Mosapride/ Pantoprazole
- I. Introduction to Mosapride and Pantoprazole
- II. Composition and Properties
- III. Mechanism of Action
- IV. Uses of Mosapride and Pantoprazole
- V. Off-label Uses of the Combination
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- VIII. Important Precautions and Warnings
- IX. Special Considerations in Administration
- X. Handling Overdoses and Emergencies
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Interaction with Other Medications
I. Introduction to Mosapride and Pantoprazole
Overview of Mosapride and Pantoprazole
Mosapride and Pantoprazole work together as a combination in treating different gastrointestinal issues. Mosapride helps in moving things along, in the system while Pantoprazole reduces the amount of stomach acid produced.
Brief History and Development
The creation of Mosapride and Pantoprazole can be linked to advancements in treating stomach and intestinal issues. Introduced at times using them together has become a critical method of treatment in recent years.
Importance of Combination Therapy in Gastrointestinal Disorders
Using both Mosapride and Pantoprazole together is crucial for treating conditions like reflux disease (GERD) and other motility disorders. This method helps address symptoms from different angles, leading to better results for patients due to the combined effectiveness.
II. Composition and Properties
Chemical Composition of Mosapride
Mosapride Citrate, commonly known as Mosapride is recognized for its makeup that aids in activating serotonin receptors with a focus, on the 5 HT4 receptors found in the digestive system.
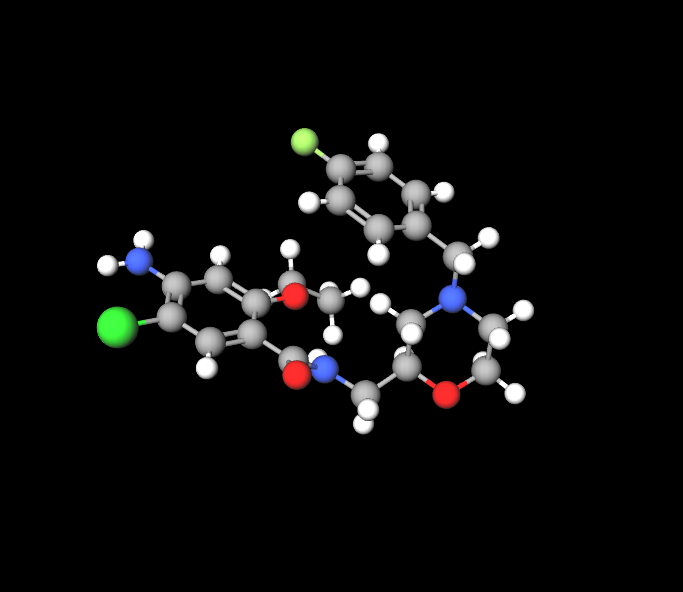
Chemical Composition of Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole works by being a type of derivative that specifically blocks the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme system on the surface of gastric parietal cells, leading to a decrease in the production of stomach acid.
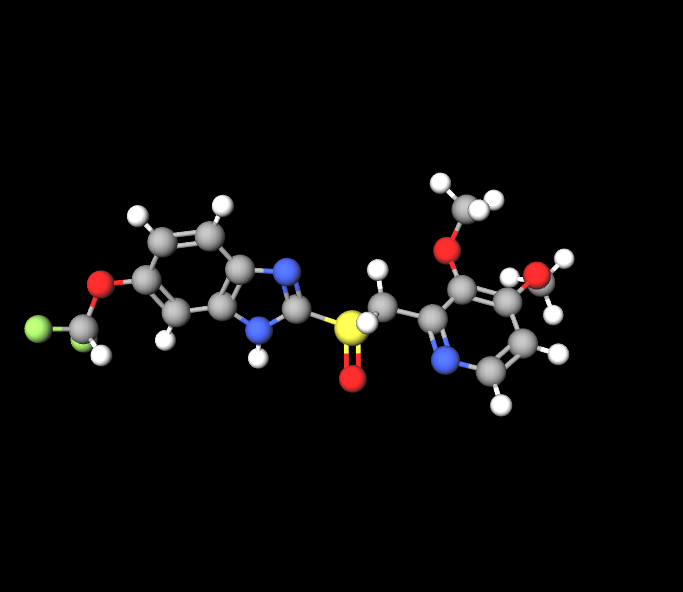
Pharmacological Properties of the Combination
The combination of Mosapride and Pantoprazole improves the functioning of the tract and reduces the risk of acid related issues leading to better treatment results.
