Minocycline
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Minocycline
- III. How Minocycline Works
- IV. Uses of Minocycline
- V. Off-label Uses of Minocycline
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Special Administration Circumstances
- VIII. Side Effects of Minocycline
- IX. Interactions of Minocycline
- X. Contraindications
- XI. Warnings and Precautions
- XII. Overdosage
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precactions
- XIV. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Definition and general information about Minocycline
Minocycline, a synthetic tetracycline antibiotic, is widely recognized for its broad antibacterial effects. It has long been used to treat acne and certain infections because it can effectively hinder the growth of bacteria. This medication works by disrupting the process of protein synthesis in bacteria, thereby preventing their multiplication.
B. Historical context of Minocycline use
Minocycline has been used since the 1960s as a versatile option compared to other tetracycline antibiotics. Throughout the years Minocycline has maintained its significance in the field of medicine, standing firm despite the introduction of medications. Its proven effectiveness in treating conditions such as acne and specific infections has solidified its place in history.
C. Importance and relevance in the medical community
Minocycline has proven to be a treatment option in the medical field, standing the test of time. It is frequently used as a choice for addressing moderate to severe acne and various bacterial infections. Its importance can be attributed to its strong ability to fight bacteria, its safety record, and its cost-effectiveness.
II. Composition of Minocycline
A. Active ingredient explanation
Minocycline contains a component called minocycline hydrochloride, which falls under the category of antibiotics known as tetracyclines. This substance disrupts the process of protein production in cells hindering their growth and reproduction.
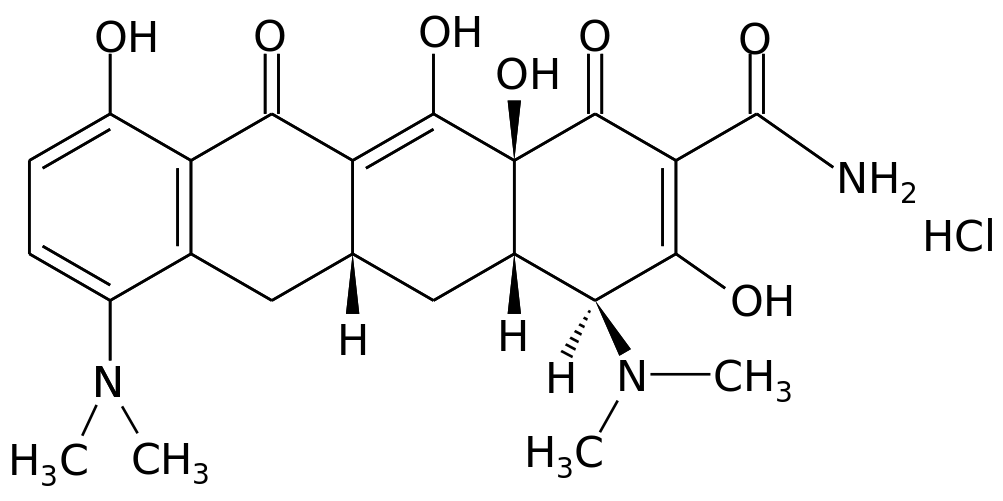
B. Additional ingredients and their functions
Apart from the component Minocycline formulations may include certain additives like magnesium stearate, lactose, and gelatin. These extra ingredients serve purposes. For example; Magnesium stearate; acts as a flow agent during the manufacturing process. It helps in evenly distributing the active ingredient throughout the formulation. Lactose; Often used as a filler or binder, it provides the volume for tablet or capsule preparation. Gelatin; primarily used in capsule shells ensures that the active ingredient is securely enclosed and assists in releasing the drug when consumed.
C. Forms and variations available in the market
Minocycline comes in forms to meet various needs and preferences. These options include capsules and tablets, topical gels and creams, as well as intravenous formulations. Each type of medication has absorption rates and target areas making it more adaptable, to the specific needs of each patient.
