Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection
- Introduction
- Composition and Bupivacaine duration of action
- Bupivacaine uses
- Off-Label Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Administration to Specific Populations
- Bupivacaine side effects
- Bupivacaine warnings and Precautions
- Bupivacaine contraindications
- Bupivacaine interactions
- Handling and Storage
- Overdosage and Management
- Important Precautions
- Special Considerations for Healthcare Professionals
- Conclusion
Introduction
Overview of Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection
Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection is an anesthetic commonly used in spinal anesthesia to provide precise pain relief during surgeries by effectively targeting specific nerve pathways.
Brief History and Development
Marcain was first introduced in the twentieth century to meet the growing need for enhanced options in regional anesthesia as it evolved over time to become more dependable and suitable for spinal procedures. Resulting in the development of Marcain Spinal Heavy, with refined efficacy accumulated over several decades.
Purpose and Significance in Modern Medicine
This approach plays a role in guaranteeing the well-being of patients undergoing treatments by transforming pain relief methods with custom anesthetics designed for each patient's unique requirements.
Bupivacaine nerve block
The primary application of bupivacaine is in performing epidural nerve blocks due to its ability to effectively distinguish between sensory and motor blockades—an advancement that has established it as the preferred anesthetic for obstetric procedures.
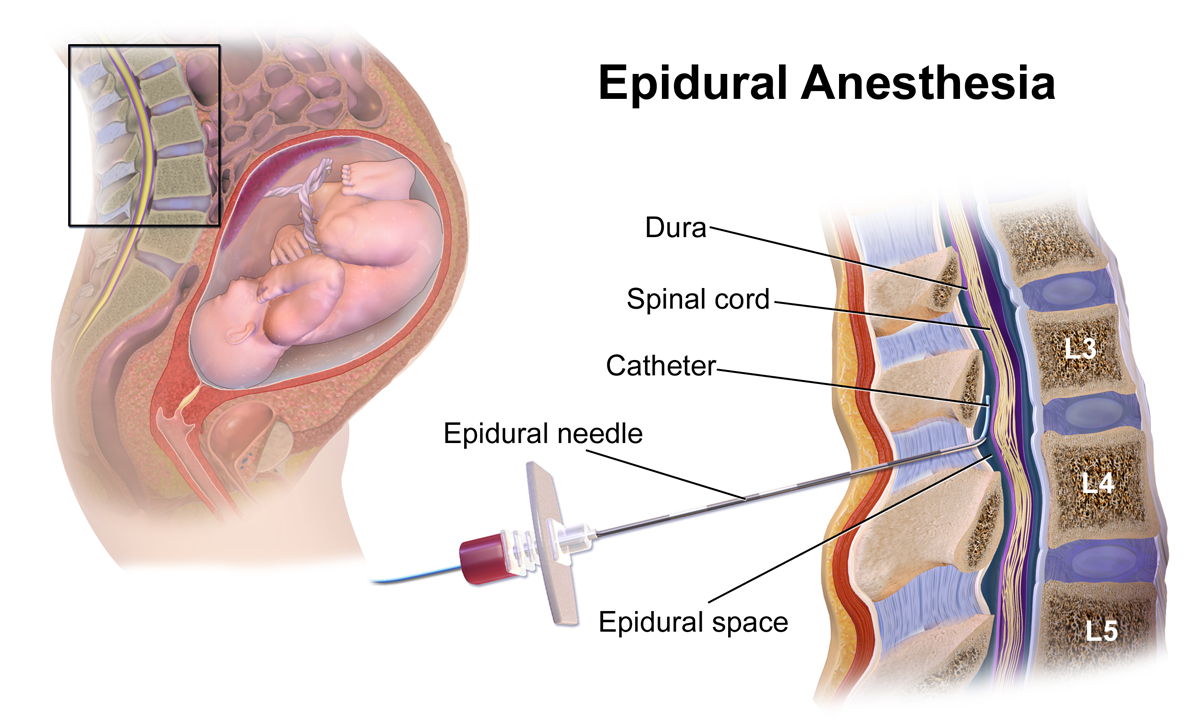
Composition and Bupivacaine duration of action
Active Ingredients and Their Roles
Marcain Spinal Heavy consists primarily of bupivacaine hydrochloride, a potent amide local anesthetic, augmented with glucose for enhanced density and targeted action.
How Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection Works in the Body
Upon administration, it selectively inhibits sodium ion channels in neuronal membranes, disrupting pain signal transmission while maintaining motor function integrity in controlled regions.
