Roxatidine
- Introduction
- Uses of Roxatidine
- How Roxatidine Works
- Off-Label Use
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition
- Common Side Effects
- Side Effects
- Interaction
- Warning
- Contraindication
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to the Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Over Dosage
- Storage
- Handling Precautions
Introduction
The history and development of Roxatidine began in the 20th century, and since then, it has become a fundamental medication for suppressing gastric acid. Initially designed to address gastrointestinal problems, it significantly changed how we approach specific digestive tract ailments. Roxatidine holds great importance in the field as a potent H2 receptor antagonist. It plays a role in managing and treating peptic ulcers. Its introduction has offered clinicians an effective and safer alternative to existing treatments reshaping the way we provide care for gastroenterological conditions.
Uses of Roxatidine
Roxatidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits gastric acid secretion and is used to treat peptic ulcers, gastric acid reduction, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)1. Peptic ulcers are erosions in the lining of the stomach or duodenum that are usually caused by Helicobacter pylori infection or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)2. GERD is when the stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, causing heartburn, regurgitation, and inflammation3. Roxatidine can relieve the symptoms and promote the healing of these conditions by reducing the amount and acidity of gastric juice1.
References:
1: Medications for the Treatment of Gastric Acidity 2: Peptic Ulcer Disease - Gastrointestinal Disorders - MSD Manual … 3: Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease
How Roxatidine Works
Roxatidine works in the body by blocking histamine at H2 receptors found in the stomach cells. This action helps reduce the amount of gastric acid produced, relieving symptoms and aiding in the healing process for conditions. Regarding its properties, Roxatidine's effectiveness is matched by its interesting pharmacokinetics. It is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak plasma levels within 3 hours. Additionally, it has a distribution throughout the body and undergoes metabolism resulting in an elimination half-life that suits both acute and long-term therapies.
Off-Label Use
Roxatidine is a medication used to treat stomach ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Although Roxatidine is not specifically designed for the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and dyspepsia, several studies have suggested its effectiveness in managing them1. In the case of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, where excessive stomach acid is produced Roxatidine's counteractive properties have shown to be beneficial1.
Here are some references:
Dosage and Administration
Adults with ulcers are advised to take 150 mg of medication before bed. However, the dosage may vary depending on the severity of the condition and how the patient responds. In severe cases or when quick relief is needed, taking the medication twice a day may be necessary. Special populations like those with kidney problems might require personalized dosing. Roxatidine is usually taken orally, either with or without food. Remember to swallow the tablets for optimal absorption and effectiveness.
Composition
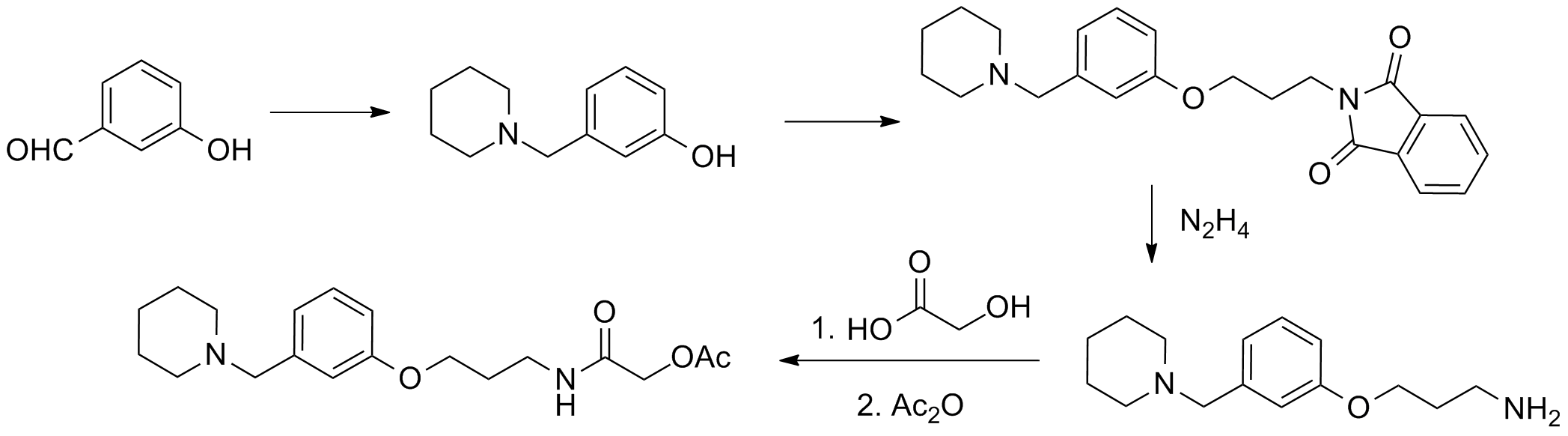
The effectiveness of Roxatidine primarily comes from its component called Roxatidine acetate hydrochloride. Additionally, the medication may include ingredients to ensure stability and proper administration. Regarding brand names and generic versions, there can be variations in elements, packaging, and price. Nevertheless, they generally maintain therapeutic effects.