III. How Minocycline Works
A. Understanding the mechanism of action
Minocycline works by blocking protein synthesis, essential for bacterial growth and reproduction. It does this by binding to the 30S subunit inside the bacterial cell preventing transfer RNA from attaching to the ribosome and disrupting the creation of new proteins. This disruption hampers multiplication.
B. Interaction with bacterial cells
Minocycline effectiveness relies heavily on its ability to penetrate cell walls. Once it enters the cell, it disrupts the machinery responsible, for protein synthesis specifically focusing on the ribosomes. This disruption hinders the capacity of the bacteria to produce proteins impeding its growth and ability to multiply.
C. Impact on human biological systems
While Minocycline is mainly focused on targeting bacteria it also has effects on biological systems. Research has demonstrated its ability to reduce inflammation, which can be pretty helpful in treating acne and similar conditions. Additionally, due to its lipid solubility, Minocycline can easily pass through biological barriers like the blood-brain barrier. This makes it a promising option for the treatment of specific neurological disorders.
IV. Uses of Minocycline
Minocycline is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat bacterial infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, skin infections, severe acne, chlamydia, tick fever, gonorrhea, and syphilis1. It is also used for the treatment of acne and rheumatoid arthritis1. Minocycline has been in therapeutic use for over 30 years and has been reported to have anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities and inhibition of proteolysis, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- 1Minocycline - Wikipedia
- 2Minocycline: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects - Drugs.com
- 3Minocycline: Uses, Side Effects. Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
Primary uses
Minocycline is primarily prescribed for the treatment of acne and various skin infections. Additionally, it is utilized to address urinary tract infections, as well as sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea12. Furthermore, it can effectively combat infections caused by Rickettsia bacteria which are responsible for illnesses such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever1. Moreover, Minocycline is employed in tackling infections caused by Mycoplasma bacteria that can lead to pneumonia and other respiratory tract infections3. Lastly, it is used to treat Lyme disease resulting from Borrelia bacteria1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- 1Minocycline (Minocin): Uses, Side Effects, Alternatives & More - GoodRx
- 2Minocycline: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects - Drugs.com
- 3Minocycline Capsules & Tablets: Uses & Side Effects - Cleveland Clinic
Uncommon uses in special scenarios
Minocycline has shown effectiveness in treating meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis bacteria1. Additionally it has been employed in managing infections resulting from Yersinia pestis bacteria, which is responsible for causing bubonic plague12.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- 1Antimicrobial Treatment and Prophylaxis of Plague: Recommendations for Naturally Acquired Infections and Bioterrorism Response | MMWR
- 2Minocycline - Wikipedia
Global usage statistics and trends
Minocycline is extensively utilized globally. In the United States, over 5 million prescriptions for minocycline are prescribed annually. Moreover, the drug enjoys usage in Europe and Asia as well.
Here is a reference that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
V. Off-label Uses of Minocycline
Minocycline is commonly prescribed for infections but also applies to other off-label uses. For instance, it has been studied in conditions such as osteoporosis, schizophrenia, cystic fibrosis, and MS1. Other off-label minocycline uses include purulent cellulitis, leprosy, nocardiosis, prosthetic joint infection, infective endocarditis, and sarcoidosis2. Minocycline has anti-inflammatory effects and has been used off-label in treating rheumatoid arthritis3.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- 1Meds Used Off Label | National Multiple Sclerosis Society
- 2Minocycline: Uses, Side Effects. Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
- 3Minocycline for rheumatoid arthritis: What to know - Medical News Today
Exploration of known off-label uses
Minocycline is sometimes used off-label for treating arthritis. Although we don’t fully understand how it works, research suggests that minocycline can reduce inflammation in the joints and alleviate symptoms of arthritis. Another off-label use of minocycline is for the treatment of sclerosis. Studies indicate that minocycline can help decrease inflammation in the brain and spinal cord, potentially slowing down the progression of the disease.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- Minocycline for rheumatoid arthritis: What to know - Medical News Today
- Meds Used Off Label | National Multiple Sclerosis Society
Case studies illustrating effectiveness in off-label scenarios
There have been instances where researchers have shown how minocycline can effectively treat conditions not explicitly approved by regulatory authorities. For example, a study demonstrated the effectiveness of minocycline in treating individuals diagnosed with stage Parkinsons' disease. Similarly, another research found outcomes when using minocycline for patients with schizophrenia.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Minocycline:
- Minocycline for Parkinson’s Disease - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov
- Minocycline for Schizophrenia - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov
Legal and ethical considerations of off-label use
Using medications for purposes than those specified on the label presents legal and ethical concerns. While physicians have the authority to prescribe medications for off label uses pharmaceutical companies are prohibited from promoting their drugs for purposes. Patients must engage in a discussion with their doctors, about the potential risks and benefits associated with any off label use before commencing treatment.