Bupivacaine half life
The duration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in adults, is 2,700 minutes, while in newborns, it lasts for around 8,100 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics and Dynamics
- Absorption: Rapid onset due to its hyperbaric nature.
- Distribution: Localized action with minimal systemic dispersion.
- Metabolism: Processed in the liver via enzymatic pathways.
- Excretion: Primarily eliminated through renal pathways.
Hyperbaric bupivacaine
The concentrated (hyperbaric form of bupivacaine is created by combining glucose (80 mg/mL)) with plain bupivacaine, with experts theorizing that the variation in density between these two types influences how they spread and disperse upon being injected into the intrathecal space.
Bupivacaine vs lidocaine
After receiving an injection of lidocaine, as a term solution, the effects typically wear off within one to two hours, whereas bupivacaine is known for its longer-lasting impact, lasting from two hours to possibly more than four hours.
Ropivacaine vs bupivacaine
The effects of ropivacaine are quite similar to those of bupivacaine in terms of how they start working and the extent and length of the block they provide; however, ropivacaine results in a shorter period of motor blockade and is considered to have a more favorable safety profile.
The effects of ropivacaine are quite similar to those of bupivacaine concerning how quickly they start working and the type and length of numbness they provide; however, ropivacaine causes interference with movement. Is considered safer overall.
Bupivacaine with epinephrine
The combination injection of bupivacaine and epinephrine is commonly administered to areas of the body for various medical procedures such as surgery or dental work as well as during childbirth situations. The inclusion of epinephrine enhances the pain relief effects provided by bupivacaine.
Bupivacaine uses
Approved Uses in Anesthesia and Pain Management
Common Surgical Procedures Where Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection is Utilized
These include cesarean sections, hip replacements, and prostate surgeries. Its application ensures precise anesthesia with a quick recovery time.
Role in Postoperative Pain Relief
The injection extends its benefits into the postoperative phase by mitigating residual pain, thus enhancing patient recovery trajectories.
Comparison to Other Local Anesthetics
Unlike lidocaine and ropivacaine, Marcain offers prolonged duration and heightened sensory blockade, making it ideal for extended surgical procedures.
Off-Label Uses
Potential Applications in Chronic Pain Management
Studies suggest its efficacy in managing chronic pain syndromes such as sciatica, leveraging its profound analgesic properties.
Emerging Research and Case Studies on Alternative Uses
Preliminary investigations highlight potential benefits in treating complex regional pain syndromes and refractory neuropathic conditions.
Regulatory Considerations for Off-Label Use
Healthcare providers should ensure compliance with ethical standards and obtain informed consent when exploring off-label applications.
Dosage and Administration
Bupivacaine dosage
The standard dose varies between 1.5 to 4 ml depending on the surgery type and patient factors such as weight and comorbidities.
Bupivacaine max dose
Avoid injecting more than 175 mg of bupivacaine in a single dose, and do not exceed a total of 400 mg within 24 24-hour window period for optimal safety measures. Furthermore keep the dosage within the range of 225 mg per dose to maintain a threshold of 225 mg per single administration.
Techniques for Spinal Administration
Precision and strict aseptic measures are crucial for achieving results when injecting into the subarachnoid area using a needle.
Monitoring and Safety Measures During Administration
Keeping an eye on signs at all times helps to catch any potential negative reactions early on and ensures that the patient's safety is maintained throughout the entire procedure.
Adjustments for Special Populations
Adjusting the dosage is essential for groups like the elderly and individuals with liver issues to reduce risks.
Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly Patients
It is advisable to lower the doses because the body's reserves are reduced, and there is increased sensitivity to anesthetics.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Marcin is considered to be relatively safe for performing sections. It is important to be cautious due to its presence, in breast milk.
Pediatric Patients
When giving medication to children it's important to be extra cautious because of their bodies and organs that are still developing.
Bupivacaine side effects
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Headache
- Hypotension
Rare but Serious Side Effects
These can lead to nerve damage, neurotoxicity, irregular heartbeats, cardiac arrhythmias, and intense allergic responses, severe allergic reactions sometimes requiring attention and immediate medical intervention.
Management of Side Effects in Clinical Settings
Prompt identification and timely intervention can help minimize responses by utilizing fluids or supportive drugs.
Bupivacaine warnings and Precautions
Situations Requiring Cautious Use
Administer Marcain in patients with heart conditions or blood clotting disorders.
Bupivacaine toxicity
At the onset of toxicity, signs, like ringing in the ears and feeling dizzy or having numbness around the mouth, should prompt stopping the treatment.
