Timentin Inj Vial
- Introduction to Timentin Injection Vial
- Composition of Timentin Injection Vial
- Primary Uses of Timentin Injection Vial
- Off-Label Uses of Timentin Injection Vial
- Mechanism of Action: How Timentin Works
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Common Side Effects of Timentin Injection Vial
- Serious and Rare Side Effects
- Interactions with Other Drugs
- Warnings and Precautions for Timentin Injection Vial
- Contraindications of Timentin Injection Vial
- Important Precautions Before Using Timentin
- Special Considerations for Specific Populations
- Overdose and Management
- Storage and Handling of Timentin Injection Vial
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Timentin Injection Vial
Overview of Timentin
The medication Timentin is designed to treat infections caused by bacteria that are resistant to other treatments. It contains two ingredients that work together to improve its effectiveness in eradicating bacteria and aiding in managing infections.
Brief History and Development
After research and development efforts, Timentin was created to combat infections unresponsive to traditional antibiotics. Its effectiveness in treating intricate infections has established it as a notable milestone in the field of anti-infective treatments.
Purpose and General Application in Medical Treatment
Timentin is widely utilized in hospital and critical care settings for treating infections where other antibiotics are less effective. Its applications include respiratory, urinary, and skin infections, especially those caused by resistant bacteria. This robust antibacterial option is invaluable in the fight against challenging infections.
FDA-Approved Uses and Introduction to Off-Label Uses
The FDA approved Timentin for specific infections. It is effective against respiratory and skin infections and serious hospital-acquired infections. Off-label, it has been used in cases where alternative therapies prove inadequate or ineffective.
Composition of Timentin Injection Vial
Active Ingredients: Ticarcillin and Clavulanate Potassium
Timentin's efficacy stems from its two active compounds: Ticarcillin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, and Clavulanate Potassium, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Together, these ingredients combat resistant bacteria with increased effectiveness.
Role of Each Component in the Formulation
Ticarcillin damages cell walls' structure to eliminate the bacteria it targets. Clavulanate Potassium boosts Ticarcillin's effectiveness by blocking beta-lactam enzymes that some bacteria create to combat antibiotics.
Available Forms and Packaging Details
Timentin is provided in vials for injections to guarantee its effectiveness through storage and handling practices. It is typically found in single dose packaging designed for the convenience of healthcare professionals.
Explanation of Pharmaceutical Formulation and Excipients
Timentin includes stabilizing components along, with the ingredients to maintain its effectiveness over time and during transportation and storage processes, in environments.
Ticarcillin vs amoxicillin
Both ticarcillin and amoxicillin are antibiotics that work well against various types of bacteria. Amoxicillin can target a spectrum of gram-positive bacteria and a few gram-negative ones as well. On the other hand, ticarcillin is known for its effectiveness against gram-negative organisms, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Piperacillin and ticarcillin
In this group of patients it seems that Piperacillin/tazobactam works better than ticarcillin/clavulanate and is usually well received by them.
Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium
Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium is a type of antibiotic that has received approval, from the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is used to treat infections like lower respiratory tract infections such as community acquired pneumonia as well, as ear and sinus infections and skin infections.
Cefpodoxime proxetil and potassium clavulanate tablets
The Cefprozil and Clavulanate Potassium tablet is prescribed for treating a range of infections, including tonsillitis, ear infections, throat infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), bronchitis, and others.
cefixime and potassium clavulanate
The combination of Cefixime and Potassium Clavulanate is prescribed for the treatment of infections affecting various parts of the body, such as the urinary tract, ears, lungs, throat, tonsils, and skin. It is also used to combat infections like typhoid fever and gonorrhea.
Primary Uses of Timentin Injection Vial
Potassium clavulanate uses
Timentin is mainly used for combating infections in the respiratory system, skin, and urinary tract. It proves highly efficient against strains that show resistance to conventional antibiotics.
