Quinine Sulphate
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Quinine Sulphate
- III. How Quinine Sulphate Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Quinine Sulphate
- V. Off-Label Use of Quinine Sulphate
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Quinine Sulphate
- VII. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- VIII. Possible Side Effects of Quinine Sulphate
- IX. Contraindications and Warnings for Quinine Sulphate Use
- X. Interaction of Quinine Sulphate with Other Substances
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions for Quinine Sulphate
I. Introduction
A. Brief Historical Background of Quinine Sulphate
The tale of sulfate starts in the vibrant and lush jungles of South America. It was during the century when the native inhabitants first discovered the antimalarial properties hidden within the bark of a tree called cinchona, famously known as the "fever tree".
The main active component found in this bark was quinine, which was later extracted by scientists Pelletier and Caventou in 1820. Realizing its potential for therapy, they went on to synthesize quinine sulfate marking an era for chemotherapeutic agents.
B. Common Medicinal Applications of Quinine Sulphate
Quinine sulfate continues to be used as a primary treatment for severe malaria, even though new antimalarial medications have been developed. While the FDA has advised against its use for muscle cramps, some individuals still rely on sulphate to alleviate nocturnal leg cramps.
Additionally, researchers have explored the potential of sulphate in managing arrhythmias, lupus, and specific forms of pain due to its unique pharmacological properties.
II. Composition of Quinine Sulphate
A. Active Ingredient: Detailed Examination of Quinine Sulphate
The main component of this formulation is sulfate, which is a natural alkaloid. It has a structure that includes a quinoline ring. The name of this compound comes from the Quechua word "quina," which means bark indicating its origins. At a level, it is considered a chiral compound with two enantiomeric forms. The S(-) form shows the significant antimalarial activity among them.
B. Inactive Ingredients: Excipients in Quinine Sulphate Formulations
Quinine sulphate formulations always contain inactive ingredients or excipients, which play a crucial role in the drug's bioavailability, stability, and patient tolerance. Examples of excipients are;
- Binders; These are substances like microcrystalline cellulose that help maintain the tablet's structural integrity.
- Disintegrants; Sodium starch glycolate, for instance, assists in breaking down the tablet within the gastrointestinal tract.
- Fillers; Lactose or mannitol may be added to increase the volume of the tablet.
III. How Quinine Sulphate Works
A. Mechanism of Action against Malaria
Quinine sulfate demonstrates its effectiveness against malaria by targeting the stage of Plasmodium parasites that occur in red blood cells. It is thought to work by interfering with the formation of hemozoin, a vital process for the survival of the parasite.
This interference causes toxic heme to accumulate, ultimately resulting in the death of the parasite. However, despite research, we have not fully comprehended the precise molecular mechanism behind this remarkable compound, highlighting both the intricate nature of biological systems and the mysterious allure surrounding it.
B. Off-target Interactions: Understanding the Broad-Spectrum Effects
The spectrum of activity exhibited by sulphate extends beyond just Plasmodium species. This compound's unique structure enables it to interact with biological targets. For instance, it has the ability to inhibit types of voltage-gated ion channels, which explains its potential as an antiarrhythmic agent.
Additionally, studies have shown that it can impact glucose metabolism and immune function leading to a range of effects, some beneficial while others may have drawbacks. As research progresses, we are discovering more about the potential of quinine sulphate and its intricate interactions with biological systems much like other natural products.
IV. Approved Uses of Quinine Sulphate
A. Role in the Treatment of Malaria
Quinine sulfate continues to be an effective tool in the fight against malaria(1). With the introduction of newer antimalarial drugs, it remains unmatched as a first-line treatment for severe cases. Its powerful action disrupts the life cycle of the Plasmodium parasite within blood cells, a crucial stage for disease progression.(2)
The importance of sulfate in combatting this disease transmitted by mosquitoes cannot be underestimated(3). In cases of malaria, intravenous quinine sulfate is commonly used alongside other antimalarial medications as a go-to solution.
