Navoban Infusion
- Introduction to Navoban Infusion
- Composition of Navoban Infusion
- Uses of Navoban Infusion
- How Navoban Infusion Works
- Dosage and Administration of Navoban Infusion
- Storage Guidelines for Navoban Infusion
- Potential Side Effects of Navoban Infusion
- Drug Interactions with Navoban Infusion
- Warnings and Precautions for Navoban Infusion
- Contraindications of Navoban Infusion
- Administration in Special Populations
- Handling Precautions for Navoban Infusion
- Overdosage of Navoban Infusion
- Key Considerations for Careful Administration
Navoban Infusion is a known medicine often used for its effectiveness in reducing feelings of nausea and vomiting. This specific medication has received praise in settings such as oncology and postoperative care.
Classification and Therapeutic Category
Navoban is categorized as a type of 5 HT₃ receptor antagonist. It is used in the field of treatment to effectively address symptoms that impact the overall well-being of patients.
Importance in Medical Treatment
Navoban plays a role in care, providing comfort to patients and helping maintain the effectiveness of vital treatments such as chemotherapy by mitigating severe side effects.
Brief History and Approval Status
Since its approval, in the early 20th century, Navoban has been, through extensive clinical trials, to confirm its safety and effectiveness. It is now widely accepted in healthcare networks worldwide holding onto endorsements.
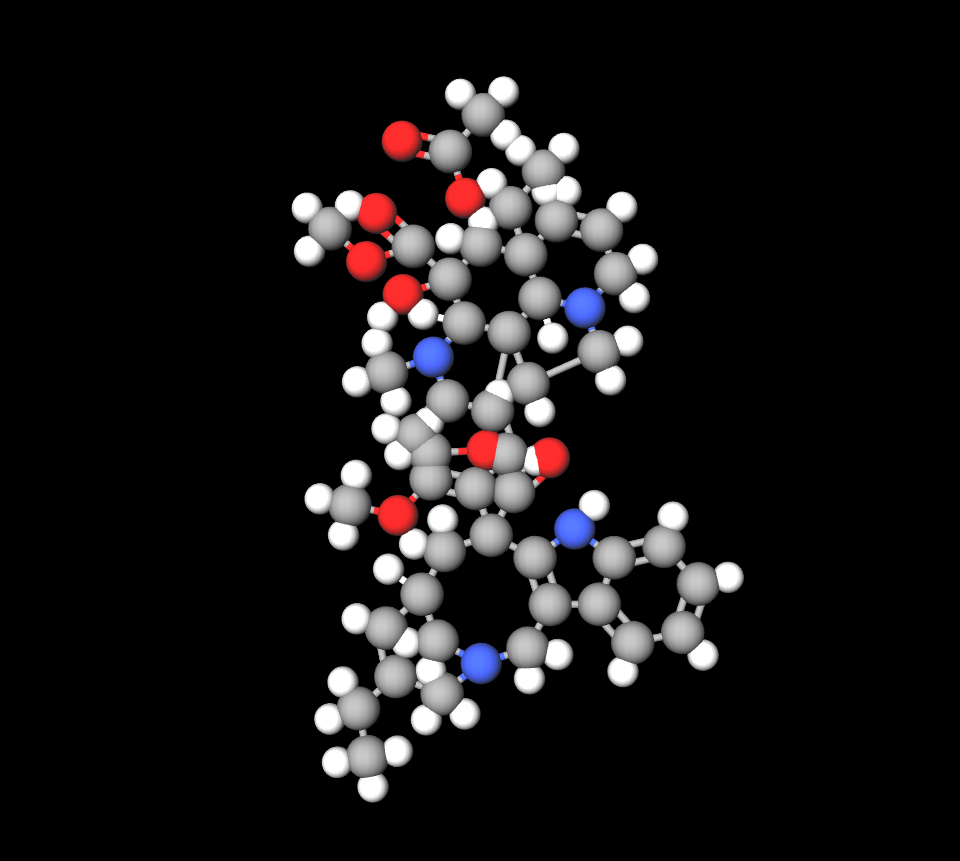
Active Ingredient and tropisetron structure
Navoban Infusion contains tropisetron hydrochloride as its ingredient, which functions by blocking activity at certain receptors to help lessen the urge to vomit.
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation Details
The active ingredient is accompanied by components, like sodium chloride and water, for injection to maintain stability and facilitate easy administration for infusion purposes.
Available Concentrations and Packaging
Navoban Infusion comes with strengths. It is usually packaged in either ampoules or vials to offer dosages tailored to specific clinical requirements.
Tropisetron vs ondansetron
In the hours following the surgery's completion, Ondansetron could potentially provide relief from intense nausea, whereas tropisetron might excel in lowering the frequency of nausea at a stage.
Primary Therapeutic Uses
Navoban Infusion is chiefly utilized in preventing and managing nausea and vomiting associated with:
Off-Label Uses
- Treatment of hyperemesis gravidarum
- Management of nausea during radiation therapy
- Potential application in cases of severe motion sickness

Tropisetron mechanism of action
Navoban works to reduce nausea by attaching to and blocking 5 HT₃ receptors found in both the peripheral nervous systems.
