Polymyxin B
- 1. Introduction to Polymyxin B
- 2. Polymyxin b mechanism of action
- 3. Approved Medical Uses of Polymyxin B
- 4. Off-Label Uses of Polymyxin B
- 5. Dosage and Administration of Polymyxin B
- 6. Composition and Formulation of Polymyxin B
- 7. Storage and Stability of Polymyxin B
- 8. Common Side Effects of Polymyxin B
- 9. Rare but Serious Side Effects of Polymyxin B
- 10. Drug Interactions with Polymyxin B
- 11. Contraindications for Polymyxin B Use
- 12. Important Precautions for Polymyxin B Administration
- 13. Careful Administration of Polymyxin B
- 14. Administration of Polymyxin B to Special Populations
- 15. Overdosage and Toxicity of Polymyxin B
- 16. Handling Precautions for Polymyxin B
- 17. Warnings and Special Considerations for Polymyxin B Use
1. Introduction to Polymyxin B
Overview of Polymyxin B
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic used to treat infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria effectively and decisively known for its potent ability to kill bacteria within the polymyxin class of antibiotics highly valued when other antibiotics prove ineffective, focusing on combating drug-resistant organisms that are hard to treat.
Historical Background and Development
Polymyxins, unearthed during the 1940s, became a tool in combating infections. Their widespread use was initially common, but it decreased due to their kidney-damaging effects until recently, when the resurgence of resistance against antibiotics demanded their revival in the field of medicine.
Role of Polymyxin B in Modern Medicine
In medicine today, Polymyxin B is gaining significance. Its effectiveness against germs has positioned it as a key player in fighting infections that resist typical treatments. It plays a role in hospitals treating infections from organisms resistant to carbapenems.
2. Polymyxin b mechanism of action
Mode of Action at the Cellular Level
Polymyxin B works by attaching to the lipopolysaccharides found in the membrane of Gram bacteria and causing damage to the membrane's structure. This ultimately results in cell death due to the release of internal components.
Impact on Gram-Negative Bacteria
Polymyxin B is most effective against Gram bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Acinetobacter baumannii. Its targeted action avoids harming Gram bacteria, which makes it a suitable choice for treating infections.
Disruption of Bacterial Cell Membranes
Polymyxin B works by damaging the cell membrane of bacteria, which not only interferes with cell functions but also causes the bacteria to break down completely through bacteriolysis. This results in the cell becoming nonfunctional. It helps quickly clear up the infection.
Spectrum of Activity and Resistance Patterns
Although Polymyxin B is efficient against Gram bacteria to some extent, there are worries about its effectiveness as some bacteria have started developing resistance to it lately. Despite this resistance issue, it still plays a role in fighting drug pathogens.
3. Approved Medical Uses of Polymyxin B
Primary Indications for Polymyxin B
Polymyxin B is recommended for treating infections caused by types of Gram-negative bacteria, which can be life-threatening, especially when other antibiotics have not been successful.
Treatment of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
Polymyxin B has proven effective in treating infections resistant to antibiotics, such as carbapenem-resistant Enterobactericeae (CRE) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are resistant to many drugs.
Use in Septicemia
In cases of septicemia, a bloodstream infection that can be life-threatening, Polymyxin B is frequently prescribed when standard antibiotics prove ineffective as a last resort measure to fight the infection off effectively.
Polymyxin B for Respiratory Tract Infections
In cases of infections acquired in hospitals, such as ventilator—associated pneumonia caused by drug-resistant bacteria, Polymyxin B is seen as a powerful treatment choice.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Polymyxin B topical products are frequently applied to address skin and soft tissue infections in cases where Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa are involved.
Use in Urinary Tract Infections
In cases of tract infections attributed to bacteria that are resistant to multiple drugs, Polymyxin B serves as a beneficial form of treatment. It proves potent in scenarios where alternative antibiotics prove ineffective in eradicating the pathogen.
4. Off-Label Uses of Polymyxin B
Off-Label Use in Cystic Fibrosis Management
Polymyxin B's prescribed off label to improve lung function and decrease bacterial load, in individuals with cystic fibrosis who have chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections, in their lungs.
Use in Ophthalmic Infections
Polymyxin B is frequently utilized in treatments to address conjunctivitis and various severe eye infections despite lacking official approval, for such use.
Intrathecal Administration for CNS Infections
Polymyxin B has been used through the cord to treat infections in the nervous system (brain and spinal cord), like meningitis, caused by bacteria that are resistant to certain antibiotics from the Gram-negative group.
