Salmeterol
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Salmeterol
- III. How it Works
- IV. Side Effects of Salmeterol
- V. Common Side Effects
- VI. Off-Label Use
- VII. Dosage and Administration
- VIII. Composition
- IX. Storage
- X. Interaction
- XI. Warning
- XII. Contraindication
- XIII. Careful Administration
- XIV. Important Precautions
- XV. Administration to Elderly
- XVI. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- XVII. Administration to Children
- XVIII. Overdosage
- XIX. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
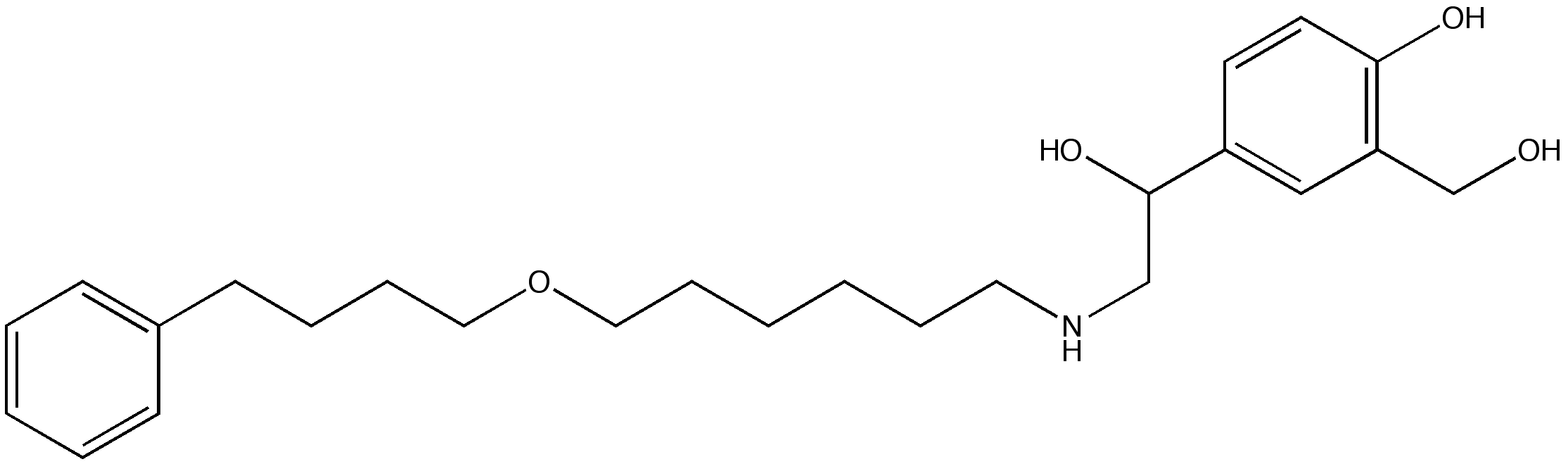
Salmeterol is a medication derived from saligenin commonly used to treat disorders. It works as a bronchodilator by helping to improve airflow into the lungs. Developed in the 1980s, Salmeterol was created as a longer-lasting alternative to short-acting beta2 agonists and has since gained significant recognition as an effective treatment option. Its primary use is for preventing asthma attacks than providing immediate relief from bronchospasm. Instead, it helps to keep the airways open over some time.
II. Uses of Salmeterol
Managing asthma; Individuals with asthma often find comfort in using Salmeterol, especially when short term treatments fail to provide the desired relief. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); Salmeterol proves beneficial for patients, with COPD, a lung condition as it helps alleviate symptoms like difficulty breathing and chronic cough. Preventing exercise induced bronchoconstriction; For those who experience breathing difficulties during activity Salmeterol acts as a protective barrier preventing sudden bronchial spasms.
References:
2: Salmeterol - Wikipedia 1: Salmeterol (Inhalation Route) - Mayo Clinic 3: Salmeterol (Inhalation Route) Proper Use - Mayo Clinic
III. How it Works
Salmeterol works by relaxing the muscles in the tubes. This relaxation happens because it activates receptors called beta2 adrenergic receptors in the smooth muscle of the bronchial tubes, which causes them to widen. Salmeterol is unique because it binds not only to receptors on the outside of cells but also to receptors inside cells, contributing to its long-lasting effects. Speaking of how it starts working and how long its effects last, Salmeterol stands out. After inhaling it, you can notice its effects within 10 to 20 minutes. It can protect against bronchospasm for up to 12 hours, so it's recommended twice daily.
IV. Side Effects of Salmeterol
Regarding the overview of side effects, it's important to note that, like any other medication, Salmeterol is not without its own side effects. However, how these effects appear can differ from person to person—often depending on the dosage and individual tolerance. It's crucial to differentiate between side effects and those that are rare. While most people may experience reactions, there is a slight chance that some individuals might encounter severe but uncommon consequences.