Impact on Serotonin Receptors
Blocking these receptors helps reduce the chain of reactions caused by the release of serotonin and is a factor in preventing nausea and vomiting.
Onset and Duration of Action
Tropisetron dosage
The standard dose varies based on the indication:
- CINV: 5 mg/day prior to chemotherapy
- PONV: 2 mg administered shortly before surgery
Administration Methods
Navoban is given through a vein for treatment purposes, with planned infusion methods to maintain a supply and reduce the risk of unwanted side effects.
Adjustments for Special Populations
- Elderly: Dose adjustments based on renal and hepatic function
- Pediatrics: Weight-based dosing to ensure safety
Optimal Storage Conditions
Remember to keep Navoban stored in a place below 25°C and away from sunlight; it's best not to refrigerate it unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Stability and Shelf Life
The item will stay in condition for two years, from the production date, as long as it is stored properly.
Instructions for Handling Opened Vials
Remember to use it after opening to avoid any contamination, and make sure to discard any leftovers that are not used.
Tropisetron side effects
Like with any medication there, Navoban might bring about some side effects, but usually they're not too severe and don't last long.
Common Side Effects

Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Allergic reactions, such as rash or anaphylaxis
- Cardiovascular complications, including arrhythmias
Commonly Interacting Medications
- Other serotonin-modulating agents
- Medications metabolized by the CYP450 system
Effect of Interaction on Efficacy and Safety
Using Navoban alongside medications could. Reduces its intended benefits and requires thorough assessment by healthcare professionals.
Guidelines to Avoid Adverse Interactions
Make sure to inform your doctor about all the medications you are currently taking and steer clear of using medicines that are known to extend QT intervals at the time.
Important Safety Warnings
Strict compliance with the recommended instructions is crucial when administering Navoban Infusion to minimize any risks involved in its use. This treatment should be strictly monitored by professionals and especially in patients with existing health conditions or undergoing treatments that could potentially interfere with its effectiveness. Regular evaluations are vital to guarantee the safety of the patients.

Monitoring Parameters During Treatment
During treatment with Navoban, close monitoring of vital signs and symptomatic changes is crucial. Key parameters include:
- Cardiac rhythm and blood pressure
- Liver function tests
- Signs of hypersensitivity reactions
Signs and Symptoms Warranting Immediate Discontinuation
Please stop using Navoban if patients show strong allergic reactions, like anaphylaxis or major changes in heart rhythm, or if they experience severe side effects such as constant vomiting or neurological issues that are difficult to manage.
Absolute Contraindications
Navoban Infusion is strictly contraindicated in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to tropisetron or any of its components
- Severe hepatic impairment
- History of drug-induced arrhythmias
Conditions Requiring Alternative Treatments
When dealing with blockages, in the system or untreated electrolyte imbalances consider focusing on different treatments first to prevent worsening these issues.
Precautionary Use in Specific Medical Histories
Patients with a history of QT intervals or bradyarrhythmias and those taking medications that affect levels should proceed with caution when starting treatment due to the potential risks involved.
Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
Specific Risks and Considerations
The older generation frequently shows changes in how their bodies process medications because their kidney and liver functions decrease with age, requiring attention to prevent any effects from occurring.
Adjustments in Dosage and Monitoring
The dosage needs to be customized for each person. It's important to assess how well the treatment is working and how well it's being tolerated by the individual's body. Being vigilant about monitoring kidney function is especially crucial in this group of people.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, Navoban should be used cautiously, weighing its benefits against risks as indicated by studies that show low teratogenic risks.
Recommendations for Breastfeeding
It is recommended for mothers who are nursing to either stop breastfeeding or avoid taking Navoban because the effects of excretion in breast milk have not been extensively researched.
Administration to Children
Age-Specific Guidelines and Safety Concerns
Pediatric dosages are typically calculated based on a child's weight to ensure safety and effectiveness are optimized for their needs, and the age range under 2 years old requires assessment before administration due to the lack of established safety and efficacy data in this age bracket.
Safe Preparation of Infusion
Ensure that the Navoban Infusion is prepared in conditions to avoid any contamination risks making sure that the equipment used for the infusion is sterile and suitable for the medication being administered.
Avoiding Contamination and Proper Disposal
Discard any leftover infusion immediately, as per the guidelines, when disposing of waste to reduce environmental risks.
Guidance for Healthcare Providers on Safe Use
Healthcare professionals should always wear gloves when dealing with Navoban Infusion to prevent contact with the skin or mucous membranes, and it is crucial to be well-versed in emergency procedures for accidental exposure.
