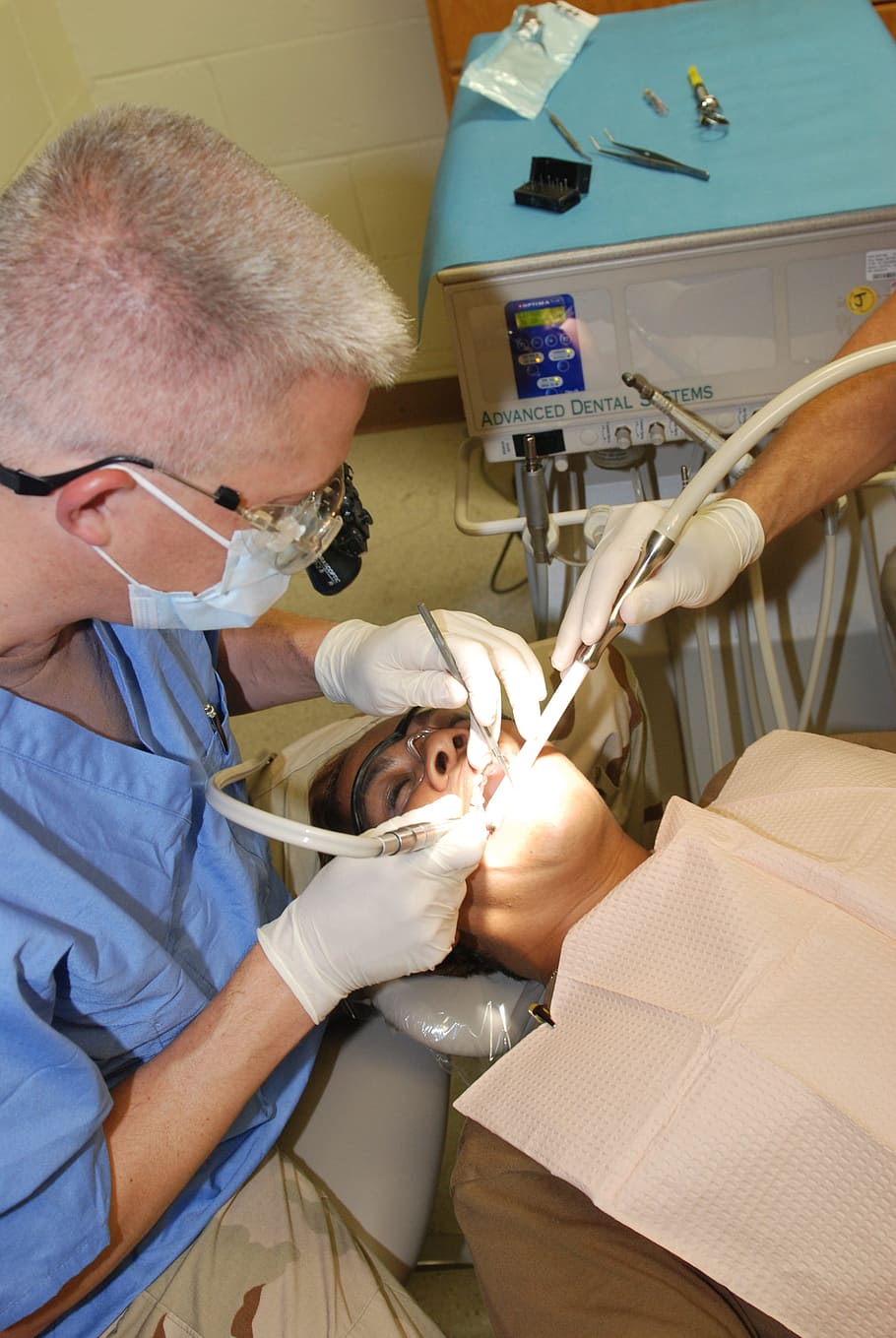
Dental procedure with Lignocaine
B. For Minor Surgical Procedures
Lignocaine Gel also plays a crucial role in minor surgical procedures. Its pain-relieving properties make it an excellent choice for procedures requiring surface anesthesia, ensuring both comfort and the procedure's success.(1)
Lignocaine Gel is commonly used in dermatology for surgical procedures such as biopsies, excision, and sutures. It creates an environment making it an essential component in dermatological anesthesia.(2)
Furthermore, Lignocaine Gel is frequently utilized in urology for catheterization and cystoscopy procedures. By reducing discomfort and minimizing the sensation of an object Lignocaine Gel greatly enhances patient comfort during these urological interventions.(3)
1. National Library of Medicine - Recent Advances in Local Anesthesia: A Review of Literature
C. Other Medical Scenarios
Lignocaine Gel has gained recognition in dentistry and minor surgery, but its effectiveness extends far beyond that. It proves to be versatile and widely valuable for medical scenarios.
- For example, during endotracheal tube insertion, Lignocaine Gel can be utilized to minimize discomfort and suppress the cough reflex, making the process smoother.
