Tazarotene
- I. Introduction to Tazarotene
- II. Composition of Tazarotene
- III. Mechanism: How Tazarotene Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Tazarotene
- V. Off-label Uses of Tazarotene
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Tazarotene
- VII. Interaction of Tazarotene with Other Substances
- VIII. Common and Serious Side Effects of Tazarotene
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Tazarotene Use
- X. Careful Administration of Tazarotene
- XI. Special Precautions with Tazarotene
- XII. Administration of Tazarotene to Specific Populations
- XIII. Overdosage of Tazarotene: Symptoms and Management
- XIV. Storage and Handling Precautions for Tazarotene
I. Introduction to Tazarotene
A. Brief overview of Tazarotene
Tazarotene serves as a remarkable testament to the vast therapeutic capabilities of retinoids. It is a third-generation topical retinoid (1) that stands out for its impressive effectiveness in treating various skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and certain forms of skin discoloration(2). What sets Tazarotene apart is its unique structure and how it works, giving it a distinct pharmacological profile compared to other similar drugs.
1. Teratogen update: Topical use and third-generation retinoids
2. Tazarotene topical: 7 things you should know
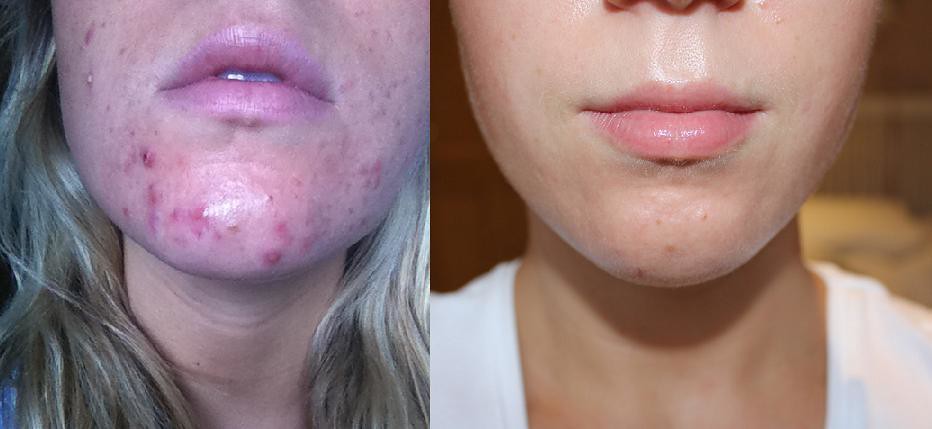
Acne before and After
B. Pharmaceutical classification of Tazarotene
Tazarotene is classified as a pharmaceutical synthetic retinoid prodrug. It belongs to the retinoid family, and its structure is similar to vitamin A (retinol). The term 'prodrug' refers to its inactive form in topical preparations. However, once it is applied to the skin, it undergoes a metabolic transformation into an active form. This compound's classification sheds light on its effectiveness in dermatological therapeutics.
II. Composition of Tazarotene
A. Active and inactive ingredients
In order to optimize effectiveness and patient satisfaction. Tazarotene-based formulations are typically blended with supplementary inactive ingredients. These additions serve multiple purposes such as;
- Improving stability by including stabilizers
- Facilitating skin absorption through emollients
- Preventing the growth of microorganisms with preservatives.
The precise composition may vary based on both manufacturer preference and desired application.
B. Available forms and strengths
Regarding availability, Tazarotene primarily manifests through two primary options: gel and cream formulations. The preference leans towards prescribing the gel form to address acne-related concerns; in contrast, healthcare professionals often turn towards utilizing the cream variant when confronted with situations encompassing psoriasis or skin discoloration disorders that require immediate attention. Worth mentioning is that this particular topical medication encompasses a wide range of strengths, including but not limited to standard concentrations such as 0.05% or even further fortified concentrations bound within a scale measuring up to 0.1%. Consequently, enabling healthcare providers an ample range of choices to adapt and personalize efforts based on the unique requirements presented by each patient.
