Lincomycin Syrup
- Introduction to Lincomycin Syrup
- Composition of Lincomycin Syrup
- Uses of Lincomycin Syrup
- How Lincomycin Syrup Works
- Dosage and Administration of Lincomycin Syrup
- Side Effects of Lincomycin Syrup
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Interactions of Lincomycin Syrup
- Administration to Special Populations
- Handling and Storage of Lincomycin Syrup
- Overdose Management of Lincomycin Syrup
- Important Precautions When Using Lincomycin Syrup
- Careful Administration Guidelines
- Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Lincomycin Syrup
Introduction to Lincomycin Syrup
Overview of Lincomycin Syrup
Lincomycin Syrup is a potent antibiotic formulation designed to combat various bacterial infections. Known for its broad spectrum of activity, it is frequently prescribed for conditions resistant to other medications. This syrup-based preparation ensures ease of administration, especially for individuals with swallowing difficulties.
History and Development of Lincomycin
Originally introduced during the 1960s, Lincomycin represented an achievement in the realm of progress. It was sourced from the bacterium Streptomyces lincolnensis residing in soil and soon garnered attention for its effectiveness against gram microbes. As time passed, it found uses that mirrored the progress made in studies.
Importance in Modern Medicine
In a time when antibiotic resistance is on the rise, Lincomycin Syrup continues to be a treatment for stubborn infections due to its targeted action against certain bacteria while preserving the body's natural microbial balance—a testament to its importance in clinical practice.
Composition of Lincomycin Syrup
Active Ingredient and Its Role
The main ingredient in this medication is lincomycin hydrochloride, which works by stopping the production of proteins in bacteria to prevent their growth and spreading infections.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Purpose
Additional components, like sugars and additives, are used to improve the taste and longevity of the syrup while also maintaining well-being and adherence to safety standards.
Variations in Formulation
Lincomycin Syrup comes in strength to meet medical requirements effectively for accurate dosages tailored for children and elderly patients.
Uses of Lincomycin Syrup
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Lincomycin Syrup is mainly used to treat severe infections that do not respond well to initial antibiotics, making it an important choice in antimicrobial treatment options.
Specific Indications
- Respiratory tract infections: Effective against pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and soft tissue infections: Commonly used for cellulitis, abscesses, and wound infections.
Use in Dental Infections
Off-Label Uses
New findings indicate uses in addressing infections like bone and joint ailments; however, these need confirmation through clinical trials.

How Lincomycin Syrup Works
Mechanism of Action
Lincomycin hampers the production of proteins in bacteria by attaching to the 50 S subunit and stopping growth efficiently, with minimal impact on human cells.
Spectrum of Activity
The medicine shows effectiveness against types of bacteria like gram positive pathogens and specific anaerobes such as Clostridium species; this makes it crucial, in treating severe infections.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
After taking the medication by mouth, it quickly enters the bloodstream, leading to effectiveness at levels and better absorption when consumed without food.
Dosage and Administration of Lincomycin Syrup
Recommended Dosages
Patients' dosages are customized based on their age and weight, regardless of the seriousness of the infection they have contracted. Treatment plans usually consist of administering 10 to 20 milligrams, per kilogram each day which is then divided into doses throughout the day.
Dosage Adjustments
Patients who have kidney or liver issues might need their medication doses adjusted to avoid buildup and potential harm from the drugs.
Administration Guidelines
- Shake well before use.
- Administer with a calibrated measuring device for accuracy.
- Take on an empty stomach to enhance absorption.
Side Effects of Lincomycin Syrup
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Although Lincomycin Syrup is usually well received by people without issue, it can lead to reactions in certain cases. It is important to notify healthcare providers of any symptoms to guarantee timely assistance and support.
Common Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea and diarrhea.
- Allergic reactions such as rashes and itching.
Rare but Severe Side Effects
Rare occurrences, like colitis and anaphylactic reactions, require medical care.
Warnings and Contraindications
Situations Where Lincomycin Syrup Should Not Be Used
It is not recommended for individuals who have had reactions to lincomycin or clindamycin in the past.
Warnings for Pre-Existing Conditions
Patients who have issues or liver conditions should be careful when taking this medication as it may worsen their symptoms.