- Additionally, it serves as a remedy for easing pain and discomfort caused by skin conditions like burns and abrasions, showcasing its role in managing symptoms.
- In obstetrics and gynecology, Lignocaine Gel finds application in relieving pain and facilitating speculum introduction during gynecological examinations.
This demonstrates its relevance across areas of medicine.
V. Off-label Uses of Lignocaine Gel
A. Pain Management Outside Clinical Settings
Lignocaine Gel isn't just limited to settings. Its powerful numbing properties have proven useful in medical scenarios requiring quick pain relief.
- In sports, Lignocaine Gel can provide comfort for minor injuries like sprains and strains, helping with prompt pain management.
- Equally notable is how Lignocaine Gel has been incorporated into first aid practices. It's used on wounds, burns, or abrasions to ease discomfort and offer immediate relief showcasing its significant role beyond the confines of a clinic.
B. Potential Uses in Dermatology
Lignocaine Gel has shown potential in dermatology extending its applications beyond the usual scope. While it is not traditionally prescribed for these purposes, evidence suggests its benefits are worth investigating.
- One area of interest is acne treatment. Initial findings indicate that Lignocaine Gel could help alleviate acne-related pain and complement existing approaches.
- Moreover, researchers have also explored the use of Lignocaine Gel in managing chronic skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema. This opens up possibilities for symptomatic relief in these complex disorders.
C. Investigational Areas and Ongoing Research
With the progress of science, scientists are continuously exploring new applications for well-established substances such as Lignocaine Gel. These research areas have the potential to change current treatment approaches and enhance patient care.
- One area under investigation is the use of Lignocaine Gel in managing pain caused by cancer. Researchers are particularly interested in its potential to alleviate mucositis from chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Another aspect worth exploring is the application of Lignocaine Gel in treating neuropathic pain. Clinical trials are underway to assess its effectiveness in relieving these conditions' persistent and often debilitating pain.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Lignocaine Gel
A. General Guidelines for Use
Lignocaine Gel is a pain reliever, so it's crucial to use it carefully to get the most benefits and avoid any risks. It's extremely important to follow the guidelines a healthcare professional provides when using Lignocaine Gel.
- Changing the dosage or frequency on your own can have effects and may even be dangerous.
- The gel should be stored in an environment to ensure that it remains effective. A cool, dry place away, from direct sunlight. This will help maintain its potency and effectiveness over time.
B. Dosage for Different Age Groups and Conditions
Considering the diversity in demographics, the dosage of Lignocaine Gel varies depending on different age groups and specific conditions.
- For adults, the usual dosage typically falls within the 2-5% range ofconcentration of Lignocaine. However, the exact quantity needed depends on the treatment situation.
- In the case of pediatrics patients, lower concentrations and volumes are recommended due to their higher susceptibility to systemic absorption and potential toxicity.
- It is advisable to adopt a personalized approach when dealing with pain conditions. The dosage should be carefully adjusted based on the patient's pain levels and response to therapy.
C. Administration Procedures: Best Practices
When using Lignocaine Gel, following the recommended guidelines can enhance its pain-relieving effects while minimizing any negative impacts.
- Here's how to apply it Apply a thin layer of the gel on the affected area, being careful to avoid any broken skin or sensitive membranes.
- Leave the gel in place for the duration advised by your healthcare provider, usually until you achieve the desired numbing effect.
VII. Warnings and Contraindications of Lignocaine Gel
A. Specific Health Conditions
Some health conditions require healthcare providers to be cautious and potentially adjust the usage of Lignocaine Gel. It's important for them to know about these contraindications in order to ensure the safety of patients.
- For patients with cardiac conditions, they may be more vulnerable to the systemic effects of Lignocaine so its use should be approached with caution.
- Similarly patients with liver disease may have higher levels of the drug, in their body as Lignocaine is metabolized in the liver. This can potentially lead to toxicity, so it's important to consider this when administering the medication.
B. Drug Interactions and Risks
Before starting treatment with Lignocaine Gel, it is important for patients to inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are currently taking. This is because there may be interactions between Lignocaine and other drugs that can affect its effects.
- For example, medications like Amiodarone and Beta-blockers used to treat arrhythmias can potentially worsen the effects of Lignocaine.
- Additionally, certain antibiotics, like Erythromycin can interfere with the metabolism of Lignocaine, increasing the risk of toxicity.
C. Allergy and Hypersensitivity Precautions
People with a history of allergies or sensitivity to Lignocaine or other amide-based anesthetics should avoid using Lignocaine Gel. Moreover, individuals should be vigilant for any indications of reactions and promptly seek medical assistance if they notice any such signs.
VIII. Administration of Lignocaine Gel: Special Populations
A. Elderly Patients: Precautions and Dosage Adjustments
Due to their lower metabolic function and the possibility of having other health issues, older patients need to be given special attention when using Lignocaine Gel. It is generally recommended to administer a dosage at a slower pace and closely monitor their condition.
B. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile
Although Lignocaine Gel is generally safe to use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, healthcare providers should exercise caution. Before prescribing this medication to women or nursing mothers, they should carefully weigh the potential benefits against any possible risks.
C. Children: Age Considerations and Dosage Limits
When using Lignocaine Gel with children, it's essential to consider their age, weight, and overall health condition. It is generally recommended to use dosages to minimize the chances of the gel being absorbed into the body and causing any harm. Healthcare professionals should closely observe these patients to ensure the treatment is safe and effective.
IX. Side Effects and Managing Overdose of Lignocaine Gel
A. Common Side Effects and Their Management
Like any medication, Lignocaine Gel can have side effects. They are usually not serious and go away on their own.
- Sometimes patients may notice redness, swelling, or mild discomfort, in the area where the gel is applied. These symptoms usually resolve without any treatment. Suppose they continue for a long time, it's best to consult a doctor.
- Some patients may sometimes experience dizziness, nausea, or minor headaches. However, these symptoms should improve over time. If they persist or get worse, it's important to seek attention promptly.
B. Rare, But Serious Side Effects
In some cases, Lignocaine Gel may cause severe side effects that require immediate medical attention.
- If you notice symptoms such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, it could indicate an allergic reaction, and you should seek immediate medical care.
- Similarly, if you experience seizures, intense dizziness, fainting spells, or confusion after using Lignocaine Gel, it may suggest levels of the medication in your system and require urgent medical attention.
C. Signs of Overdose and First Aid Measures
Identifying an overdose of Lignocaine Gel is crucial to take immediate first aid actions and seek medical assistance.
Signs of an overdose may include
- Muscle twitching
- Convulsions
- Loss of consciousness
- Potentially respiratory or cardiac arrest.
If you suspect an overdose, it is important to stop using the medication, ensure the airway is clear, and urgently seek medical help.
X. Storage, Interaction, and Handling Precautions for Lignocaine Gel
A. Proper Storage Conditions
To ensure the effectiveness and safety of Lignocaine Gel it is important to store it. The gel should be kept at room temperature avoiding heat or cold. It is also essential to hold the gel in a place away, from any moisture as this helps maintain its pharmacological properties.
B. Drug, Food, and Alcohol Interactions
It is important to be aware of the effects of certain substances, on the functioning of Lignocaine Gel. Therefore it is crucial to inform healthcare providers about any medications you may be taking, as some antiarrhythmic drugs and antibiotics can interact with Lignocaine. Additionally, it is advisable to avoid using Lignocaine Gel with alcohol as this combination could worsen the central nervous system effects of Lignocaine.
C. Handling Precautions and Disposal Guidelines
It is important to handle and dispose of Lignocaine Gel properly to ensure the safety of patients and the protection of the environment.
- When using the gel, it is essential to wash your hands afterwards to prevent accidental absorption unless you are applying the gel on your hands.
- If you have any expired Lignocaine Gel it should be disposed of according to local waste disposal guidelines or by seeking guidance, from a pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
XI. Essential Precautions When Using Lignocaine Gel
A. Importance of Following the Prescription
It is crucial to follow the prescribed guidelines when using Lignocaine Gel. This includes not the recommended dosage and frequency but also instructions regarding how to apply it, how long the treatment should last, and how to store it properly. By being careful, in adhering to these instructions, you can experience the therapeutic outcomes while minimizing any potential adverse effects.
B. Ensuring Safe Use in Homes and Medical Settings
It is absolutely essential to use Lignocaine Gel whether at home or, in a medical setting. When applying the gel it is important for individuals to maintain cleanliness and sterility avoid using it on damaged skin or mucous membranes and keep it out of reach of children. For professionals, accurate dosage administration monitoring for any negative reactions and taking necessary precautions during procedures are crucial.
C. Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up During Treatment
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of Lignocaine Gel treatment, it is important to monitor patients for any potential side effects. Patients should be informed about the side effects and advised to consult a healthcare professional if they experience any. Follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider are crucial to evaluate the treatment's effectiveness and make any required modifications.
XII. Conclusion: Key Takeaways on Lignocaine Gel
A. Recap of Benefits and Risks
In summary, Lignocaine Gel has shown effectiveness as a pain-relieving medication in clinical situations due to its strong local numbing properties. However, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with its use. These risks range from issues like local irritation to more severe adverse effects such, as allergic reactions and potential harm if used improperly.
B. Importance of Medical Guidance
The main idea that emerges from discussions about Lignocaine Gel is the importance of medical guidance. Even though it is available without a prescription in places, this doesn't diminish the need for professional supervision to ensure safe and effective use. It's always advisable for patients to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning this medication and maintain communication throughout the treatment process.
C. Looking to the Future: New Developments in Lignocaine Use
With the continuous progress of science, our comprehension and utilization of Lignocaine Gel are also advancing. Recent studies indicate that its applications might extend beyond the indications presenting intriguing possibilities for future use. Course any further advancements will prioritize patient safety and effectiveness, upholding the commitment, to enhancing patient care.