Mesalamine
- I. Introduction to Mesalamine
- II. Understanding How Mesalamine Works
- III. The Composition of Mesalamine
- IV. Approved Uses of Mesalamine
- V. Off-Label Uses of Mesalamine
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Special Considerations for Mesalamine Administration
- VIII. Understanding Mesalamine's Side Effects
- IX. Interactions and Contraindications of Mesalamine
- X. Warning and Precautions for Mesalamine Use
- XI. Careful Administration and Monitoring of Mesalamine
I. Introduction to Mesalamine
A. Definition and General Information
Mesalamine, which is often regarded as an example of modern pharmacology, is a medication classified as an aminosalicylate drug. It is primarily utilized to treat bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. This medication functions as an inflammatory agent and is specifically formulated to target the gastrointestinal tract reducing the intensity of inflammation ulcers and other symptoms related to these conditions.
B. History and Development
The use of Mesalamine, also known as 5 aminosalicylic acid, has its roots in the middle of the century. Then a compound called sulfasalazine containing sulfapyridine and 5 aminosalicylic acid was used as an anti-inflammatory treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
Interestingly researchers noticed an improvement in symptoms related to ulcerative colitis in patients who took this compound. This led to the exploration and development of Mesalamine, where the effective component. 5 aminosalicylic acid Was isolated and transformed into what we know as Mesalamine.
Throughout the years, efforts have been made to enhance mesalamine absorption and targeted delivery to maximize its benefits while minimizing any potential side effects on the body.
II. Understanding How Mesalamine Works
A. Mechanism of Action
There is still a lot of curiosity surrounding how Mesalamine works. However, most scientists agree that its ability to reduce inflammation is what makes it an effective treatment. Specifically, Mesalamine works by stopping the production of certain chemicals that cause inflammation in the colon, like prostaglandins and leukotrienes. It does this by blocking the enzymes cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase, which are responsible for producing these chemicals.
B. Effect on the Body's Immune Response
Mesalamine affects the immune response by directly affecting the gastrointestinal tract. It helps to control the immune response that occurs in inflammatory bowel diseases preventing excessive inflammation while still allowing the body to maintain its necessary defenses. By regulating cells and cytokines, Mesalamine ultimately decreases inflammation in the intestines, a common feature of conditions such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
III. The Composition of Mesalamine
A. Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main active substance found in Mesalamine is called 5 aminosalicylic acid, which's responsible for producing the desired therapeutic effects when treating inflammatory bowel diseases. It works by reducing inflammation preventing tissue damage, and alleviating diarrhea by interfering with chemicals in the body.
In addition to the ingredient Mesalamine also contains several inactive components that are essential for its composition. These include substances like cellulose, starch, magnesium stearate, and specialized coatings that help control the release of the ingredient. While these inactive ingredients don't have any effects on their own, they play a crucial role in giving structure to the medication aiding in its absorption, and regulating how the active ingredient is released over time.
B. Forms and Presentations
Mesalamine is available in formulations, each designed to maximize its therapeutic effects while ensuring patient comfort and adherence. For administration, there are delayed-release tablets and extended-release capsules that release the medication slowly in the colon. Additionally, rectal forms like suppositories and enemas are available for application to inflamed areas. These various options enable healthcare providers to customize treatment based on individual disease presentation and patient tolerance.
IV. Approved Uses of Mesalamine
A. Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Mesalamine plays a role in the treatment options available for ulcerative colitis(1), which is a long-term inflammatory bowel disease with no known cause. The condition manifests as inflammation in the colon's mucous membrane.(2)
Mesalamine is used both to initiate and sustain remission. It works by suppressing the production of substances and providing localized relief to the inflamed colon. As a result, Mesalamine effectively alleviates symptoms associated with colitis(3), such as abdominal discomfort, frequent bowel movements, and rectal bleeding.
1. WebMD - Mesalamine for Ulcerative Colitis
2. MedlinePlus - Mesalamine
3. PubMed - Mesalamine in the treatment and maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis
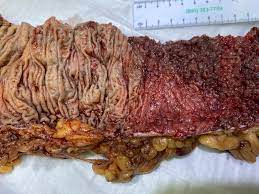
Severe Ulcerative Colitis
B. Management of Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease, which is a type of bowel disease but less prevalent than ulcerative colitis, can also be treated with Mesalamine. While it may not work for everyone and is often used alongside treatments, Mesalamine is effective in managing mild to moderate Crohn's disease affecting the ileum or colon. It helps control symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss associated with the disease.