VI. Dosage and Administration
A. General dosage guidelines
Like other antibiotics, the amount of Minocycline prescribed can differ based on the type and seriousness of the treated infection. Typically for adults, they are taking 200 mg daily and 100 mg every 12 hours after that is suggested. Nevertheless, the dosage may be altered depending on how an individual responds to the medication and at the discretion of their doctor.
B. Administration methods: oral, injection, etc.
Minocycline is typically taken by mouth in the form of tablets or capsules. Remember to drink enough water while taking it to avoid irritation of the esophagus. In severe situations or when oral intake is impossible, healthcare professionals may administer Minocycline through an intravenous injection while closely monitoring the patient.
C. Special considerations for varying patient conditions
Certain patient conditions may necessitate changes in the dosage and administration of Minocycline. These conditions include impairment, hepatic dysfunction, and the concurrent use of specific medications. For example, patients with renal impairment might need to adjust their dosage because the drug is eliminated from their body at a slower rate. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for treatment plans.
VII. Special Administration Circumstances
A. Administration to elderly patients: precautions and considerations
Extra care must be exercised when giving Minocycline to individuals. As people age, their bodies undergo changes that can affect kidney function. Consequently, adjusting the dosage or increasing the time between doses for adults may be necessary. Monitoring them for any potential side effects is essential since they may be more susceptible to adverse reactions.
B. Administration to pregnant women and nursing mothers: safety and recommendations
Minocycline should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks to the baby. Studies have shown that this medication can pass through the placenta and may affect fetal growth. Likewise, breastfeeding mothers should avoid taking Minocycline since it can be excreted in breast milk and potentially impact the well-being of their infant. In some situations, exploring alternative antibiotics as a safer option is advisable.
C. Administration to children: guidelines and cautionary measures
Minocycline is generally not recommended for children under the age of 8 due to the possibility of tooth discoloration. It should only be considered for children if other treatments have proven ineffective or unsuitable. The dosage should be adjusted according to their body weight. It's crucial to monitor for any potential side effects closely.
VIII. Side Effects of Minocycline
A. Common side effects: listing and explanation
Minocycline can cause side effects such as feeling nauseous, vomiting, experiencing diarrhea feeling dizzy, and being tired. Usually, these side effects are mild. Don't last long. However,, it's important to inform your healthcare provider if they continue or worsen. Furthermore, antibiotics using Minocycline may lead to the growth of nonsusceptible organisms. In cases, you might need to stop taking the medication.

B. Rare but severe side effects: recognition and management
While it is uncommon, Minocycline can lead to adverse effects. These can include drug-induced lupus, hypersensitivity syndrome, and severe skin reactions. If you experience symptoms like a rash, fever, or joint pain it is crucial to seek medical assistance. In some cases, Minocycline should be stopped, and appropriate steps should be taken to address the adverse reaction.
C. Understanding individual variation in side effects
It's important to mention that the side effects of Minocycline can differ from person to person based on factors such as age, genetics, existing health conditions, and concurrent medication use. As a result, what might be considered a severe side effect for one individual could be mild or even absent for another. Hence it is crucial to tailor the management of side effects on a level.