III. Mechanism: How Tazarotene Works
A. Biological action of Tazarotene
When applied to the skin. Tazarotene converts into tazarotenic acid through enzymatic processes(1). This conversion mainly occurs in the keratinocytes(2), which are the primary cells found in the outer layer of the skin. Tazarotenic acid then binds to specific retinoic acid receptors (RARs), Specifically RARβ and RARγ (3). Within the nucleus of the cell. This binding plays a role in regulating gene expression. Leading to controlled cell growth and differentiation. Additionally. Tazarotene has anti-inflammatory effects that contribute to its effectiveness in treating acne and psoriasis.
1. Tazarotene: The first receptor-selective topical retinoid for the treatment of psoriasis
2. Use of tazarotene foam for the treatment of acne vulgaris
3. Tazorac: 7 things you should know
B. Tazarotene in the context of retinoid therapy
Tazarotene is well regarded in retinoid therapy for its notable attributes, such as its ability to selectively bind to receptors, increased tolerability, and strong anti-inflammatory effects. The drugs' effectiveness and manageable side effects highlight its importance in modern dermatology. Making it an essential tool in the treatment of retinoid-related conditions. However, to fully utilize tazarotene benefits, it is crucial to thoroughly understand its pharmacological properties, clinical indications, and potential adverse effects by adopting a knowledge-based approach towards Tazarotene. We can maximize its therapeutic potential and improve patient outcomes in dermatology.
IV. Approved Uses of Tazarotene
A. Use in the treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis(1) is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and scaling. It can cause significant discomfort and negatively impact ones quality of life. Fortunately. Tazarotene, a synthetic retinoid with powerful properties(2). Offers considerable relief. By acting as a keratolytic agent. It helps normalize the excessive growth of skin cells. Multiple clinical studies have highlighted Tazarotenes therapeutic superiority. Especially when incorporated into a holistic treatment plan for psoriasis(3). It effectively reduces the raised plaques, dryness, and redness associated with this condition. However healthcare professionals often advise combining Tazarotene with moisturizers or emollients to counter any potential irritation to the skin.(4)
1. Teratogen update: Topical use and third-generation retinoids
2. Tazarotene: A review of its pharmacological profile and potential for clinical use in psoriasis
3. Tazarotene: The first receptor-selective topical retinoid for the treatment of psoriasis
4. Tazarotene
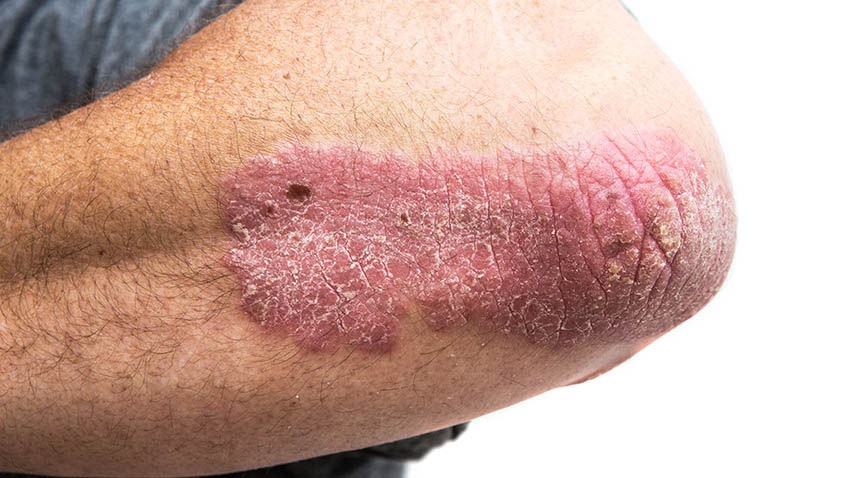
Psoriasis on Elbow
B. Use in Acne management
Acne vulgaris, a common skin condition that often affects adolescents, has found an effective treatment in Tazarotene. Tazarotene targets various stages of acne development primarily by normalizing the shedding of skin cells, decreasing the formation of clogged pores, and reducing inflammation.
- Tazarotene achieves these effects by inhibiting the growth and differentiation of keratinocytes in hair follicles. Which helps prevent the formation of comedones (clogged pores).
- This medication has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the redness and swelling associated with acne because it addresses both noninflammatory and inflammatory acne lesions.
