Novalgin
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Novalgin
- III. How Novalgin Works
- IV. Dosage and Administration
- V. Composition of Novalgin
- VI. Side Effects
- VII. Common Side Effects
- VIII. Off-label Use of Novalgin
- IX. Interactions with Other Drugs
- X. Warnings
- XI. Contraindications
- XII. Careful Administration and Monitoring
- XIII. Important Precautions
- XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
- XV. Overdosage
- XVI. Storage
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
A brief account of the origins and discovery of Novalgin: Novalgin, also known as metamizole, was first introduced in the century. It quickly gained recognition within the community due to its ability to relieve pain. As time went on, Novalgin became a medication in countries' pharmacopeias.
Its medical classification and significance in pain management: Categorized as an opioid analgesic, Novalgin plays a vital role in managing pain, particularly for individuals seeking relief from mild to moderate discomfort without the strong effects of opioids. Additionally, it has been found effective in reducing fever, giving it a dual-purpose role as an agent.
II. Uses of Novalgin
Novalgin is a medication that is typically prescribed for conditions such as post-operative pain, toothache, headache, and dysmenorrhea. It is also suitable for fever management 1. The following are the primary indications for prescription:
- Post-operative pain relief
- Toothache and headache mitigation
- Dysmenorrhea management
- Fever reduction
Novalgin acts swiftly, providing rapid relief. Its dual properties offer both pain alleviation and fever reduction, providing a holistic therapeutic approach 1.
Here are the HTML links to the references:
III. How Novalgin Works
How Novalgin works in the body: Novalgin primarily acts by inhibiting the COX enzymes, which are responsible for hindering the production of prostaglandins. These molecules play a role in mediating pain and fever in the body.
Comparisons with pain relievers: Although other analgesics like paracetamol function similarly, Novalgin is often preferred for its more substantial anti-inflammatory effects. However, it's essential to use Novalgin due to its potency and associated risks, unlike accessible, over-the-counter remedies.
IV. Dosage and Administration
Dosage recommendations may vary depending on the age, weight, and severity of the patient's condition. Generally, adults are prescribed dosages compared to patients.
For adults, the recommended dosage is 500 1000mg taken up to three times a day. In the case of children, the dosage is adjusted based on their weight and age.
The administration methods for Novalgin include intake, intramuscular injection, or intravenous infusion as determined by requirements and physician advice.
Several factors, such as age, kidney and liver function, and concurrent medications, can influence the need for adjusting the dosage.
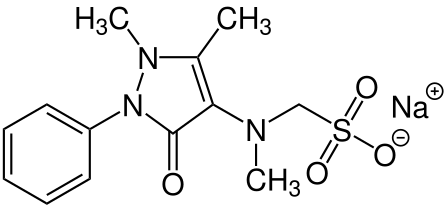
V. Composition of Novalgin
Inactive components: Novalgin contains metamizole sodium as its ingredient. The formulation of Novalgin involves procedures to guarantee its purity and effectiveness. After synthesis, the active ingredient is combined with excipients, including starch, magnesium stearate, and specific dyes. Stringent quality control evaluations are then conducted to ensure the product's standards.
VI. Side Effects
An overview of the side effects; Although Novalgin is effective it does have some side effects. These can range from stomach issues to severe allergic reactions.
Differentiating between rare side effects: Common side effects may include feeling nauseous or experiencing skin rashes. On the hand, rare but more severe side effects could involve agranulocytosis, which is a significant decrease, in white blood cells.
VII. Common Side Effects
Here is a list of reported side effects;
Feeling
Experiencing dizziness or vertigo
Developing mild rashes on the skin
Experiencing discomfort in the abdomen
To manage and alleviate these side effects it's important to note that most of them are temporary and will go away on their own without any intervention. However, if the symptoms persist, it is advisable to consult with a professional. Additionally ensuring that you take the dosage as prescribed and following the guidelines provided can also help minimize these effects.
VIII. Off-label Use of Novalgin
Clinicians sometimes prescribe Novalgin for conditions beyond its approved indications, such as specific neuralgias or chronic pain disorders. Such prescriptions stem from empirical observations and individual patient needs 1.