Symptoms of Overdose
An overdose of Navoban can manifest as:
- Neurological effects: dizziness, confusion, and seizures
- Cardiovascular symptoms: tachycardia, hypotension, or arrhythmias
Immediate Management and Treatment Protocols
If someone takes much of the medication by mistake or on purpose and experiences an overdose situation, Stop giving the medication away and offer care to help them. Give activated charcoal if the person swallowed it not ago. Think about using ECG monitoring to check for heart issues.
Long-Term Follow-Up After Overdose Recovery
Patients who have had an overdose should have checkups to make sure there are no delayed impacts on their liver and heart functions.
Key Considerations for Careful Administration
Conditions Requiring Close Monitoring
Navoban Infusion requires caution in patients with:
- Pre-existing cardiac conditions, such as arrhythmias or heart failure
- Liver function impairment due to increased risk of toxicity
Adjustments for Concomitant Illnesses
Conditions that occur together, like kidney disease or imbalances in electrolytes, require dosing adjustments and regular lab tests.
Ensuring Patient Compliance and Understanding of Treatment
It is crucial to educate patients on the significance of following their treatment plans and being aware of any symptoms for successful recovery outcomes, as good communication between healthcare professionals and patients plays a vital role in guaranteeing safety and effectiveness.
Navoban Infusion FAQ
- Is tropisetron FDA approved?
- What are the benefits of tropisetron?
- What is the difference between Ondansetron and tropisetron?
- How long does tropisetron last?
- What are the side effects of tropisetron?
- What is the use of tropisetron injection?
- What are the contraindications for tropisetron?
- What class of drug is a tropisetron?
- What is the route of tropisetron?
- How long does tropisetron take to work?
- What is the half life of tropisetron?
- What are the benefits of tropisetron?
- What are the side effects of tropisetron?
- What is the bioavailability of tropisetron?
- Is tropisetron FDA approved?
- What are the benefits of tropisetron?
- What is the difference between Ondansetron and tropisetron?
- What are the side effects of tropisetron?
- What is the use of tropisetron injection?
- What are the contraindications for tropisetron?
- What is the route of tropisetron?
- How long does tropisetron take to work?
- What is the half life of tropisetron?
- What is the bioavailability of tropisetron?
Is tropisetron FDA approved?
Yes
What are the benefits of tropisetron?
Preventing nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy
What is the difference between Ondansetron and tropisetron?
In studies involving patient groups, it has been found that Ondansetron is the first member of its class and has a short elimination half-life while being effective in its action. Tropisetron is another 5 HT₃ receptor blocker, with an elimination half life compared to ondasentron.
How long does tropisetron last?
24hrs
What are the side effects of tropisetron?
Some individuals may experience feelings of dizziness or fatigue when taking this medication.
What is the use of tropisetron injection?
Medication is prescribed to alleviate feelings of sickness and queasiness resulting from cancer therapy.
What are the contraindications for tropisetron?
Patients with managed blood pressure should avoid taking medications that affect heart rhythm or may prolong the QT interval due to potential risks during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
What class of drug is a tropisetron?
Class of serotonin (5HT3) antagonists
What is the route of tropisetron?
The primary way tropisetron is broken down is through hydroxylation, followed by sulfation and glucuronidation of the resulting metabolites.
How long does tropisetron take to work?
The highest level of plasma concentration is reached within three hours.
What is the half life of tropisetron?
After receiving tropisetron through injection or by mouth, its half-life in the body was 6 hours.
What are the benefits of tropisetron?
preventing nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy
What are the side effects of tropisetron?
Constipation, as occasional occurrences of dizziness and fatigue, may be experienced. Other potential side effects include drowsiness and gastrointestinal issues like stomach pain or changes in appetite.
What is the bioavailability of tropisetron?
Tropisetron taken orally is absorbed into the bloodstream with an approximate bioavailability of 60%.
Is tropisetron FDA approved?
Yes
What are the benefits of tropisetron?
Preventing nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy
What is the difference between Ondansetron and tropisetron?
The first member of this group is Ondansetron, which has a period for elimination from the system, and its effectiveness has been proven through studies involving diverse patient groups. Tropisetron is another 5 HT₃ receptor blocker that stays in the body longer compared to ondanestron's elimination life.
What are the side effects of tropisetron?
Some individuals may experience drowsiness or lassitude as a side effect of this medication.
What is the use of tropisetron injection?
A medication prescribed to alleviate nausea and vomiting triggered by cancer therapy
What are the contraindications for tropisetron?
Patients with blood pressure and heart rhythm issues should avoid taking medications that lengthen the QT interval, during pregnancy, or while breastfeeding.
What is the route of tropisetron?
The primary way tropisetron is broken down is through hydroxylation, followed by sulfation and glucuronidation of the resulting metabolites.
How long does tropisetron take to work?
The highest level of the drug in the bloodstream is reached after three hours.
What is the half life of tropisetron?
After receiving tropisetron through injection or oral intake, the drug's remaining half-life was 6 hours in the body.
What is the bioavailability of tropisetron?
Tropisetron taken orally is absorbed into the bloodstream with a bioavailability of approximately 60%.










