Propecia Finasteride
- 1. Introduction to Propecia (Finasteride)
- 2. Composition and Properties of Propecia
- 3. Mechanism of Action: How Propecia Works
- 4. Approved Uses of Propecia
- 5. Off-Label Uses of Finasteride
- 6. Administration Guidelines for Propecia
- 7. Side Effects of Propecia
- 8. Important Precautions and Warnings
- 9. Handling and Storage of Propecia
- 10. Overdose and Emergency Procedures
- 11. Detailed Overview of Clinical Studies and Research
- 12. Legal and Ethical Considerations
- 13. Patient Education and Care Considerations
1. Introduction to Propecia (Finasteride)
Overview of Propecia
Propecia, also known as Finasteride, is a medication commonly used to treat male pattern baldness. Its effectiveness in slowing down hair loss and promoting hair growth has made it a popular choice in dermatology treatments.
Historical Background and FDA Approval
Introduced by Merck & Co., Finasteride was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1992. Originally intended for treating prostatic hyperplasia, its ability to promote hair growth was discovered incidentally, resulting in its approval for androgenetic alopecia in 1997.
Scope of the Article
This article seeks to provide an analysis of Propecia discussing its ingredients how it works, approved and experimental applications, as well, as essential usage instructions and possible adverse reactions.
2. Composition and Properties of Propecia
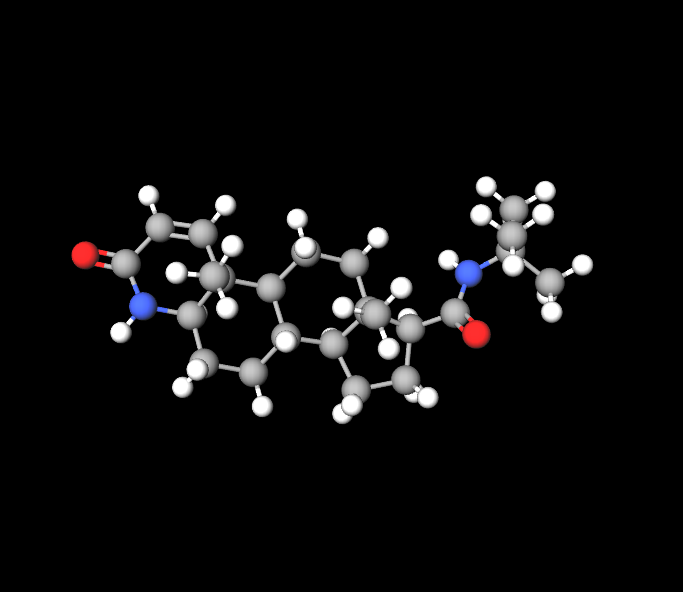
Active Ingredient: Finasteride
Finasteride is a man-made compound known as a blocker of Type II 5α reductase, an enzyme inside the body that changes testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Inactive Ingredients and Their Roles
- Lactose monohydrate helps maintain the stability of the tablet formulation.
- Microcrystalline cellulose is used as a filler to add volume to the tablet.
- Pregelatinized starch acts as a disintegrant to assist in tablet dissolution.
Pharmacological Classification
Finasteride falls under the category of a 5 alpha reductase inhibitor mainly affecting the enzyme processes that control the balance essential, for the health of hair follicles.
Rogaine vs propecia
Propecia, also known as Finasteride, and Rogaine, also called Minoxidil, are treatments for male-pattern hair loss in men. Rogaine or Minoxidil is specifically approved for female-pattern hair loss or androgenic alopecia in women.
Proscar vs propecia
Proscar and Propecia are both brand names for a medication called finasteride. The key contrast lies in their dosage and recommended uses. Proscar contains 5 mg of finasteride and is prescribed for managing BPH, while Propecia contains 1 mg of finasteride and is specifically meant for addressing male pattern baldness.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Propecia Works
Biochemical Interaction with Hormones
Propecia effectively disrupts the biochemical processes by specifically blocking the transformation of testosterone into DHT, which helps lower the androgen levels on the scalp.
Impact on Hair Growth Cycle
Propecia works by reducing DHT levels, which helps to extend the growth phase of the hair cycle and stops hair follicles from shrinking.
Effects on Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Levels
Consistently taking Propecia can lower scalp and serum DHT levels by around 60% with daily use.
Does propecia regrow hair
Propecia can halt hair loss in 90% of men after a year of use. It's possible that you'll notice a decrease in the speed at which your hair is thinning. Additionally around two thirds of men using Propecia experience some level of hair growth so you may see regrowth in areas where hair was previously lost.
how long does propecia take to work
It's possible to see some changes shortly after beginning finasteride. Yet it may take around 6 months for the medication to have its effect, on an enlarged prostate. In terms of hair loss, improvements could become noticeable within 3 to 6 months.
4. Approved Uses of Propecia
Treatment of Male Pattern Baldness
Dosage Recommendations for Optimal Efficacy
The advised amount of Propecia is a tablet (1 mg) to be consumed once a day whether with or, without food.
