Ornidazole
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Ornidazole
- III. How Ornidazole Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Ornidazole
- V. Off-label Uses of Ornidazole
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Ornidazole
- VII. Side Effects of Ornidazole
- VIII. Drug Interactions with Ornidazole
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Special Considerations for Administration
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Brief Overview of Ornidazole
Ornidazole is a highly effective antimicrobial medication widely used to treat infections caused by protozoa and anaerobic bacteria. This drug belongs to the five nitroimidazole class and has been proven to manage diseases like amoebiasis, giardiasis, and trichomoniasis effectively.
B. Historical Development and Approval
Ornidazole, initially synthesized in the late 1960s was developed with the goal of creating powerful antimicrobial agents, following rigorous clinical trials. Its safety and effectiveness were validated. Multiple health authorities worldwide including the esteemed World Health Organization (WHO) have since approved Ornidazole as an essential medicine.
C. Role in Modern Medicine
Given the escalating concern surrounding antimicrobial resistance, Ornidazole has emerged as an indispensable asset in modern medicine. It is pivotal in effectively managing infectious diseases caused by protozoa and anaerobic bacteria while demonstrating notable efficacy and tolerability. Additionally, its usage extends to surgical prophylaxis for procedures with an elevated anaerobic infection risk.
II. Composition of Ornidazole
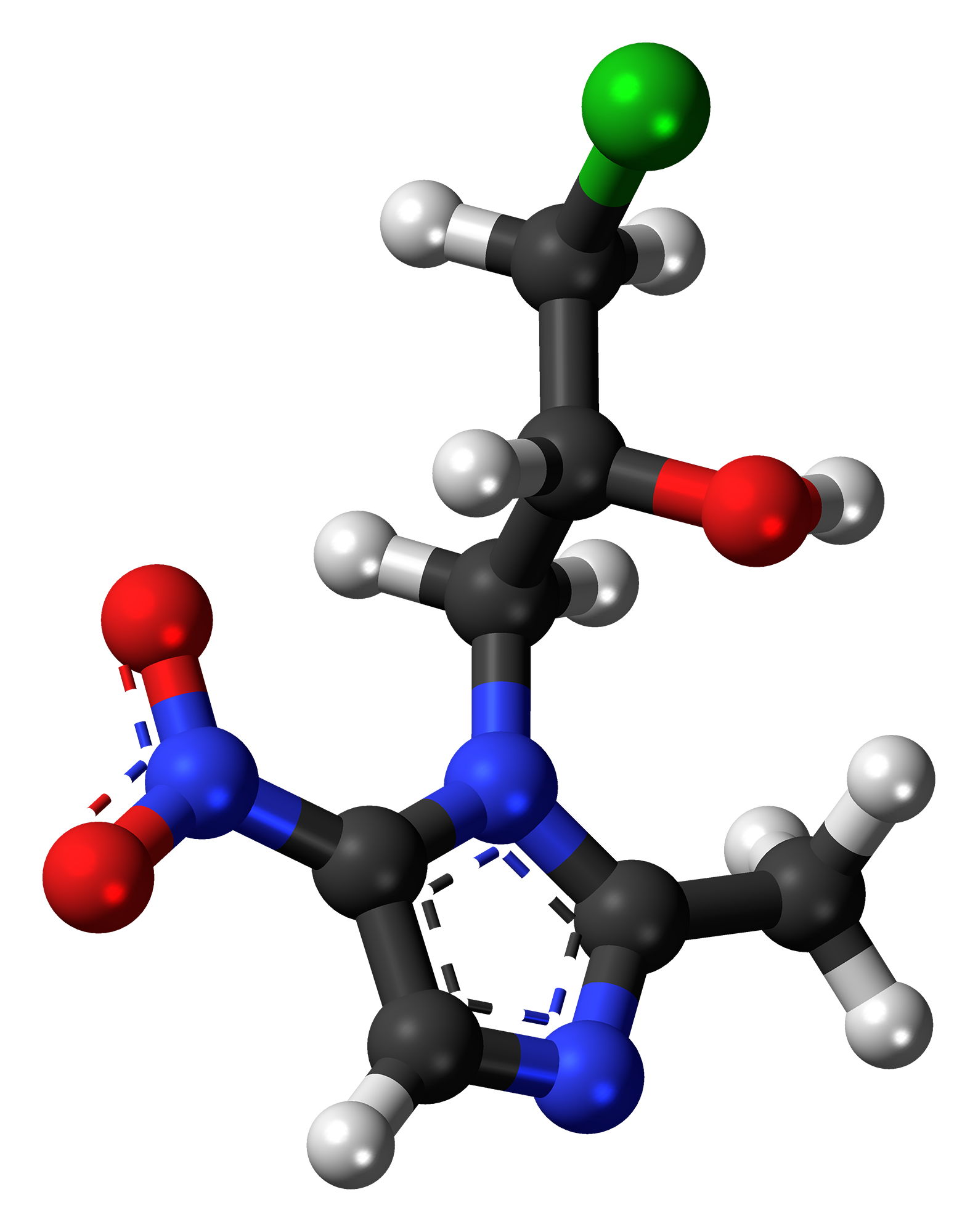
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Ornidazole's unique chemical structure features a five-nitroimidazole ring as its backbone. This particular structure is vital to its antimicrobial effects as it facilitates the interference of DNA synthesis in invading microorganisms. With a molecular weight of 219.15 g/mol, this compound demonstrates moderate solubility in water.