III. Mechanism of Action
How Mosapride Works in the Gastrointestinal System
Mosapride is effective in regulating movement in the digestive system by activating serotonin receptors. This helps speed up the stomach's emptying and enhances coordination between the antrum and duodenum.
How Pantoprazole Reduces Stomach Acid
Pantoprazole works by irreversibly blocking the proton pump, a key element in acid secretion. This leads to an efficient decrease in gastric acid production.
Synergistic Effects of Mosapride and Pantoprazole
Using Mosapride and Pantoprazole together not only targets different aspects of gastrointestinal issues but also collaborates to lower the chances of symptoms returning and improve overall digestive wellness.
IV. Uses of Mosapride and Pantoprazole
-
Mosapride:
- Mosapride is used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcer disease.
- It helps manage symptoms in chronic gastrointestinal diseases and provides therapeutic intervention in dyspeptic symptom complexes1.
-
Pantoprazole:
- Pantoprazole is used to treat erosive esophagitis (damage to the esophagus from stomach acid caused by GERD) in adults and children who are at least 5 years old.
- It is usually given for up to 8 weeks at a time while the esophagus heals2.
-
Combination Therapy:
- The combination of Pantoprazole and Mosapride significantly mitigates GERD symptoms, including heartburn and regurgitation, by improving gastric emptying and reducing acid exposure to the esophagus.
- In conditions characterized by delayed gastric emptying (e.g., gastroparesis), this combination plays a crucial role in enhancing gastric motility and alleviating associated symptoms34.
V. Off-label Uses of the Combination
Exploring Non-approved Applications
- Pantoprazole may be used off-label for various purposes, including:
- Aspiration prophylaxis in patients undergoing anesthesia.
- Barrett’s esophagus.
- Functional dyspepsia.
- Helicobacter pylori eradication.
- Primary prevention of NSAID-induced ulcers.
- Stress ulcer prophylaxis.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Many of these off-label uses are recognized in international and national guidelines2.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The usual recommendation is to take Mosapride three times a day before meals and Pantoprazole daily, preferably before breakfast.
Adjustments for Special Populations
It's important to adjust the dosage for groups like older adults, individuals with liver issues, and those with kidney problems to reduce risks and improve treatment effectiveness.
Methods of Administration and Timing
Maintaining a schedule for taking medication not only helps the drugs work best but also keeps the levels of treatment steady, lowering the chances of negative reactions.
How long does it take for pantoprazole to work
It might take around four weeks for pantoprazole, so you could still experience symptoms during this period. If you purchased pantoprazole over the counter and do not notice any improvement after 2 weeks, make sure to inform your doctor.
VII. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common Side Effects of Mosapride and Pantoprazole
- Some individuals may experience stomach issues like diarrhea and queasiness.
- Additionally a few patients might encounter headaches and feelings of dizziness.
Serious Adverse Reactions to Monitor
Severe skin reactions and imbalances, in electrolytes are uncommon but important side effects that may require medical care.
Can Pantoprazole cause anxiety
Some individuals may experience side effects from Pantoprazole. It appears that anxiety is not commonly associated with its use. Headaches were mentioned by participants during clinical trials involving Pantoprazole. Additionally, more than 2% of individuals in these trials reported experiencing symptoms of depression and vertigo (feeling dizzy).

Managing Side Effects in Clinical Practice
Managing side effects effectively requires modifying the dosage providing treatments and occasionally stopping the medication to ensure the well being of the patient.
VIII. Important Precautions and Warnings
Precautionary Measures for Specific Populations
When healthcare professionals recommend Mosapride and Pantoprazole, they should take into account the health requirements of different groups. For example, people with liver or kidney issues might need dosage adjustments to avoid worsening their conditions. Moreover, individuals with a past of heart rhythm abnormalities need monitoring because Mosapride could potentially prolong the QT interval.