IX. Interactions of Minocycline
A. Drug-drug interactions: common co-administered drugs and potential concerns
Minocycline, like any medication, can interact with various other drugs. Notable examples of interactions include retinoids, anticoagulants, and other antibiotics. When used together with retinoids primarily prescribed for acne treatment, it may cause an increase in pressure within the skull. The effectiveness of anticoagulants could be heightened, leading to a risk of bleeding complications. Concurrent usage with antibiotics, especially those that kill bacteria directly, can disrupt Minocycline's ability to slow down bacterial growth. Therefore it is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including counter drugs and supplements.
B. Drug-food interactions: dietary restrictions and guidelines
The absorption of Minocycline may be affected if it is taken together with foods or substances. For example, dairy products, antacids, and iron supplements can combine with Minocycline to create a complex that cannot be absorbed. As a rule, patients should take Minocycline 1 or 2 hours before or after consuming these products to ensure optimal absorption.
C. Drug-disease interactions: cautions for patients with specific conditions
People who have health conditions should be careful when using Minocycline. This applies to individuals with liver disease, kidney disease, or a previous case of hypertension. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage for patients with these conditions. It is essential to monitor them for any possible adverse effects closely.
X. Contraindications
A. Absolute contraindications: when to avoid Minocycline
Individuals with a known sensitivity to antibiotics in the tetracycline class should not use Minocycline. It is important to note that Minocycline is strictly prohibited for children under eight as it may cause tooth discoloration and enamel hypoplasia. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also avoid Minocycline due to the risks it may pose to the developing fetus or infant.
B. Relative contraindications: when to use Minocycline with caution
Some situations where it may be best to avoid using Minocycline are if you have issues with your liver or kidneys. In those cases, adjusting the dosage and keeping a close eye on how you're doing is essential. Additionally, if you've had lupus erythematosus in the past, it's wise to be cautious when using Minocycline since it could worsen the condition.
Suppose someone has had an allergic reaction or sensitivity to any tetracycline antibiotic; it is advised that they avoid using Minocycline. Allergic reactions can manifest as a rash, fever, or even anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic response. In some cases, it is important to explore alternative antibiotics instead.
XI. Warnings and Precautions
A. Precautionary measures for safe Minocycline use
To ensure the use of Minocycline, it is essential to follow certain precautions. These precautions include taking the medication exactly as prescribed, informing your healthcare provider about your history and any other medicines you are currently taking, and promptly reporting any side effects. If you are a long-term user, you may need to undergo liver and kidney function tests to monitor for any possible damage to these organs.
B. Warning signs of adverse reactions
People taking Minocycline should be cautious about indications of severe adverse effects. If you experience headaches, blurry vision, skin rash, yellowing of the eyes or skin, or extreme fatigue, it's important to seek immediate medical help.
C. Essential actions if a problem arises
If any issues occur while using Minocycline, such as experiencing side effects or symptoms, it is important to stop taking the medication immediately. After discontinuation, seeking medical attention to evaluate the situation and appropriately address any adverse reactions is crucial. Patients should never attempt to handle responses without proper guidance from healthcare professionals.
XII. Overdosage
A. Symptoms of Minocycline overdose
Taking much Minocycline can worsen the usual side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and experiencing dizziness. In severe cases, it can cause kidney problems, liver toxicity, and anemia. Additionally, it may also trigger symptoms like headaches and changes in vision, which could indicate issues with increased pressure inside the skull.
B. Immediate response and management strategies
If you suspect that someone has taken much Minocycline, it is crucial to seek medical help right away. The primary approach to managing an overdose is providing supportive care. Since Minocycline binds strongly to proteins, it is not easily eliminated through hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Getting attention promptly is essential for minimizing any potential harm caused by an overdose.
C. Long-term implications and recovery from overdose
The potential consequences of taking much Minocycline depend on how quickly and effectively it is managed. If treated promptly and correctly, patients can usually recover without any lasting effects. However, a severe overdose could potentially result in lasting damage to the kidneys or liver which would require treatment and monitoring.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precactions
A. Proper storage conditions for Minocycline
Minocycline must be stored at room temperature from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. It should also be kept out of reach of children. Minocycline is sensitive to light and might lose effectiveness if not stored correctly. Always make sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions for storage conditions.
