Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Introduction
Ursodeoxycholic Acid, also known as UDCA, is a derivative of bile acid that's important in treating liver and digestive system issues. To fully appreciate its benefits in therapy, it's essential to grasp its importance and how it works.
Overview of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA)
Ursodeoxycholic Acid, commonly known as UDCA, is a natural bile acid, in small amounts, in the human body. It is mainly produced in the liver from cholesterol. Makes up a substantial portion of the bile acids found in bile. The use of UDCA has brought about advancements in treating specific liver and gallbladder disorders. Its medicinal benefits have been thorough. Utilized in medical practice.
Historical Perspective
Throughout history, bile acids have been utilized in medicine for a period tracing back to ancient writings. Nevertheless, it was not until the part of the 20th century that Ursodeoxycholic Acid gained recognition as a valuable treatment.
In the 1960s, scientists delved into the possibilities of UDCA to address issues associated with gallstones. Further investigations showcased its effectiveness in eradicating cholesterol gallstones and enhancing liver health in liver ailments.
Mechanism of Action
UDCA works in ways to provide its therapeutic benefits mainly focusing on the liver and digestive system.
- One way is by increasing the solubility of cholesterol in bile, which helps dissolve cholesterol gallstones.
- Additionally, it has properties that help safeguard liver cells from damage caused by bile acids and oxidative stress.
- UDCA also influences responses, particularly in conditions like Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC), and helps regulate the movement of bile in the biliary tract to support proper flow and reduce the risk of cholestasis.
Uses of Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Approved Medical Uses
Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a naturally-occurring bile acid that constitutes a minor fraction of the human bile acid pool11. Its first use in traditional medicine dates back more than a hundred years, and it has been employed to treat liver disease for decades11. Here are its key indications:
- Treating Gallstones: UDCA is recommended for breaking down cholesterol gallstones in patients who are not willing or suitable for surgery1[1]22.
- Managing Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC): UDCA plays a crucial role in treating PBC by slowing down the progression of the disease and enhancing liver function1[1]33.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): Although the evidence is not as strong as with PBC, UDCA is frequently prescribed to alleviate symptoms and potentially slow down the progression of PSC11.
Emerging Medical Uses
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): UDCA shows promise in addressing NAFLD and NASH by improving liver steatosis and inflammation. However, further research is needed to fully understand its impact on advanced NASH11.
- Cholestasis of Pregnancy: Preliminary data indicates that Ursodeoxycholic Acid could help alleviate itching and enhance liver function in mothers with intrahepatic cholestasis during pregnancy11.
- Cystic Fibrosis Liver Disease: UDCA exhibits encouraging results in enhancing liver function and reducing inflammation of the bile ducts among patients with fibrosis-related liver issues11.
- Bile Reflux Gastritis: Ursodeoxycholic Acid might offer relief by decreasing the reflux of bile acids into the stomach and thereby alleviating symptoms associated with this condition11.
Dosage and Administration
Adult Dosage Guidelines
The amount of Ursodeoxycholic Acid needed can vary based on the medical condition being addressed.
- For Gallstone Dissolution, the usual dosage is 8 to 10 mg/kg/day, split into two to three doses taken with meals lasting up to six months.
- In Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC), the suggested dosage is 13 to 15 mg/kg/day, either taken at once or divided into two doses.
- For Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC), the dosing schedules are not as standardized, typically ranging from 13 to 15 mg/kg/day.

Pediatric Dosage Recommendations
When it comes to children, the dosage depends on their weight and the reason for treatment
Guidelines for Ages; Pediatric dosages usually fall between 10 to 20 mg per kilogram per day with modifications based on age and weight.
Calculating Dosage for Kids: There are formulas to figure out the right amount of UDCA for children based on their body size or weight.
Dosage Adjustments in Special Populations
Certain groups, like individuals expectant mothers and those with liver issues, might need changes in medication dosages:
Older Individuals: Considering how aging affects drug processing, it's advisable to start with lower UDCA doses for elderly patients and adjust gradually depending on how they respond and tolerate it.
Expectant Breastfeeding Women: Although UDCA is usually deemed safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it's crucial to monitor the dosing in these cases to promote the best outcomes for both mother and baby.