Types of Infections Commonly Treated
- Respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Severe infections acquired in hospital settings
Use in Hospital-Acquired Infections, Including Severe Cases
In hospitals, the medicine Timentin is given to treat infections contracted within healthcare settings like care units. It's an important choice for treating infections in patients with weakened immune systems.
Benefits in Combating Penicillin-Resistant Bacterial Strains
Timentin's unique formulation enables it to counteract penicillin-resistant bacteria, offering a solution where other antibiotics fail. This advantage is pivotal in treating patients with resistant bacterial infections.
Off-Label Uses of Timentin Injection Vial
Treatment of Specific Bacterial Infections Not Approved by FDA
Clinicians sometimes prescribe Timentin for infections outside its FDA-approved indications, particularly when resistant organisms are suspected, or standard antibiotics are ineffective.
Use in Prophylactic Treatment Before Surgeries
Off-label, Timentin may be administered before certain surgeries to prevent potential infections, especially in cases where the patient is at a high risk of developing resistant infections post-operatively.
Potential Use in Multidrug-Resistant Infections
Researchers have been looking into Timentin as a treatment option, for infections that're resistant, to types of antibiotics and provide a glimmer of hope for cases where treatment choices are limited.
Overview of Research Studies Supporting Off-Label Use
Research has shown that Timentin has been effective, in standard uses and has proven valuable in treating infections that are resistant, to other treatments. Ongoing studies are still investigating the uses of Timentin in managing infections.
Mechanism of Action: How Timentin Works
In-Depth Explanation of How Ticarcillin and Clavulanate Work Synergistically
Timentin's power lies in the synergistic action of Ticarcillin and Clavulanate. Ticarcillin disrupts bacterial cell walls, while Clavulanate inhibits enzymes that might neutralize Ticarcillin's effects.
Mechanism of Action in Bacterial Cell Wall Inhibition
The main action of Ticarcillin is to inhibit the cell wall of bacteria which leads to the loss of their integrity resulting in stopping replication and helping control infections.
Role of Clavulanate in Combating Beta-Lactamase Producing Bacteria
Clavulanate works against the beta lactase enzymes that bacteria create to fight off antibiotics by stopping these enzymes from working and thus allowing Ticarcillin to keep working.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Overview
Timentin is quickly absorbed post-injection, reaching effective concentrations in various body fluids. Its dual-action mechanism ensures comprehensive bacterial coverage.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage Recommendations for Adults and Children
The amount of medication required varies according to the individual's age, weight, and the seriousness of the infection
Route of Administration and Injection Guidelines
Administer Timentin through an IV for results following the recommended dilution and infusion rates to improve absorption and reduce any side effects.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Infection Severity and Patient Condition
Higher doses may be recommended for severe infections. Additionally, dosage adjustments are made for patients with specific health conditions to prevent toxicity.
Guidelines for Dosage in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Patients with kidney or liver issues should consider lowering their dosage or spacing out their medication to prevent any build-up of drugs in their system and ensure their safety and well-being.
Common Side Effects of Timentin Injection Vial
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Dermatological Reactions
Some people may experience rashes or itching, which are usually mild and can improve over time or with intervention.
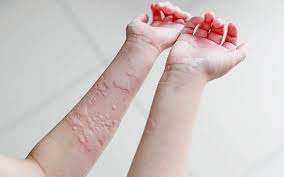
Injection Site Reactions
Pain or redness at the injection site is occasionally reported. These reactions usually subside on their own without additional treatment.
Serious and Rare Side Effects
Potential for Anaphylaxis and Allergic Reactions
While it is uncommonly seen in peoples experiences; there may be cases where individuals suffer from reactions or anaphylaxis requiring urgent medical attention.
Risk of Clostridium Difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
Prolonged use can lead to CDAD, a condition requiring specific medical management. Patients should report any severe diarrhea to their healthcare provider.
Hepatic, Renal, and Hematologic Adverse Effects
Timentin may affect liver, kidney, or blood parameters, particularly with long-term use. Regular monitoring helps in early detection and intervention.