B. Active and Inactive Ingredients
The active ingredient found in Ornidazole is the ornidazole molecule itself. This molecule is known for its ability to penetrate bacterial cells and disrupt their DNA synthesis, enabling it to provide therapeutic effects. In addition to the active ingredient, several inactive ones are present in the formulation. These inactive ingredients, also known as excipients, are essential in ensuring the drugs' stability, effectiveness, and ease of administration. They can include binders, disintegrants, lubricants, and coating agents. All of these components work together harmoniously to optimize the drugs' performance.
III. How Ornidazole Works
A. Mechanism of Action
In its chemical makeup, ornidazole operates within organisms afflicted by infection by possessing an essential constituent called the nitro group. This antibiotic engages with intracellular enzymes that undertake reduction processes upon administration, giving rise to reactive compounds as a pivotal outcome. Subsequently, these biologically active agents harm bacterial DNA by inhibiting synthesis activities crucial for replication. In essence, ornidazole effectively restrains bacterial multiplication while thwarting their overall growth trajectory through this intricate mode of action.
B. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
Upon oral administration, Ornidazole is quickly and thoroughly absorbed. You are demonstrating exceptional bioavailability. Furthermore, it is extensively distributed throughout the body, achieving therapeutic levels in most tissues. It is worth mentioning that it has the ability to penetrate the central nervous system and attain cerebrospinal fluid concentrations equivalent to those found in plasma. The liver plays a significant role in metabolizing Ornidazole, but this process renders the resulting metabolites devoid of antimicrobial activity. Finally, the drug is eliminated through the kidneys with a half-life ranging from approximately 12 to 14 hours.
IV. Approved Uses of Ornidazole
A. Use in the Treatment of Protozoal Infections
Ornidazole is an antiprotozoal medication that has shown remarkable effectiveness in treating severe conditions such as Amoebiasis caused by the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica and can be life-threatening. Additionally, it has proven effective in addressing Giardiasis, an infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellate protozoan Giardia lamblia. Furthermore, Ornidazole is a valuable treatment for Trichomoniasis, a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. This exceptional efficacy is due to its ability to impair DNA synthesis in these parasites, thus impeding their growth and proliferation.
Here are some references for you:
2. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research
3. Indian Journal of Pharmacology
B. Use in the Management of Anaerobic Bacterial Infections
In addition to its efficacy against protozoal infections, Ornidazole holds great potential as a treatment for various anaerobic bacterial infections. These include Bacteroides infections that often manifest as abdominal cavity issues, pelvic area complications, or skin ailments. Clostridium infections that commonly arise from conditions such as gangrene, tetanus, and botulism can be effectively addressed with Ornidazole. Furthermore, the ability of Ornidazole to target bacterial synthesis helps combat these anaerobic pathogens, making it an invaluable component of the therapeutic armamentarium.
Here are some references for you:
2. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research
3. Indian Journal of Pharmacology
C. Role in Surgical Prophylaxis
In surgical prophylaxis, Ornidazole is vital in guarding against anaerobic infections commonly arising from specific procedures. By administering Ornidazole beforehand, particularly with colorectal and gynecological surgeries, clinicians can effectively diminish the potential for postoperative infections.
Here are some references for you:
2. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research
3. Indian Journal of Pharmacology
V. Off-label Uses of Ornidazole
A. Investigational Use in Crohn's Disease
Ornidazole has been studied for its potential use in Crohn's disease, a chronic inflammatory condition primarily affecting the gastrointestinal tract. The disease has been linked to an imbalanced gut microbiota. Ornidazole's antimicrobial properties could offer therapeutic benefits in this context. However, additional research is needed to fully understand its role in treating Crohn's disease.
