Loperamide
- I. Introduction to Loperamide
- II. Composition of Loperamide
- III. How Loperamide Works
- IV. Therapeutic Uses of Loperamide
- V. Off-Label Uses of Loperamide
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Loperamide
- VII. Common Side Effects of Loperamide
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Careful Administration of Loperamide
- X. Handling and Storage Precautions for Loperamide
- XI. Important Precautions to Consider
I. Introduction to Loperamide
A. Definition and Function
Loperamide is a highly effective synthetic antidiarrheal molecule that is commonly known as Imodium(2). This medication plays a crucial role in reducing both acute and chronic diarrhea(1). It achieves this by slowing intestinal movement and decreasing fluid production, allowing for better water absorption and resulting in firmer stools. As a widely recommended treatment for loose stools, Loperamide is an invaluable tool in the management of gastrointestinal issues.
1. PubMed - Loperamide
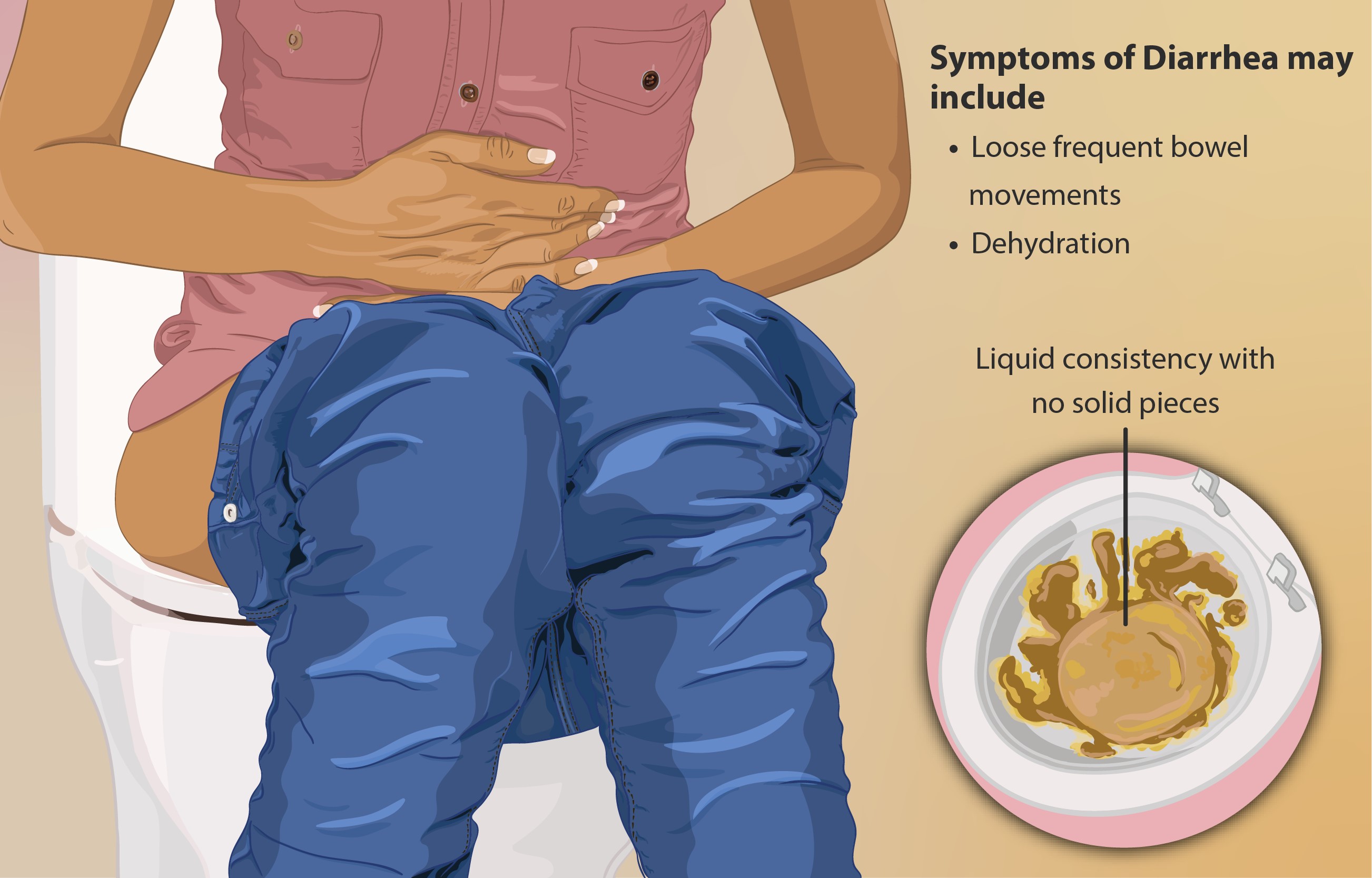
Symptoms of Diarrhea
B. Development History
Loperamide, a pharmaceutical discovery by Janssen Pharmaceutica in the late 1960s, has gained recognition for its effectiveness and availability in the pharmaceutical industry. Its approval by the FDA in 1976 further contributed to its prominence.
