Topiramate
- I. Introduction to Topiramate
- II. Composition and Properties of Topiramate
- III. How Topiramate Works: Mechanism of Action
- Approved Therapeutic Uses of Topiramate
- Off-label Uses of Topiramate
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Topiramate
- VII. Administration to Special Populations
- VIII. Topiramate Interactions
- IX. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions to Topiramate
- X. Precautions and Warnings When Using Topiramate
- XI. Overdose Scenarios and Management
- XII. Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Topiramate
I. Introduction to Topiramate
A. Brief History and Development
Topiramate, known as Topamax, was introduced as an antiepileptic medication in the late 20th century. When it was first approved by the FDA in 1996, it was considered a groundbreaking treatment option because it had two ways of working, which was uncommon for antiepileptic drugs. Since then, topiramate has been widely used in medical fields, gaining recognition as a versatile pharmaceutical.
B. Role in Modern Medicine
Topiramate has become widely recognized in medicine for its effectiveness in preventing epileptic seizures and migraines. This medication reduces the frequency of nerve signals in the brain, which helps control the neuronal activity responsible for these conditions. Due to its therapeutic outcomes and safety record, topiramate is increasingly embraced for other off-label purposes indicating its growing importance in contemporary pharmacotherapy.
C. Overview of Medical Importance
The medical importance of topiramate should not be underestimated. With more than 65 million individuals worldwide affected by epilepsy and migraines being a prominent cause of disability, topiramate plays an invaluable role in managing these conditions. Furthermore, its versatility extends to treating disorders ranging from mental health conditions, like bipolar disorder, to addressing weight management concerns, thus highlighting its significance in the wide-ranging field of medicine.
II. Composition and Properties of Topiramate
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Topiramate is derived from an occurring sugar called D fructose and has a distinct structure with a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide. This unique composition allows it to dissolve in fats, allowing it to pass through the protective barrier of the brain quickly. The molecular formula of topiramate (C12H21NO8S) reflects its structure highlighting the intricate design behind this powerful medication.
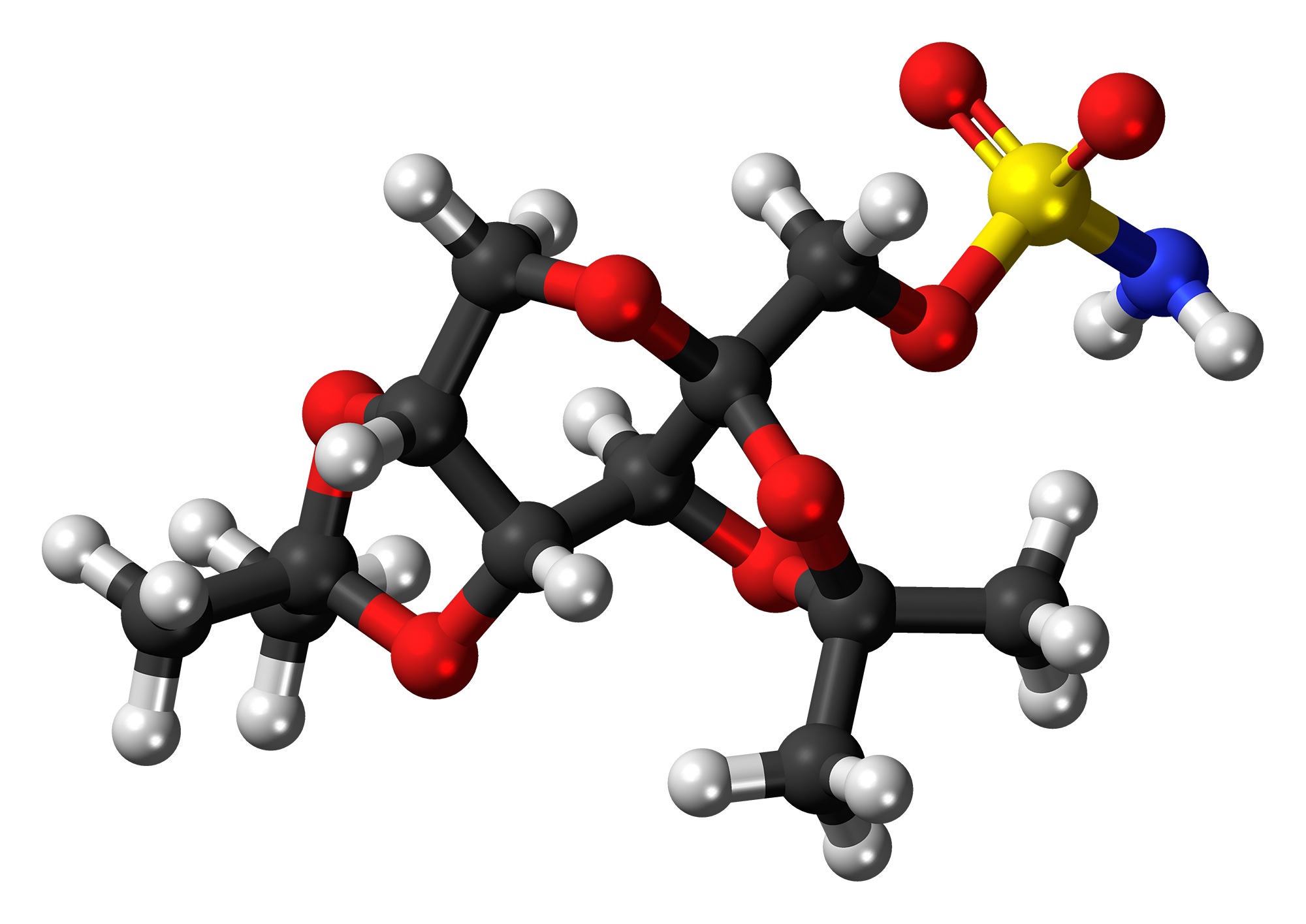
B. Pharmaceutical Formulation