Tazarotene is often recommended as a first-line treatment for moderate to severe cases of acne.
C. Role in the treatment of Photodamage
Photodamage refers to skin aging caused by excessive sun exposure. It can cause undesirable cosmetic issues like wrinkles, rough skin texture, and hyperpigmentation. Tazarotene has received approval for treating facial photodamage because of its unique properties. At a molecular level, Tazarotene boosts collagen production and decreases collagenase expression resulting in improved skin texture and reduced wrinkles. Additionally, it helps disperse pigments and lighten hyperpigmented spots. As a result, the pharmacological abilities of Tazarotene go beyond therapeutic purposes to cater to cosmetic dermatology as well. This makes it an effective tool against the damaging effects of time and sun exposure.
V. Off-label Uses of Tazarotene
A. Potential benefits in Ichthyosis treatment
Ichthyosis is a genetic skin disorder characterized by dry and scaling skin that can either be thickened or very thin. Treating this condition poses challenges, but Tazarotene has the potential as a therapeutic agent. At the same time, dermatology typically uses Tazarotene for other purposes. It has been evaluated for its effectiveness in treating ichthyosis. Its keratolytic properties are believed to help speed up the shedding of the outer layer of the skin, which could potentially improve the appearance and texture of ichthyotic skin. Initial clinical trials have shown promising results suggesting that Tazarotene could be a viable alternative or addition to existing therapies. However, more rigorous research is needed to establish its role in managing ichthyosis.
B. Experimental use in skin cancer prevention
Current scientific discussions have provided valuable insights into the potential use of Tazarotene in preventing skin cancer. Its ability to regulate cell growth and differentiation is promising for preventing squamous and basal cell carcinoma.
Studies conducted on animals prior to human trials have yielded encouraging results demonstrating that Tazarotene can reduce the occurrence and number of skin tumors. Given these findings, it is crucial to further investigate Tazarotenes' chemopreventive properties through extensive and controlled trials.
It is important to note, however, that this remains an experimental application of Tazarotene and does not yet have approval from regulatory authorities for this purpose.
C. Other exploratory areas of use
Continual exploration is being conducted to uncover other potential uses of Tazarotene thanks to its broad spectrum retinoid activity. One exciting area of investigation is the management of chronic hand eczema, where Tazarotenes' effective anti-inflammatory and keratolytic properties have shown promise. Additionally, preliminary findings suggest that Tazarotene therapy might be beneficial in treating alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss. These diverse applications highlight the versatility of Tazarotene and its potential to pave the way for new therapeutic advancements in dermatology and beyond
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Tazarotene
A. Standard dosage for approved indications
The dosage of Tazarotene depends on the specific medical condition being treated, and in the case of psoriasis, applying a thin layer of either 0.05% or 0.1% Tazarotene cream or gel to the affected skin once every evening for acne. It is usually suggested to apply a thin layer of 0.1% Tazarotene gel or cream once daily in the evening. Lastly, for photodamage applying a thin layer of 0.1% Tazarotene cream to the face once daily in the evening is typically advised.
B. Dosing considerations for off-label uses
It is advisable to exercise caution when considering off-label use of Tazarotene. This is important given the possible advantages and risks involved. The appropriate dosage and frequency will depend on the specific condition being treated, the patients response to treatment, and the treating physician's discretion. At the same time, the approved dosages mentioned earlier can provide a guideline. Adjustments may need to be made to cater to individual patient requirements.
C. Directions for proper application
To ensure optimal usage of Tazarotene apply only on areas of skin that are affected by the condition being treated before each application session commences its' 's important for you to meticulously clean and dry the specific region being addressed by this medication. While applying it onto your skin surface area make a conscious effort to avoid any contact with sensitive regions such as eyes or mucous membranes including inside your mouth for instance. After you have administered the medication, be sure to give your hands a thorough washing. It should be noted that applying excessive amounts of this topical treatment does not yield an increase in its efficacy but may instead lead to an augmented risk of experiencing adverse reactions.
VII. Interaction of Tazarotene with Other Substances
A. Known drug-drug interactions
Tazarotene is usually well tolerated, but it may interact with certain medications. When using other topical products with strong drying effects at the same time. There may be an increased risk of irritation. Therefore. It is essential to use caution when co-administering tazarotene with drugs like salicylic acid, sulfur, resorcinol, or benzoyl peroxide.