Polymyxin B in Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Infections
In some cases, for individuals receiving peritoneal dialysis treatment, for peritonitis—an infection affecting the peritoneum—Polymyxin B may be prescribed to address the infection's resistance to treatments.
5. Dosage and Administration of Polymyxin B
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
In adults, the usual amount of Polymyxin B is between 15,000 and 25,000 units per kilogram per day given intramuscularly. The exact dosage varies based on the seriousness and nature of the infection.
Pediatric Dosage Considerations
Dosage adjustments in patients need to be tailored according to their body weight and kidney function levels for optimal efficacy. Safety measures in place tend to be lower with closer monitoring intervals for children.
Adjusting Dosage for Renal Impairment
Adjusting the dosage is crucial for patients with kidney issues due to the effects it can have. It's important to keep an eye out for any signs of kidney problems to avoid any complications.
Intravenous Administration Guidelines
The method used for treating widespread infections is administering medications intravenously, with Polymyxin B usually being diluted and slowly infused over a span of 60 to 90 minutes to prevent any potential issues.
Topical and Ophthalmic Preparations
Topical products can be used for skin infections, and ophthalmic treatments are employed for eye infections to target specific areas for drug administration purposes.
6. Composition and Formulation of Polymyxin B
Chemical Structure and Properties
Polymyxin B is an antibiotic made up of a cyclic heptapeptide core with a fatty acyl tail. Due to its amphipathic nature, it can interact with membranes, ultimately resulting in cell death.
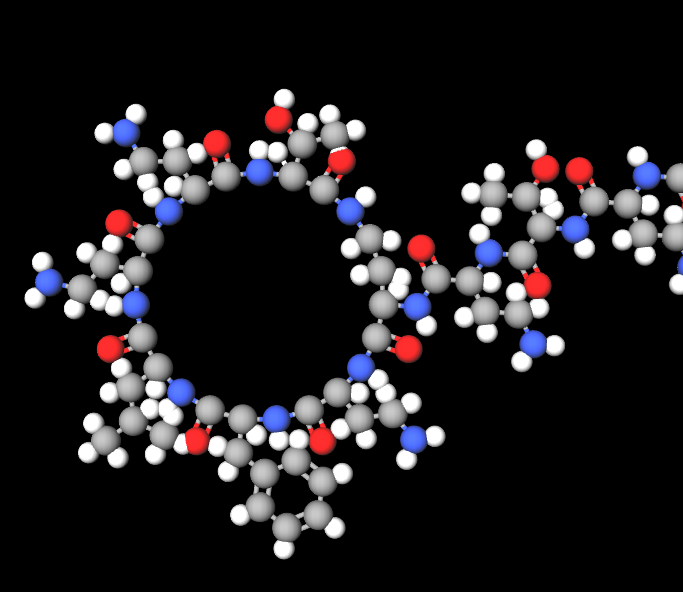
Available Formulations (Topical, Injectable, Ophthalmic)
Polymyxin B comes in forms, like skin creams and eye drops, to treat infections effectively.
Active Ingredients and Excipients
Polymyxin B formulations contain polymyxin B sulfate as the component while also including various excipients, such as stabilizers and preservatives, to uphold the drug's strength and effectiveness.
Polymyxin b sulfate
Polymyxin B is used to treat infections, in the tract and bloodstream well as those affecting the meninges. It is effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains that are susceptible, to it.
Polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim
Polymyxin B and trimethoprim belong to the antibiotic class of medications and are utilized for treating eye infections, such as conjunctivitis and blepharoconjunctivitis. They function by either eradicating bacteria or hindering their proliferation.
Neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates
Neomycin and polymyxin B are categorized as antibiotics and function by either eradicating bacteria or inhibiting their proliferation in the body system. Hydrocortisone is a type of steroid medication prescribed to alleviate the inflammation-induced symptoms, such as redness and itching, associated with ear infections.
Neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone
Neomycin and polymyxin B, with hydrocortisone ear drops are utilized for treating infections in the ear canal and easing redness and discomfort associated with ear issues. Additionally it helps in addressing ear infections that may arise following procedures, like mastoidectomy or fenestration surgery.
Bacitracin zinc and polymyxin b sulfate
Zinc Bacitracin and Polymyxin B Sulfate Ophthalmic Ointment is used to treat eye infections caused by bacteria, such as conjunctivitis and keratitis.