Topiramate is made for taking by mouth. It comes in two primary forms; regular tablets and sprinkle capsules. The tablets are meant to be swallowed and are available in different strengths, making it easier to adjust the dosage. On the hand, the sprinkle capsules contain small coated particles of the medication, allowing them to be taken with or without food. They can even be sprinkled onto food, which is a convenient choice, for people who have trouble swallowing.
III. How Topiramate Works: Mechanism of Action
A. Neurological Impact
The way topiramate works is quite complex as it has effects that contribute to its diverse potential for therapy. Its primary function is to increase the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which's the brain's primary neurotransmitter responsible for inhibiting signals. By enhancing GABAs impact, topiramate helps reduce excessive neuronal activity, a shared factor in conditions such as epilepsy and migraines.
B. Metabolic Processes Involved
At the time, topiramate blocks the activity of glutamate, which is another important neurotransmitter that promotes nerve excitement. It does this by slowing down the function of kainate/AMPA receptors which are responsible for the effects of glutamate. Additionally, topiramate also reduces the activity of sodium and calcium channels that depend on voltage, further preventing nerve firing. By orchestrating these two actions, topiramate helps restore the balance between inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission, ultimately bringing back stability to the neural system.
Approved Therapeutic Uses of Topiramate
Epilepsy Management
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant medication that is commonly used to manage epilepsy in both children and adults. It is specifically used to treat Lennox Gastaut syndrome, characterized by seizures and developmental delays.
Here are the references for the information provided:
Migraine Prevention
Topiramate is also prescribed for the prevention of headaches and to reduce their frequency. It can be used as a treatment or in combination with other medications to manage specific types of seizures, such as primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (previously referred to as grand mal seizures, which affect the entire body) and partial onset seizures (seizures that impact only a specific part of the brain).
Here are the references for the information provided:
- Topiramate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Topiramate (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic
Off-label Uses of Topiramate
Weight Loss and Obesity Control
Sometimes doctors prescribe Topiramate for purposes than what it is officially approved for. One such use is to help manage binge eating and purging habits. Interestingly studies have found that Topiramate can lead to weight loss when utilized for controlling seizures or preventing migraines.