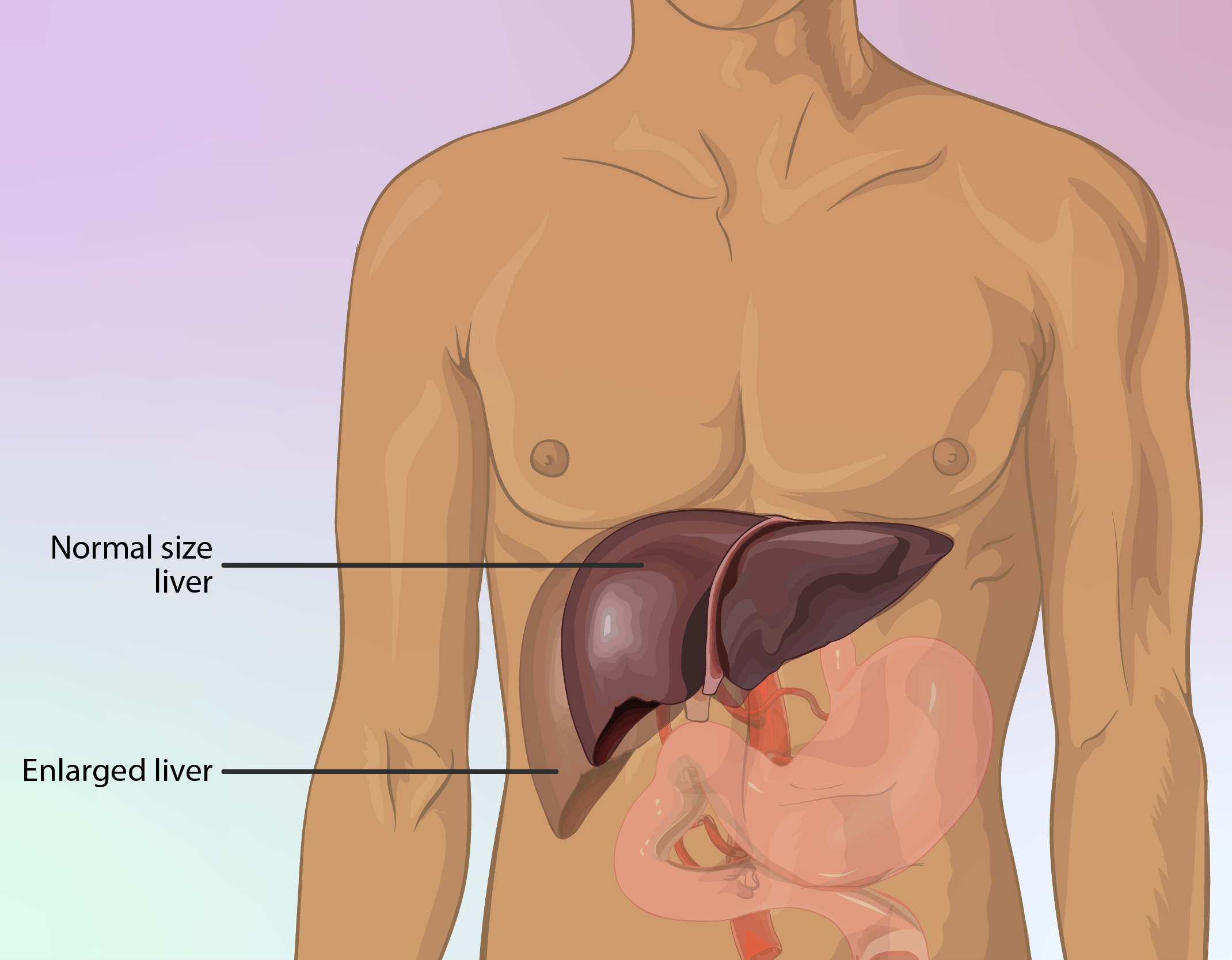
Cross-Reactivity with Other Medications
Consider cross-reactivity with clindamycin. Be mindful of interactions with neuromuscular blocking agents while undergoing treatment.
Interactions of Lincomycin Syrup
Interaction with Other Antibiotics
Using Lincomycin Syrup at the same time as erythromycin could lessen its effectiveness; hence, it's best to avoid taking them unless a healthcare professional recommends otherwise.
Impact on Anticoagulants
Lincomycin could enhance the impact of blood thinners. Require checks on blood clotting levels for safety measures.
Foods and Supplements to Avoid
- It's best to steer off dairy products while taking your medication to ensure absorption.
- It's best to take iron and calcium supplements at times to avoid any interactions between them.
Administration to Special Populations
Elderly Patients: Considerations for Reduced Metabolism
Elderly patients often exhibit diminished metabolic and renal function, necessitating cautious administration of Lincomycin Syrup. Reduced clearance can lead to prolonged drug exposure, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is crucial in this demographic.
- Start with lower dosages and titrate based on therapeutic response.
- Monitor for side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions.
- Consider concurrent conditions that may exacerbate drug effects.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile and Potential Risks
Lincomycin Syrup should be prescribed to pregnant women only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks. While animal studies have not shown significant teratogenic effects, comprehensive human studies are lacking. Nursing mothers should exercise caution, as the drug may pass into breast milk, posing risks to the infant.
