Progesterone Injection
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Progesterone Injection
- III. Uses of Progesterone Injection
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Progesterone Injection
- V. How Progesterone Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Progesterone Injection
- VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Important Precautions
- XI. Special Considerations
I. Introduction
Overview of Progesterone as a Hormone
Progesterone, a steroid hormone plays a crucial role in controlling the menstrual cycle and supporting the initial phases of pregnancy. It serves as a precursor to key hormones, like corticosteroids and androgens aiding in numerous bodily functions.
Historical Development of Progesterone Injections
Progesterone injections have been around since the 1900s, with the goal of treating hormonal imbalances and boosting fertility treatments. Over time, these injections have been enhanced to make them more effective and safer.
Significance in Medical Treatments
Progesterone injections play a role in various medical treatments, including hormone replacement therapy and assisting gestational processes in fertility treatments. Their impact goes beyond reproductive health, affecting aspects like mood control and maintaining bone density.
II. Composition of Progesterone Injection
Active Ingredients
The main component found in these shots is progesterone, designed to replicate the functions of the hormone naturally produced in the body. This hormone, identical to our own, plays a role in achieving the intended effects of the medication.
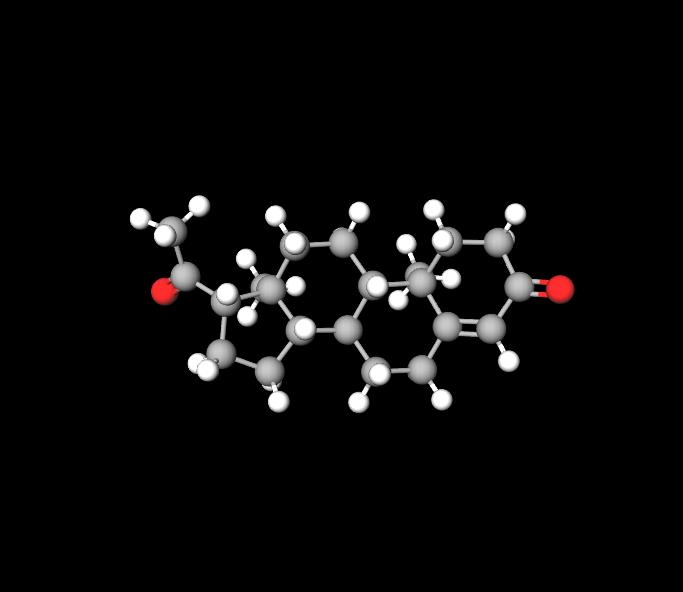
Excipients and Their Functions
- Carriers help improve the ability of the ingredient to dissolve and remain stable.
- Preservatives are used to stop bacteria from growing, thus prolonging the lifespan of the medicine.
- Stabilizers work to uphold the effectiveness of progesterone across storage environments.
III. Uses of Progesterone Injection
-
Menstrual Regulation:
- Progesterone injections are used to stimulate menstruation in nonpregnant women.
- They help address conditions such as amenorrhea (absence of periods) and abnormal uterine bleeding 1.
-
Symptom Relief:
- Progesterone injections effectively reduce symptoms related to hormonal fluctuations.
- These symptoms include hot flashes, mood swings, and other vasomotor symptoms 2.
-
Menstrual Issues:
- Progesterone injections can address menstrual irregularities, including missed periods and period pains.
- By rebalancing hormones, they support regular menstrual cycles 1.
-
Pregnancy Support:
- During pregnancy, progesterone plays a crucial role in maintaining the uterine lining.
- Doctors administer progesterone injections to strengthen the uterine walls, helping the embryo attach and improving the chances of a successful pregnancy 2.
IV. Off-Label Uses of Progesterone Injection
Management of Specific Female Infertility Issues
Use in Certain Non-Gynecological Conditions
These injections are also used to treat conditions beyond gynecology, such as being a treatment for specific cancer and hormonal issues.