B. Interactions with food and dietary supplements
Tazarotene being a topical medication. Has minimal interaction with food and dietary supplements. It is worth noting that certain dietary supplements, such as vitamin A, also exhibit retinoid activity. It may pose a potential risk of hypervitaminosis A if consumed excessively.
C. Impact of alcohol and tobacco on Tazarotene efficacy
It is important to note that no well-established studies demonstrate a considerable connection between Tazarotene, alcohol, and tobacco. Nonetheless, it is worth mentioning that alcohol could potentially lead to skin dryness and might worsen any dryness already caused by Tazarotene. Conversely, smoking is recognized as a contributor to skin aging and may counteract the positive impacts of Tazarotene in treating photodamage.
VIII. Common and Serious Side Effects of Tazarotene
A. Most frequent side effects encountered
Local reactions are the most frequently encountered side effects associated with Tazarotene. These reactions generally involve
- Skin irritation
- Dryness
- Redness
- Peeling
- Itching
B. Potential severe adverse reactions
Severe adverse reactions are uncommon but may occasionally occur. These reactions could manifest as signs of a serious allergic reaction, such as
- Rash
- Itching
- Swelling (particularly of the face, tongue, or throat)
- Severe dizziness
- Difficulty breathing.
C. Long-term side effects
The prolonged use of Tazarotene can result in heightened skin sensitivity, particularly to UV light. It is advisable for patients who have been using Tazarotene for an extended period to shield their skin from sun exposure and abstain from using tanning booths and sunlamps. When spending time outdoors. The use of a high-protection sunscreen and protective clothing is recommended.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Tazarotene Use
A. Absolute contraindications
There are certain situations where Tazarotene should not be used due to the possibility of adverse effects. Specifically, women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should avoid using this drug because it has been found to have teratogenic properties. Additionally,, individuals with a known sensitivity to Tazarotene or any of its components should refrain from using it to prevent severe allergic reactions.
B. Relative contraindications
Tazarotene use should be cautiously approached in individuals with eczematous skin as it can potentially cause significant irritation. Similarly, patients who have experienced local tolerance problems with other retinoids should exercise caution when using Tazarotene. For individuals with severe liver disease or those suffering from chronic or acute paronychia, Tazarotene should be used under close medical supervision.
C. Warning signs to watch for during treatment
Patients employing Tazarotene are urged to exercise vigilance in detecting potential adverse reactions. It's crucial to be conscious that severe skin irritation might arise alongside signs denoting an allergic reaction like hives, itching, difficulty breathing; facial or oral swelling; and alterations in skin coloration. To guarantee immediate medical attention during such occurrences would be prudent indeed.
X. Careful Administration of Tazarotene
A. Tips for minimizing adverse effects
To minimize any potential adverse effects, it is advised for patients to apply Tazarotene in a conservative manner only on the areas that are affected. It is recommended to use it once daily in the evening as the excessive application does not improve its effectiveness but can instead lead to an increased risk of skin irritation. Additionally, patients should utilize a moisturizer to prevent dryness of the skin and should also avoid excessive exposure to the sun.
B. Managing unexpected reactions
In case patients experience unexpected reactions like excessive skin irritation or any signs indicating an allergic reaction, it is recommended that they stop using the medication and promptly consult a healthcare professional. Reducing the application frequency or temporarily discontinuing use may also be necessary to alleviate these reactions.
C. Importance of regular follow-ups during therapy
Attending regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider while undergoing Tazarotene therapy is crucial. These appointments monitor progress, assess side effects, and modify the treatment plan if needed. It is essential for patients to openly communicate any side effects they may be experiencing and inform their healthcare provider about any changes in their condition.
XI. Special Precautions with Tazarotene
A. Important safety measures during treatment
It is essential to consider certain safety precautions while undergoing Tazarotene treatment. One should be extremely cautious in avoiding or reducing exposure to sunlight and UV light. Additionally, it is imperative not to apply Tazarotene on sunburned skin, wounds, or areas affected by eczema. Moreover, it is advisable to avoid using other skin products that may irritate, such as harsh soaps or cosmetics.
