Seroxat
- Introduction
- Uses of Seroxat
- How Seroxat Works
- Off-label Use of Seroxat
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition of Seroxat
- Side Effects of Seroxat
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- Special Populations: Administration Details
- Overdosage of Seroxat
- Storage and Handling Precautions
Introduction
Historical development and approval of Seroxat
With a history rooted in the development of medications Seroxat, also known as Paroxetine scientifically established itself as an essential player in the field of antidepressants. After undergoing clinical trials and meticulous evaluation, Seroxat received approval, from health regulatory authorities. Its arrival can be seen as an advancement providing optimism and solace to numerous individuals struggling with challenging psychiatric conditions.
Common perceptions and misconceptions about Seroxat
Seroxat is a topic that sparks a range of opinions. Some people praise it as a source of comfort, while others have doubts and concerns. The main point of discussion revolves around its effectiveness in improving episodes. On the other hand, some misunderstandings arise, with some mistakenly believing that it can cause sadness or worsen depressive symptoms.
Uses of Seroxat
Approved indications: depression, panic disorder, etc.
Seroxat is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant that is used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) 123.
1: Drugs.com 2: Patient.info 3: Netdoctor.co.uk
Benefits observed in clinical trials and real-world settings
In real-life settings with regulations, Seroxat has demonstrated its effectiveness in relieving symptoms related to the mentioned conditions. Moreover, numerous personal accounts confirm these results as many people praise its life-changing effects.
How Seroxat Works
Mechanism of action in the brain
The complex interactions between neurotransmitters create a cerebral environment. Seroxat, classified as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), mainly works by preventing the reabsorption of serotonin in the brain. In effect, this results in increased levels of serotonin in the spaces between neurons, potentially improving mood and mitigating symptoms of depression.
Impact on neurotransmitters and neural pathways
Apart from serotonin, Seroxat also has effects on other neurotransmitters. However, its main therapeutic benefits are primarily attributed to its influence on serotonergic pathways. By increasing levels, it promotes the growth of new neurons and enhances the connections between key regions of the brain.
Off-label Use of Seroxat
Overview and definitions of off-label prescribing
Off-label prescribing is when doctors use medications for conditions that are not officially approved. This happens when they have received evidence of some preliminary research or have expertise in the field.
Common off-label uses for Seroxat
Seroxat is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant that is primarily used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) 1 . Although Seroxat has not been officially approved for other uses, doctors have prescribed it for off-label uses based on real-world evidence and studies that highlight the advantages of using Seroxat for purposes other than its main approved uses .
There is limited evidence on the effectiveness of Seroxat in treating generalized anxiety disorder. However, some studies have suggested that Seroxat may be effective in treating this condition .
It is important to note that the use of Seroxat for off-label purposes should only be done under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional, who can assess the risks and benefits of such use .
1: Drugs.com : Patient.info : Netdoctor.co.uk : Dermatology Advisor
Research supporting off-label uses
Although there isn't much data supporting its primary uses, several studies shed light on the effectiveness of Seroxat in off-label applications. While these investigations are still in the stages, they suggest that Seroxat has significant therapeutic possibilities.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended starting doses
Many adults who start a treatment with Seroxat are usually advised to begin with a daily dose of 20 mg. However, the dosage may be adjusted depending on the condition being treated.
Adjustments based on patient response and tolerance
Although Seroxat has a pharmacological profile, it is necessary to adjust the dosage based on individual differences periodically. Monitoring and patient feedback help determine whether the dosage should be increased or decreased.
Dosing schedules and considerations for different indications
Usually, it is recommended to take the medication a day. However, the approach may vary depending on the condition being treated. For example, if you're managing panic disorder, your doctor might suggest gradually increasing the dosage to minimize side effects.
Composition of Seroxat
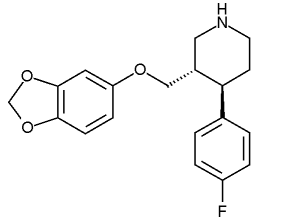
Active ingredient: Paroxetine
Paroxetine is a powerful SSRI, the component of Seroxat's therapeutic effectiveness. Its molecular structure has been carefully crafted to influence the pathways of serotonin in a manner.
Inactive components and their roles
Apart from Paroxetine, Seroxat consists of additional substances. These inactive ingredients, including binders and preservatives, are added to improve the drug's stability, effectiveness, and taste.
Different formulations: tablets, liquid, etc.
Seroxat offers a range of options to cater to different patient preferences and requirements. These options include tablets in different strengths liquid formulations for those who prefer not to take solid doses and extended-release variants that provide sustained therapeutic effects.
Side Effects of Seroxat
Overview of clinical trial data
Clinical trials, which serve as the cornerstone of evaluating pharmaceuticals, have shed light on the side effects linked to Seroxat. Despite its therapeutic advantages, like any medication, it carries the possibility of unfavorable reactions.