Here are the references for the information provided:
- Topiramate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Topiramate (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic
- Topiramate in the Treatment of Binge Eating Disorder Associated with Obesity: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Topiramate in the Treatment of Binge Eating Disorder Associated with Obesity: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Alcohol Dependence
Topiramate is sometimes prescribed for alcohol dependence even though it is not officially approved. A study published in the Journal of Diabetes Research found that topiramate was effective in reducing pain and improving nerve function in patients with diabetic neuropathy1. Another study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that topiramate was effective in reducing chronic low back pain2.
Here are the references for the information provided:
- Topiramate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Topiramate in the Treatment of Binge Eating Disorder Associated with Obesity: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Bipolar Disorder Management
Topiramate's sometimes used off-label to treat bipolar disorder. According to a review published in 2010, there seems to be a benefit of using topiramate to alleviate symptoms of borderline personality disorder. However it's important to note that this conclusion was drawn from a randomized controlled trial, and further research is needed for validation.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Topiramate
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
Topiramate is a medication that is used for various purposes. When it comes to the dosage, there is a pattern followed. Generally, the treatment starts with a dose of 25mg daily and then gradually increases weekly by 25 50mg. This gradual increase helps maximize the benefits while minimizing the chances of side effects. The recommended maintenance dose for epilepsy usually falls between 200 and 400mg daily, divided into two doses. However, a daily dose of 100mg split into two doses for migraine prevention is often sufficient.
B. Adjustments for Specific Patient Populations
While the recommended dosage guidelines provide a starting point, it's important to remember that they can be flexible. In some cases, adjustments to the dosage may be needed for specific patient groups. For example, people with kidney problems often require a dosage because their bodies clear the medication slower. Additionally, patients taking medication for epilepsy may need personalized dosages to prevent any potential interactions that could worsen any adverse effects.
VII. Administration to Special Populations
A. Topiramate Use in Elderly Patients
As people age, they face the issue of taking medications and becoming more prone to experiencing side effects. This means that when administering topiramate to the elderly, it is essential to be extremely careful. Elderly patients start with dosage and gradually increase it to avoid potential side effects. It is crucial to monitor their cognitive function because topiramate has the potential to cause cognitive impairment in this age group.
B. Topiramate Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
It is essential to consider the use of topiramate during pregnancy due to the potential risks of birth defects. Research has found a link between topiramate and cleft lip/palate in babies in the trimester. As a result, deciding whether to use topiramate in women involves weighing the potential benefits against the associated risks. In the case of breastfeeding mothers, topiramate can be passed on to the infant through breast milk. We are uncertain about its effects. Therefore it is advisable to proceed with caution and explore options whenever possible.
C. Topiramate Use in Pediatric Patients
Topiramate is a treatment option for children between the ages of 2 and 16 who have epilepsy. It is essential to adjust the dosage based on the child's weight, typically starting at around 25mg per day and gradually increasing it over a week until reaching a maintenance dose of 5 9mg per kilogram per day. Since children may be more prone to side effects such, as reduced sweating and increased body temperature it is essential to carefully monitor them while undergoing topiramate therapy.
VIII. Topiramate Interactions
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
Topiramate, similar to other medications, can interact with other drugs, which may affect its efficacy or lead to undesired side effects. Some notable interactions are as follows; When used alongside antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), it can change the concentration of either medication in the bloodstream, which may require dosage adjustments. Combining topiramate with metformin can heighten the chances of developing metabolic acidosis. Additionally, taking contraceptives with topiramate might reduce their effectiveness, increasing the risk of unintended pregnancy.
B. Food and Lifestyle Interactions
Topiramate effectiveness as a treatment may also be affected by food and lifestyle factors. Drinking alcohol can potentially enhance the effects of topiramate, resulting in increased drowsiness or dizziness. If one follows a high-fat diet for a period of time, it may reduce the drug's ability to control seizures. It is essential to exercise caution when engaging in demanding tasks, such, as driving as topiramate may have cognitive side effects that could impact alertness.