C. Prevalence of Usage
The wide utilization of Loperamide stems from its remarkable efficacy in treating diarrhea, considering the widespread occurrence of this condition worldwide and its impact on countless individuals annually. It comes as no surprise that the use of Loperamide is prevalent. Furthermore, its accessibility without requiring a prescription allows both healthcare practitioners and ordinary individuals to have easy access to this valuable tool in managing diarrhea.
II. Composition of Loperamide
A. Active Ingredient
Loperamide Hydrochloride is the main ingredient of this medication. It is responsible for its effectiveness, It plays a crucial role in providing relief from diarrhea by reducing the movement of the intestines.
B. Excipients and their Roles
In addition to Loperamide Hydrochloride, the drug's formulation contains several excipients that serve various functions. They include ;
- Binders, such as Microcrystalline Cellulose, maintain the tablet's integrity.
- Disintegrants like Croscarmellose Sodium aid in the tablets' breakdown in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Colorants and flavorings are added to enhance the drugs' appearance and taste.
- Preservatives are included to prevent microbial contamination and extend the drug's shelf life.
C. Available Forms and Concentrations
Loperamide is commonly found in the form of capsules, tablets, and liquid solutions that are taken orally. The standard dosage for the capsules and tablets contains 2mg of Loperamide Hydrochloride, but the concentration may differ in liquid solutions. The appropriate form and concentration can be determined based on factors such as the severity of the condition and individual patient characteristics.
III. How Loperamide Works
A. Mechanism of Action
In its role as an antidiarrheal agent. Loperamide primarily acts by binding to µ opioid receptors found within the myenteric plexus located in our large intestine, through this mechanism, Loperamide effectively inhibits acetylcholine release and disrupts peristalsis—the coordinated contractions crucial for proper bowel movement. Consequently, This results in a lengthened transit time within our intestines, promoting increased fluid absorption while minimizing stool volume and decreasing bowel movement frequency.
B. Onset of Action and Duration
Loperamide exhibits a relatively rapid onset of action, Typically providing relief from symptoms within 1 to 3 hours after being taken. Moreover, the effects of this medication can endure for around 24 to 48 hours. This prolonged duration of action contributes to the favorable outcome of Loperamide in effectively managing both acute and chronic diarrhea.
C. Body Systems Affected
Loperamide primarily acts on the gastrointestinal system, but it can also impact other body systems. This is because of its mechanism of action and the side effects it may cause. One such system that can be affected is the nervous system, which can result in side effects like dizziness, fatigue, or. In rare instances of overdose. Opioid-like effects. Due to these potential risks. It is crucial for patients to strictly follow their prescribed dosage and adhere to the instructions provided.
IV. Therapeutic Uses of Loperamide
A. FDA-Approved Uses
Loperamide possesses a distinct therapeutic index that has been duly recognized and verified by the FDA. Its principal applications encompass the following:
1. Acute Diarrhea
Loperamide is a highly effective remedy for acute diarrhea, characterized by the sudden onset of three or more loose or liquid stools daily. This condition can cause significant distress and incapacitation. Thankfully, Loperamide has a remarkable ability to reduce the movement of the intestines and enhance water absorption, Leading to prompt relief from symptoms. Solidifying stools and decreasing their frequency offer much-needed comfort to those affected.
2. Chronic Diarrhea
Although Loperamide is commonly known for its effectiveness in treating acute diarrhea, it also holds great potential in managing chronic diarrhea. Chronic diarrhea refers to prolonged loose stools lasting for at least four weeks. It can have a profound impact on an individual's overall well-being. In this regard, Loperamide's ability to decrease gut motility becomes incredibly valuable as it enables consistent regulation of bowel movements and assists in the ongoing management of this condition.
