Tamsulosin / Finasteride
- Introduction to Tamsulosin and Finasteride
- Composition and Pharmacological Properties
- Mechanisms of Action: How Tamsulosin and Finasteride Work
- Primary Uses and Therapeutic Indications
- Off-Label Uses and Emerging Therapies
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Administration Considerations for Specific Populations
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Potential Side Effects and Management
- Important Precautions and Warnings
- Overdose: Symptoms, Emergency Procedures, and Antidotes
- Storage, Stability, and Disposal of Tamsulosin and Finasteride
- Handling Precautions and Safety Measures
Introduction to Tamsulosin and Finasteride
Overview of Tamsulosin and Finasteride
Tamsulosin and Finasteride are medications used to treat male urological issues.
Tamsulosin, an alpha blocker, mainly helps relax the smooth muscles around the bladder neck and prostate.
Similarly, Finasteride, an inhibitor of 5 alpha-reductase, functions by lowering the levels of dihydrotestosterone in the body, leading to a decrease in prostate size and relief from hyperplasia symptoms.
Importance in Treating Urological Conditions
These medicines are crucial for managing prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition marked by the enlargement of the prostate gland that can cause significant urinary issues. Not only do these medications improve the symptoms, but they also help change the course of the disease, leading to a better quality of life for those affected.
Why take Tamsulosin and Finasteride together
Combining finasteride and tamsulosin is advised by experts for individuals facing the possibility of prostate surgery due to BPH. This combination can effectively reduce the likelihood of requiring surgery or postpone the need for it.
Composition and Pharmacological Properties
Active Ingredients and Their Roles
Tamsulosin works by relaxing muscles in the tract, while Finasteride helps maintain hormonal balance to address prostate enlargement.
Pharmacokinetics of Tamsulosin and Finasteride
Tamsulosin and Finasteride have ways of working in the body, especially when it comes to how they are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated.
These processes are tailored to improve the health of the urinary tract and prostate. Tamsulosin works quickly once taken, while Finasteride may take months to show its full benefits.
Mechanisms of Action: How Tamsulosin and Finasteride Work
Tamsulosin: Role in Muscle Relaxation
Tamsulosin works by inhibiting alpha 1 adrenergic receptors in the prostate and bladder, which decreases muscle tension and improves urine flow.
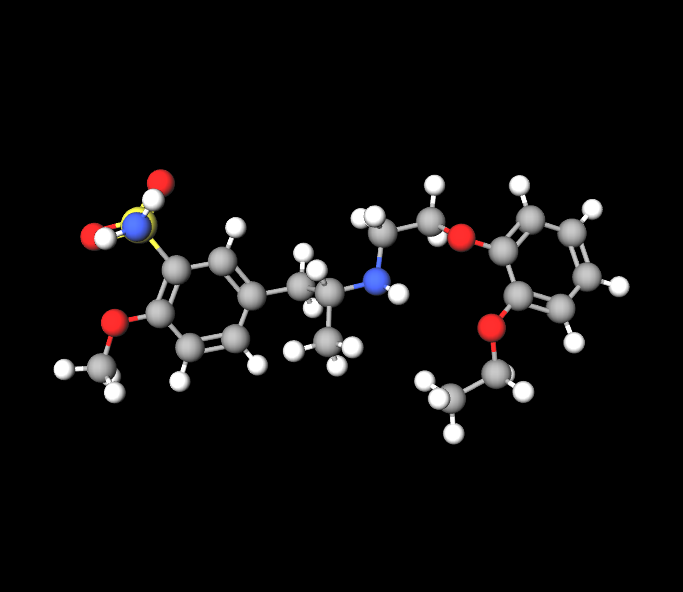
Finasteride: Impact on Hormone Regulation
Finasteride works by decreasing the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) within the prostate, which is a powerful hormone linked to prostate enlargement. This helps alleviate the symptoms of BPH over time.
Primary Uses and Therapeutic Indications
-
Tamsulosin and Finasteride Combination for BPH:
- Tamsulosin and Finasteride are commonly used together for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men with an enlarged prostate.
- The combination aims to improve symptoms, reduce the risk of surgery (including transurethral resection of the prostate and prostatectomy), and minimize symptomatic progression of BPH1.
- Dosage: The recommended dose is 200 mcg of Tamsulosin and 5 mg of Finasteride once daily, which can be titrated up to 400 mcg of Tamsulosin and 5 mg of Finasteride once daily1.
- Administration: Take the medication with food, approximately 30 minutes after a meal1.
- Contraindications: Avoid in patients with a history of orthostatic hypotension or severe hepatic insufficiency1.
- Special Precautions: Evaluate for prostatic carcinoma before starting therapy, monitor sustained increases in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, and be cautious in patients with severe renal impairment or a history of Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS)1.
- Adverse Reactions: Common side effects include ejaculation disorder, dizziness (with Tamsulosin), decreased libido, decreased ejaculation volume, breast enlargement, tenderness, and rash (with Finasteride)1.
-
Evidence-Based Guideline:
-
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms:
Off-Label Uses and Emerging Therapies
- Off-Label Use of Finasteride for Hair Loss Treatment:
- Finasteride is commonly used off-label for male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the scalp.
- Evidence: While Finasteride is FDA-approved for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), its effectiveness in hair loss treatment has been well-documented in clinical studies and real-world use1.