Common Side Effects
The commonly reported side effects include dizziness, headaches, and gastrointestinal disturbances. To manage these side effects, it is essential to note that they are usually temporary and not severe. Simple remedies such as getting rest staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers can often be helpful. However, if the symptoms persist, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is crucial.
Side Effects
Frequently occurring and uncommon adverse reactions may include thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), elevated liver enzymes, and interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidney). These side effects, while not common require attention due to their potential seriousness. They can develop gradually over a period of days to weeks. Detecting them early and managing them appropriately is crucial to prevent any complications.
Interaction
Some medications and substances can have an impact on how Roxatidine works. For example, if you take ketoconazole along with Roxatidine, it might affect how well your body absorbs the medication. Additionally, taking antacids at the time, such as Roxatidine, could reduce the drug's effectiveness. It's essential to be aware of these interactions because they can either weaken the intended effects of Roxatidine or potentially increase adverse side effects. That's why it's crucial to provide your doctor with a history of all the medications you're taking to ensure that you achieve the best and safest therapeutic outcomes possible.
Warning
It's essential to exercise caution when using Roxatidine in clinical situations. Patients with a history of porphyria, liver or kidney problems fall into this category and should be closely monitored during treatment. Although rare there is a possibility of reactions so regular blood tests, throughout the treatment can help detect any issues early on. If you experience any unusual symptoms, it's crucial to promptly inform your healthcare provider.
Contraindication
It is not recommended to use Roxatidine in conditions or situations. These include being hypersensitive to Roxatidine and experiencing episodes of porphyria. If Roxatidine is unsuitable for an individual, other options, such as H2 antagonists or proton pump inhibitors, may be considered. However, it is essential to seek the guidance of a medical professional before making any decisions.
Careful Administration
To ensure treatment, it is advisable to regularly monitor liver and kidney functions, especially when undergoing prolonged therapy. This helps in the detection and prompt management of any abnormalities. In situations with reduced kidney function, dosage adjustments are necessary to prevent the build-up of the medication. Similarly, patients with liver dysfunction may need modified dosing schedules or quantities.
Important Precautions
Here are some guidelines to ensure the use of Roxatidine; 1. Always take Roxatidine as prescribed by your doctor. 2. Avoid drinking alcohol while taking this medication. 3. It's important to review your medications with your doctor to prevent any potential interactions. Before starting treatment with Roxatidine, there are a few things patients should know; 1. Be aware of the side effects of the medication. 2. It's crucial to undergo monitoring during treatment. 3. If you experience any symptoms, report them immediately. 4. Understanding how the drug works and staying informed about its effects will help achieve therapeutic outcomes. Remember, following these steps and being proactive in your treatment will contribute to your well-being.
Administration to the Elderly
One important thing to remember is that older individuals often experience a decline in kidney function, which can impact how Roxatidine is cleared from the body. Additionally, they may be taking medications, which increases the likelihood of potential drug interactions. To mitigate these risks, starting with doses of Roxatidine and adjusting gradually based on how the individual responds, and any side effects they experience is recommended. It's also crucial to monitor their kidney function and conduct hematologic assessments to ensure their well-being in this population.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety profile and potential risks of using Roxatidine during pregnancy should be carefully considered. It is uncertain whether Roxatidine is excreted in human breast milk. Caution is advised when administering it to nursing mothers. Exploring alternatives with a well-established safety record during pregnancy and breastfeeding is advisable whenever possible. Prior consultation with a gynecologist or pediatrician is crucial before starting any treatment.
Administration to Children
Safety and effectiveness in children The safety and efficacy of Roxatidine in children have not been definitively established. As a result, caution should be exercised when considering its use in this age group. Dosage recommendations and special considerations If Roxatidine is deemed necessary for children, the dosage should be personalized according to their weight and clinical condition. Close monitoring is advised due to the data available for this specific population.
Over Dosage
Signs of overdosing on Roxatidine include muscle cramps, vomiting, and a fast heartbeat. If the overdose is severe, it can disrupt the functioning of muscles in the body. It is crucial to seek medical attention in such cases. Treatment primarily involves providing support. It may also include administering activated charcoal if the overdose is identified early on.
Storage
Store Roxatidine at a temperature range of 15°C to 30°C in an optimal storage environment, protecting it from light and moisture. It is essential to discard any medication that has exceeded its expiration date. Before using, carefully examine the medicines for any alterations in their appearance or scent.
Handling Precautions
To ensure handling and disposal, avoiding direct contact with broken or crushed tablets is important. When disposing of the medication, follow guidelines or consult a pharmacist for environmentally safe methods. For maintaining quality and potency, storing the medicine in its container and keeping it away from direct sunlight is recommended. Regularly check the medication for any changes in appearance or integrity. Refrain from using it if you notice any discrepancies.