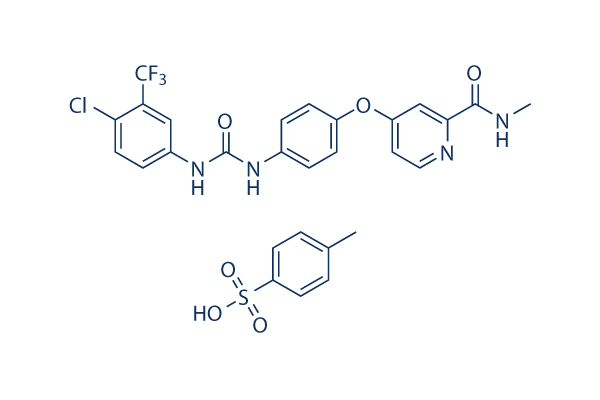
Sorafenib
- Analyze How Sorafenib Works
- Sorafenib Mechanism of Action
- Establish an Appropriate Dosage
- Sorafenib Desmoid: A Promising Treatment Option
- Sorafenib Tosylate: A Powerful Cancer-Fighting Compound
- Recognize Potential Side Effects
- Identify Contraindications and Precautions
- Sorafenib Success Rate: Evaluating Treatment Outcomes
- Compare Sorafenib with Other Cancer Treatments
- Buy Sorafenib: Comprehensive Guide to Cancer Treatment
Explore the advantages of Sorafenib, a medication that has proven to be a lifesaver in cancer treatment. The FDA has approved its use in managing renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Additionally, ongoing research is investigating its effectiveness in treating various other forms of cancer.
Treating Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the prevalent form of kidney cancer, comprising approximately 90% of all cases. When surgical procedures or alternative treatments are not options, Sorafenib has demonstrated its effectiveness in managing advanced RCC. Clinical trials have shown that patients treated with Sorafenib have observed progression-free survival rates compared to individuals who underwent placebo treatments.
Managing Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma, commonly known as liver cancer, is frequently a result of long-term liver disease or cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or C infections, excessive alcohol consumption, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (source). In cases where surgical removal of HCC is impossible (unresectable), Sorafenib provides an alternative treatment option that can effectively slow down tumor growth and enhance overall survival rates.
Potential Use in Other Cancer Types
Ongoing research is being conducted to explore the advantages of Sorafenib in treating various types of cancer. For instance, studies have shown promising outcomes when using Sorafenib for thyroid cancer (source) and desmoid tumors (source). However, further investigation is necessary before these applications can be approved.
In summary, Sorafenib provides hope to patients with RCC or unresectable HCC by offering an effective treatment option to enhance survival and quality of life. By understanding the benefits of Sorafenib, patients can make decisions about whether this medication is suitable for them. Analyzing how Sorafenib works will also provide insights into its effectiveness and potential side effects. As an FDA-approved drug for renal cell carcinoma and unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, Sorafenib brings hope to individuals battling cancer.
Analyze How Sorafenib Works
Let's look at how Sorafenib works and what it does to cancer cells. Sorafenib is a type of treatment that targets explicitly enzymes called kinases, which play a role, in the growth and division of cells, by inhibiting these kinases Sorafenib effectively. It even halts the growth of cancer cells.
Inhibiting Cancer Cell Growth
Sorafenib is designed to target kinases that are responsible for the growth of tumor cells. These kinases include Raf 1 kinase, B Raf kinase, and members of the endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) kinase family. These proteins are vital in signaling pathways that control cells' survival and programmed cell death (apoptosis). By inhibiting these kinases, it disrupts these pathways, ultimately resulting in a decrease in tumor growth.
Blocking Angiogenesis
In addition to targeting tumor cells, Sorafenib also impacts angiogenesis, forming new blood vessels from existing ones. Tumors rely on a supply of nutrients and oxygen to thrive and achieve this by triggering angiogenesis in their surroundings. This is done through the production of VEGF, a protein that encourages the formation of blood vessels. Substances like Sorafenib, or inhibitors, block VEGF receptors on endothelial cells that line the blood vessels within tumors. As a result, these tumors are deprived of the nutrients they require for their ongoing growth and expansion.
Tumor Microenvironment Impact
- Hypoxia: When Sorafenib inhibits angiogenesis, it reduces the oxygen supply within the tumor microenvironment, leading to hypoxia. This condition makes cancer cells more vulnerable to cell death.
- Immune Response: Recent research indicates that Sorafenib may impact tumor response by influencing specific immune cells like T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
These studies suggest that Sorafenib could modify the tumor microenvironment by affecting immune cells, which might enhance anti-tumor immunity. To summarize, Sorafenib's unique ability to target both cancer cell growth and angiogenesis makes it a powerful weapon against types of cancers. It is essential for individuals to understand how Sorafenib works in order to make decisions about their treatment plans. Now let's delve into the mechanism of action behind Sorafenib and its effects on the body.