Additionally, when malaria becomes complicated with issues quinine sulfate serves as a key therapeutic option along, with supportive treatments.(4)
1. Drugs.com - Quinine Sulphate Prescribing Information
2. PubChem - Quinine Sulphate
3. WebMd - Quinine Sulphate
4. Wikipedia - Quinine
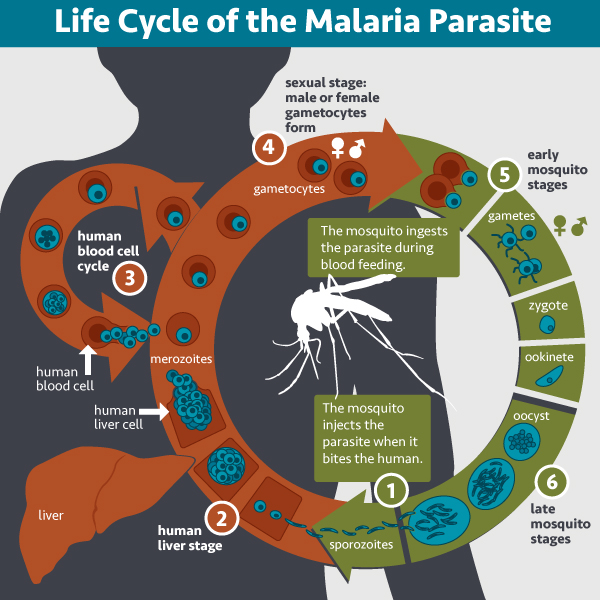
Malaria Mosquito Life Cycle
B. Management of Nocturnal Leg Cramps
Apart from its known use as an antimalarial medication quinine sulfate has also been utilized in the treatment of nocturnal leg cramps. While its effectiveness for this purpose is still debated, there are reports suggesting positive outcomes.
The idea behind this theory is that quinine can reduce muscle cramps by decreasing the excitability of the motor end plate and stabilizing the muscle membrane. However, healthcare providers need to be cautious when prescribing quinine sulphate for off-label use due to side effects.
When considering leg cramps, it is important to carefully assess the balance between risks and benefits based on individual cases and lack of comprehensive clinical evidence.
V. Off-Label Use of Quinine Sulphate
A. Efficacy in Treating Babesiosis
Quinine sulphate has shown versatility by being used off-label to treat babesiosis a tick-borne disease caused by protozoan parasites from the Babesia genus. These parasites have similarities to the Plasmodium species for malaria which could explain why quinine is effective in treating babesiosis.
Hemolytic anemia is a common characteristic of babesiosis and treatment often involves combining sulphate with clindamycin. However, it's important to approach this off-label use with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
It's worth noting that comprehensive clinical trials for this use are lacking, so careful evaluation and vigilant monitoring during treatment are necessary.
B. Potential Benefits in Managing Lupus and Arthritis
Quinine sulphate has caught the attention of researchers due to its potential to manage disorders like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. The causes of these diseases are complex. Involve inflammation and immune system imbalances. Quinines anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties make it a possible candidate for treatment.
However, it's important to note that these applications are still being tested, and there is a lack of clinical trials to confirm the effectiveness and safety of using quinine sulphate for these conditions.
Some initial studies hint at therapeutic benefits, but more research is needed before drawing definitive conclusions. Considering the stage of research, it is recommended that the use of quinine sulphate, in lupus and rheumatoid arthritis should be limited to research or clinical trial settings.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Quinine Sulphate
A. Standard Dosing Guidelines
Like any medication, the recommended dosage of sulphate can vary based on factors such, as the specific condition being treated the patient's overall health, and other medications they may be taking.
For malaria treatment, a common adult dose is usually 600mg of quinine sulphate taken three times a day for 5 7 days.
However, it's important to remember that these dosages are just guidelines and may differ based on regional treatment protocols and individual patient needs.
B. Adjustments Based on Patient Condition and Response
Administering quinine sulfate requires an understanding of the patients health status. If a person has kidney or liver issues adjustments to the dosage might be necessary because their bodies process and eliminate drugs differently.
Additionally, it is crucial to monitor the treatment's effectiveness and make changes to ensure optimal results while minimizing any negative side effects.
C. Administration Techniques for Optimal Efficacy
Quinine sulfate is usually taken by mouth. It is not greatly influenced by food intake. Therefore you can have it with your meals to reduce any discomfort in your stomach. In cases of malaria quinine sulfate may be given intravenously while being closely monitored by medical professionals.