7. Storage and Stability of Polymyxin B
Ideal Storage Conditions
Polymyxin B needs to be kept at temperatures between 2 °C and 8°C to maintain its effectiveness; exposing it to heat or freezing conditions may diminish its efficacy.
Stability and Shelf Life of Polymyxin B
When stored correctly, Polymyxin B can maintain its stability for two years. Nonetheless, its shelf life reduces considerably once it has been reconstituted, and it should be utilized within a timeframe.
Handling Instructions for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to be cautious when dealing with Polymyxin B by employing methods to avoid contamination during the preparation and delivery process of the medications forms.
8. Common Side Effects of Polymyxin B
Frequently Reported Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Respiratory complications
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
Nephrotoxicity
The side effect that worries doctors the most is kidney damage known as nephrotoxicity, which affects several patients undergoing treatment, necessitating monitoring of renal function throughout the process.
Neurotoxicity
The neurotoxic impacts may present as feelings of lightheadedness or fatigue. They can even lead to nerve damage, in some cases.They tend to vary based upon the dosage and are usually reversible by reducing the dosage level.
Respiratory Distress
Polymyxin B has been linked to weakening of the muscles involved in breathing. It should be used cautiously alongside blocking agents to prevent respiratory issues from arising.
Gastrointestinal Reactions
During treatment, stomach issues, like feeling sick and throwing up, may occur, which are usually temporary and don't require stopping the treatment.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Allergies can sometimes lead to uncommon but possible reactions, with symptoms such as skin rashes and itching or, in some scenarios, even anaphylaxis.
9. Rare but Serious Side Effects of Polymyxin B
Severe Neurotoxic Reactions
Occasionally, in instances, Polymyxin B might trigger neurotoxic responses such as seizures, misunderstanding, and lack of coordination. Prompt medical assistance is essential in scenarios.
Anaphylaxis and Severe Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is a reaction that can be life-threatening and needs immediate medical attention. Its symptoms may include trouble breathing swelling in the face and throat and a sudden decrease, in blood pressure.
Acute Kidney Injury
Polymyxin B can precipitate acute kidney injury (AKI), especially in patients with pre-existing renal disease or those receiving nephrotoxic drugs. Early recognition and intervention are critical.
10. Drug Interactions with Polymyxin B
Interaction with Other Antibiotics
Polymyxin B can be combined with antibiotics; however, caution is essential to prevent any opposing effects. Adjunctive interactions with antibiotics may boost its effectiveness.
Interaction with Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Use caution when combining Polymyxin B with neuromere-blocking agents, as this can increase their impact and potentially cause paralysis.
Caution with Nephrotoxic Drugs
When you are using Polymyxin B along with medications, like aminoglycosides or vancomycin simultaneously, it can heighten the chances of kidney harm occurring; therefore, it is crucial to observe the renal function in these situations closely.
11. Contraindications for Polymyxin B Use
Known Allergies to Polymyxins
People who have a known sensitivity to polymyxins like Polymyxin B should steer clear of this antibiotic, as it can lead to responses such as skin rashes and itching or, in severe instances, trigger anaphylactic shock that requires urgent medical attention.
Pre-existing Neurological Disorders
Patients who have had conditions like myasthenia gravis or epilepsy are more likely to face side effects when given Polymyxin B medication. The drug's neurotoxicity may worsen symptoms. Result in issues such, as muscle weakness or seizures.
Contraindications in Patients with Renal Impairment
Polymyxin B is mostly removed from the body through the kidneys; this puts people with kidney issues at a chance of Polymyxin B buildup and potential harm from toxicity issues. People, with kidney problems should not be given Polymyxin B unless closely monitored and with adjusted dosages to ensure safety.
12. Important Precautions for Polymyxin B Administration
Monitoring Renal Function During Treatment
Because Polymyxin B has the potential to harm the kidneys (nephrotoxicity), it's important to monitor the kidney function of patients taking it. It is advisable to check the levels of serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (also known as BUN). This helps spot any signs of kidney problems and enables adjustments in dosage as needed.
Precautionary Measures for Avoiding Neurotoxicity
Polymyxin B presents a danger of neurotoxicity, with symptoms like lightheadedness, tingling sensations, and nerve damage in extremities such as arms and legs. To reduce this risk effectively, it is crucial to monitor and regulate dosage for individuals with existing neurological ailments during treatment. The patient's neurological condition must be regularly evaluated throughout therapy sessions to ensure their well-being.