Key Takeaway: Sorafenib is a therapy that effectively slows down or halts cancer cell growth by inhibiting multiple kinases responsible for cell division. Additionally, it impacts angiogenesis by blocking receptors found on endothelial cells lining blood vessels within tumors, thereby reducing tumor growth. With its dual-action approach, Sorafenib proves itself as a weapon against different forms of cancers.
Sorafenib Mechanism of Action
Sorafenib's effectiveness in treating cancer stems from its way of working. This medication falls under a category known as multikinase inhibitors, which aim to target cellular pathways involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. By blocking these pathways Sorafenib can effectively slow down the progression of types of cancers.
One important aspect of how Sorafenib works is its ability to inhibit angiogenesis. Angiogenesis refers to the formation and development of blood vessels, which tumors rely on for their continuous growth and spread. Sorafenib inhibits tyrosine kinases that are crucial for angiogenesis;
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors (VEGFRs); These receptors stimulate the growth and maintenance of blood vessels within tumors. By blocking VEGF from binding to these receptors, Sorafenib reduces the blood supply to tumor cells.
- Derived Growth Factor Receptors (PDGFRs); PDGF signaling plays a significant role in tumor vascularization, proliferation, and migration abilities. By inhibiting PDGFR activity with Sorafenib, these processes are disrupted.
- Raf Kinases: Raf kinases are part of a signaling pathway that regulates cell division, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis. Targeting Raf kinases directly or indirectly through kinase targets, like BRAF or CRAF inhibition, helps prevent uncontrolled replication of cancerous cells.
Apart from its ability to reduce blood vessel growth, Sorafenib effectively prevents the division of tumor cells by impacting various signaling pathways within cancer cells. This unique combination of actions makes Sorafenib a potent treatment against forms of cancer, including advanced renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma that cannot be surgically removed. It is crucial to determine the dosage for each patient, considering the complex mechanism of action associated with Sorafenib. Understanding how this medication functions within the body can help determine the dose based on individual needs. With its ability to inhibit angiogenesis and limit tumor cell growth, Sorafenib is a kinase inhibitor targeting various pathways involved in cancer development and survival. #cancerresearch
Establish an Appropriate Dosage
Finding the amount of Sorafenib to take is significant to get the best results and avoid any unwanted effects. Below you'll find the dosage for adults and any necessary changes for specific conditions.
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The recommended dose for Sorafenib in adults is 400 twice a day, with an ideal gap of 12 hours between each dose. Taking this medication on a stomach at least one hour before or two hours after a meal is essential. Make sure to follow your doctor's instructions regarding the dosage, as they may adjust it based on your specific needs and how you respond to the treatment.
Adjustments for Specific Conditions
- Hepatic Impairment; Patients with liver problems (Child Pugh A) don't need any adjustment to their Sorafenib dose. However, if you have Child-Pugh B) or severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment, it's important to consult your healthcare provider before starting treatment. There isn't data available about the right dosages in these cases so it's best to seek medical advice.
- Renal Impairment; Patients with mild to kidney dysfunction don't require any dosage adjustments when taking Sorafenib. However if you have renal impairment, caution should be exercised when using this medication. It's advisable to discuss any risks of Sorafenib on your kidney function and other medications with your doctor.
- Dose Modifications; Your healthcare provider may adjust your Sorafenib dosage depending on the severity of side effects experienced or if you're taking medications that could interact with it. Make sure to inform your doctor about all prescription and over the counter medicines, well as vitamins and supplements you're currently taking.
In conclusion, it is crucial to work with your healthcare team in order to determine the appropriate dosage of Sorafenib, for your specific situation. By following their guidance and carefully monitoring any side effects, you can optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing risks. It is essential to consider factors such as age, weight, and medical history when deciding on the dosage of sorafenib. Once the correct dosage has been determined, let's explore how sorafenib can be utilized in the treatment of tumors. In summary; Finding the dose of sorafenib is crucial to ensure its effectiveness while minimizing any potential side effects. The standard adult dosage is 400 mg, which should be taken twice a day with a 12-hour interval between doses. Adjustments may be necessary depending on circumstances like hepatic or renal impairment and it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, for guidance.
Sorafenib Desmoid: A Promising Treatment Option
Desmoid tumors, which are also referred to as fibromatosis, are uncommon soft tissue tumors that invade locally and can lead to significant health issues. Although surgery is typically the treatment option for these tumors, the chances of recurrence are still relatively high. As a result, there is growing interest in exploring therapies such as Sorafenib, a targeted drug therapy that holds promise for patients with desmoid tumors.
How Sorafenib Works on Desmoid Tumors
Sorafenib works by blocking the activity of kinases that play a role in cell growth and forming new blood vessels. In the case of tumors, this action helps halt tumor progression and may even cause existing tumors to shrink by disrupting vital pathways necessary for their survival.