B. Handling procedures for safety and efficacy preservation
To ensure safety and maintain the effectiveness of Minocycline, it is essential to handle the medication with hands and use it within the recommended timeframe after opening. It is advised not to use any medication that has changed color or contains particles. Additionally, try to avoid shaking the medication bottle as this could lead to unnecessary exposure to air.
C. Shelf-life and expiry: understanding and checking for degradation
The expiration date of Minocycline is usually indicated on the packaging of the medication. After it has expired, the drug may lose its effectiveness. Even pose potential harm. Hence it is essential to dispose of expired medication properly. If uncertain, seeking guidance from a pharmacist or healthcare professional is advisable.
XIV. Conclusion
A. Recap of Minocycline's importance, uses, and considerations
Minocycline, an adaptable antibiotic from the tetracycline family, is crucial in treating various bacterial infections. Its significance stems from its versatility, effectiveness, and overall safety record. However, it is essential to consider the recommended dosage and administration guidelines, potential interactions with other medications, possible side effects, contraindications, and specific situations to ensure its safe and effective usage.
B. Role of healthcare providers in effective use
Healthcare professionals play a role in ensuring the safe and efficient utilization of Minocycline. They achieve this by prescribing it, educating patients, and continuously monitoring their progress. Healthcare providers aim to optimize the advantages while minimizing potential risks using Minocycline.
C. The ongoing research and potential future developments in Minocycline application
Ongoing research on Minocycline is revealing benefits beyond its well-known antibiotic properties. Recent studies are investigating its potential as an inflammatory and neuroprotective agent, indicating a more comprehensive range of applications for this powerful medication. These advancements highlight the changing field of medicine and the exciting possibilities that Minocycline offers for future medical advances.
Minocycline FAQ
- What are the side effects of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline used for in treating acne?
- What causes Minocycline black bones?
- What are the uses of Minocycline?
- How does Minocycline compare to Doxycycline?
- What is Minocycline Hydrochloride?
- What is Minocycline 100 mg used for?
- Is Minocycline an antibiotic?
- Can Minocycline be used with alcohol?
- What is Minocycline hyperpigmentation?
- What is Minocycline topical?
- What is a Minocycline pill?
- What are Minocycline side effects for acne?
- Can Minocycline be used for a sinus infection?
- What are Minocycline interactions?
- Can Minocycline be used for dogs?
- What is Minocycline foam?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep throat?
- What is the drug class of Minocycline?
- What is the brand name of Minocycline?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep throat?
- What are Minocycline reviews for acne?
- What are Minocycline warnings?
- What is a Minocycline allergic reaction?
- What is the before and after of using Minocycline?
- Can Minocycline be used for an ear infection?
- Can Minocycline be used for a tooth infection?
- What is Minocycline HCL 100 mg?
- What is the interaction between Minocycline and alcohol?
- What is a Minocycline rash?
- What are Minocycline reviews?
- Can Minocycline be used for an ear infection?
- What is Minocycline blue skin?
- What is Minocycline topical foam?
- What is the cost of Minocycline?
- What is the interaction between Minocycline and birth control?
- How does Minocycline compare to Doxycycline for acne?
- What is Minocycline skin discoloration?
- What are Minocycline side effects on teeth?
- What is the Minocycline UTI dosage?
- What is Minocycline perioral dermatitis?
- Can Minocycline treat UTI?
- What is Minocycline medication?
- Is Minocycline available over the counter?
- What is a Minocycline capsule?
- What is Minocycline cream?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep?
- What is the difference between Minocycline and Doxycycline?
- What is the class of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline sun sensitivity?
- Does Minocycline cause weight gain?
- What are Minocycline uses for skin?
- What is Minocycline pigmentation?
- What is a Minocycline allergy?
- What is the generic name for Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline GoodRx?