- Discuss alternative therapies if risks are significant.
- Observe infants for signs of diarrhea or rash if the mother is on Lincomycin Syrup.
Children: Specific Dosages and Safety Precautions
Children require meticulously calculated dosages based on body weight to ensure safety and efficacy. Caregivers must strictly adhere to dosing schedules and avoid exceeding recommended concentrations. Pediatric patients should be monitored closely for any signs of adverse reactions or allergic responses.
- Administer using a calibrated measuring device to ensure accuracy.
- Report any unusual symptoms, such as persistent diarrhea, to a healthcare provider.

Handling and Storage of Lincomycin Syrup
Ideal Storage Conditions
Remember to store Lincomycin Syrup in a dry spot that is shielded from sunlight and moisture to maintain its quality and prevent any potential contamination; it is best kept in its original container at temperatures ranging from 15°C to 25°C.
Shelf Life and Signs of Spoilage
The expiration date of the syrup is usually mentioned on the packaging itself. If you notice any changes, like a change in color or an odd smell, or if the contents seem separated from each other, it's best to throw the medication away.
Safe Handling Practices for Caregivers
Caregivers must wash their hands before and after administering the medication. Avoid contact with the syrup's dispensing cap or measuring device to prevent contamination.
- Store out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Ensure the bottle is tightly sealed after each use.
Overdose Management of Lincomycin Syrup
Symptoms of Overdose: Toxicity and Related Complications
Excessive consumption might show up as stomach issues. Feeling lightheaded can even make it hard to breathe normally. High levels of toxicity could worsen kidney or liver problems. May cause issues throughout the body.
Immediate Steps to Take in Case of Overdose
If an overdose is suspected, induce medical attention promptly. Supportive care, such as gastric lavage or activated charcoal, may be necessary to reduce absorption.
Long-Term Management and Monitoring
Post-overdose care includes monitoring renal and hepatic function. Patients may require hospitalization to manage symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Important Precautions When Using Lincomycin Syrup
Ensuring Adherence to Prescribed Duration
Finishing the course of Lincomycin Syrup is crucial to avoid resistance as stopping early can result in treatment not working and the infection returning.
Monitoring for Signs of Adverse Reactions
Patients need to inform healthcare providers of any issues, like constant diarrhea or skin rashes, for timely evaluation and management of potential side effects, which can be effectively addressed through routine checkups.
Avoiding Misuse and Overuse to Prevent Resistance
Misusing antibiotics by using them for infections or taking more than the recommended amount can lead to increased resistance to these medications in the future. It's crucial to educate people on how to use them.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Ensuring Correct Dosage Measurement
To ensure you get the dose for your medication or supplement intake, accurately measure it with a calibrated device of using regular household utensils that could cause incorrect dosing.
Importance of Completing the Prescribed Course
It is important for patients to finish the treatment regimen despite feeling better in order to completely eliminate the infection.
Addressing Missed Doses
If you forget to take a dose of medication at the time and remember later on. It is almost time for the next dose anyway. Just take the missed dose then and there. Avoid taking two doses at once to make up for the one you missed; that's not advisable.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Lincomycin Syrup
Current Off-Label Applications
Lincomycin Syrup is occasionally prescribed for conditions affecting bones and joints or when dealing with infections that other medications may not effectively treat. This showcases its flexibility and effectiveness, in situations.
Research and Clinical Trials Exploring New Uses
Research is currently being conducted to explore how it can help treat diseases like drug tuberculosis and uncommon anaerobic infections potentially broadening its use, in settings, down the line.
Lincomycin Syrup FAQ
Why use lincomycin?
Lincomycin injection is used to treat infections. It may also be administered to individuals with allergies to penicillin antibiotics.
When to use lincomycin?
Lincomycin is used to treat infections caused by certain strains of streptococci and staph bacteria in patients with penicillin allergies or when penicillin is not suitable for the situation.
Lincomycin what class?
Lincosamide class
What lincomycin used for?
Infections affecting the ears, throat, and lungs are common, along with skin infections, bone and joint infections, and blood infections too.
How does lincomycin work?
Lincomycin functions as an antibiotic by stopping growth or eradicating them, achieved through attaching to the 50s subunit of bacteria and impeding the synthesis of crucial proteins necessary for bacterial existence.
How lincomycin works?
It operates by eliminating bacteria or inhibiting their proliferation.
Can lincomycin treat sore throat?
Yes
Can lincomycin treat staphylococcus?
Yes
Can lincomycin treat boil?
No
Are clindamycin and lincomycin the same thing?
Lincomycin and clindamycin are antibiotics; however, they both belong to the category of medications known as Lincosamides and operate in similar ways.