Evidence Supporting Sorafenib Use in Desmoid Tumors
In a clinical trial by the National Cancer Institute, encouraging outcomes were observed when using Sorafenib to treat patients with desmoid tumors. The trial documented a response rate of 33% among participants, while an additional 53% experienced stable disease. For information on this study, refer to the provided source. Furthermore, anecdotal evidence from individual case reports suggests that Sorafenib may effectively manage recurrent desmoid tumors. However, conducting extensive studies to confirm its efficacy is crucial.
Considerations for Sorafenib Treatment in Desmoid Patients
While Sorafenib demonstrates potential as a treatment option for desmoid tumors, it is crucial to consider the possible side effects and contraindications. Common adverse reactions include fatigue, diarrhea, skin rash, and hand-foot syndrome. Although severe complications are less frequent, they may still arise (source). Before initiating any medication, you must consult with your healthcare provider to be aware of potential side effects and complications. In summary, Sorafenib holds promise as a treatment choice for tumors. However, further research is required to confirm its effectiveness. The results from phase II trials and anecdotal evidence suggest that it could be a suitable alternative to surgery for certain patients.
Nevertheless, evaluating the potential side effects and contraindications is essential before starting the treatment. Seek advice from your healthcare provider to determine if Sorafenib is appropriate for you. Sorafenib has proven effective in treating tumors—an uncommon type of tumor—by impeding cell growth and angiogenesis through targeted therapy. To ascertain its suitability for your situation, consult with your healthcare provider.
Sorafenib Tosylate: A Powerful Cancer-Fighting Compound
Sorafenib, which contains the active component sorafenib tosylate, is a substance that has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in the treatment of different forms of cancer. Acting as a kinase inhibitor, sorafenib tosylate focuses on various pathways within cells that are associated with the development and spread of cancerous cells.
Targeting Key Cellular Pathways
Sorafenib tosylate is a medication that hampers the activity of protein kinases, which are key players in cell division and the formation of new blood vessels. Interrupting these pathways effectively hinders growth. Spread of cancer cells. Some essential kinases that sorafenib targets are VEGFR ( endothelial growth factor receptor) PDGFR (platelet-derived growth factor receptor), and RAF kinase.
Treating Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Sorafenib, an approved treatment for renal cell carcinoma, has shown promising results in patients who have not responded to other therapies. Clinical trials have demonstrated enhancements in progression-free survival compared to a placebo (source). In the case of hepatocellular carcinoma, sorafenib has also shown its effectiveness by prolonging overall survival rates compared to a placebo.
Potential Use in Other Cancer Types
Although Sorafenib is primarily prescribed for hepatocellular carcinoma, ongoing research indicates its potential effectiveness against other types of cancer as well. For instance, studies have shown promising outcomes in treating thyroid cancer and desmoid tumors. However, further research must confirm its efficacy in addressing these cancer types. Patients need to exercise caution when taking Sorafenib tosylate as a targeted therapy drug for cancer treatment, as there may be side effects. Before initiating the treatment with Sorafenib tosylate, patients should be aware of these adverse effects and discuss them with their healthcare provider.

Recognize Potential Side Effects
It is essential for patients receiving treatment to understand the side effects of Sorafenib. While some reactions can be anticipated and handled, there are others that may require medical attention due, to their severity.
Common Side Effects
- Feeling queasy and throwing up,
- Having a skin rash or redness,
- Experiencing dry skin or itchiness,
- Losing hair (alopecia).
These usual side effects are mild or moderate in intensity and may get better as your body gets used to the medicine. It's essential to keep your healthcare provider informed about any symptoms you encounter so they can help you manage these side effects effectively.
Serious Side Effects to Watch Out For:
Chest discomfort or difficulty breathing could indicate a heart condition like congestive heart failure (source). If you experience bleeding issues, you may notice blood in your urine, stool, vomit, or even cough-up blood. Before starting Sorafenib treatment, both patients and healthcare providers need to consider the outcomes ranging from mild to severe carefully. It is crucial to review any contraindications and take necessary precautions. Patients should stay informed about the side effects of Sorafenib and maintain open communication with their healthcare provider. Look for any symptoms, such as chest pain or bleeding problems.
Identify Contraindications and Precautions
It's essential, for cancer patients undergoing treatment to be aware of the situations where Sorafenib should not be used and the potential drug interactions. In this section, we will cover the contraindications and precautions related to Sorafenib.
Situations Where Sorafenib Should Not Be Used
Allergies: If you have a known allergy or sensitivity to Sorafenib or any of its components, it is essential to avoid using this medication. Allergic reactions may manifest as a rash, itching, swelling, dizziness or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms after taking the medication, it is advisable to seek medical assistance.
Pregnancy: Sorafenib falls under category D in the FDA classification system for pregnancy drugs. This means that it can potentially harm the developing fetus if taken during pregnancy. Therefore, it is recommended that women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant consult their healthcare provider before starting this medication.
Drug Interactions To Be Aware Of
Certain medications have the potential to interact with Sorafenib. It may cause adverse effects on your health. Some known drugs that may interact with Sorafenib include:
- Blood thinners like warfarin, which, when used together, can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Another drug, Rifampin, has the potential to lower blood levels of Sorafenib, thereby reducing its effectiveness.