Monitoring and Management of Severe Side Effects
Healthcare providers should closely monitor patients with known risk factors, managing adverse reactions promptly and adjusting dosages as needed.
Clavulanate potassium side effects
If you experience discomfort or watery/bloody diarrhea (even after a considerable time since your last dose) along, with symptoms, like pale or yellow skin tone. Additionally look out for urine or fever accompanied by confusion or weakness. Loss of appetite and upper stomach pain are also signs to watch for. Reduced urination may also occur.
Interactions with Other Drugs
Timentin may interact with other antibiotics, potentially enhancing or reducing therapeutic effects. Close monitoring is required in polypharmacy cases.
Potential Interactions with Anticoagulants and NSAIDs
When anticoagulants and NSAIDs are taken together with Timentin it can affect the effectiveness of the medication or raise the risk of bleeding. It is important to adjust doses when using these medications concurrently.
Interactions with Diuretics and Implications for Renal Function
When combined with diuretics, Timentin may affect kidney function. Periodic renal function tests are essential in patients receiving this combination therapy.
Guidance on Monitoring and Dosage Adjustments for Interacting Drugs
Healthcare professionals need to modify the dosage of Timentin according to its interactions to maintain efficacy while safeguarding patient well being.
Warnings and Precautions for Timentin Injection Vial
Precautions in Patients with a History of Penicillin Allergy
Patients who are allergic to penicillin may experience cross reactions when taking Timentin medication so it's important to conduct allergy tests before administering the drug to avoid any reactions.
Liver Function Monitoring in Long-Term Use
Extended use may impact liver function. Periodic monitoring of liver enzymes is recommended for patients on prolonged therapy.
Risk of Superinfection with Prolonged Use
Long term usage raises the chances of developing infections; therefore it is important to administer the treatment and regularly evaluate the patients condition.
Avoidance in Patients with Mononucleosis Due to Risk of Rash
In patients with mononucleosis, Timentin can cause severe rashes. Alternatives are advised for these individuals to prevent adverse skin reactions.
Contraindications of Timentin Injection Vial
Absolute Contraindications for Use
Patients, with a known allergy to any components of Timentin or similar antibiotics should avoid using it as it can lead to reactions like anaphylaxis that pose a risk, to their health and well being.
Contraindication in Patients with a Known Allergy to Penicillins or Beta-Lactams
People who have allergies to penicillins or beta-lactams antibiotics should steer clear of Timentin as they are more likely to experience reactions ranging from skin rashes to serious systemic issues. It's important to delve into the backgrounds of individuals to pinpoint those, at risk before giving them the medication.
Situations Where Risks Outweigh Benefits
In cases where the potential benefits of Timentin are outweighed by its risks, alternative therapies should be considered. These situations may include patients with compromised renal function, advanced liver disease, or those with histories of severe drug allergies.
Important Precautions Before Using Timentin
Pre-Treatment Testing for Penicillin Allergy
Prior to starting a Timentin treatment regimen for patients in healthcare settings, it is advisable for healthcare professionals to perform assessments for penicillin allergies or sensitivities to minimize the likelihood of reactions in individuals with uncertain drug tolerances.
Importance of Liver and Kidney Function Tests Before Initiation
Assessing liver and kidney function before prescribing Timentin ensures appropriate dosing and helps prevent potential toxicity. Impaired hepatic or renal function can lead to accumulation of the drug, increasing the risk of adverse reactions.
Considerations for Potential Interactions with Existing Medications
When taking Timentin medication make sure to consult with your doctor about interactions, with medications like blood thinners and water pills (diuretics). It's important to review all your medications to check for any interactions that could require changes, in dosage or closer monitoring.
Avoidance of Alcohol During Treatment
Alcohol should be avoided during treatment with Timentin, as it can exacerbate potential side effects like dizziness and gastrointestinal discomfort. Additionally, alcohol may interfere with the drugâs effectiveness in eradicating infections.