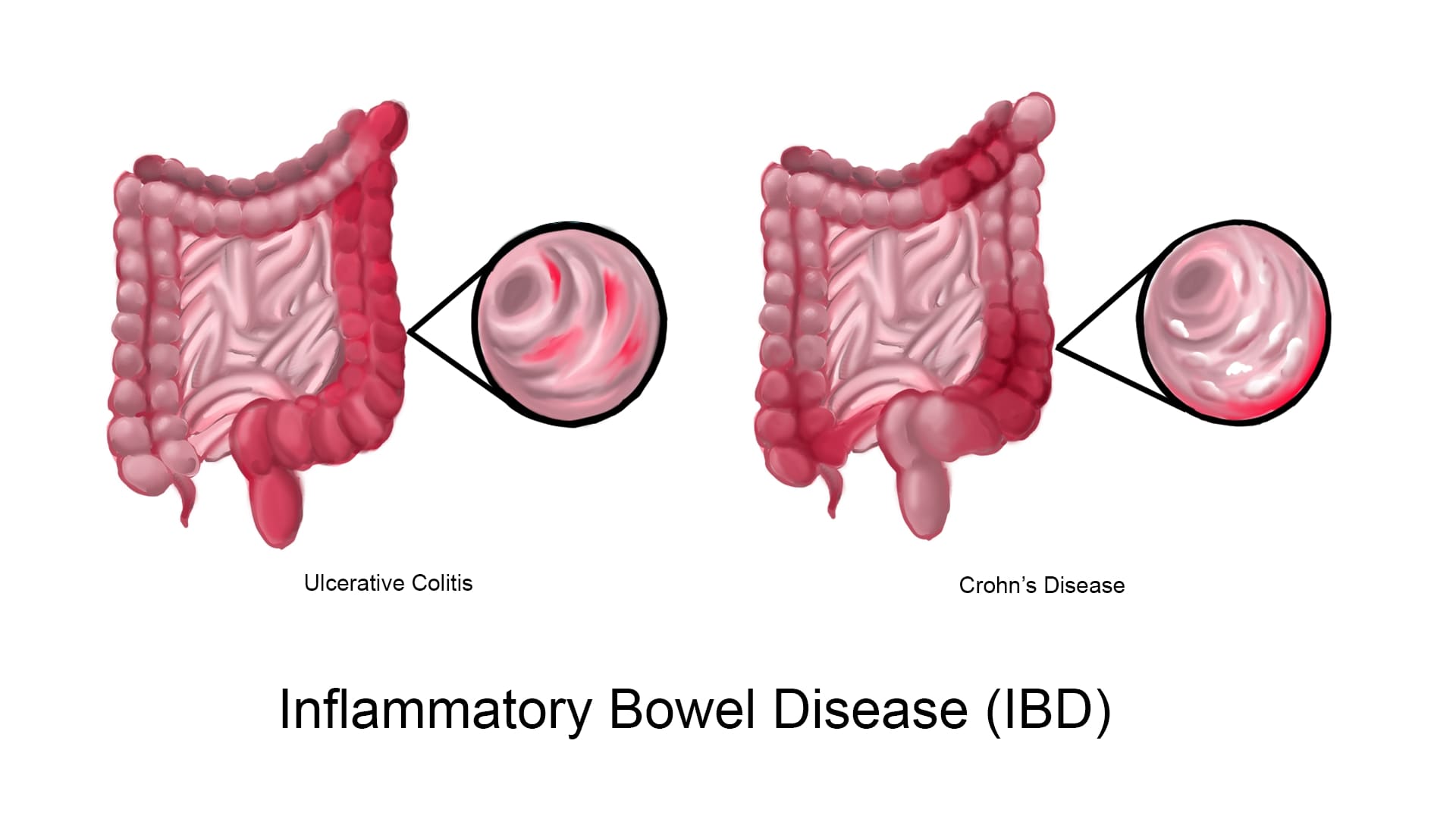
Inflammatory bowel disease
C. Prevention of Colitis Flares
In addition to relieving symptoms, Mesalamine has a broader scope that includes preventing flare-ups of colitis. For people who're in remission, Mesalamine can be used as an ongoing treatment to prevent recurring episodes of inflammation.