- Additionally Dexamethasone can also decrease blood levels of Sorafenib. Impact its ability to effectively treat cancer cells.
Please bear in mind that this list is not exhaustive. It's crucial to inform your doctor about all the medications, supplements, and herbal products you are taking to avoid any potential drug interactions. It is essential for patients considering Sorafenib treatment to be aware of these contraindications and precautions. Before starting Sorafenib treatment, you should consult with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the option for you. Understanding the risks and precautions associated with taking Sorafenib is essential in ensuring its safe use. Now let's explore the success rate of Sorafenib as a treatment option for specific conditions."Patients undergoing cancer treatment should be informed about the contraindications and precautions associated with taking Sorafenib. It's crucial to consult your healthcare provider before using this medication.
Sorafenib Success Rate: Evaluating Treatment Outcomes
It is essential for patients who are considering Sorafenib as a treatment option to have an understanding of its success rate. Numerous studies have indicated that Sorafenib can be highly effective in treating types of cancer.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
According to a study, Sorafenib had an impact on the progression-free survival of advanced RCC patients compared to those who received a placebo. The median progression-free survival for patients treated with Sorafenib was 5.5 months, while those in the placebo group only experienced a progression-free survival of 2.8 months.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
A crucial research study conducted on HCC demonstrated that Sorafenib significantly enhanced overall survival and time progression rates compared to a control group. The patients who were administered Sorafenib exhibited a broad survival period of 10.7 months, whereas those who received the placebo had an average general survival period of only 7.9 months.
Tips for Maximizing Treatment Success:
- To ensure that you get the results from your medication, strictly following the prescribed dosage and administration schedule is essential.
- Making lifestyle changes like maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise can also help improve how your body responds to the treatment.
- It's crucial to stay closely connected with your healthcare team and attend all scheduled appointments for checkups. This will allow them to monitor your progress effectively.
When considering Sorafenib as a treatment option for cancer, it is essential to have a discussion with your doctor about its potential benefits and risks. They will consider factors such as the type of cancer, its stage, and your overall health status before determining whether Sorafenib is suitable. Sorafenib has proven effective in treating types of cancer, showing success rates ranging from 40% to 50%. It would be beneficial to compare Sorafenib with available cancer treatments to understand their respective efficacy. Specifically, Sorafenib has demonstrated success in treating renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. By adhering to the dosage and making necessary lifestyle changes while attending regular check ups, you can maximize the effectiveness of this treatment approach. Remember; #cancer #pharmacy
Compare Sorafenib with Other Cancer Treatments
When considering options for cancer treatment, it is crucial to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of each choice. In this section, we will compare Sorafenib with available therapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- For RCC treatments, there are several targeted therapies approved besides Sorafenib. These include Sunitinib, Pazopanib, Axitinib, Cabozantinib, and Lenvatinib combined with Everolimus and Bevacizumab combined with Interferon alfa.
- In the case of HCC, where surgery or liver transplantation is not possible due to various reasons such as tumor size or location, alternative options to Sorafenib include Lenvatinib as a first-line therapy and Regorafenib and Cabozantinib treatments in later lines.
Determining the suitable treatment option for an individual patient requires careful consideration of factors such as the specific type of cancer being treated, the patient's overall health status, potential side effects associated with each drug, and treatment goals—whether they aim to prolong survival or improve quality of life. Patients should collaborate with healthcare professionals like oncologists or pharmacists who can advise based on their medical history and preferences. In some cases, Sorafenib may be preferred due to its demonstrated efficacy in extending overall survival and delaying disease progression for RCC and HCC patients. When considering treatment options for RCC and unresectable HCC, it is important to compare Sorafenib with other cancer treatments. It is advised to seek personalized guidance from a healthcare professional to make the decision. Don't hesitate to consult a healthcare expert for information on Sorafenib and other potential treatment options.
Buy Sorafenib: Comprehensive Guide to Cancer Treatment
Understanding Sorafenib's benefits and mechanisms of action is essential for patients considering purchasing it. Determining the dosage and being aware of potential side effects before starting the treatment is crucial. Moreover, it is necessary to identify any contraindications and take precautions to ensure a successful outcome. If you want to buy Sorafenib, Buy Pharma provides an online platform for purchasing this medication. With prices and efficient shipping options, Buy Pharma allows you to access the required treatments. Don't hesitate. Purchase Sorafenib today. Take charge of your cancer treatment journey!
Sorafenib FAQ
- Sorafenib side effects?
- Sorafenib mechanism of action?
- Sorafenib package insert?
- Sorafenib tosylate?
- Sorafenib brand name?
- Sorafenib price?
- Sorafenib for AML?
- Sorafenib HCC?
- Sorafenib Nexavar?
- Sorafenib in HCC?
- Sorafenib for liver cancer?
- Sorafenib liver cancer?
- Sorafenib for HCC?