Here are some references for you:
2. Mayo Clinic
3. Mayo Clinic
4. Wikipedia
B. Potential Role in Periodontitis Treatment
Periodontitis is a severe gum infection that causes damage to the soft tissue and leads to the loss of bone supporting the teeth. Ornidazole has caught considerable attention for its potential use in treating periodontitis. Initial research indicates that Ornidazole when used in conjunction with other therapies, could potentially aid in controlling the bacterial imbalance responsible for this condition.
Here are some references for you:
1. DrBicuspid
2. Perioiap
3. Mayo Clinic
C. Use in Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Ornidazole has demonstrated potential in treating infections caused by Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium associated with gastric ulcers and stomach cancer. By incorporating Ornidazole into combination therapy, it can aid in the elimination of this formidable pathogen and assist in the management of related illnesses.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
2. PubMed
3. Wikipedia
VI. Dosage and Administration of Ornidazole
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before initiating Ornidazole treatment. The recommended dosage depends on the specific condition under consideration in cases of amoebiasis in adults. A regimen of 1.5g taken once daily for three days is typically advised, whereas individuals affected by giardiasis or trichomoniasis may be prescribed a single dose of 1.5g. It should be noted that these dosage instructions are general guidelines. And individual circumstances such as overall health and infection severity should also be considered.
B. Dosing Adjustments in Special Populations
Special populations include the elderly, children, and individuals with renal or hepatic impairment. It may require modifications in the dosing of Ornidazole. For instance, when it comes to children. Their dosage is typically determined by taking their body weight into account. Similarly, individuals with liver disease may need a lower dosage to avoid the buildup of the drug in their system. The crucial aspect is developing personalized treatment strategies that maximize therapeutic results while minimizing potential adverse effects.
C. Instructions for Safe and Effective Use
For the utmost safety and efficacy when using Ornidazole, it's crucial that patients respect these guidelines: Be sure to consistently take the medication exactly as directed by your healthcare provider. Under no circumstances should treatment be discontinued prematurely without first consulting with a healthcare provider - even if symptoms appear to improve. If a dose has been missed, promptly take it as soon as you remember; however. If your next scheduled dose is near, it would be wise to skip the missed one instead. It's essential that overdosing is avoided at all costs; in any suspected case of an overdose seeking immediate medical attention becomes imperative.
VII. Side Effects of Ornidazole
A. Common Side Effects: Nausea, Headache, Dry Mouth
Ornidazole. Like any other medication. Is known to have potential side effects—these commonly experienced effects, such as nausea, headache, and dry mouth. Often fade away as the body adapts to the medication. It is important to note that in most cases, these side effects do not necessitate medical intervention unless they endure or worsen over time.
B. Serious Side Effects: Seizures, Neuropathy, Severe Skin Reactions
Although its rarity as an adverse effect of Ornidazole usage cannot be overlooked, its capability to cause significant side effects such as seizures, neuropathy (nerve damage), and severe skin conditions demands immediate medical attention. Seizures take form in uncontrollable shaking movements, whereas manifestations tied to neuropathy include feelings of numbness or tingling within body extremities . Concurrently, harsher skin reaction(s) can also provoke noticeable changes like rashes, itching, or swelling.
C. Management and Mitigation of Side Effects
To ensure effective management of side effects, It is essential to adhere to the instructions provided by healthcare providers closely. Any adverse effects that arise should be promptly communicated to a healthcare professional for appropriate attention and assistance. Furthermore properly hydrating oneself and consuming the medication alongside meals can alleviate gastrointestinal side effects like nausea.
VIII. Drug Interactions with Ornidazole
A. Potential Interactions with Other Antimicrobials
Ornidazole has the potential to interact with other antimicrobials, which could result in changes to the effectiveness of the drugs or an increase in side effects. For instance, when used concomitantly with warfarin another antimicrobial. There is a possibility of enhancing the blood thinning effect. As a result, close monitoring of coagulation parameters is necessary.
B. Effect on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
Ornidazole, being a part of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, has the potential to impact the metabolism of other drugs processed by this system, as a result. It can alter the plasma levels and effectiveness of these drugs. Therefore, Informing your healthcare provider about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and dietary supplements is important.
C. Safe Use with Alcohol and Food
Maintaining abstinence from alcohol consumption is vital when undergoing treatment with Ornidazole, as it could result in unfavorable effects like nausea, vomiting, and an accelerated heartbeat. Although there are no known food interactions related to this medication, explicitly ingesting Ornidazole alongside a meal can aid in diminishing any potential discomfort experienced in the gastrointestinal region.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. General Warnings: Liver Disease, Nervous System Disorders
Patients with liver disease and nervous system disorders should take special care when using Ornidazole. The presence of liver disease may hinder the body's ability to break down the drug resulting in its build-up in the body. In addition, Ornidazole has possible side effects, such as seizures and neuropathy, that can worsen neurological disorders.
B. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, First Trimester of Pregnancy
It is important to note that individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Ornidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives should avoid its use as it may lead to unpleasant reactions such as itching, rashes, swelling, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing. Additionally, Ornidazole should not be taken during the first trimester of pregnancy due to potential risks it may pose to the developing fetus.
C. Careful Administration with Other Health Conditions
Patients with specific health conditions, such as kidney disease, blood disorders, or a history of seizures are advised to consult with their healthcare provider before starting treatment with Ornidazole. It is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment by carefully adjusting the dosage and closely monitoring the patient's progress.
X. Special Considerations for Administration
A. Administration to Elderly: Dose Adjustments, Monitoring
Special consideration may be needed for elderly patients because of the physiological changes that occur with aging, such as reduced organ function. These changes can impact the way Ornidazole is processed in the body requiring adjustments to the dosage. It is also important to closely monitor elderly patients to promptly detect and address any potential adverse effects.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Benefits
Ornidazole should be used by pregnant women, particularly those in the early stages of their pregnancy. And nursing mothers only if the potential benefits of the medication outweigh any potential risks. However, studies conducted on animals have not shown any teratogenic effects. There is a lack of sufficient and well-controlled studies on pregnant women. Likewise, they are considering that Ornidazole is excreted in breast milk. It is essential to exercise caution when giving it to nursing mothers.
C. Administration to Children: Safety and Efficacy
Ornidazole is considered a secure and efficient option for children if given in the correct dosage based on their body weight. Nonetheless, healthcare providers must oversee its usage closely. Similar to any medication, it is essential to thoroughly observe children for any potential adverse effects while undergoing treatment.
D. Overdosage: Symptoms, Management, and Prevention
When an individual surpasses the recommended intake of Ornidazole unknowingly or unintentionally – whether due to negligence or miscalculation – they may manifest assorted signs indicating excessive consumption, including dizziness, nausea, vomiting as well as convulsions, consequently, having any inkling of an overdose should prompt an immediate insistence on seeking medical care to forestall any potential complications that might arise from that place. Amidst handling a case of Ornidazole overdosage, it is pivotal that supportive measures be taken adeptly to address both symptom management and the sustenance of vital physiological functions. To mitigate any chances of experiencing said overshoot, it would be judicious, on behalf of patients or caregivers alike, to meticulously abide by officially directed guidelines regarding administration while assuring secure storage conditions beyond juveniles' access.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Proper Storage Conditions for Ornidazole
It is essential to store Ornidazole properly to ensure its effectiveness. At room temperature, the recommended storage temperature is between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius, away from direct light and moisture. Additionally, it is essential to keep the drug out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion. Storing the medication in a bathroom cabinet should be avoided due to the high humidity levels that can impact its strength.
B. Precautions for Safe Handling and Disposal
Adhering to standard safety guidelines applicable to medications is crucial when handling Ornidazole. This includes neither sharing this medication with others nor using it off-label but strictly as directed by healthcare professionals. Furthermore. Once no longer necessary or past its expiration date. Ornidazole should not be disposed of via wastewater or general household trash bins. To guarantee safe disposal while protecting others' welfare and preserving our environment's integrity returning Ornidazole to designated drop-off points at pharmacies or contacting local waste disposal services is strongly recommended.
XII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Ornidazole's Medical Importance
Conquering anaerobic bacterial and protozoal infections has been greatly aided by the remarkable advancements of Ornidazole. This drug has become an essential component of modern medicine. They are playing a crucial role in combating these infections. However, caution must be exercised due to potential side effects when administering ornidazole responsibly under medical supervision. It offers substantial therapeutic advantages. Dosage, contraindications, and administration are expertly customized to meet each patient's unique needs and conditions to ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
B. Potential Future Developments in Ornidazole Research
Preliminary investigations suggest that the therapeutic implications of Ornidazole might surpass its existing applications. Ongoing research is shedding light on its potential effectiveness in managing conditions like Crohn's disease and Helicobacter Pylori infection and hinting at its remarkable adaptability. With a growing understanding of its pharmacology, we can expect further elucidation and the identification of unexplored therapeutic avenues for Ornidazole usage. Consequently, this progress holds promise for enhancing patient outcomes and expanding our arsenal against infectious diseases.



