Necessary Precautions in Patients with Hypersensitivity Reactions
Patients who have previously shown sensitivity to antibiotics should be carefully monitored when starting treatment with Polymyxin B medication. Those at risk of allergies may benefit from taking antihistamines or corticosteroids beforehand to lower the chances of an allergic reaction occurring.
13. Careful Administration of Polymyxin B
Polymyxin B in Immunocompromised Patients
Individuals with weakened systems, like those with HIV or receiving chemotherapy, need to be given Polymyxin B to account for their increased vulnerability to infections and potential side effects; close observation is vital to strike a balance between effectiveness and the risk of harmful effects.

Considerations for Patients with Liver Dysfunction
While Polymyxin B is mostly removed through the kidneys, liver issues could impact how the drug is processed. It's important to be cautious and conduct liver function tests before and during treatment to prevent any liver-related complications.
Use in Patients with History of Allergies
Patients who have experienced reactions to any medications should use Polymyxin B cautiously. It is important to thoroughly review their allergy history to assess the appropriateness of using Polymyxin B and prevent any possible hypersensitivity reactions.
14. Administration of Polymyxin B to Special Populations
Polymyxin B in Elderly Patients
Older individuals face an increased chance of encountering impacts from Polymyxin B because of age-related changes in kidney function, which need to be taken into consideration before starting therapy.
Age-Related Dosing Adjustments
It's important to adjust the Polymyxin B dosage based on the individual's function. Lower doses might be needed to avoid kidney damage, and dose changes should be made as per the results of checks.
Renal Monitoring in Older Adults
Regularly checking the kidneys is important for individuals. Since kidney function tends to decrease with age, conducting standard examinations to detect signs of potential kidney damage early on can help prevent serious long-term issues in these patients.
Polymyxin B Use During Pregnancy
It's important to reserve the use of Polymyxin B for pregnancy situations where it is truly essential and the benefits outweigh the risks significantly since its effects on women haven't been extensively researched yet.

Risks of Polymyxin B in Pregnant Women
The potential risks associated with using Polymyxin B while pregnant remain unclear at this time. Nonetheless, there are concerns, in theory, about the harm to the baby's system and kidneys. Decisions regarding the use of Polymyxin B, during pregnancy should be based on needs and circumstances.
Placental Transfer and Fetal Effects
There is no information about whether Polymyxin B can pass through the placenta barrier. Like antibiotics, though, there's a chance it might impact the development of the fetus, especially when it comes to the kidneys and nervous system. So it's something that should be thought about carefully.
Polymyxin B Use in Breastfeeding Mothers
Polymyxin B has not been extensively researched in mothers who breastfeed their babies, and there is some uncertainty surrounding its presence in breast milk.
Potential Transfer to Breast Milk
While the chances of a quantity of Polymyxin B getting into breast milk are minimal because of its molecular size, it is still important to be careful. If the mother is being treated with Polymyxin B, it is advisable to observe the infant for any indications of toxicity.
Recommendations for Nursing Mothers
If it is determined that nursing mothers require Polymyxin B, treatment options other than breastfeeding might need to be explored to prevent any harm to the infant, or breastfeeding might have to be stopped.
Polymyxin B Use in Pediatric Patients
Using Polymyxin B in patients necessitates evaluation due to the ongoing development of children's renal function, leading to varying rates of drug excretion and an increased risk of toxicity.
Safety and Efficacy in Children
Polymyxin B may be employed to address infections in children; however, its safety record with this age group is not as well documented as with adults. The dosage needs to be accurate. Children need monitoring for any potential negative reactions.
Pediatric Dosing Guidelines
Doctors usually determine the amount of Polymyxin B in children based on their weight. Kidney function should be considered carefully to reduce the chances of kidney damage.
15. Overdosage and Toxicity of Polymyxin B
Signs and Symptoms of Polymyxin B Overdose
In cases of an intake of Polymyxin B medication, patients could experience symptoms like kidney problems, breathing difficulties, and neurological issues such as disorientation, loss of coordination, or epileptic seizures. Urgent medical intervention is crucial to avert health risks.
Immediate Steps in Overdose Management
Treating a Polymyxin B overdose involves stopping the medication and providing care along with treating symptoms as needed; in situations of kidney or nerve-related issues, renal replacement therapy or intensive care might be required for treatment.
Long-Term Effects of Overdosage
The lasting impacts of taking Polymyxin B could lead to permanent harm to the kidneys or ongoing neurological issues, so it's important to act early and handle the overdose with care to reduce any long-term consequences.