V. Common Side Effects
Respiratory responses; Certain individuals may notice a throat, occasional coughing, and even an unexpected tightening of the airways. Cardiovascular; Instances of heart palpitations and an elevated heart rate have been documented. Musculoskeletal; In cases, users have mentioned experiencing muscle cramps, particularly in the calves and hands. Neurological; Mild headaches and fleeting nervousness can occur during the medication's early stages.
VI. Off-Label Use
Regarding off-label use, we're talking about using Salmeterol for conditions that aren't officially approved. Some examples of these traditional uses include treating allergic rhinitis and, in certain situations, cystic fibrosis. However, doctors usually make these decisions based on their judgment and the unique circumstances of each patient. It's important to note that there aren't clinical studies supporting the effectiveness and safety of these uses, so it's necessary to be cautious when prescribing and closely monitor patients.
References:
1: Steroid treatment in cystic fibrosis 2: Pharmacotherapy of allergic rhinitis - UpToDate 3: Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis | AAFP
VII. Dosage and Administration
The appropriate doses depend on the health condition being addressed the age of the patient and any other existing medical conditions. To ensure the use of inhalers, it is essential to prime the device before using it take deep inhalations and rinse the mouth afterward to reduce the chance of developing thrush. For groups such as older individuals, children, or those, with kidney problems it is crucial to make dose adjustments and closely monitor their condition.
VIII. Composition
Salmeterol contains an ingredient called salmeterol xinafoate and various inactive compounds that help improve its effectiveness and stability. It is offered in forms and strengths, such as dry powder inhalers or metered dose inhalers, to cater to individual patient's specific requirements and preferences.
IX. Storage
It is crucial to store Salmeterol to ensure that it remains effective and lasts for a long time. The drug in any form needs conditions to maintain its potency. The ideal temperature for storage is usually room temperature, which falls between 20°C to 25°C. It should be protected from humidity and kept away from direct light. If not appropriately stored, especially if exposed to temperatures, humidity, or light, the drug can degrade quickly and become less effective or completely ineffective.
X. Interaction
How a drug works goes beyond its direct effects and includes how it interacts with other substances. There are medications like beta blockers, diuretics, and some antidepressants that can hinder the effectiveness of Salmeterol. On the other hand, since Salmeterol is a bronchodilator, it can potentially enhance the effects of other drugs with similar therapeutic targets. Additionally, over-the-counter treatments, like antihistamines and epinephrine-based medications, may interfere with salmeterol action.
XI. Warning
It is essential to be aware of the adverse effects of Salmeterol even though they are rare. These effects can vary from reactions to severe breathing difficulties. In some cases, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience paradoxical bronchospasm, hives, or any signs of an allergic reaction.
XII. Contraindication
Although Salmeterol offers hope for individuals with conditions there are certain situations where it should be avoided. These include patients who have cardiac arrhythmias or a solid hypersensitivity for the drug or its ingredients. If there has been an allergic reaction, in the past, it is necessary to completely stop using and avoid this medication.
XIII. Careful Administration
There are situations or circumstances where it is advisable to be cautious when using Salmeterol. These could include patients who already have issues or those who have low potassium levels. In cases, it is essential to closely monitor these individuals, which may involve regular heart checkups and periodic testing of their potassium levels.
XIV. Important Precautions
Ensuring the safety of patients goes beyond prescribing medication. It involves follow-up and monitoring to ensure the drug's positive effects are achieved without any accompanying negative side effects. A crucial aspect of this vigilance is identifying signs of complications ranging from a persistent cough to abnormalities in cardiovascular health.
XV. Administration to Elderly
As the saying goes age plays a role in pharmacokinetics, and it's not just a mere number. When it comes to dosages, we need to take into account the impact of age on metabolic rates. Additionally, the safety aspects and considerations vary for more vulnerable individuals, to adverse effects. This calls for adjustments or increased monitoring to ensure their well-being.
XVI. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The impact of drug safety on babies and young children is an important consideration. Although there is no evidence of Salmeterol being directly harmful, it is recommended to exercise caution. The guidance for its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding primarily focuses on weighing the risks against the benefits when no other alternatives are available.

XVII. Administration to Children
The guidelines for treating children must consider their changing metabolism and organ development. This involves adjusting the dosage for pediatric patients and thoroughly reviewing safety information. Additionally, it's essential to consider age-related factors as infants may require a treatment plan compared to adolescents.
XVIII. Overdosage
Accidental or intentional cases of taking much medication though uncommon, require immediate action. The symptoms can vary from a racing heart to seizures. Here's what you should do as an aid; make sure the person's airway is clear, stop them from taking more drugs, and seek urgent medical attention. As for procedures, the doctor might suggest gastric lavage or giving activated charcoal. In the run, monitoring the patient until they are stable and their condition has improved is essential.
XIX. Handling Precautions
From the moment a prescription is written until the time of disposal, it is crucial to handle medications. This involves taking all measures to maintain the drug's integrity throughout its lifecycle and ensuring it remains in optimal condition.