- How do Minocycline and Doxycycline compare?
- Can Minocycline cause depression?
- Can Minocycline be used for rheumatoid arthritis?
- Is Minocycline a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
- What is Minocycline acne medication?
- Can Minocycline be used for chlamydia?
- Can Minocycline treat chlamydia?
- What are Minocycline tablets?
- What is the use of Minocycline in horses?
- Can Minocycline cause weight gain?
- Can Minocycline be used for Lyme disease?
- Can Minocycline be used for folliculitis?
- Can Minocycline be taken with birth control?
- What is the difference between Minocycline and Tetracycline?
- What is the coverage of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation?
- Is Minocycline safe in pregnancy?
- What are the side effects of Minocycline hydrochloride?
- Can Minocycline cause headaches?
- Can Minocycline cause hair loss?
- Can Minocycline cause hives?
- What are the side effects of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline used for in treating acne?
- What causes Minocycline black bones?
- What are the uses of Minocycline?
- How does Minocycline compare to Doxycycline?
- What is Minocycline Hydrochloride?
- What is Minocycline 100 mg used for?
- Can Minocycline be used for urinary tract infections (UTI)?
- Is Minocycline an antibiotic?
- Can Minocycline be used with alcohol?
- What is Minocycline hyperpigmentation?
- What is Minocycline topical?
- What is a Minocycline pill?
- What are Minocycline side effects for acne?
- Can Minocycline be used for a sinus infection?
- What are Minocycline interactions?
- Can Minocycline be used for dogs?
- What is Minocycline foam?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep throat?
- What is the drug class of Minocycline?
- What is the brand name of Minocycline?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep throat?
- What are Minocycline reviews for acne?
- What are Minocycline warnings?
- What is a Minocycline allergic reaction?
- What is the before and after of using Minocycline?
- Can Minocycline be used for an ear infection?
- Can Minocycline be used for a tooth infection?
- What is Minocycline HCL 100 mg?
- What is the interaction between Minocycline and alcohol?
- What is a Minocycline rash?
- What are Minocycline reviews?
- Can Minocycline be used for an ear infection?
- What is Minocycline blue skin?
- What is Minocycline topical foam?
- What is the cost of Minocycline?
- What is the interaction between Minocycline and birth control?
- How does Minocycline compare to Doxycycline for acne?
- What is Minocycline skin discoloration?
- What are Minocycline side effects on teeth?
- What is the Minocycline UTI dosage?
- What is Minocycline perioral dermatitis?
- Can Minocycline treat UTI?
- What is Minocycline medication?
- Is Minocycline available over the counter?
- What is a Minocycline capsule?
- What is Minocycline cream?
- What is the price of Minocycline?
- Can Minocycline be used for strep?
- What is the difference between Minocycline and Doxycycline?
- What is the class of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline sun sensitivity?
- Does Minocycline cause weight gain?
- What are Minocycline uses for skin?
- What is Minocycline pigmentation?
- What is a Minocycline allergy?
- What is the generic name for Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline GoodRx?
- How do Minocycline and Doxycycline compare?
- Can Minocycline cause depression?
- Can Minocycline be used for rheumatoid arthritis?
- Is Minocycline a treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
- What is Minocycline acne medication?
- Can Minocycline be used for chlamydia?
- Can Minocycline treat chlamydia?
- What are Minocycline tablets?
- What is the use of Minocycline in horses?
- Can Minocycline cause weight gain?
- Can Minocycline be used for Lyme disease?
- Can Minocycline be used for folliculitis?
- Can Minocycline be taken with birth control?
- What is the difference between Minocycline and Tetracycline?
- What is the coverage of Minocycline?
- What is Minocycline-induced hyperpigmentation?
- Is Minocycline safe in pregnancy?
- What are the side effects of Minocycline hydrochloride?
- Can Minocycline cause headaches?
- Can Minocycline cause hair loss?
- Can Minocycline cause hives?



