- Sorafenib dose?
- Sorafenib dosage?
- Sorafenib 200 mg?
- Sorafenib cost?
- Sorafenib desmoid?
- Sorafenib success rate?
- Sorafenib AML?
- Sorafenib wiki?
- Sorafenib generic?
- Sorafenib structure?
- Sorafenib target?
- Sorafenib FLT3?
- Sorafenib tablet?
- Sorafenib tablets?
- Sorafenib chemotherapy?
- Sorafenib chemo?
- Sorafenib dosage?
- Sorafenib 200 mg?
- Sorafenib cost?
- Sorafenib desmoid?
- Sorafenib success rate?
- Sorafenib AML?
- Sorafenib wiki?
- Sorafenib generic?
- Sorafenib structure?
- Sorafenib target?
- Sorafenib FLT3?
- Sorafenib tablet?
- Sorafenib tablets?
- Sorafenib chemotherapy?
- Sorafenib chemo?
- Sorafenib dosage?
- Sorafenib 200 mg?
- Sorafenib cost?
- Sorafenib desmoid?
- Sorafenib success rate?
- Sorafenib AML?
- Sorafenib structure?
- Sorafenib target?
- Sorafenib FLT3?
- Sorafenib tablet?
- Sorafenib tablets?
- Sorafenib chemotherapy?
- Sorafenib chemo?
Sorafenib side effects?
Although known for its effectiveness in treating several diseases effectively through inhibition of multiple kinases within cells—Sorafenib has several noticeable drawbacks worth mentioning too related to its usage. Common secondary effects reported by users involve symptoms such as fatigue while others could encounter dietary challenges like loss of appetite along with skin conditions ranging from mild rashes to dry skin complications manifesting later on —with more severe consequences including bleeding, heart issues, and liver damage reported too. Given that these risks are a real concern for some patients, healthcare providers must ensure that all possible side effects for Sorafenib are explicitly discussed.
Sorafenib mechanism of action?
Sorafenibs mechanism of action lies in its ability to target multiple signaling molecules involved in cancer development. By suppressing both intracellular (c Rafand b Raf)and extracellular kinases(KIT,-FLT 3,-RET,-VEGFRs and PDGFRB) Sorafenib efficiently halts the division of tumorigenic cells while simultaneously preventing their vascularization. As such Sorafenib presents as a potent anti cancer agent with remarkable efficacy against various types of tumors.
Sorafenib package insert?
One of the most critical pieces of literature that any person using Sorafenib should have at hand is its package insert. It contains salient details such as dosage instructions, storage recommendations, contraindications and possible side effects relevant to any user seeking safe and effective therapy outcomes. Prior to commencing treatment with Sorafenib users should read this document thoroughly or seek expert advice from their pharmacist or prescribing physician.
Sorafenib tosylate?
When doctors need an effective weapon against advanced renal cell carcinoma or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (along with certain other cancers), they often turn to Sorafenib tosylate. The complete chemical identity of this powerful medication is Sorafenib; however, "tosylate" signifies that it exists as a salt form compound. This characteristic can be quite impactful since it has been known to affect stability levels along with aspects such as solubility or absorption rates.
Sorafenib brand name?
Nexavar is the trade name for Sorafenib, a medication manufactured and distributed by Bayer, a renowned multinational pharmaceutical corporation.
Sorafenib price?
The price of Sorafenib may fluctuate due to various factors such as location, pharmacy availability and type of health coverage offered by an insurer. Given its critical role in treating cancer patients coupled with unique chemical composition; Sorafenib remains a pricey medication option for many individuals and families affected by cancer. Ensuring accurate pricing information would require one contacting their local pharmacies or insurers for advice.
Sorafenib for AML?
Investigated as a possible solution for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Sorafenib reveals encouraging potential in its early stages. Reports show that using it alongside other therapies may offer significant advantages to certain patients with FLT3 ITD mutations. Nevertheless more research is imperative to substantiate these results and determine how best to use Sorafenib appropriately for optimal outcomes in treating AML.
Sorafenib HCC?
Sorafenib is a primary treatment for advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) which is the most widespread liver cancer type. This medication has demonstrated improved survival rates, achieved by restricting tumor cell growth and angiogenesis.
Sorafenib Nexavar?
When it comes to combating different types of cancer, Sorafenib or Nexavar stands out as an effective multi kinase inhibitor. This medication has yielded impressive results in managing ailments including but not limited to advanced renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sorafenib in HCC?
Sorafenib has emerged as a leading therapy choice for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) mainly when dealing with advanced cases. This medication offers unique benefits by targeting tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis through its multi-kinase inhibition mechanism. Research has supported its effectiveness in delaying the progression of tumors while simultaneously improving overall survival rates among HCC patients who receive this treatment option first line.
Sorafenib for liver cancer?
For those diagnosed with advanced liver cancer, specifically Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Sorafenib is frequently advised as a treatment option. Its efficacy can be attributed to the suppression of multiple kinases that play significant roles in the development of tumors and angiogenesis. Thusly patients are likely to see positive results regarding prolonged survival periods and gradual advancement of the disease.