Its preventive role is based on its ability to control the immune response that is dysregulated, thus decreasing the frequency and severity of disease flare-ups.
Mesalamine enhances the quality of life for individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases and lowers the risk of complications like colorectal cancer.
V. Off-Label Uses of Mesalamine
A. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Although it is not commonly recommended, Mesalamine has been used off-label to manage bowel syndrome (IBS) (1) . IBS is a disorder that is different from inflammatory bowel diseases.
It is characterized by symptoms such as pain and changes in bowel habits without any apparent structural abnormalities.
While the effectiveness of Mesalamine in treating IBS is still being studied, there is speculation that its anti-inflammatory properties may provide some relief for patients with evidence of inflammation or post-infectious IBS.
1. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology - Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
B. Role in Diverticulitis Management
Mesalamine is sometimes used off-label to treat diverticulitis, a condition characterized by inflammation or infection of pouches (diverticula) that can develop in the lining of the digestive system. While antibiotics are usually the choice for treatment, Mesalamine has been investigated as an additional option, especially for patients with chronic and uncomplicated diverticulitis.
This is because Mesalamine has inflammatory properties that may help alleviate symptoms and potentially prevent future episodes, although further research is required to establish its effectiveness more conclusively.
C. Potential Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis
It's interesting to note that researchers have looked into the use of Mesalamine in treating rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation. This idea stems from the fact that the parent compound of Mesalamine, called sulfasalazine, was initially developed to help with arthritis before its effectiveness in inflammatory bowel disease was discovered.
Because both conditions involve inflammation, there is a hypothesis that Mesalamine's anti-inflammatory properties could be helpful in managing arthritis. However, it's important to acknowledge that this application is still mostly speculative and requires extensive research.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
A. Standard Dosage for Adults
The typical recommended dosage of Mesalamine for adults varies between 1.2 and 4.8 grams per day depending on the condition being treated and the type of product used. For instance, when treating ulcerative colitis, the initial daily dose may start at 1.2 grams and can be adjusted based on how well the patient responds to treatment and their tolerance to it.
It's important to stress that the dosage should be personalized with the guidance of a healthcare professional, taking into account factors such as disease severity response to therapy and potential side effects.
B. Adjustments for Specific Conditions
In situations, it may be necessary to make changes. For instance, patients who have liver or kidney problems might need to have their dosage carefully adjusted and closely monitored because there is a possibility of increased absorption into the body. Similarly, suppose the patient has health conditions or is taking other medications at the same time. In that case, adjustments in dosage may be needed to prevent any potential interactions between drugs and ensure that the treatment works optimally.
C. Administration Methods
The way Mesalamine is taken depends on how it's formulated. If you're taking the forms like tablets or capsules, make sure to have a full glass of water with it. Remember not to crush or chew the medication because that could interfere with the coating meant for extended-release.
On the other hand, if you're using rectal forms like suppositories or enemas, they are only meant for use in the rectum. Follow the instructions given by your healthcare provider or those provided in the product package when administering them.
VII. Special Considerations for Mesalamine Administration
A. Administration to the Elderly
Older individuals might have a vulnerability to the overall impact of Mesalamine due to age-related alterations in kidney function and a greater chance of having other health conditions or taking multiple medications. As a result, it is important to exercise caution when prescribing Mesalamine to this group considering the possibility of reducing the dosage and closely monitoring function.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Considering the availability of reliable data on human pregnancy, it is advisable to only use Mesalamine during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Although Mesalamine can be found in breast milk, we are unaware of its impact on nursing infants. Therefore it is recommended that nursing mothers consult their healthcare provider to make a decision about whether to continue or discontinue using the medication while breastfeeding.
C. Administration to Children
Although Mesalamine may be prescribed for treating colitis in children, it is important to note that its safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients under the age of 5 years. Like with any patient group, the dosage of Mesalamine should be personalized based on factors such as the severity of the disease, the child's weight, and the specific product being used. It is crucial that any administration of Mesalamine, to children is done under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
VIII. Understanding Mesalamine's Side Effects
A. Common Side Effects
Similar to medications used for therapy, Mesalamine can have a range of possible side effects. The frequently observed side effects are headaches, abdominal discomfort, feeling nauseous experiencing diarrhea, and gas. Generally, these side effects are mild or moderate. Tend to lessen as the body becomes accustomed to the medication. However, if any side effects persist or become bothersome, it's important to inform your healthcare provider.