B. Comparisons with Other Anti-diarrheal Medications
Loperamide offers distinct advantages when compared to other antidiarrheal medications.
Unlike Diphenoxylate Atropine (Lomotil), Loperamide has a more favorable side effect profile and a lower likelihood of causing unpleasant anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth, urinary retention, and blurred vision.
In addition, Loperamide does not require a prescription in many jurisdictions, making it more easily accessible for immediate relief compared to Racecadotril.
Furthermore, unlike Bismuth subsalicylate Loperamide exhibits a more significant antidiarrheal effect and does not result in blackened stools which are frequently experienced with Bismuth-based medications.
Ultimately, The combination of accessibility, potency, and favorable side effect profile make Loperamide a prominent choice for managing both acute and chronic diarrhea.
V. Off-Label Uses of Loperamide
Loperamide is a pharmaceutical agent recognized for alleviating acute and chronic diarrhea symptoms. Its effectiveness and availability have long been appreciated. However, this anti-diarrheal medication goes beyond its conventional use and exhibits surprising versatility in treating a range of conditions off-label. From managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) symptoms to addressing chemotherapy-induced diarrhea, the diverse applications of Loperamide underline its multifaceted therapeutic efficacy.(1)
1. American Family Physician - Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
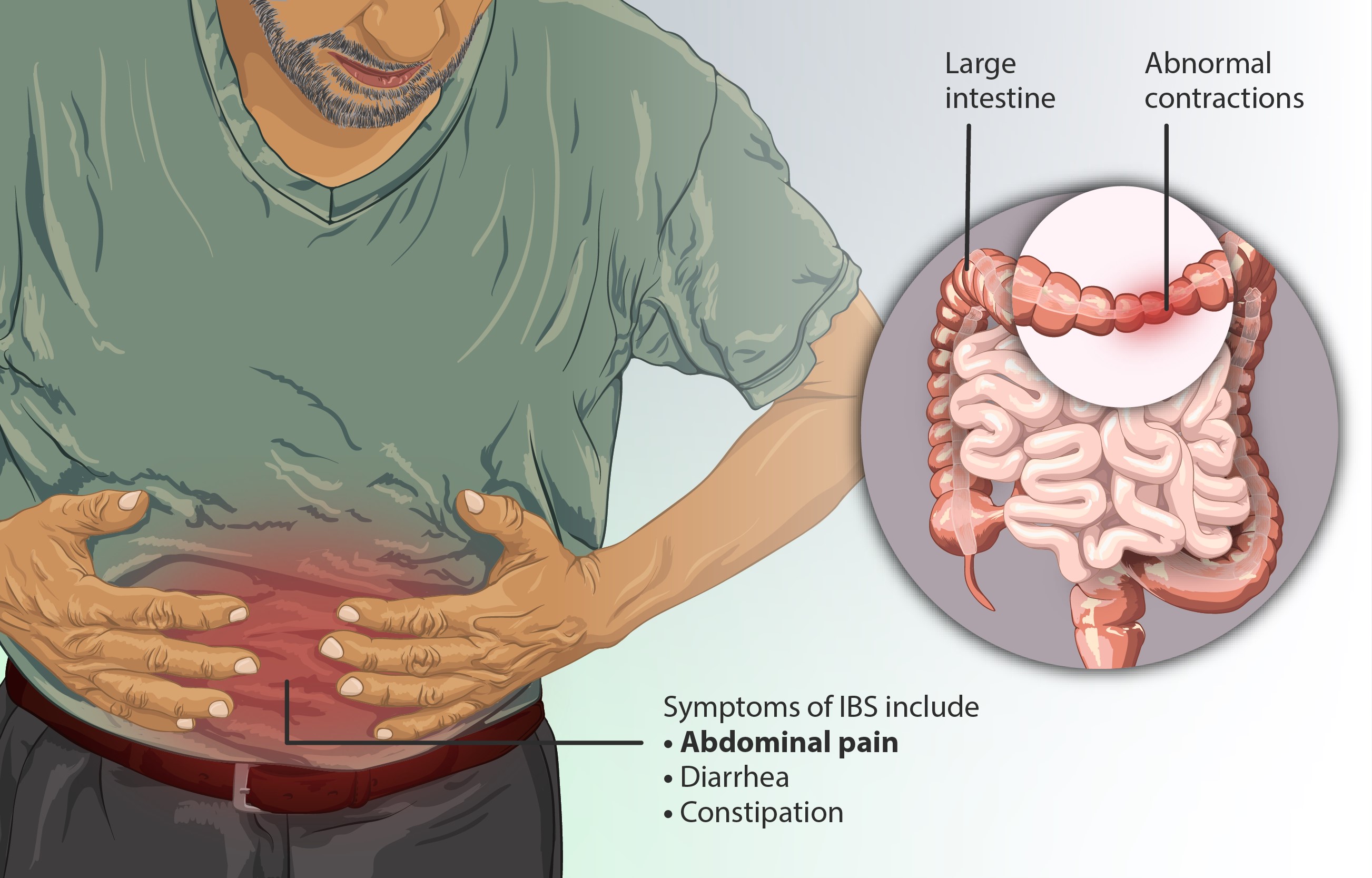
Symptoms of IBS
A. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
One of the first off-label uses explored for Loperamide is its role in managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by recurring bouts of abdominal pain, bloating and changes in bowel habits. The unpredictable and severe symptoms of IBS often lead to a significant deterioration in the quality of life for patients.