Sorafenib liver cancer?
To combat advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) the most commonly diagnosed type of liver cancer physicians may administer Sorafenib. This drugs ability to promote longer overall survival and hinder tumor progression has been shown in clinical trials.
Sorafenib for HCC?
For individuals dealing with advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Sorafenib provides an optimal initial line of defense. The drugs ability to negate certain proteins responsible for spurring cancer cell growth coupled with its capacity to obstruct new vessel formation in tumors makes it an invaluable resource.
Sorafenib dose?
Twice daily administration of Sorafenib usually involves taking two 200mg tablets amounting to a total of 400mg. Patients are advised not to eat before or immediately after taking these doses – waiting for at least an hour before ingestion or preferably delaying consumption for up to two hours after mealtime. Nevertheless, what might work as an ideal dose can depend on individual reactions and tolerance levels when exposed to this medication and its side effects. Thus any changes in dosing must solely occur with medical oversight while abiding by prescribed instructions.
Sorafenib dosage?
Administration of Sorafenib commonly involves taking a standard dose of 400 mg twice daily, leading to an overall intake of 800 mg each day. However, healthcare providers might deviate from this approach considering specific patient conditions such as responsiveness and tolerability.
Sorafenib 200 mg?
When prescribed with Sorafenib treatment, you'll receive compact yet potent 200mg tablets for easier consumption. To achieve optimal results with this medication, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a dose consisting of two tables taken twice daily- translating into an overall dosage of 800mg each day. To ensure maximum effectiveness of this drug, always remember to take it without food one hour before or two hours after eating.Sorafenib cost?
Sorafenib is used for oncology treatment and is a high-priced medication. Patients must analyze several factors, such as insurance coverage, location, and choice of pharmacy, when determining the cost of this drug. Patients are advised to consult with their local pharmacy or insurance provider to obtain exact figures regarding its pricing structure.
Sorafenib desmoid?
Sorafenib is a possible treatment option for those with desmoid tumors - an unusual and challenging type of nonmetastatic tumor. Although initial research suggests that this medication may benefit patients with progressive, symptomatic, or recurring desmoid tumors, more extensive clinical trials are required before any definitive conclusions can be reached.
Sorafenib success rate?
The outcome of Sorafenib relies on multiple aspects, such as tumor classification and progression level, as well as patient vitality combined with drug compatibility. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma cases have demonstrated a significant prolonging effect in terms of overall survival following the administration of Sorafenib treatment. However, it is essential to recognize that these success rates may diverge from person to person, and a consultation with a healthcare provider is critical for further evaluation.
Sorafenib AML?
The examination of Sorafenib as an Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) treatment option has included a focus on patients with particular genetic mutations like FLT3. Although preliminary evidence shows potential therapeutic advantages further inquiry is necessary to determine the precise role and impact that Sorafenib may have in managing AML.
Sorafenib wiki?
When speaking on matters relating to Sorafenib its not uncommon for people to mention "Sorafenib wiki." This term generally refers to the Wikipedia page that provides comprehensive coverage on many aspects of this drug- from its mechanism of action down to possible adverse reactions experienced by users alongside relevant clinical trials data.
Sorafenib generic?
The patent for Sorafenib (branded as Nexavar) elapsed, rendering generic versions available via legal channels. Nevertheless, it is pertinent to mention that accessibility to these alternatives may fluctuate based on various factors such as geographical location and local pharmaceutical laws.
Sorafenib structure?
With its specialized molecular makeup, sorafenib serves as an adept multi-kinase inhibitor that binds itself to various kinases while obstructing their activity. Its unique design enables precise interaction with the ATP-binding sites of these enzymes which stops them from functioning correctly. Ultimately resulting in stunted cancer cell growth and deterred proliferation.
Sorafenib target?
Sorafenib is an innovative therapy that effectively tackles cancer by inhibiting several key enzymes. Specifically it targets tyrosine protein kinases and Raf kinases that are critical players in the complex signaling pathways responsible for regulating cell activity. By doing so Sorafenib can help to curb tumor growth and stop disease progression.
Sorafenib FLT3?
Sorafenibs mechanism against Fms like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT 3) equates to hindering cell growth and partitioning. In cases where Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is present individuals tend to exhibit multiple alterations within their FLT 3 gene leading to an enhanced growth rate amongst leukemia cells. Sorafenibs ability to inhibit FLT 3 makes it a vital agent for subduing such proliferation.
Sorafenib tablet?
For those seeking Sorafenib treatment, its tablet form is taken by mouth. Typically, each tablet holds 200 mg of Sorafenib. To follow prescribed dosing guidelines, the standard routine would be taking two tablets twice daily.
Sorafenib tablets?
For optimal results when taking Sorafenib tablets, it is suggested to take two 200mg pills twice daily while avoiding food intake during dosing times. It is crucial to note that these must be swallowed whole and not crushed or broken.