Bupivacaine toxicity symptoms
Experiencing chest pain, feeling out of breath, heart palpitations, dizziness, sweating, low blood pressure, fainting spells, and a sudden drop in function leading to collapse are all concerning symptoms to watch out for in terms of heart health.
Bupivacaine toxicity treatment
The latest recommendations suggest administering lipid emulsion (IV) as a treatment to counteract the heart and nerve-related impacts of anesthetic toxicity.
Avoidance in Patients with Specific Health Conditions
Not recommended for people with liver problems or those who are highly sensitive to amide-based anesthetics.
Bupivacaine nursing considerations
Keep an eye out for any seizures or a rise in seizure frequency. Also, keep track of any heart-related symptoms both at rest. While exercising watch out for any signs of heart issues.
Bupivacaine contraindications
Absolute Contraindications Based on Medical History
Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection should not be used in people who are allergic to amide-type anesthetics or have severe liver problems that affect metabolism speed as they are at high risk of complications from the treatment area if there is a severe infection present.
Conditions That Increase the Risk of Adverse Reactions
Patients who have existing heart conditions or low blood pressure and those with blood clotting issues face risks when utilizing Marcain medication. The thorough assessment of patients helps reduce the likelihood of complications.
Bupivacaine allergy alternative
For individuals who are allergic to anesthetics, Diphenhydramine (DPH) can serve as a substitute for bupivacaine.
Bupivacaine interactions
Drug Interactions Affecting Efficacy or Safety
When Marcain is used alongside medications, like beta blockers or antiarrhythmics, such as amiodarone, simultaneously, it may enhance the effects and potentially impact its efficacy and safety profile.
Guidelines for Managing Potential Interactions
- Review patient history for concurrent drug usage.
- Adjust dosages appropriately to mitigate risks.
- Closely monitor cardiovascular and CNS function during administration.
List of Commonly Interacting Medications
Notable interacting agents include:
- Anticoagulants can increase bleeding risk.
- Opioids can enhance central nervous system depression.
- Tricyclic antidepressants have a heightened potential for toxicity.
Handling and Storage
Recommended Storage Conditions for Optimal Stability
Remember to keep Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection in a dry place that is shielded from sunlight to maintain its quality effectively without any damage from freezing temperatures, between 15°C and 25°C.
Proper Handling Techniques to Maintain Sterility
- Use sterile gloves and equipment during handling.
- Inspect the vial for discoloration or particulate matter before use.
- Seal opened vials promptly if reuse is necessary.
Disposal Guidelines for Unused or Expired Injections
Make sure to follow the guidelines for disposing of any expired items, especially medical waste, and remember to seal them properly to avoid any accidental contact with them.
Overdosage and Management
Signs and Symptoms of Marcain Overdose
Taking medication can show up as increased activity in the central nervous system, which may cause feelings of unease or shake, and in some cases, even seizures can occur as a result of an overdose situation becoming more serious, potentially leading to a decrease in heart rate or even stopping the heart altogether in extreme cases.
Emergency Interventions and Supportive Measures
- Discontinue administration immediately upon detecting overdose signs.
- Administer oxygen and ensure airway patency.
- Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy may counteract toxicity.
Long-Term Implications of Overdose Incidents
Lasting impacts are not common. It may involve neurotoxic effects or lingering heart issues after an event has passed, which emphasizes the importance of thorough monitoring and rehabilitation afterward.
Important Precautions
Ensuring Proper Patient Assessment Before Use
It's crucial to assess a person's history by checking for allergies and current medications to minimize any potential risks involved in the treatment process. Physical examinations play a role, in spotting any contraindications that could affect the course of action.
Guidelines for Informed Consent
Before the treatment begins, patients should receive an explanation of the procedure along with information about any risks and anticipated results for better trust-building and informed choices.
Steps to Minimize Risks During and After Administration
- Employ aseptic techniques to prevent infections.
- Continuously monitor vital signs during the procedure.
- Provide post-procedural care instructions to mitigate complications.
Special Considerations for Healthcare Professionals
Training and Expertise Required for Administration
Healthcare professionals should have an understanding of anesthesia methods and the pharmacology of Marcain with regular training updates being advised.
Strategies to Ensure Patient Safety
- Adopt standardized protocols for dosage and monitoring.
- Maintain emergency response equipment readily available.
- Regularly review and update safety guidelines.
Importance of Adherence to Clinical Protocols
Adhering closely to approved clinical guidelines guarantees results and reduces risks while maintaining detailed records of procedures, which is essential for maintaining quality standards and meeting legal requirements.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection serves as an indispensable tool in modern anesthesia, offering precise and long-lasting effects. Its utility spans a range of surgical applications, with safety ensured through meticulous adherence to guidelines.