- To begin with, Loperamide is an anti-diarrheal agent which helps combat one of the main manifestations of IBS known as diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS D).
- By slowing down gut motility, It enables better absorption of water and electrolytes, resulting in the formation of well-formed stools and a decrease in bowel movement frequency.
- Additionally, Loperamides' indirect modulation of visceral sensitivity may have a positive impact on reducing abdominal pain - another distressing symptom experienced by those with IBS.
- It is important to note, however, that Loperamide is not a cure-all solution and should be used cautiously while considering the individual's specific subtype and symptom profile. Physicians must also be vigilant about the potential risk of toxic megacolon - a rare yet severe complication associated with its use.
B. Chemotherapy-Induced Diarrhea
Furthermore, within the field of oncology, Loperamide has emerged as a valuable tool in managing chemotherapy-induced diarrhea (CID), posing considerable challenges for cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic treatment. While not typically considered a primary form of intervention. Loperamide displays immense potential as an adjunctive medication within this context.
- Thanks to its potent anti-diarrheal properties, this medication can effectively alleviate both the severity and frequency of CID episodes - providing afflicted individuals with improved comfort levels while adhering to their treatment plans.
- This becomes especially significant considering how it acts as a crucial buffer against complications such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances triggered by persistent diarrhea.
- Moreover, its ability to control CID may also minimize instances requiring dose reductions or delays in administering treatments - allowing chemotherapy regimens to maximize their therapeutic impact.
However, healthcare professionals involved in CID management need sound clinical judgment; meticulous dose adjustment and diligent side effect monitoring are imperative components of this process.
C. Other Off-Label Applications
Beyond the domains of IBS and CID, Loperamides' application extends even further, Showcasing its significant versatility in therapeutic settings. Additional off-label applications involve conditions characterized by excessive gut motility or secretory processes, where the drugs' ability to modulate can be harnessed to manage symptoms and enhance the quality of life effectively.
Although Loperamide primarily serves as a diarrhea management tool, its off-label uses indicate its broader therapeutic potential by implementing careful monitoring and exercising astute judgment. Clinicians can leverage this medication to provide substantial relief across various clinical conditions, highlighting the adaptable nature of pharmaceutical agents.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Loperamide
It is paramount to adhere to proper dosage and administration practices to ensure favorable therapeutic outcomes and minimize potential side effects associated with Loperamide treatment for gastrointestinal disorders. This section provides comprehensive information, including general usage guidelines—recommended dose modifications based on specific conditions. Considerations are particular to certain populations. And protocols to follow in missed doses or cases involving an overdose.
A. General Guidelines
First and foremost, it is crucial to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional when administering Loperamide. The patient's condition, age, and overall health status should be carefully considered. It is generally advised to take Loperamide after experiencing a loose bowel movement rather than following a regular schedule.
B. Dosage for Different Conditions
The prescribed dosage of Loperamide may vary depending on the specific condition being treated when it comes to acute diarrhea, The usual adult dose is initially 4mg. Followed by 2mg after each unformed stool. On the other hand, in chronic conditions such as IBS, the dosage may need to be customized in order to achieve 1 2 formed stools per day. This often requires regular consultation with a healthcare professional and adjustments to the dosage as needed.