While there is sparse research on Novalgin’s off-label use, some anecdotal evidence and smaller-scale studies hint at its potential in off-label scenarios, necessitating further comprehensive research 2.
Here are the HTML links to the references:
1: Meds Safety Home 2: PubMed Central
IX. Interactions with Other Drugs
Here are some medications that can potentially interact with Novalgin;
Other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Anticoagulants
Alcohol
antihypertensives
It's essential for physicians to carefully review a patient's complete medication regimen to avoid any possible drug interactions. Taking the precautions is vital.
X. Warnings
Instances where it is essential to be careful; Individuals who have previously experienced hypersensitivity reactions, particular blood disorders, or significant impairments, in kidney and liver function should exercise caution.
Recommendations for monitoring while undergoing Novalgin treatment; Regularly conducting blood tests assessing liver and kidney function and maintaining an approach towards hypersensitivity can enhance safety during the administration of Novalgin.
XI. Contraindications
Health conditions and situations where Novalgin should not be used; Novalgin, although it can benefit people, may not be suitable, for everyone. Individuals with a known allergy or sensitivity to metamizole or any of its components those with metabolic disorders like intermittent porphyria and individuals with specific blood disorders should avoid using Novalgin.
Individuals who have a known allergy or sensitivity to metamizole
Those affected by porphyria
People with specific blood dyscrasias
Alternative pain management options for individuals, with these contraindications include paracetamol, ibuprofen or other non NSAID pain relievers. However, it is essential to consult a physician before considering any medication.
XII. Careful Administration and Monitoring
Steps to ensure administration; The proper use of Novalgin involves following the recommended dosage avoiding the use of contraindicated medications at the time, and promptly reporting any side effects.
The significance of health monitoring during treatment; Consistent health checkups, which include blood tests and evaluations of liver function are crucial for ensuring that the medication has an impact on the body and, for the timely identification of any possible complications.
XIII. Important Precautions
1. It is crucial to adhere to the dosage.
2. Refrain from consuming alcohol while undergoing treatment.
3. If you experience dizziness it is advisable to avoid driving or operating machinery.
4. Patients with a history of hepatic disorders those taking medications simultaneously, and individuals experiencing unusual symptoms should be closely monitored and may require dosage adjustments.
Please note that these guidelines are essential for your well-being and should be followed diligently throughout your treatment.
XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
Elderly; Considering how medications may work in individuals it might be necessary to adjust dosages. It becomes essential to monitor function tests due to the decline in kidney function that often occurs with age.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: The safety of Novalgin during pregnancy is still uncertain based on research. Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate the benefits versus risks. For nursing mothers deciding whether to stop breastfeeding or continue taking the medication depends on how important the drug are for the mother's well-being.
Children: Extra caution should be taken when administering medications to children. Age dosages must be tailored according to their body weight and overall health condition. Parents should also remain observant of any side effects, such as disturbances, in the system.
XV. Overdosage
Signs and indications of an overdose of Novalgin; An overdose may present as feelings of nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, disturbances, in kidney and liver function, or in cases conditions such as agranulocytosis.
What to do immediately and treatment options; If an overdose occurs it is crucial to seek assistance. Standard therapeutic approaches involve procedures like stomach pumping and administration of activated charcoal. Providing treatment.
XVI. Storage
To ensure the storage of Novalgin, it is recommended that you keep it in a dry location away from direct sunlight. The temperature should be maintained below 25°C.
When storing Novalgin and preserving its effectiveness, remember to keep it where children and pets cannot access it. It's essential to dispose of any expired medication as its efficacy decreases over time.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Here are the revised instructions for handling and disposal. It's essential to handle the tablets with your hands and tighten the bottle cap after use securely. If you have expired or unused medication, it's best to dispose of it. You can do this by participating in take-back programs or following the pharmacist's guidance.
Let's also consider the impact: Indiscriminate disposal of medications can be harmful, to our environment. To prevent any harm, please avoid flushing the drug down the toilet or pouring it into drains unless instructed otherwise.