Future Outlook for Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection in Clinical Practice
Ongoing research continues to explore new applications, enhancing its therapeutic potential. Its versatility positions it as a cornerstone in advanced anesthetic strategies.
Encouragement for Safe and Informed Use
Healthcare professionals are urged to prioritize patient safety and remain abreast of emerging best practices. Responsible use ensures the continued efficacy and reliability of Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection in clinical settings.
Marcain Spinal Heavy Injection FAQ
- What is heavy Marcain in spinal Anaesthesia?
- What is the drug Marcain used for?
- What happens if bupivacaine is given IV?
- Which is stronger bupivacaine or lidocaine?
- What is the difference between isobaric and heavy bupivacaine?
- What is the benefit of bupivacaine?
- What is the risk of bupivacaine?
- What is the antidote for bupivacaine?
- What happens if you inject bupivacaine into a vein?
- How long does bupivacaine last?
- Why is heavy bupivacaine used?
- Can bupivacaine cause nerve damage?
- How many times can you have nerve block injections?
- What are the advantages of bupivacaine?
- Is bupivacaine fast acting?
- What are the precautions for bupivacaine?
- How long does bupivacaine stay in your system?
- How to use bupivacaine injection?
- What are the two types of bupivacaine?
- What are the indications for bupivacaine?
- What are the side effects of bupivacaine in the heart?
- Is bupivacaine an anti inflammatory?
- Can bupivacaine cause seizures?
What is heavy Marcain in spinal Anaesthesia?
It induces a leg muscle relaxation that typically lasts 2 to 2 hours.
What is the drug Marcain used for?
MARCAINE is used to provide regional anesthesia or pain relief for procedures such as dental surgeries and diagnostic tests and treatments; it is also employed for obstetric procedures.
What happens if bupivacaine is given IV?
Certain anesthetics, like bupivacaine, used for pain relief, may lead to heart and nerve-related issues.
Which is stronger bupivacaine or lidocaine?
It usually takes a bit longer for bupivacaine to start working compared to lidocaine. Its effects also tend to last.
What is the difference between isobaric and heavy bupivacaine?
The hyperbaric solution leads to an onset of motor block but shorter durations of motor and sensory blocks compared to the solution, which has a slower onset and longer duration for both sensory and motor blocks.
What is the benefit of bupivacaine?
A bupivacaine injection is administered to alleviate pain in an area of the body before or after procedures such as surgery or childbirth.
What is the risk of bupivacaine?
The potential risks involve effects on the system or heart and lung function, leading to unconsciousness and potentially ending in breathing difficulties resulting in a halt in breathing movements.
What is the antidote for bupivacaine?
Lipid emulsion therapy
What happens if you inject bupivacaine into a vein?
Severe systemic harm could occur due to absorption in a blood vessel or accidental injection into a vein.
How long does bupivacaine last?
6 to 8 hours
Why is heavy bupivacaine used?
Before undergoing surgery on the abdomen and lower limbs, Bupivacaine spinal heavy BNM is administered to prevent or alleviate pain.
Can bupivacaine cause nerve damage?
In restricted regions, bupivacaine may lead to a nerve condition that could be due to a high concentration of the medication in that specific area.
How many times can you have nerve block injections?
You might have the option to perform the process from three to six times within 12 months.
What are the advantages of bupivacaine?
Prolonged anesthesia
Is bupivacaine fast acting?
The effects of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride start quickly.
What are the precautions for bupivacaine?
The injection process must be handled with caution to prevent risks such as confusion and convulsions or breathing and heart-related complications, like depression or stimulation.
How long does bupivacaine stay in your system?
2.7 hours in adults and 8.1 hours in neonates
How to use bupivacaine injection?
Only a doctor or nurse should administer Bupivacaine Injection BP through an injection into the skin to a nerve or into an area with many nerves (such as during an epidural injection near the spinal cord).
What are the two types of bupivacaine?
Isobaric and hyperbaric bupivacaine
What are the indications for bupivacaine?
In adults, Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is used to provide regional anesthesia or pain relief for surgeries and dental procedures as well as for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures and obstetrical care purposes.
What are the side effects of bupivacaine in the heart?
Convulsions, coma, and respiratory arrest
Is bupivacaine an anti inflammatory?
No
Can bupivacaine cause seizures?
It's extremely rare to experience tonic-clonic seizures following the injection of bupivacaine into the spine.