C. Adjustments for Special Populations
1. Administration to the Elderly
In geriatric patients, caution is advised as they might have an increased sensitivity to Loperamide. It is important to carefully select the dosage, typically opting for the lower end of the range, and closely monitor for any potential side effects to ensure their well-being.
2. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Only if a significant benefit exceeds any hypothetical risk to the fetus should Loperamide be utilized during pregnancy. Caution must be exercised by nursing mothers as consideration must be given to its presence in human milk.
3. Administration to Children
It is generally not advisable to administer Loperamide to children younger than 6. However, the dosage should be adjusted for older children according to their weight and the seriousness of their symptoms. Nonetheless, it is crucial to monitor their condition closely.
D. Missed Dose and Overdose Procedures
Typically Loperamide is taken as needed, so the likelihood of missing a dose is low. Nevertheless, if an overdose occurs, it is vital to seek immediate medical assistance. Symptoms of an overdose may manifest as constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, or even fainting.
VII. Common Side Effects of Loperamide
Despite being generally well tolerated. Loperamide may elicit specific side effects. Familiarizing oneself with these side effects enables patient education and facilitates the timely identification of adverse reactions. Thereby allowing for appropriate measures to be taken when necessary.
A. Frequency of Side Effects
It deserves attention that most people using Loperamide do not experience severe side effects. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that each individual's response to medication can vary significantly, Leading to variability in the occurrence of side effects accordingly.
B. Mild and Transient Side Effects
Mild and short-lived adverse effects like dizziness, constipation, and nausea are commonly observed with this medication. Most individuals notice a decline in these symptoms as their body gets used to the drug. Nonetheless. If symptoms persist or worsen over time. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
C. Serious Side Effects and Their Signs
Rare but serious side effects of Loperamide include abdominal pain or distention, uncomfortable fullness of the stomach, severe constipation, and allergic reactions. It is essential to be aware that irregular heart rhythms can occur, especially in overdose situations or if the medication is taken in doses higher than recommended, In such cases, immediate medical intervention is necessary.
To summarize, although Loperamide can provide significant relief for specific gastrointestinal issues, it is crucial to thoroughly understand its proper dosage, administration, and potential side effects. It is always advisable to seek the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional when considering any treatment plan involving Loperamide.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
The use of Loperamide carries certain risks that should not be overlooked. Therefore, It is crucial to carefully consider any warnings, contraindications, and potential interactions with other medications before starting treatment. It is important to identify individuals who may be at greater risk, understand the contraindications of the drug and recognize conditions where the use of Loperamide should be avoided. These factors play a significant role in ensuring the safe administration of the medication.
A. Individuals at Risk
Specific populations may have a higher vulnerability to the negative effects of Loperamide, So it is essential to exercise caution. These populations include older individuals, who may have increased sensitivity, and children, especially those under two years old, Who are at risk of severe dehydration. In addition, Individuals with liver dysfunction should be closely monitored as the drug undergoes hepatic metabolism.
B. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Before starting Loperamide therapy, it is important to consider several drug interactions.
- Specifically, using Loperamide together with medications like quinidine, ritonavir, itraconazole, or gemfibrozil can have an impact on Loperamide metabolism and lead to an increase in its plasma levels. Consequently, this raises the risk of experiencing unwanted effects. Both quinidine and ritonavir can potentially increase Loperamide exposure by inhibiting CYP3A4 and P glycoprotein. These enzymes play a crucial role in the metabolism and transport of Loperamide.
- Furthermore, itraconazole, a strong inhibitor of P glycoprotein and CYP3A4, may raise plasma levels of Loperamide as a result. Adjustments in dosage or considering alternative therapies may be necessary.
- Additionally, gemfibrozil, another inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P glycoprotein, could also lead to increased levels of Loperamide. It is important for healthcare providers to be aware of these potential drug interactions when prescribing Loperamide therapy.
C. Conditions and Diseases Contraindicated with Loperamide Use
Lastly, certain conditions must be considered as contraindications to the use of Loperamide. These conditions include individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Loperamide, those experiencing abdominal pain without diarrhea,, and patients with bacterial enterocolitis caused by invasive organisms. Furthermore, it is highly recommended for individuals with acute dysentery characterized by blood in stools and high fever to refrain from using Loperamide.
IX. Careful Administration of Loperamide
The successful therapeutic outcomes of Loperamide go beyond just the dosage and contraindications. It encompasses thorough assessments before administering, vigilant monitoring throughout the treatment, and appropriate follow-up after the treatment.