Sorafenib chemotherapy?
To treat cancer, Sorafenib employs targeted therapy rather than traditional chemotherapy by pinpointing specific proteins integral to the propagation and spread of malignant cells. Despite its contrast to conventional chemotherapy drugs, its side effects are occasionally similar; thus, it is frequently grouped with them.
Sorafenib chemo?
Cancer patients undergoing treatment commonly receive Sorafenib even though it doesn't belong to the established cohort of standard chemotherapy medications. The mechanism of action behind this drug relies on targeted therapy by binding with crucial proteins implicated in promoting tumor growth and angiogenesis. Although some parallels may exist between the side effect profiles seen with traditional chemo agents versus those observed in users of Sorafenib, interchangeable use between these two terms reflect varied customs within medical communities.
Sorafenib dosage?
A typical prescription for Sorafenib specifies taking two doses each day- each being a sizeable quantity of 400mg- which adds up to an overall daily intake of 800mg. That said, medical professionals have discretion in adjusting these amounts depending on factors like how well patients' bodies respond and how much they can tolerate.
Sorafenib 200 mg?
In order to address specific health concerns or illnesses with Sorafenib therapy medical professionals often prescribe the medicine as 200 mg tablets for their patients. The standard dosage requires taking two tablets twice each day - thus reaching a daily intake of approximately 800 mg per day. This medication should be administered without food; experts suggest taking it either one hour before consuming any meals or waiting at least two hours after finishing your last meal for best results and minimal adverse effects.
Sorafenib cost?
As many people know from personal experience or hearsay from others going through oncology treatment- Sorafenib is an expensive medication. Specialized use cases warrant high costs that are influenced by various elements like geographical location and availability of pharmacies dispensing this drug, among other factors like insurance coverage type. For reliable pricing specifics pertinent to your situation, we recommend consulting your local pharmacist or health insurer for up-to-date data quotes in line with your budgetary requirements.
Sorafenib desmoid?
Desmoid tumors are a type of tumor that are both rare and non metastatic and Sorafenib has emerged as an attractive option for their treatment. Some studies have suggested that this drug may show promise in treating patients who are experiencing symptoms or recurrence related to their desmoid tumor. Nevertheless additional clinical trials must be completed in order to affirm the positive results seen thus far.
Sorafenib success rate?
The degree of success when treating cancer with Sorafenib varies predominantly due to several interrelated factors - namely cancer type and progression, overall patient health, and individual drug response patterns. While there have been promising results treating advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with Sorafenib - inducing a noteworthy prolongation of life expectancy - exact success rates remain unique per person. Thus consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for personalized insight into one's potential outcomes with this medicine.
Sorafenib AML?
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) patients harboring specific genetic mutations like FLT3 have demonstrated hopeful responses to the drug Sorafenib. Yet it remains necessary to conduct more comprehensive studies to fully comprehend the value of Sorafenib as an effective AML treatment.
Sorafenib wiki?
The phrase "Sorafenib wiki" probably denotes the Wikipedia page dedicated to Sorafenib- an all-inclusive web-based database containing valuable information about the medication. This comprehensive resource highlights essential details about Sorafenib such as its mechanisms of action, purposes for which it is prescribed alongside associated harmful reactions and important clinical investigations.
Sorafenib generic?
Sorafenib (sold under the brand Nexavar) is no longer protected by patent. This has opened up opportunities for companies to create generic forms of this medication. However, it's worth noting that access to these drugs may differ across various countries depending on local pharmaceutical regulations.
Sorafenib structure?
Sorafenib's small yet mighty stature lies in its multi-kinase inhibition capabilities that allow it to successfully bind and inhibit different kinases. Its structure has been specifically engineered for optimal interaction with the ATP-binding sites of these enzymes, rendering them inactive. The result? Cancerous cells are unable to grow or proliferate in response.
Sorafenib target?
The anti-cancer properties of Sorafenib are attributed to its ability to selectively target several tyrosine protein kinases and Raf kinases crucial to signaling pathways governing cellular proliferation and angiogenesis. By impeding these proteins' activities, Sorafenib arrests the growth of tumors.
Sorafenib FLT3?
The ability of Sorafenib to impede Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) is unparalleled in the medical sphere. This protein takes charge of cell growth and division processes. In cases like Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), FLT3 gene mutations are commonplace among patients. However, suppressing this kinase's function can curb the rapid expansion of leukemia cells effectively.
Sorafenib tablet?
Sorafenib delivers a convenient option for patients searching for an oral medication option as its available in tablet form. A standard tablet contains 200 mg of Sorafenib while the recommended dose involves taking two tablets twice daily.
Sorafenib tablets?
For Sorafenib medication, each tablet tends to weigh in at 200 mg. The prescribed method of taking them requires ingesting two tablets, twice a day - always on an empty stomach. Crushing or breaking the pills should not even remotely be considered - they must always be swallowed whole.
Sorafenib chemotherapy?
