Polycarbophil
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition
- III. How it Works
- IV. Uses
- V. Off-label Use
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interactions
- X. Warning
- XI. Contraindication
- XII. Careful Administration
- XIII. Important Precautions
- XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
- XV. Overdosage
- XVI. Storage
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Historical context and discovery
The history of development is filled with breakthroughs that have significantly impacted medical research. Polycarbophil, although not widely recognized, has a role in this story. Looking back at its origins, Polycarbophil was first introduced as a polymer with promise in drug delivery and long-lasting formulations.
Importance in modern medicine
Polycarbophil has become a component in the modern field of medicine. Its diverse uses, from delivering medication to providing relief for constipation, highlight the impact of past innovations on today's medical treatments.
II. Composition
Chemical structure and properties
Polycarbophil has a molecular structure that consists of polyacrylic acid, which gives it the ability to absorb water and become hydrophilic. This unique property and its cation exchange capacity make it valuable in various pharmaceutical applications. It also has a high molecular weight, which adds to its structural strength. In terms of solubility, Polycarbophil has a limited ability to dissolve in water, which's vital for its ability to form hydrogels. Additionally, it shows stability under different pH conditions, making it versatile for use in various scenarios.
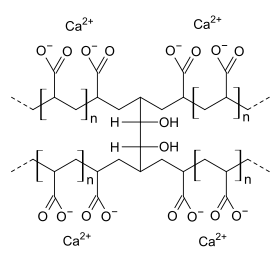
Active and inactive components
The effectiveness of Polycarbophil mainly comes from its ingredient, the polyacrylic acid structure. Additionally, it includes some components that serve as stabilizers or excipients. These components help improve the formulation properties of Polycarbophil, although they don't directly contribute to its effects.
III. How it Works
Mechanism of action in the human body
The way Polycarbophil works is quite intriguing. When you take it orally, it functions as a laxative that helps add bulk to your stool. Its ability to absorb water, due to its nature, increases the size of the stool and encourages movement in the intestines. This not helps relieve constipation but also maintains a healthy gut environment.
Cellular interactions and effects
At this level, Polycarbophil interacts with the cells in the intestines regulating how they absorb water. Maintaining this balance is essential for promoting healthy bowel movements. It also affects the microorganisms in the gut, supporting the gastrointestinal system overall.
IV. Uses
Primary indications and therapeutic applications
The primary use of Polycarbophil is in treating conditions. It primarily works as a yet effective laxative to relieve constipation. Additionally, it helps balance the gut environment, which can help alleviate diarrhea. Polycarbophil can also be used as a therapy for stomach ulcers providing relief from associated symptoms.
References:
- Calcium Polycarbophil - Uses, Side Effects, and More - WebMD1
- Polycarbophil Oral Tablet | Cleveland Clinic2
- Polycarbophil Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com3
Benefits in managing specific conditions
The advantages of Polycarbophil go beyond relieving symptoms. It helps restore the balance in the gut, promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, and ensures that nutrients are absorbed optimally. Many patients have noticed improved digestion, less bloating, and better regularity in bowel movements.
References:
- Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: major fermentation products and their impact on host health - Microbiome1
- The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Host Metabolism Through the Regulation of Gut Hormone Release - Frontiers in Physiology2
- IBS Supplements: Fiber, Probiotics, Prebiotics, and More - WebMD3
V. Off-label Use
Emerging research and applications
The potential applications of Polycarbophil continue to broaden with research. Emerging evidence supports its use in areas including weight management, modulation of metabolic syndrome, and even in specific dermatological preparations.
References:
- Cardiovascular risk and obesity | Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome1
- Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Psoriasis Treatments in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome - Dermatology and Therapy2
- Metabolic syndrome - Diagnosis & treatment - Mayo Clinic3
Case studies supporting off-label usage
There have been real-life stories and medical case studies that emphasize the versatility of Polycarbophil. For example, one study discussed how it could help with feeling full, making it a potential addition to weight management plans. Another interesting case showed how it can be used as a gel to relieve skin conditions.