- Dosage: The standard dose for hair loss treatment is 1 mg Finasteride tablet taken orally once daily1.
- Tamsulosin for Chronic Prostatitis Symptoms:
- Tamsulosin, an alpha-blocker, is primarily indicated for BPH. However, it has been explored for managing symptoms associated with chronic prostatitis.
- Mechanism: Tamsulosin relaxes smooth muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, potentially easing pelvic discomfort.
- Clinical Trial:
- A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial investigated the effect of perioperative Tamsulosin on successful ureteral access sheath placement during kidney stone removal procedures. Preoperative Tamsulosin improved the insertion of large ureteral access sheaths2.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions
The usual amount of Tamsulosin for therapy is between 0.4 and 0.8 mg each day, whereas Finasteride is given at a dose of 5 mg daily to manage BPH.
Instructions for Administration and Timing of Doses
It is recommended that both medications be taken at the same time. Finasteride is not as affected by meal timing. Tamsulosin should be taken after eating the same meal every day to keep plasma levels steady.
Administration Considerations for Specific Populations
Elderly: Adjustments and Monitoring
Elderly individuals require observation and dosage modifications to minimize the chances of experiencing side effects like orthostatic hypotension.

Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile and Recommendations
It is not recommended to use during pregnancy and nursing mothers should also avoid it because of the possible risks to the unborn child and newborn. Tamsulosin should be used cautiously and under medical supervision in these groups.
Pediatric Use: Safety and Efficacy in Children
It is not advisable to administer Tamsulosin and Finasteride to children as there is research on their safety and effectiveness in this age group.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Management
The simultaneous utilization of Tamsulosin and Finasteride alongside medications could lead to notable pharmacological interactions.
For example, when combined with blood pressure-lowering medications, it might amplify the effects, requiring diligent monitoring of blood pressure levels.
Patients taking anticoagulants should also receive supervision, as Tamsulosin has the potential to raise the risk of bleeding. It is crucial to make strategic dosage modifications and conduct monitoring to handle these interactions effectively.
Contraindications for Use of Tamsulosin and Finasteride
Tamsulosin should not be given to individuals who are sensitive to alpha-blockers. Conversely, women and children should avoid using Finasteride as it is not recommended for them. Pregnant women, in particular, should steer clear of Finasteride due to the risk of birth defects. Individuals with liver issues need to be cautious when using Finasteride since it undergoes metabolism in the liver.
Potential Side Effects and Management
Common Side Effects: Identification and Management
When individuals use Tamsulosin, they might feel lightheaded, tired, or have high blood pressure when changing positions. On the hand, Finasteride could cause a decrease in sexual desire and function. If these effects continue or become troublesome it's important to adjust the medication dosage or consider treatment options. Patients should promptly inform their healthcare provider about any reactions for timely assistance.
Serious Adverse Reactions and Emergency Responses
Severe responses may involve difficulty in urination with Tamsulosin and intense feelings of sadness in individuals using Finasteride. It is vital to seek medical help when facing such severe signs, and promptly stopping the medication might be required with the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Important Precautions and Warnings
Risks Associated with Long-Term Use
Extended use of Tamsulosin and Finasteride may raise the chances of developing cataracts. Worsening existing cataract conditions can potentially result in increased breast tissue. It is advisable for individuals receiving treatment to undergo frequent eye checkups and keep track of any alterations in their breasts.

Precautions for Patients with Other Medical Conditions
People who have kidney or liver issues or are getting surgery, particularly cataract removal, should be extra careful when using these medications. It is recommended that the treatment be tailored to each person, and regular consultation with healthcare providers is recommended to get the results and reduce any potential risks.
Overdose: Symptoms, Emergency Procedures, and Antidotes
Recognizing Symptoms of Overdose
Recognizing signs of an overdose is important for treatment as they can include extremely low blood pressure, feelings of lightheadedness, nausea, or difficulty breathing. Early detection plays a role, in managing the situation effectively.
Immediate Actions and Treatments Available
In case of an overdose, it is crucial to focus on ensuring the patient's airway breathing and circulation. Immediate medical assistance should be sought to provide supportive care. There are no remedies for Tamsulosin or Finasteride overdoses; therefore, treatment mainly involves offering supportive measures.
Storage, Stability, and Disposal of Tamsulosin and Finasteride
Optimal Storage Conditions
Make sure to keep both Tamsulosin and Finasteride in a dry place at room temperature. It's important to store them from moisture and direct sunlight to ensure they remain effective, for a longer period. Keeping these medications under the conditions helps maintain their stability.
Safe Disposal Practices to Prevent Misuse
It's important to dispose of any medications that are not being used or have expired correctly to avoid harming the environment and prevent misuse. It's recommended that patients return these medications through take-back programs or follow the FDA's guidelines for throwing them in household trash, making sure they are kept away from children and pets.
Handling Precautions and Safety Measures
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
Healthcare professionals need to be cautious when dealing with these medications, especially when treating women, as unintended exposure to Finasteride can result in birth defects. It's important to educate patients on the handling procedures to prevent accidental exposure or ingestion by others, especially children.
Safety Measures During Transport and Storage
When moving these medicines it's crucial to make sure they are securely stored and maintained at the temperature to avoid any loss of their effectiveness. Following these guidelines guarantees that the medications will work as intended whether you're picking them up from the pharmacy or bringing them home.