How Ursodeoxycholic Acid Works
Bile Acid Chemistry
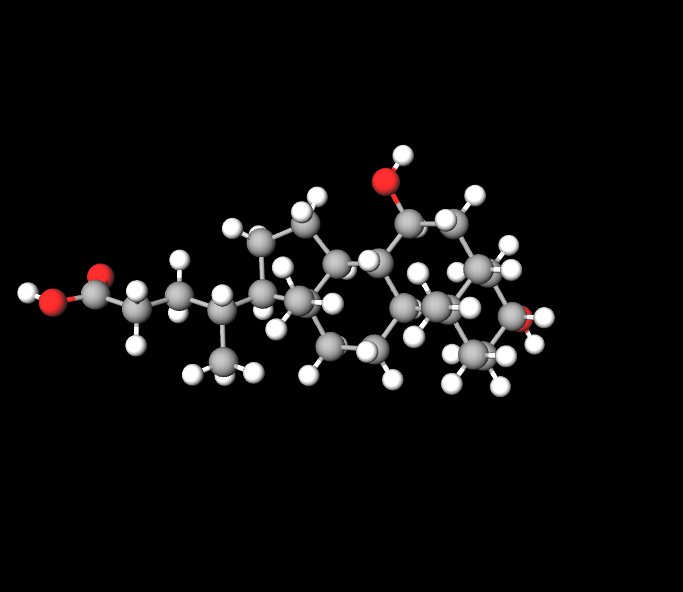
Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) is a type of bile acid produced in the liver through the breakdown of bile acids. It falls under the category of hydrophilic bile acids, which are known for their chemical makeup and healing qualities.
- Formed from cholesterol within the liver, UDCA is combined with glycine or taurine to create bile salts. In contrast to bile acids, UDCA is hydrophilic in nature, enabling it to dissolve cholesterol and support the flow of bile without causing harmful effects on cells.
- Its chemical composition, featuring a hydroxyl group at the carbon position, plays a key role in its specific medicinal properties, such as breaking down gallstones and safeguarding liver health.
Mechanism of Action in Gallstone Dissolution
The way Ursodeoxycholic Acid helps dissolve cholesterol gallstones is quite complex. Involves various processes.
- Firstly, UDCA competes with hydrophobic bile acids to enhance the solubilization of cholesterol in micelles, thus decreasing cholesterol saturation in bile and aiding in the dissolution of cholesterol-rich gallstones.
- Additionally, by boosting the solubility index of cholesterol and decreasing the formation of cholesterol crystals, UDCA assists in dissolving existing gallstones, leading to their gradual breakdown and removal.
- Moreover, UDCA modifies the composition and thickness of bile, promoting secretion and reducing stagnation, which helps prevent the recurrence of gallstones.

Effects on Biliary Tract Motility
Biliary tract movement is important for controlling bile flow and avoiding cholestasis.
Ursodeoxycholic Acid affects biliary movement by causing muscle relaxation, regulating sphincter tone, and improving bile flow. It helps relax muscle cells in the biliary system, widen ducts for better bile movement, regulate the sphincter of Oddi to ensure coordinated bile flow into the duodenum and enhance bile secretion while preventing the reabsorption of certain bile acids. This results in a smoother bile composition—improved clearance in the biliary system.
Hepatoprotective Properties
Ursodeoxycholic Acid does not impact bile acid metabolism and biliary tract motility but also shows protective qualities for the liver, which contribute to its effectiveness in treating different liver conditions. It acts as an antioxidant by neutralizing oxygen species (ROS) and preventing lipid damage, shielding liver cells from oxidative stress-related harm and cell death. Additionally, it has inflammatory properties by regulating immune responses and reducing pro-inflammatory signals, leading to decreased liver inflammation and scarring while supporting liver healing and renewal. Moreover, Ursodeoxycholic Acid inhibits pathways that trigger cell death caused by bile acids and inflammation, thus preserving the health and function of hepatocytes in various liver disorders.
Composition and Formulations
Pharmaceutical Formulations
Ursodeoxycholic Acid comes in types of medications designed to meet specific patient needs and dosage requirements.
- Tablet and UDCA tablets are often prescribed for oral intake, making dosing convenient and therapy titration precise.
- Capsule; UDCA capsules provide sustained release benefits maintaining levels, in the blood for longer periods and improving bioavailability.
- Liquid Suspension: UDCA liquid suspensions are preferred for children, older adults, or patients who have trouble swallowing, making administration easier and allowing for adjustments.
Excipients and Inactive Ingredients
Pharmaceutical versions of Ursodeoxycholic Acid could include additives and nonactive substances to improve stability, taste, and absorption; Fillers and Binders; Inactive materials like lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, and starch are commonly added to create tablet or capsule forms of UDCA.
- Coatings: Tablets or capsules may have enteric coatings to shield the active ingredient from stomach acid breakdown and ensure it is released in the small intestine as intended.
- Flavorings and Sweeteners: Liquid UDCA suspensions might be flavored with sweeteners to make them more palatable and help patients stick to their treatment plan.
Purity and Quality Standards
Ursodeoxycholic Acid formulations need to meet purity and quality criteria to guarantee safety, effectiveness, and compliance with regulations. This includes adhering to Pharmacopeial Standards, following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and conducting Stability Testing to assess shelf life and storage conditions to maintain product quality and efficacy.