References:
- Polycarbophil Gel - Amazon.com1
- Polycarbophil Uses, Side Effects & Warnings - Drugs.com2
- Replens Reviews: What’s the Deal with Vaginal Moisturizers? - Healthline3
VI. Dosage and Administration
General dosage guidelines
The proper dosage is crucial to guarantee effectiveness and safety. For adults, the recommended dose usually falls within 1 to 4 grams. It's best to take it with plenty of water to ensure gel formation in the intestines and achieve the desired therapeutic outcome.
Factors influencing dosage
It is essential to understand that there is no solution for everyone. Adjusting the dosage may be necessary depending on factors; 1. Weight; heavier Individuals might need a higher dose. 2. Age; Elderly patients may have pharmacokinetic profiles. 3. Medical condition; Having medical conditions can affect the required dosage. It's crucial to consider these factors when determining the dosage for each individual.
Mode of administration and best practices
The recommended way to take Polycarbophil is by swallowing it with a glass of water. It's essential to follow the instructions, avoid using it for an extended period without medical supervision, and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
VII. Side Effects
Understanding potential risks
Although Polycarbophil is generally well tolerated, it is not, without its risks. Some people may encounter digestive discomfort, bloating, or even an allergic response.
Physiological effects of prolonged use
Excessive and prolonged intake, without proper medical supervision, may cause imbalances in the gut environment. This could lead to issues with absorbing nutrients or having an altered gut microbiome. It highlights the importance of evaluation and careful usage.
VIII. Common Side Effects
List and description of most reported side effects
In pharmacology, despite the development of treatments, it cannot guarantee complete immunity to side effects. While polycarbophil is generally considered safe, some individuals have experienced discomfort such as bloating, gas, or a sensation of fullness. Mild and temporary stomach cramps have also been reported. In some cases, allergic reactions like rashes, itching, or swelling may occur, especially in areas, like the face, tongue, or throat.
Management and mitigation techniques
To effectively manage these incidents, it is vital to take a two-fold approach: proactive and reactive in mitigation. Most gastrointestinal side effects can be avoided by ensuring water intake, adjusting dosage as needed, and maintaining a balanced diet. In the case of reactions seeking immediate medical assistance is crucial.
IX. Interactions
Drugs and substances that interact with Polycarbophil
Sometimes the effectiveness of a drug can be affected by interactions. In the case of Polycarbophil, some substances and medications can interfere with its therapeutic benefits. For example, Antacids, those that contain aluminum and magnesium. Other laxatives; Using them at the same time might enhance the laxative effect.
Potential effects of these interactions
These interactions have the potential to reduce the effectiveness of polycarbophil benefits, cause imbalances in electrolytes, or worsen gastrointestinal symptoms. When a patient is well informed, they can navigate these challenges. Maintain the integrity of their treatment.
X. Warning
Critical alerts for patients and healthcare professionals
Being cautious is crucial when it comes to pharmacotherapy. Although Polycarbophil plays a role in maintaining gastrointestinal balance, certain warning signs require immediate attention; 1. Persistent symptoms; If constipation or diarrhea persists for more than a week without any improvement, it is essential to seek medical advice promptly. 2. Allergic reaction; If you experience a severe allergic reaction, it is imperative to seek immediate medical attention without any delay or negotiation.
Situations where Polycarbophil should be avoided
If there are bowel obstructions, upcoming surgeries, or a known history of hypersensitivity to the drug, it is not recommended to use it.
XI. Contraindication
Medical conditions incompatible with Polycarbophil
It is essential to exercise caution in pharmaceuticals and know when it is not appropriate to administer a drug. In the case of Polycarbophil, there are situations where its usage should be avoided. For instance, 1. Bowel Obstructions; It is not recommended as its laxative properties may worsen the condition. 2. Severe Dehydration; Its usage can further complicate the existing dehydration condition.
Potential risks of ignoring contraindications
Ignoring these contraindications can lead to gastrointestinal problems, worsen dehydration, and in rare cases cause systemic consequences.
XII. Careful Administration
Best practices for safe use
To achieve the treatment results, following the prescribed instructions carefully is crucial. This includes taking the recommended doses, drinking water alongside them, and regularly evaluating how well the treatment works.
Monitoring parameters and routine checks
As part of monitoring, it's essential to observe the consistency of bowel movements, check for proper hydration, and ensure no signs of allergies.