B. Serious and Rare Side Effects
Frequently but still significantly, Mesalamine can lead to a condition called acute intolerance syndrome, which resembles a worsening of ulcerative colitis. It may also cause impairment and hypersensitivity reactions, like ;
- Rash
- Itching
- Anaphylaxis
Although rare, there have been cases of liver damage and inflammation of the heart muscles (myocarditis). Given the seriousness of these side effects, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms are suspected.
C. Management of Side Effects
The way to handle side effects caused by Mesalamine depends on the severity and type of the side effect. If someone experiences gastrointestinal issues, they can usually manage them with symptom relief measures and may not need to stop taking the medication.
However, if the symptoms are more severe or persistent, indicating a severe reaction or organ damage, its generally advised to discontinue the drug and seek appropriate medical assistance. As always, patients should be instructed to inform their healthcare provider about any unusual or concerning symptoms they experience.
IX. Interactions and Contraindications of Mesalamine
A. Potential Drug Interactions
Mesalamine can potentially interact with other medications affecting how they work or their side effects. For example, using Mesalamine at the time as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) azathioprine or 6 mercaptopurine may increase the risk of kidney damage.
Likewise combining it with anticoagulants may raise the risk of bleeding due to the combined effects, on blood clotting. It is important to monitor and adjust doses when using these medications together with Mesalamine.
B. Known Contraindications and Risk Factors
Mesalamine should not be used in patients who are known to have hypersensitivity to salicylates or aminosalicylates or any of the components found in Mesalamine formulations. It is important to note that individuals with kidney problems are at risk of experiencing Mesalamine induced toxicity, so caution should be exercised when considering the use of this drug in such cases.
Additionally, patients with existing liver disease or a history of myocarditis or pericarditis may also face an increased risk of reactions. Before starting treatment, with Mesalamine, it is crucial to conduct an analysis weighing the risks and benefits associated with its use.
X. Warning and Precautions for Mesalamine Use
A. Signs of Overdosage and Management
Overdosing on Mesalamine should not be ignored, as it can lead to symptoms like ringing in the ears, rapid breathing, and seizures. If there is a suspicion of an overdose, it is important to stop taking Mesalamine and provide supportive care.
This may involve giving activated charcoal to prevent absorption of the medication, ensuring proper hydration for effective elimination through the kidneys, and closely monitoring vital signs and kidney function.
B. Important Precautions to Follow
People who are prescribed Mesalamine need to be careful and watch out for any signs of intolerance syndrome. These signs may include symptoms like cramps, stomach pain, bloody diarrhea, and sometimes even fever, headache, or a rash. It's important to assess kidney function before starting the treatment and at intervals during it, especially for those with pre-existing kidney problems.
Additionally, if someone has stenosis, the release of the medication in the stomach may be delayed, so closer monitoring would be required for these patients.
C. Safe Handling and Storage Tips
Store Mesalamine at room temperature away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. It's also crucial to keep it out of the reach of children. Please avoid disposing of this medication through wastewater or household waste. Instead, consult your pharmacist or waste disposal company for proper guidance on how to safely dispose of it. Remember, like any medication, make sure not to consume Mesalamine beyond its expiration date.
XI. Careful Administration and Monitoring of Mesalamine
A. Importance of Regular Medical Follow-ups
Scheduled medical checkups are crucial for effectively managing conditions that require the use of Mesalamine. These appointments provide an opportunity to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment, address any side effects, and make any necessary adjustments to the dosage. It is important to attend these checkups in order to ensure the drug is being used safely and effectively.
B. Adherence to Dosage and Administration Guidelines
It is crucial to follow the dosage and administration guidelines to achieve the best treatment results. Take Mesalamine exactly as instructed by your healthcare provider at the time every day to ensure a consistent level of the medication, in your body. Remember not to change the dose, frequency or duration of therapy without consulting a healthcare professional.
C. Observing and Reporting Side Effects
It is extremely important for people who are prescribed Mesalamine to be aware of any side effects and promptly inform their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms. Detecting and addressing side effects on can help prevent complications and enhance the overall safety of the medication. Maintaining communication with your healthcare provider will facilitate this process and improve the effectiveness of your Mesalamine treatment.