16. Handling Precautions for Polymyxin B
Safety Protocols for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals working with Polymyxin B must follow safety guidelines, such as wearing gloves and managing the medication in a sterile setting, to avoid contamination or unintended contact.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Polymyxin B
It is important to dispose of any expired Polymyxin B using biohazard procedures. This drug should not be thrown away in household or regular waste systems because of its strength and potential harm to the environment.
Guidelines for Safe Handling in Clinical Settings
In environments, it is crucial to maintain the sterility and effectiveness of Polymyxin B by handling it appropriately. Adequate training for healthcare staff regarding the handling and use of Polymyxin B is vital to protect patients and reduce dangers.
17. Warnings and Special Considerations for Polymyxin B Use
Risk of Developing Resistance
Excessive or incorrect usage of Polymyxin B could lead to the emergence of bacteria that are resistant to drugs, so healthcare providers must be careful to prescribe the medication when necessary and for the shortest time needed to be effective.
Limitations of Polymyxin B in Treating Certain Bacterial Strains
Although Polymyxin B is effective in combatting Gram bacteria on a scale, it lacks efficacy against Gram-positive organisms and anaerobes, as well as in cases of bacterial infections with resistance mechanisms, like those influenced by the mcr. 1 gene.
Black Box Warnings and Regulatory Considerations
Polymyxin B comes with a warning about the risk of harming the kidneys and nervous system. Government agencies like the FDA have set rules on how it should be used for patients who are more susceptible to harm. Before using Polymyxin B, it's important to consider the risks involved and make sure to monitor its effects.
Polymyxin B FAQ
- How long does it take for polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim to work?
- What is polymyxin b sulfate?
- What is polymyxin b sulfate used for?
- What is neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates?
- What is polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim?
- What are neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic solutions used for?
- What is polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim used for?
- How to use neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates?
- What is neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic solution used for?
- Is polymyxin b sulfate safe for dogs?
- Does neomycin and polymyxin b expire?
- Can you use neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates on dogs ears?
How long does it take for polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim to work?
Most people will see a difference in their eye infections within two days. Improvement should be noticeable in ear infections in a few days.
What is polymyxin b sulfate?
Polymyxin B is prescribed for treating tract infections (UTIs), meningitis, and bloodstream infections caused by various types of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria.
What is polymyxin b sulfate used for?
Polymyxin B is used to treat infections in the tract and bloodstream caused by types of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria.
What is neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates?
Neomycin and polymyxin B are antibiotics that fight bacteria by either killing them or stopping their growth processes. Dexamethasone is a steroid medication commonly used to alleviate the discomfort of eye infections such, as redness and swelling accompanied by itching sensations.
What is polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim?
Polyneomycin B and trimethoprim are often prescribed together to treat eye infections, such as conjunctivitis and blepharoconjunctivitis. They are antibiotics that function by eliminating bacteria or inhibiting their growth.
What are neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic solutions used for?
Neomycin and polymyxin B, with hydrocortisone ear drops, address infections in the ear canal and ease redness and discomfort linked to ear issues. These drops also effectively treat ear infections that may arise from ear surgeries like mastoidectomy or fenestration.
What is polymyxin b sulfate and trimethoprim used for?
The combination of Polymyxin B and trimethoprim is utilized to treat eye infections such as conjunctivitis and blepharoconjunctivitis as they are classified as antibiotics that combat bacteria by either eliminating them or inhibiting their growth.
How to use neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates?
Remember to shake the bottle before each application and then tilt your head slightly before pressing your finger beneath the lower eyelid to create space for the medicine to be dropped into it carefully; after that, release the eyelid and softly close your eye.
What is neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates and hydrocortisone otic solution used for?
Neomycin combined with polymyxin B and hydrocortisone ear drops are utilized for treating infections in the ear canal and alleviating redness and discomfort associated with ear issues. They are also used to manage ear infections following procedures like mastoidectomy or fenestration.
Is polymyxin b sulfate safe for dogs?
If your dog has an eye infection, like conjunctivitis, using Polymyxin B Sulfate and Trimethoprim Ophthalmic solution should be safe. They could help clear up the issue effectively.
Does neomycin and polymyxin b expire?
You can continue using neomycin, polymyxin B sulfates, and dexamethasone ophthalmic suspension after you have opened it until the expiry date mentioned on the bottle.
Can you use neomycin and polymyxin b sulfates on dogs ears?
Neomycin sulfate is commonly employed in forms such as shampoo or ointment for the care of pets, such as dogs and cats.