XIII. Important Precautions
Protective measures to ensure patient safety
Ensuring the safety of patients goes beyond monitoring their therapy. It involves educating patients about side effects recognizing signs of overdose, and emphasizing the significance of maintaining open communication with their healthcare provider.
Guidelines to avoid misuse or over-reliance
Polycarbophil, like any other medication, should be used with caution. It is essential to seek supervision when using it for an extended period, avoid increasing the dosage without consulting a healthcare professional, and refrain from relying on it as a cure-all for all gastrointestinal issues. Misusing Polycarbophil can have consequences.
XIV. Administration to Specific Populations
a. Administration to the Elderly
Due to changes in their body's response to medications, older patients may need a treatment approach.
Adjusted dosages and potential risks
Reducing the dosage becomes essential when considering decreased metabolism and related health conditions. Risks include increased susceptibility to side effects and the possibility of drug interactions due to multiple medications being taken simultaneously.
Monitoring and special considerations
It is essential to monitor the functioning of the digestive system, hydration levels, and kidney function. Moreover, it becomes crucial to evaluate interactions between medications as elderly patients often take various medications.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Potential risks to the fetus or infant
Although there haven't been any confirmed reports of effects, it is possible that fetal health could be impacted by the absorption of the substance into the body. For nursing mothers, even though the risk is minimal, the drug can be transmitted through breast milk.

Guidelines and best practices
It is essential to use this under medical guidance, carefully considering the potential risks and benefits. If you decide to use it, make sure to keep the dosage low, as possible and limit the duration of usage.
c. Administration to Children
Age-specific dosages and precautions
Children have dosage requirements compared to adults, often needing lower amounts. Giving them much medication can lead to severe problems like intense diarrhea and electrolyte imbalances.
Monitoring growth and development
Regular monitoring is necessary when using chronically to identify any abnormalities in growth or development. It is crucial to have pediatric checkups to ensure that the growth is progressing normally.
XV. Overdosage
Symptoms of Polycarbophil overdose
The realm of pharmaceuticals is a landscape where vigilance is crucial to avoid the dangers of overdose. In the case of Polycarbophil, an overdose can exhibit symptoms such as; Severe Diarrhea; An increase in bowel movements potentially watery in nature. Stomach Cramps; discomfort or spasms in the abdominal region. Electrolyte Imbalances; This may manifest as muscle twitching, unusual fatigue, or changes in the state. Awareness of these signs and taking necessary precautions to prevent adverse effects is essential.
Immediate actions and interventions
When dealing with a suspected overdose, it is crucial to implement three strategies;
1. Stop giving any medication immediately.
2. Provide care by monitoring vital signs ensuring hydration, and alleviating symptoms.
3. Seek advice from experts as they may consider administering activated charcoal or other necessary interventions.
XVI. Storage
Optimal storage conditions for efficacy and longevity
The effectiveness of a medication's healing potential depends on how it's stored. In the case of Polycarbophil, it is best to hold it in the conditions; Temperature; Keep it in a cool place, ideally between 20°C and 25°C. Humidity; Make sure the environment is dry to prevent any moisture exposure. Light; Store it away from sunlight to maintain its molecular integrity.
Signs of degradation or expiration
Expired or compromised Polycarbophil could reveal its condition through changes in texture, such as becoming more complex or unusually soft. Any variations in its color could indicate discoloration, while uncharacteristic or strong odors may suggest degradation.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Safe handling techniques for healthcare professionals
In the healthcare field, protocols are in place to maintain the integrity of Polycarbophil; 1. Hand Hygiene; It is crucial to prioritize cleanliness by washing hands before and after handling the drug. 2. Gloves; gloves are essential for providing a barrier, especially if there are any signs of damage or compromise in the drug container. 3. Surface Disinfection; Regularly disinfecting storage surfaces helps minimize the risk of contamination. These measures are implemented to ensure that Polycarbophil remains safe and uncontaminated for those working on the frontlines of healthcare.
Disposal and environmental considerations
When Polycarbophil reaches the end of its use, it's essential to dispose of it. One way to do this is through medication take-back programs in the community. This helps ensure that any leftover medication doesn't end up in waste thus protecting the environment. Before disposing of the medication make sure the container is securely sealed to prevent any exposures.