B. Handling photosensitivity reactions
To ensure patient safety while using Tazarotene, awareness must be given to its ability to heighten skin sensitivity towards sunlight, consequently raising the likelihood of sunburn. Therefore. It is highly recommended that individuals take precautions such as utilizing sunscreen with a high protection factor and wearing protective clothing when venturing outdoors, particularly during peak hours. In case any indications of photosensitivity reaction present themselves. Prompt consultation with one's healthcare provider becomes indispensable for appropriate treatment and management measures.
C. Precautions for users with specific conditions
Patients who have specific conditions, such as liver disease. Should exercise caution when using Tazarotene. Moreover. Individuals with a history of allergies. Particularly to medications related to Vitamin A. May face a heightened risk of experiencing an allergic reaction. These patients must disclose their complete medical history to their healthcare provider before initiating Tazarotene therapy.
XII. Administration of Tazarotene to Specific Populations
A. Guidelines for elderly patients
Despite no conclusive disparities noted regarding safety or effectiveness among elderly patients compared to younger ones, it is important to recognize the potential for increased skin integrity concerns. Like any other medication administering Tazarotene to older individuals should be approached cautiously. It necessitates meticulous monitoring for possible adverse effects and a careful evaluation of whether dosage adjustments might be necessary.
B. Safety in pregnant women and nursing mothers
Pregnancy Category X classification has been assigned to Tazarotene due to its association with causing harm to fetuses when administered during pregnancy. Therefore. Using this drug is not recommended for women who are currently pregnant or may become so in the near future. In case Tazarotene is used while pregnant, alternatively, if one gets impregnated while consuming this medicine, it's vital that one understands the potential risks involved towards their developing baby and takes necessary precautions accordingly. There isn't enough knowledge regarding the excretion of Tazarotene in human breast milk. In such scenarios. One should weigh the importance of the drug to their well-being and decide whether to cease breastfeeding or discontinue its usage.
C. Considerations for administration to children
The safety and effectiveness of Tazarotene have not been established in pediatric patients under 12 years old for treating acne. Therefore the use of Tazarotene in this population for other purposes should be cautiously approached. It is important to note that pediatric patients may be more susceptible to using too much Tazarotene topically or absorbing it systemically, so they should be monitored closely for any potential adverse effects.
XIII. Overdosage of Tazarotene: Symptoms and Management
A. Signs of Tazarotene overdosage
Excessive use of Tazarotene on the skin can result in noticeable redness, peeling, or discomfort. While these side effects are not life-threatening they have the potential to cause significant irritation.
B. Immediate actions and potential antidotes
If an overdose of Tazarotene is suspected. It is important to discontinue its application immediately and begin appropriate symptomatic treatment. In the case of accidental oral ingestion, symptomatic and supportive care should be provided. It is worth noting that as Tazarotene is a topical treatment there is no specific antidote available for overdose incidents.
C. Long-term management of an overdosage
If an overdose of Tazarotene is experienced over a prolonged period, it may be advisable to temporarily halt its usage until the skin has fully regained its health. Additionally, a less frequent application schedule or a formulation with a lower concentration might be needed. It is crucial to continue vigilant monitoring for any potential negative effects as well.
XIV. Storage and Handling Precautions for Tazarotene
A. Proper storage conditions
To properly store Tazarotene, it should be kept away from light and heat sources at average room temperature conditions. It is essential to place this product in a spot inaccessible to children and pets for safety reasons. Ensuring its effectiveness can be achieved by firmly closing the tube when not utilizing the medication.
B. Safety precautions during handling
To ensure safety when using Tazarotene, it is important to take precautions and avoid contact with the eyes or mucous membranes. However, if accidental contact does occur, it is advised to thoroughly rinse the affected area with water. Additionally, it is recommended to wash your hands after applying the product for added precautionary measures.
C. Disposal of unused or expired Tazarotene
It is imperative that unused or expired Tazarotene should never be disposed of through sinks or regular trash bins. Opting for its return to a pharmacy or contacting a local waste disposal company instead is highly recommended. This approach serves as a practical measure towards preserving our environment while guaranteeing that the medication does not fall into unauthorized possession.