A. Pre-Administration Assessments
Before beginning Loperamide treatment, gathering a comprehensive medical history to identify any potential contraindications is essential. Moreover, a thorough assessment of the patient's current medications is necessary to avoid any possible drug interactions in certain populations. Conducting baseline measurements, including liver function tests, may also be advantageous.
B. Monitoring During Treatment
Continual surveillance is of utmost importance during Loperamide therapy by paying close attention to alterations in bowel habits, frequency, and characteristics of stools. Valuable insights into the effectiveness of treatment can be gained. Additionally, it is essential to remain vigilant for any potential side effects or indications of overdosage, such as unusual drowsiness or stomach distention.
C. Post-Treatment Follow-Up
After the therapy, it is important for the clinician to conduct a post-treatment follow-up to evaluate the success of the treatment and to keep an eye out for any possible delayed adverse effects. This includes checking for any changes in symptoms and overall health status and in some cases conducting lab tests to confirm that the problem has been resolved and that the organs are functioning normally.
In summary, Loperamide, despite being a commonly used anti-diarrheal medication, Should be administered with caution and monitored closely. Adhering to these precautions will ensure that it is used safely and effectively, maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential harm.
X. Handling and Storage Precautions for Loperamide
The effectiveness and safety of any medication depend on the careful storage and handling it receives. In the case of Loperamide, It is essential to take into account its optimal storage conditions, shelf life, and proper disposal procedures.
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
Loperamide should be stored in a controlled room temperature environment, Usually ranging from 20°C to 25°C. While ensuring it is shielded from light and moisture by keeping the medication in its original packaging until required and storing it in a place inaccessible to children. One can maintain its quality and prevent unintended consumption.
B. Shelf Life and Expiration
Like many other medications, Loperamide has a specific shelf life usually mentioned on the product packaging. It is important to note that using the medication after its expiration date might decrease its effectiveness and, in rare cases, could even lead to potential toxicity. Therefore, regularly checking for expiration dates and disposing of expired medication is advisable.
C. Disposal Procedures
Safely disposing of unused or expired Loperamide is an integral part of managing medication. It is important to note that medications should not be disposed of by flushing them down the toilet or throwing them in the garbage bin. Instead, it is recommended to seek guidance from local waste disposal authorities or consult a healthcare professional for proper guidelines. It is worth mentioning that many communities have established drug take-back programs to promote environmentally friendly disposal methods.
XI. Important Precautions to Consider
It is important to exercise caution when using Loperamide, just like any other therapeutic agent. By understanding its limitations acknowledging the possibility of dependence and taking steps to prevent misuse and abuse we can greatly enhance the safety and effectiveness of this medication.
A. Limitations of Use
Loperamide is indeed an effective antidiarrheal agent. However, it is important to note that it is not a panacea for all types of diarrhea. Its primary purpose is to provide symptomatic relief for acute nonspecific diarrhea and chronic diarrhea linked to inflammatory bowel disease. It should be emphasized that this medication is unsuitable for patients suffering from bacterial enterocolitis or pseudomembranous colitis resulting from broad-spectrum antibiotics.
B. Understanding the Risk of Dependence
Loperamide. Despite being readily available without a prescription. Presents a potential risk of dependency, Especially when consumed in doses higher than what is recommended. Consistent and excessive use can result in physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. This underscores the significance of following the recommended dosage and consulting a healthcare professional for prolonged usage.
C. Measures to Prevent Misuse and Abuse
To prevent misuse and abuse of Loperamide, it is important to implement various measures.
- Education plays a crucial role in this regard. Patients should receive proper education about the correct usage of Loperamide and the potential risks associated with taking excessive doses. This knowledge empowers patients to make informed decisions about their medication use.
- Another important measure is monitoring. Regularly monitoring the use of Loperamide can be especially beneficial for patients with a history of substance abuse by closely tracking their usage patterns. Healthcare providers can identify any signs of misuse or abuse early on.
- Proper disposal of unused medication is also essential in preventing accidental ingestion or intentional misuse. Patients should be educated on how to safely dispose of Loperamide once they no longer need it, such as through designated drug take-back programs or by following specific disposal instructions provided by healthcare professionals.
In conclusion, while Loperamide is commonly used and generally safe, it still requires careful handling, storage, and usage to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Adhering to these precautions will help both healthcare providers and patients ensure that Loperamide serves its intended therapeutic purpose without any adverse repercussions.