VII. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
A. Administration to the Elderly: Considerations and Precautions
Extra care should be exercised when administering quinine sulphate to individuals as they may be more susceptible to experiencing negative side effects. Since the effects of the drug can be affected by age it is important to consider adjusting the dosage and closely monitoring its use to ensure a balance, between effectiveness and safety.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Precautions
Quinine sulfate can pass through the placenta. Be present in breast milk. While it has been safely used in women to treat malaria, it's important to exercise caution. The potential risks to the baby or nursing child should be carefully considered in relation to the benefits, for the mother. It is recommended that pregnant women and nursing mothers consult with a healthcare provider before taking quinine sulfate.
C. Administration to Children: Dosage Adjustments and Safety Measures
Children are different from adults in terms of their physiology so it's important to adjust the dosage of sulphate accordingly. In patients, it's common to use weight-based dosing to achieve effectiveness while minimizing any potential negative effects. As always it's crucial for healthcare professionals to closely monitor the use of sulphate, in children.
VIII. Possible Side Effects of Quinine Sulphate
A. Common Side Effects: What to Expect
The typical symptoms that may occur due to sulphate use include feeling nauseous, having headaches experiencing dizziness, and even some temporary hearing loss. However, these side effects are generally mild and short-lived. They usually go away on their own without requiring you to stop taking the medication.
B. Rare but Serious Side Effects: When to Seek Medical Attention
Serious but uncommon adverse effects of sulphate may include severe skin reactions, changes in vision or irregular heartbeat. It is crucial to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.
Hemolysis, a condition where red blood cells are destroyed, can happen in people with glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
This emphasizes the significance of conducting an evaluation of patients before initiating quinine treatment.
IX. Contraindications and Warnings for Quinine Sulphate Use
A. Potential Health Conditions That May Prevent Quinine Sulphate Use
People who are known to have allergies to quinine or similar substances should avoid using quinine sulphate. It is also not recommended for individuals who have a history of hemolysis hemolytic uremic syndrome, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, severe tinnitus, optic neuritis or cardiac arrhythmias. In cases where prolonged QT interval can be problematic, caution should be exercised when using quinine sulphate to prevent any worsening of the condition.
B. Risks Associated with Overdosage: Signs, Symptoms, and Immediate Actions
Consuming amounts of quinine sulphate can result in serious and potentially life-threatening complications, including cardiac arrhythmias, acute renal failure, and low blood pressure.
Common signs of an overdose may include feelings of nausea, vomiting, impairments, hearing loss, and mental confusion.
If an overdose is suspected, it is crucial to seek medical help. The treatment primarily involves providing care to ensure the proper functioning of vital bodily functions.
X. Interaction of Quinine Sulphate with Other Substances
A. Common Drug Interactions: Complications and Consequences
Quinine sulphate has the ability to interact with medications, which can result in changes to their effects. This includes drugs like warfarin (an anticoagulant), hypoglycemic agents, antiepileptics, and digoxin.
These interactions have the potential to increase the potency of these drugs, thereby raising the risk of experiencing side effects. Therefore it is crucial to have an understanding of the patient's medication routine prior to starting quinine sulphate therapy.
B. Food and Lifestyle Interactions: What to Avoid
Although the absorption of sulfate is not greatly impacted by food, it is advised to avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking this medication.
This is because they can potentially increase the levels of quinine in the bloodstream, which may lead to a risk of experiencing harmful effects.
It's also important to mention any habits such as drinking alcohol or smoking to your healthcare provider before starting quinine therapy as these factors might influence how your body processes the medication.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions for Quinine Sulphate
A. Proper Storage Conditions for Quinine Sulphate
Quinine sulphate needs to be stored in a dry place away from direct sunlight. It's important to keep it out of the reach of children to avoid any intake.
When disposing of the drug make sure not to throw the packaging into household waste and follow local regulations, for getting rid of any expired or unused medication.
B. Handling Precautions: Ensuring Patient Safety and Medication Efficacy
It's important to handle quinine sulphate with hands and make sure the containers are tightly closed when not using it. We should be careful to avoid contaminating the medication. If there is a spill or if it comes into contact with the skin or eyes we should wash the affected area thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if irritation continues.














