IX. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions to Topiramate
A. Common Side Effects
Although most people tolerate topiramate, well there are side effects that some patients may encounter. These can include sensations of tingling in the arms and legs, weight loss, feelings of fatigue, nausea, and changes, in taste.
B. Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Sometimes topiramate may cause serious side effects, although this happens less often. It's essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following; Signs of metabolic acidosis like rapid breathing, loss of appetite, or an irregular heartbeat—symptoms of kidney stones such as severe back or abdominal pain. Changes in vision or eye pain could indicate a potentially serious eye issue, like glaucoma.
X. Precautions and Warnings When Using Topiramate
A. Contraindications for Topiramate Use
It is essential to avoid using Topiramate if a patient has a known sensitivity to the medication or any of its components. Additionally, it is advisable to be cautious when prescribing Topiramate to patients with kidney problems or a history of kidney stones.
B. Cautious Administration of Topiramate
When prescribing topiramate, it is important to take an approach by considering the potential benefits and risks. Starting with the dose possible and slowly increasing it can help reduce any adverse effects. It is also essential to evaluate how the patient responds to the medication and make any necessary adjustments to achieve the best possible treatment results.
C. Handling and Storage Precautions
Store Topiramate at room temperature, keeping it away from light and moisture and out of the reach of children. It is important not to dispose of the medication by flushing it down the toilet or throwing it in the trash bin. Instead, please consult with a pharmacist about the methods of disposal.
XI. Overdose Scenarios and Management
A. Symptoms of Topiramate Overdose
In some cases taking too much topiramate can cause various noticeable effects on the body. These may involve feeling extremely sleepy or tired, experiencing restlessness and agitation, blacking out or having seizures experiencing difficulties with speech and vision, and feeling nausea and abdominal discomfort. It's vital to be aware of these signs and promptly take measures to prevent potential severe outcomes.
B. Immediate Action and Treatment Options
If you suspect an overdose of topiramate, it's crucial to contact the poison control center or emergency department immediately. Decontamination methods like activated charcoal might be used; Their effectiveness mainly relies on how much time has passed since taking the drug. The subsequent course of action mainly focuses on providing support and addressing symptoms, such as ensuring an airway stays hydrated and monitoring vital signs.
XII. Conclusion: Balancing the Benefits and Risks of Topiramate
A. Summarizing the Role of Topiramate in Medicine
Topiramate has proven to be a tool in treating epilepsy preventing migraines and helping with weight management. Its unique way of working distinguishes it from medications making it a versatile option, in the field of therapeutics.
B. Necessity for Medical Supervision When Using Topiramate
Although topiramate offers advantages, it is essential to acknowledge the potential risks involved. To ensure administration, it is crucial to carefully monitor for any contraindications, drug interactions, and potential side effects. Understanding how the drug behaves within the body, determining the dosage, and regularly assessing for any adverse reactions are all essential factors in maximizing the therapeutic benefits of topiramate while minimizing any potential harm. When used responsibly, topiramate remains an asset in modern medicine.
Topiramate FAQ
- Why is Topiramate used with Phentermine?
- Where to buy Phentermine-Topiramate?
- Why is Topiramate used for weight loss?
- Buy Topiramate?
- Purchase Phentermine Topiramate?
- Topiramate side effects?
- Topiramate lose weight?
- Topiramate for weight loss?
- Topiramate to lose weight?
- Topiramate weight loss?
- Topiramate is used for?
- Topiramate uses?
- Topiramate 25mg?
- Topiramate and Phentermine?
- What Topiramate used for?
- What are Topiramate used for?
- Topiramate 50 mg?
- Topiramate weight loss dose?
- Topiramate dosage for weight loss?
- Topiramate dose for weight loss?
- Topiramate for migraines?
- Topiramate migraine?
- Topiramate dose?
- Topiramate dosage?
- Topiramate interactions?
- Topiramate warnings?
- Topiramate mechanism of action?
- Topiramate side effects 25 mg?
- Topiramate and alcohol?
- Topiramate weight loss reviews?
- Topiramate brand name?
- Topiramate for weight loss reviews?
- Topiramate for bipolar?