Common side effects: nausea, dizziness, etc.
Most people who take Seroxat may experience nausea, dizziness, insomnia, and dry mouth symptoms. However, it is essential to note that these side effects typically diminish as the body becomes accustomed to the medication.
Less common and rare side effects
Sometimes, a small portion of people may experience common effects like Serotonin syndrome includes various symptoms caused by increased serotonin levels. Hyponatremia refers to lower levels of sodium in the blood. Skin rashes or allergic reactions.
Interactions with Other Medications
Potential drug-drug interactions
Taking medications simultaneously as Seroxat may lead to some challenges in achieving the desired therapeutic effects. It is essential to exercise caution when using SSRIs, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), and specific antipsychotics alongside Seroxat.
Foods or substances that may alter Seroxat’s effectiveness or risk profile
Some types of food that contain high levels of tyramine or affect liver enzymes may interact with Seroxat. It is advisable to consume alcohol because it can have depressive effects on the central nervous system.
Recommendations for monitoring when taking Seroxat with other drugs
Healthcare professionals usually recommend checkups, which involve gathering patient input about their experiences and assessing objective markers such as liver function tests. This is particularly important when Seroxat is prescribed alongside medications.
Warnings and Contraindications
Populations or conditions where Seroxat should be avoided
There are groups of people who may not be suitable candidates for Seroxat therapy due to their specific physiological or pathological conditions. These groups include individuals who are currently taking MAOI medications, those who have a hypersensitivity to Paroxetine, and people who are dealing with severe liver or kidney impairments.
Genetic factors affecting response to Seroxat
Pharmacogenomics, a growing field, has shed light on the genetic differences that influence how Seroxat behaves in our bodies. Some specific gene variations could make certain individuals more susceptible to increased risks or therapeutic advantages.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring for signs of serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome can occur when there is excess activity in the central nervous system. Both clinicians and patients need to remain attentive to signs, which may include agitation or restlessness, increased heart rate, dilated pupils, muscle rigidity or tremors, fluctuations in blood pressure, and diarrhea. Recognizing these indicators makes it possible to reduce the likelihood of complications and enable intervention without delay.
Risks of abrupt discontinuation
Stopping Seroxat abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, so it is essential to reduce the dosage. These symptoms may include dizziness, sensory disturbances known as "brain zaps," difficulty sleeping, irritability, and anxiety. To avoid these effects, healthcare professionals recommend gradually reducing medication dosage.
Potential for increased suicidal ideation in certain populations
Interestingly, it is worth noting that specific individuals, teenagers, may encounter an increase in thoughts of self-harm during the early stages of therapy. Therefore, paying attention and conducting regular psychiatric evaluations is crucial, especially in the early phases of treatment.
Special Populations: Administration Details
Administration to the Elderly
Due to changes in the body, as people get older, the elderly population may need personalized treatment methods. It is essential to consider declines in kidney or liver function when determining initial dosage levels and gradually increase them as tolerated. Elderly individuals are more prone to experiencing side effects, like sodium levels or falls, so it is crucial to review their condition with medical professionals regularly.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
When considering the use of Seroxat during pregnancy, it can be complex to balance the mother's health and the fetus's well-being. The effects of Seroxat on the developing baby are not complete. We need further investigation. On the other hand, if maternal depression is left untreated, it can harm both the mother and the fetus. Regarding breastfeeding, there is a possibility that trace amounts of Seroxat may pass into breast milk. However, in some cases, the benefits of breastfeeding outweigh any potential risks, so it's important to have personalized consultations with healthcare professionals.
Administration to Children
Providing care for children comes with various challenges and complexities. When it comes to dosing for patients, it's essential to consider factors like weight, age, and the specific condition being treated. The general rule is to start with a dose and gradually adjust as needed. It's crucial to be attentive to side effects in children, especially any changes in behavior that may arise. Safety is of importance in their care.
Overdosage of Seroxat
Signs and symptoms of overdose
Going beyond the recommended limits can lead to various symptoms, including; Feeling nauseous and vomiting, Experiencing tremors, Feeling tired or even falling into a coma Having a rapid heartbeat Experiencing seizures.
Recommended management and interventions
If someone experiences an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical help. The necessary steps for managing such a situation may include Washing out the stomach ( lavage). Giving activated charcoal. Providing symptomatic and supportive care. Monitoring the person's heart and breathing continuously.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal storage conditions
It is essential to store Seroxat to maintain its effectiveness. It should be kept at room temperature. Protected from excessive moisture and heat.
Shelf-life considerations
Pharmaceuticals are not impervious to the passage of time. Therefore using Seroxat after it has expired could potentially compromise its effectiveness and safety.
Safe handling and disposal methods
Store Seroxat in a location inaccessible to children and pets to prevent consumption or negative environmental impacts. Of throwing it directly into the household garbage, it is recommended to use take-back programs or consult pharmacies for appropriate disposal methods.