Special Considerations for Specific Populations
Administration in Elderly Patients
Dosage Adjustment and Monitoring Due to Age-Related Renal Function Decline
Due to age-related declines in renal function, elderly patients often require adjusted dosages of Timentin. Regular monitoring of renal function is recommended to ensure the drugâs safety and efficacy in this demographic.
Increased Risk of Side Effects and Close Observation Guidelines
Older individuals often face a risk of experiencing side effects from medication usage. It is crucial to observe and intervene promptly to avoid or address any negative responses and promote safer treatment results.
Administration During Pregnancy and Nursing
Pregnancy Risk Category and Potential Effects on the Fetus
Pregnant women should be cautious when considering the use of Timentin due to its classification in a risk category for pregnancy-related issues. In cases where its usage is deemed essential for treating infections during pregnancy, it is crucial to weigh the impact on the development of the fetus while prioritizing both fetal well-being.

Considerations for Breastfeeding and Potential Risks to the Infant
When given to nursing mothers Timentin may pass into breast milk. Healthcare providers should carefully consider the advantages of the treatment compared to the harm to the baby. They may explore treatment options. Temporarily stop breastfeeding if needed.
Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosage Recommendations and Administration Guidance
Pediatric dosages of Timentin should be calculated carefully based on weight and infection severity. Children are more sensitive to medication dosages, making precise calculation and adherence to guidelines essential in this group.
Monitoring for Specific Side Effects in Pediatric Patients
Pediatric patients require close observation for specific side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions. Timely intervention in case of adverse effects ensures safe and effective treatment.
Overdose and Management
Symptoms of Overdose: Nausea, Vomiting, Seizures
Symptoms of Timentin overdose include severe nausea, persistent vomiting, and, in severe cases, seizures. Early detection and intervention are critical in managing overdose cases effectively.
Immediate Steps in Overdose Management
Upon suspected overdose, immediate discontinuation of the drug is advised. Patients should be stabilized, and supportive measures provided to counteract symptoms.
Treatment Options Including Activated Charcoal and Supportive Care
Activated charcoal may be administered to absorb excess drug, while supportive care, such as hydration and electrolyte balance, is vital. In cases of severe toxicity, more intensive interventions may be warranted.
Importance of Prompt Medical Attention in Overdose Cases
Prompt medical attention in overdose cases reduces the risk of severe complications. Early intervention can help mitigate the effects of toxicity, ensuring patient safety and recovery.
Storage and Handling of Timentin Injection Vial
Proper Storage Conditions for Unopened Vials
Unopened vials of Timentin should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct light and moisture. Proper storage ensures the medication's potency is preserved until use.
Guidelines for Reconstitution and Stability After Mixing
After Timentin has been mixed back together again it should be used promptly as its effectiveness decreases with time. Make sure to adhere to the recommended instructions to keep it stable and avoid any contamination.
Disposal Recommendations for Unused or Expired Vials
Expired or unused vials of Timentin should be disposed of according to medical waste regulations. This prevents accidental exposure and ensures environmental safety.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Safe Handling Practices for Medical Professionals
Medical staff should always follow safety protocols by wearing gloves and protective equipment to avoid contact, with Timentin while handling and administering it.
Guidelines for Minimizing Exposure Risks During Preparation and Administration
It's important to limit contact, with Timentin to avoid any effects since skin exposure or inhaling it can cause problems, in healthcare settings where proper ventilation and careful handling are necessary.
Instructions for Proper Disposal of Medical Waste
Proper disposal of Timentin vials and associated medical waste is vital in healthcare settings. Following waste disposal protocols ensures compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Timentin Inj Vial FAQ
- Will amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat a uti?
- Will amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium cure chlamydia?
- Why is potassium clavulanate combined with amoxicillin?
- Why is clavulanate potassium used?
- When to use clavulanate potassium?
- What does clavulanate potassium do?
- What clavulanate potassium used for?
- How does amoxicillin clavulanate potassium work?