Pantoprazole vs Omeprazole
Omeprazole can be bought over the counter for adults with heartburn, whereas pantoprazole requires a prescription. Doctors often recommend omeprazole for infants and young children, while pantoprazole is preferred for children and adults. It's worth noting that omeprazole tends to have interactions with other medications compared to pantoprazole.
Lansoprazole vs Pantoprazole
While both medications fall under the category of PPI drugs Lansoprazole tends to work quickly and effectively than Omeprazole. A research study found that a dose of 30 mg of Lansoprazole was more successful, in reducing acidity and alleviating acid reflux symptoms compared to a 20 mg dose of Omeprazole.
Pantoprazole and Alcohol
Drinking alcohol does not interfere with the effectiveness of pantoprazole. It is advisable to limit alcohol consumption as it can lead to increased stomach acid production, potentially irritating the stomach lining and exacerbating symptoms.
Warnings Related to Long-term Use
Extended use of Pantoprazole over a period can result in various issues like low levels of vitamin B12, reduced magnesium, and elevated susceptibility to gastrointestinal infections and osteoporosis. It's important to assess the need, for continuing treatment to weigh the advantages against drawbacks.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Using Mosapride with medications that prolong QT interval or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors can raise the chances of experiencing severe heart related issues.
- Pantoprazole might lower the effectiveness of drugs whose absorption depends on stomach pH like ketoconazole, erlotinib and atazanavir. It's important to note that both medications should not be used in individuals with a known allergy to any ingredients, in their formulations.
IX. Special Considerations in Administration
Administration to the Elderly: Adjustments and Monitoring
The older adults might show sensitivity to both Mosapride and Pantoprazole so it's important to make precise dosage changes and watch out for side effects, like confusion and metabolic imbalances.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Guidelines
During pregnancy, Mosapride and Pantoprazole should be used only if the benefits outweigh the risks due to clinical data. Similarly, caution should be exercised when using these medications during lactation as they may pass into breast milk and impact the health of the newborn.
Pediatric Administration: Dosage and Safety Considerations
The safety and efficacy of Mosapride in children have not been confirmed. However Pantoprazole is suitable for treating patients with GERD but it should be administered according to weight and, with thorough consideration of potential long term side effects.
X. Handling Overdoses and Emergencies
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
In cases of overdose, signs to watch out for include restlessness, mental confusion, significant stomach upset, and indications of an imbalance in electrolytes. In some situations breathing difficulties and irregularities in heart rhythm may manifest.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
In case of an overdose, seek medical help. Supportive actions, like gastric lavage and giving activated charcoal, can be used to prevent absorption of the drugs. It's crucial to monitor and stabilize both respiratory functions during this time.
Long-term Management After Overdosage
After patients have stabilized it is important to keep an eye on them for any lasting impacts. Regular check ups may be necessary to address and reduce any harm that could affect the system or other parts of the body.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper Storage Conditions for Stability and Efficacy
Remember to store Mosapride and Pantoprazole at room temperature, keeping them away from light and moisture to ensure they remain effective. It's important to check the storage conditions to avoid any deterioration of the active components.
Handling Precautions to Ensure Safety
Healthcare providers and individuals should be cautious when handling these medications, keeping the packaging undamaged to prevent contamination and preserve the medication's effectiveness.
Disposal Recommendations for Unused Medication
It is important to dispose of any expired medications correctly to avoid harming the environment and accidental ingestion. Pharmacy take-back programs are a responsible way to get rid of them.
XII. Interaction with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Management
The chance of drug interactions is high because of how Mosapride and Pantoprazole work. It's important for patients to tell their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking to make sure it's safe to take them.
Impact of Antacids, Antibiotics, and Other Agents
Antacids can be taken together with Pantoprazole for relief from symptoms. Its important to space out their intake to prevent any interference, with absorption. Erythromycin, an antibiotic can boost the impact of Mosapride by slowing down its breakdown process, which may require adjusting the dosage.
Strategies to Minimize Interaction Risks
To reduce the chances of problems linked to drug interactions its recommended to keep a record of each patients medications routinely assess how well the medications work and their safety and make changes to treatments as needed depending on clinical assessment and how the patient is responding.