Operating as a targeted therapy rather than conventional chemotherapy, Sorafenib functions by directly targeting specific proteins that play an essential role in facilitating the growth and diffusion of cancerous cells. However, even though its application involves fighting against cancer, it is frequently grouped with traditional chemotherapy medicinal products because it can lead to similar adverse effects.
Sorafenib chemo?
Sorafenib sets itself apart from run-of-the-mill chemotherapy drugs when battling cancer with medication. Rather than broadly destroying fast-dividing cells throughout the body without discretion, this treatment targets crucial growth-promoting proteins driving cancer cell multiplication and angiogenesis. Although individuals undergoing treatment with Sorafenib might face similar side effects often associated with traditional chemo treatments- explaining why some people may refer to this drug by that name- its focused mode of action distinguishes it from other types of therapies used against cancer.
Sorafenib dosage?
The recommended amount for Sorafenib is usually two doses per day at a fixed quantity of 400 mg each time. This adds up to an overall daily consumption of around 800mg. However, healthcare practitioners possess some leeway in changing this figure based on how well patients respond and tolerate it.
Sorafenib 200 mg?
The 200 mg tablets of Sorafenib are easily accessible. The conventional dosage calls for taking two pieces twice daily, which makes up a total of 800 mg every day. It's essential that you take this drug sans food--one hour before or two hours following meals.
Sorafenib cost?
Sorafenib's cost poses a significant variable depending on factors such as insurance coverage, the location of purchase, and pharmacy. Being a specialized oncology medication, it can be pricey. Patients should seek pricing information from their insurance provider or local pharmacy for accurate details.
Sorafenib desmoid?
Examined as a treatment alternative for non metastatic desmoid tumors - an infrequent occurrence - Sorafenib has shown promise. Preliminary studies indicate its effectiveness in addressing progressive or recurring desmoid tumors accompanied by symptoms. However theres a need for more comprehensive clinical investigations to confirm the apparent benefits.
Sorafenib success rate?
To accurately evaluate the efficacy rate associated with Sorafenib treatment it is essential to take into account numerous variables such as cancer type & stage, patient wellbeing & response levels. Cases dealing with advanced stages of hepatocellular carcinoma have yielded promising data pertaining to increased lifespan from application of this medication. Nonetheless due to individual variations within patients concerning success rate outcome; healthcare providers should be consulted for more information tailored specifically for one's own needs.
Sorafenib AML?
As per current findings Sorafenib has emerged as a potentially effective way of treating Acute Myeloid Leukemia in subjects who exhibit certain gene mutations such as FLT3. Although initial indications are promising further clinical evaluations ought to be conducted before establishing a conclusive understanding of how best to utilize Sorafenib in AML therapy.
Sorafenib structure?
At its core, sorafenib is an adept multi-kinase inhibitor thanks to its specialized molecular design. Through selective binding to various kinases, this powerful small molecule effectively impedes their activity by targeting key ATP-binding sites on these enzymes - leading ultimately to suppression of cancer cell growth and proliferation.
Sorafenib target?
At the core of many cellular processes lies the intricate network of tyrosine protein kinases and Raf kinases responsible for multiple signaling cascades. By specifically targeting these essential proteins Sorafenib can help impede tumor development by hindering crucial processes such as angiogenesis involved in promoting the survival of fast growing cancer cells within tumors.
Sorafenib FLT3?
Targeting FLT3, a protein that regulates cell growth and division is one way Sorafenib exerts an effect against cancer. In specific cases like Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) where mutations in FLT3 are common inhibiting this protein becomes even more critical. Sorafenib shows promise as a solution to managing the rapid growth of leukemia cells caused by these genetic alterations.
Sorafenib tablet?
Typically prescribed in its pill form, Sorafenib is a highly effective oral medication with each individual dosage carrying a concentration of 200mg. For maximum results, it's advised to adhere to the usual dosing instructions involving taking two pills twice daily.
Sorafenib tablets?
The typical sizing of Sorafenib tablets is 200 mg per tablet. The standard recommendation is to consume two tablets twice per day, without food. It's essential not to crush or break these tablets and instead swallow them whole.
Sorafenib chemotherapy?
Sorafenib offers a more specific strategy for battling cancer than traditional chemotherapy drugs do. By focusing on certain proteins linked to the development and proliferation of cancer cells this targeted therapy offers hope for effective treatment while reducing some negative side effects compared to other treatments. Nonetheless individuals undergoing this type of therapy should expect some similarity in adverse reactions when compared with conventional chemo treatments.
Sorafenib chemo?
Sorafenibs use is widespread in combating cancers but deviates from the conventional application of chemotherapy due to its focused approach. It targets particular proteins aiding tumor growth and blood vessel development through targeted therapy instead of systemic intervention. Although often associated with standard chemotherapeutic agents due to comparable adverse reactions experienced by patients on both kinds of medication Sorafenib falls under the category of targeted therapies rather than general chemo treatments.