V. How Progesterone Works
Mechanism of Action in the Female Reproductive System
Progesterone functions by attaching to progesterone receptors in the system triggering a series of biological processes that ready the womb, for pregnancy and control the menstrual cycle.
Effects on the Endometrium
Progesterone plays a role in changing the growing endometrium into a lining that supports embryo implantation and sustains pregnancy effectively.
Systemic Effects of Progesterone
Progesterone doesn't just impact the system; it also plays a role in affecting different body functions. It helps maintain moods and promotes heart health by reducing inflammation.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions
The amount of progesterone injections needed differs depending on the reason for treatment, such as hormone therapy or fertility support requiring treatment plans.
Methods of Injection – Intramuscular vs. Subcutaneous
The way progesterone injections are given can impact how well they work and how comfortable the patient feels. Doctors usually like to use injections because they release the medication slowly, but some patients might prefer subcutaneous injections if they need to give themselves the shot.
Duration of Treatment Protocols
The length of time for progesterone treatment is customized based on each patient's requirements, taking into account factors like how the treatment is working and the individual's overall health condition.
Progesterone injection wrong place
There may be discomfort, inflammation, and maybe even a lack of sensation and tingling in the legs. If the injection is not placed correctly, massaging and applying heat can provide relief.
VII. Side Effects of Progesterone Injection
Common Side Effects: Detailed Exploration
Although progesterone injections are usually well received, they may lead to side effects like reactions at the injection site, headaches, and changes in mood.
Serious Side Effects and Their Management
Severe side effects could involve blood clotting issues and heart-related problems, which may call for medical attention and could lead to the need to stop treatment.
Long-term Side Effects
Using progesterone injections for a period could lead to changes in lipid levels and potential hormone imbalances, highlighting the importance of continuous monitoring and adjustment.
VIII. Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Implications
Progesterone injections may have an impact on medications leading to changes, in how they work.
- Some typical interactions involve anticoagulants, which could raise the chance of bleeding, and specific anticonvulsants, which might reduce the effectiveness of progesterone. Anticoagulants: Increased risk of bleeding requires monitoring of blood clotting factors.
- Anticonvulsants; Dosage adjustments may be needed to ensure therapeutic levels.
Impact on Efficacy of Other Treatments
Progesterones presence can impact how other hormone therapies, like estrogen or thyroid hormone replacement, work. This is because progesterone has effects, on the metabolism and elimination patterns of hormones.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
Specific Health Conditions and Progesterone Use
Progesterone injections should not be given to individuals who have a past of blood clotting issues, liver problems, or confirmed or suspected breast cancer. Using this hormone in cases can worsen these conditions and pose serious risks.
- Thromboembolic Disorders: There is a chance of forming clots that could result in severe complications.
- Liver Disease; Poor liver function can affect how hormones are processed leading to side effects.
- Cancer: Tumors sensitive to hormones may expand with hormone treatment.
Genetic Factors Affecting Progesterone Use
Some inherited traits, like changes, in genes that control hormones can impact how safely progesterone treatment works. It's important to conduct testing before starting the therapy to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Environmental or Lifestyle Interactions
Exposure to substances that disrupt hormones and lifestyle habits, such as smoking or drinking too much alcohol, can impact how well progesterone works and its safety.
X. Important Precautions
Monitoring Health During Treatment
Regularly monitoring one's health is crucial when undergoing progesterone therapy to catch any negative reactions at an early stage. Routine checkups should involve keeping track of blood pressure, conducting liver function tests, and watching out for any indications of blood clot formation.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
To achieve treatment results and reduce risks, it may be necessary to adjust the progesterone dosage according to factors such as the patient's age, weight, and kidney function.
Managing Overdose Symptoms and Protocols
In situations where there is an intake of progesterone, individuals may experience symptoms like feeling lightheaded, having trouble seeing clearly, or suffering from intense headaches. The treatment typically includes providing support for the symptoms and, in severe instances, undergoing hormonal detoxification processes.
XI. Special Considerations
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Ensuring the management of progesterone is crucial for the well-being of both the mother and the developing baby during pregnancy.