- How does clavulanate potassium work?
- Can amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat tooth infection?
- Can amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat uti?
- What is the drug ticarcillin used for?
- Is ticarcillin given IV or oral?
- What are the precautions for ticarcillin?
- What are the side effects of Ticarcillin clavulanate?
- What is the route of administration for ticarcillin?
- What group is ticarcillin in?
- Is ticarcillin in the urine?
- What is ticarcillin disodium and clavulanate potassium?
- What is ticarcillin used for?
Will amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat a uti?
Augmentin, a blend of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, is an antibiotic mix that is specifically recommended for addressing urinary tract infections.
Will amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium cure chlamydia?
The combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium has been successful in eliminating C.trachomatis.
Why is potassium clavulanate combined with amoxicillin?
When you mix clavulanate potassium with amoxicillin, it helps the antibiotic stay effective in the body for some time.
Why is clavulanate potassium used?
Clavulanate potassium (the potassium salt of clavulanic acid) is used with amoxicillin to prevent enzymes from deactivating it by acting as a β lactamase inhibitor that binds irreversibly to β lactamase. It is also used alongside sulbactam and tazobactam inhibitors.
When to use clavulanate potassium?
Amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium are medications prescribed by doctors to treat infections, such as pneumonia affecting the lungs or sinus and ear infections, as authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). They are also used for skin infections.
What does clavulanate potassium do?
Clavulanic acid is a component in the treatment of infections caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria to combat antibiotic resistance effectively. It should be prescribed exclusively for patients with such infections.
What clavulanate potassium used for?
Treat bacterial infections
How does amoxicillin clavulanate potassium work?
This medication functions by halting the proliferation of bacteria and is effective in addressing infections.
How does clavulanate potassium work?
Amoxicillin is combined with a β lactamase inhibitor to protect it from being deactivated by enzymes.
Can amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat tooth infection?
Typically, amoxicillin is the medication for treating a tooth infection. In cases where the tooth infection is more severe, your dentist might recommend a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate (known as Augmentin).
Can amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium treat uti?
Augmentin, a blend of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, is an antibiotic mix specifically recommended for treating urinary tract infections.
What is the drug ticarcillin used for?
Ticarcillin is an extended-spectrum carboxypenicillin often prescribed for treating moderate to severe infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Is ticarcillin given IV or oral?
The mixture of ticarcillin and clavulanic acid given through an injection.
What are the precautions for ticarcillin?
Serious and sometimes fatal allergic reactions have been noted in some cases, with the use of antibiotics like ticarcillin that can lead to diarrhea associated with Clostridium infection and an increased risk of seizures if the dosage is too high, particularly in individuals with kidney problems.
What are the side effects of Ticarcillin clavulanate?
Experiencing cramps or discomfort in the stomach area may be accompanied by tarry stools and gum bleeding. Skin changes such, as blister formation or peeling can occur along with bloating. Chest pain or tightness and chills are also symptoms to be aware of.
What is the route of administration for ticarcillin?
Ticarcillin, when given, systematically spreads throughout the body in fluids and tissues.
What group is ticarcillin in?
Practical Application of Ticarcillin; Ticarcillin, a type of beta lactam antibiotic is commonly employed to combat infections, within the body functioning akin to carbenicillin, an antibiotic, with a penicillin derived origin.
Is ticarcillin in the urine?
Around 60 to 70 percent of ticarcillin is eliminated unchanged in the urine within the 6 hours following its administration.
What is ticarcillin disodium and clavulanate potassium?
The combination of ticarcillin disodium and clavulanate potassium can impact the balance of bacteria in the gut, which may result in a decrease in estrogen absorption and make combined contraceptives containing estrogen and progesterone less effective.
What is ticarcillin used for?
Ticarcillin is a type of spectrum penicillin that is commonly used to treat infections caused by gram bacteria, and it is frequently paired with an aminoglycoside medication.