- Topiramate weight loss 50 mg?
- Topiramate bipolar?
- Topiramate medication?
- Topiramate generic name?
- Topiramate side effects 50 mg?
- Topiramate pill?
- Topiramate withdrawal?
- Topiramate reviews?
- Topiramate pronunciation?
- Topiramate for anxiety?
- Topiramate anxiety?
- Topiramate with alcohol?
- Topiramate for migraines dosage?
- Topiramate dosage for migraines?
- Topiramate headache?
- Topiramate contraindications?
- Topiramate for depression?
- Topiramate/Topamax?
- Topiramate Topamax?
- Topiramate depression?
- Topiramate cost?
- Topiramate for nerve pain?
- Topiramate taper off schedule?
- Topiramate indications?
- Topiramate nerve pain?
- Topiramate ER?
- Topiramate Phentermine?
- Topiramate and weight loss?
- Is Topiramate used for weight loss?
- Topiramate and birth control?
- Topiramate mood stabilizer?
- Topiramate reviews for weight loss?
- Topiramate overdose?
- Topiramate kidney stones?
- Topiramate vs Topamax?
- Topiramate generic?
- Topiramate half life?
- Topiramate pregnancy?
- Topiramate itching how long does it last?
- Topiramate controlled substance?
- Topiramate for seizures?
- Topiramate seizures?
- Topiramate how long does it take to work?
- Topiramate for sleep?
- Topiramate with Phentermine?
- Topiramate and pregnancy?
- Topiramate other names?
- Topiramate hair loss?
- Topiramate eye side effects?
- Topiramate sleep?
- Topiramate drug interactions?
- Topiramate extended release?
- Topiramate tablet?
- Topiramate for pain?
- Topiramate for tremors?
- Topiramate for binge eating?
- Topiramate max dose?
- Topiramate off label uses?
- Topiramate tremor?
- Topiramate side effects hair loss?
- Topiramate binge eating?
- Topiramate alcohol use disorder?
- Topiramate and Wellbutrin?
- Topiramate GoodRx?
- Topiramate coupon?
- What is Topiramate used for weight loss?
- Topiramate used for weight loss?
- Topiramate price?
- Can Topiramate cause weight loss?
- Can Topiramate cause hair loss?
- Topiramate for neuropathy?
- Topiramate and metformin?
- Topiramate and kidney stones?
- Topiramate and phentermine weight loss?
- Topiramate long term side effects?
- Topiramate neuropathy?
- Topiramate prescription?
- Topiramate and bupropion?
- Topiramate XR?
- Can Topiramate cause headaches?
- Is Topiramate good for weight loss?
- Is Topiramate a blood thinner?
- Topiramate vs Gabapentin?
- Topiramate and Adderall?
- Topiramate weight gain?
- Topiramate metabolic acidosis?
- Topiramate taper schedule?
- Topiramate pregnancy category?
- Topiramate PTSD?
- Topiramate ingredients?
- Topiramate level?
- Topiramate diarrhea?
- Topiramate dosage for pain?
- Topiramate blood pressure?
- Topiramate over the counter?
- Topiramate drug?
- Topiramate what is it used for?
- What is Topiramate prescribed for?
- Can Topiramate cause weight gain?
- Is Topiramate addictive?
- Topiramate vs Phentermine?
- Topiramate and Gabapentin?
- Topiramate and Ibuprofen?
- Topiramate rash?
- Topiramate OCD?
- Topiramate glaucoma?
- Topiramate ER side effects?
- Topiramate essential tremor?
- Topiramate pill identifier?
- Topiramate in pregnancy?
- Topiramate sprinkle capsules?
- Topiramate nursing considerations?
- Topiramate names?
- Topiramate common side effects?
- Topiramate birth control?
- Topiramate brand?
- Topiramate bipolar weight loss?
- Topiramate ER coupon?
- Topiramate XR?
- Can Topiramate cause headaches?
- Is Topiramate good for weight loss?
- Is Topiramate a blood thinner?
- Topiramate vs Gabapentin?
- Topiramate and Adderall?