5. Off-Label Uses of Finasteride
Exploring Uses Beyond Male Pattern Baldness
Efficacy and Research on Off-Label Applications
Recent research indicates that using amounts of Finasteride could potentially be beneficial in these situations. However, further comprehensive clinical studies are required to confirm its effectiveness and safety.
6. Administration Guidelines for Propecia
Dosage and Administration
It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage schedule to achieve the intended treatment results.
Administration to Special Populations
- Elderly individuals usually do not need any changes in dosage.
- For nursing women, Propecia is not recommended because it may pose risks of causing birth defects.
- Regarding children it is unclear how safe and effective Propecia is, for patients. To obtain Propecia, you must consult a healthcare provider who can prescribe it for you.
7. Side Effects of Propecia
Common Side Effects and Management
Some individuals might encounter minor side effects like a decrease in sexual desire, difficulties with erectile function, or issues with ejaculation. It is recommended that counseling and regular monitoring are sought.
Long-Term Side Effects
Extended usage could heighten the likelihood of experiencing severe consequences, such as depression and advanced-stage prostate cancer.
Reporting Adverse Reactions
Patients are advised to inform their healthcare provider or contact the FDAs MedWatch program if they experience any negative reactions in order to ensure thorough safety oversight.
Propecia for women
It's important to note that finasteride is not recommended for women and should be avoided during pregnancy.
Potential side effects of finasteride in women may include harm to a developing fetus (making it unsuitable for use during pregnancy), tiredness, weight gain, feelings of sadness, worry, reduced interest in activity, sexual problems, hair loss, breast tenderness, and breast enlargement.
While other side effects are possible, they are frequently reported.
8. Important Precautions and Warnings
Contraindications for Using Propecia
Propecia should not be used in patients who have a known allergy to finasteride or any ingredient, in the medication. Furthermore, women who are pregnant or may become pregnant should avoid handling crushed or tablets to prevent potential harm to a male fetus.

Precautions for Patients with Other Medical Conditions
Patients who have liver issues need to be careful when thinking about using it since it's mainly processed in the liver. Its advised that these patients get their liver enzyme levels checked regularly to avoid making their existing conditions worse.
Interaction with Other Medications
When taking finasteride, it's important to be cautious when using medications that inhibit Cytochrome P450 3A4, such as ritonavir, as they can potentially raise the levels of finasteride in the body. Additionally if you are on anticoagulants be aware that they may have effects when combined with finasteride requiring potential adjustments, in your dosage.
9. Handling and Storage of Propecia
Optimal Storage Conditions
Remember to store Propecia in a dry place at room temperature. Keep it away from heat and moisture, and make sure the temperature stays between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Handling Precautions to Ensure Safety
Propecia tablets should not be touched by women who are pregnant or may become pregnant due to their harmful effects on fetal development. If contact happens it is advisable to wash the area, with soap and water to reduce exposure.
10. Overdose and Emergency Procedures
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
While an excessive intake of Propecia is not believed to result in life-threatening effects, possible indicators could involve a drop in blood pressure or a sudden worsening of side effects, like reduced sexual desire or feelings of lightheadedness.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
There is no known antidote for finasteride so it is important to start symptomatic and supportive measures in case of an overdose. Seeking medical attention is essential, for managing the effects effectively.
11. Detailed Overview of Clinical Studies and Research
Key Findings from Clinical Trials
Studies have repeatedly shown that Propecia is successful in boosting hair growth and enhancing hair condition leading to a decrease in the advancement of male pattern baldness, within three to twelve months.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Researchers are currently investigating the ways in which finasteride could be beneficial for treating persistent conditions such as hirsutism and preventing prostate cancer. Additionally they are delving into the lasting impacts of the medication, on hormone levels and emotional well being to enhance its recommended applications.
12. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Regulatory Status and Legal Issues
Propecia is overseen by the FDA in the US and similar regulatory bodies worldwide. Its prescription requirement means that it can only be obtained with a prescription. Legal concerns have mainly focused on the accuracy of the drug's labeling regarding risks, especially related to sexual and cognitive side effects.
Ethical Considerations in Prescription and Distribution
Ensuring the allocation of Propecia requires open and honest discussions with patients regarding the advantages and drawbacks of its usage. Healthcare professionals must take into account the physical effects of long term finasteride use guiding patients to make well informed choices.
13. Patient Education and Care Considerations
Educating Patients on the Use of Propecia
Patients should be educated thoroughly on how medications work, side effects and the significance of following the prescribed dosage. Healthcare professionals must also discuss with patients the anticipated timeframe, for observing improvements. The necessity of continuous monitoring.
Support and Resources for Managing Side Effects
Patients should receive assistance that includes counseling and medical guidance for handling side effects. Additionally, resources such as materials for patient support groups and referrals to specialists for serious side effects should be made available. Consistent follow up appointments can aid in effectively addressing and managing any reactions.
Does propecia lower testosterone
Finasteride, also known as Propecia doesn't reduce testosterone levels directly. Instead it works by decreasing the amount of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in circulation, which typically decreases by around 70%. Interestingly the levels of testosterone, in the bloodstream actually see a slight increase usually ranging from 10 to 20%.