Valaciclovir
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Valaciclovir
- III. How Valaciclovir Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Valaciclovir
- V. Off-label Uses of Valaciclovir
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Valaciclovir
- VII. Administration to Specific Populations
- VIII. Side Effects of Valaciclovir
- IX. Interactions with Valaciclovir
- X. Contraindications and Warnings of Valaciclovir Use
- XI. Careful Administration of Valaciclovir
- XII. Overdosage of Valaciclovir
- XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Valaciclovir
- XIV. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. What is Valaciclovir?
Valaciclovir is a widely prescribed antiviral medication used to treat infections caused by the herpes virus. It is crucial in treating conditions such as herpes simplex and herpes zoster. And also helps in preventing cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections. Valaciclovir is an orally available prodrug of acyclovir, making it an essential component in managing these viral infections.
B. History and Development of Valaciclovir
With its origins dating back to the early 1990s, Valaciclovir became a groundbreaking therapy that outshone acyclovir in treating herpes virus infections. Its exceptional bioavailability led to fewer dosing intervals. They were making it simpler to administer and ensuring higher patient compliance rates. Since being introduced, Valaciclovir has been invaluable in effectively managing these infections.
C. Importance and Relevance in Modern Medicine
Valaciclovir continues to hold great importance in the modern medical field. This drug is essential in managing various herpes infections thanks to its potent antiviral effects. Moreover, it is critical in preventing potential CMV infections, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients.
II. Composition of Valaciclovir
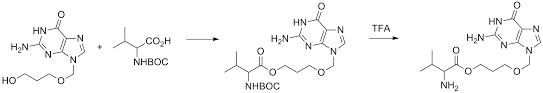
A. Chemical Properties and Structure
Valaciclovir is categorized as a prodrug and an L valine ester of acyclovir from a chemical standpoint. Its chemical structure consists of an acyclic purine nucleoside analog connected to the amino acid L valine, which aids in its oral absorption. Once in the body, it undergoes enzymatic breakdown and produces acyclovir and L valine.
B. Active and Inactive Ingredients
In Valaciclovir, it is important to note that the active component is its prodrug form once inside the body. This prodrug undergoes metabolism and transforms into acyclovir – an active antiviral substance, regarding its formulation. Inactive ingredients (excipients) can differ but frequently consist of microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, and magnesium stearate. Their inclusion serves to reinforce both the drugs' stability and bioavailability.
III. How Valaciclovir Works
A. Pharmacodynamics: Mechanism of Action
The therapeutic benefits offered by Valaciclovir hinge on its unique mode of action. Once it converts to acyclovir inside the patient's body, this medication inhibits viral DNA replication processes, an essential step for successful virus multiplication. The transformation occurs thanks to an enzyme called thymidine kinase found within viruses—acyclovir becomes acyclovir triphosphate. This crucial metabolite selectively interferes with viral DNA polymerase, ultimately thwarting the synthesis of viral DNA and impeding further replication.
B. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
Valaciclovir exhibits a pharmacokinetic profile characterized by its efficient and rapid absorption when taken orally, followed by its swift metabolism to acyclovir. And subsequent elimination through renal excretion. This prodrug is readily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver and intestines. It leads to higher levels of acyclovir in the bloodstream compared to oral administration of acyclovir. Most of the dose is excreted unchanged as acyclovir in the urine, primarily through renal excretion.
IV. Approved Uses of Valaciclovir
A. Treatment of Herpes Simplex Infections
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication for oral and genital herpes simplex virus infections. Healthcare professionals highly recommend it as it reduces outbreak duration and severity, leading to a more reasonable recovery period. Furthermore, Valaciclovir proves valuable as it helps prevent recurrent episodes among those suffering from chronic herpes.
Here are some references for you:
1. PubMed
2. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
3. Drugs.com
B. Management of Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication used to treat oral and genital herpes simplex virus infections. Healthcare professionals highly recommend it as it significantly reduces outbreak duration and severity, leading to a more reasonable recovery period. Furthermore, Valaciclovir proves valuable as it helps prevent recurrent episodes among those suffering from chronic herpes. It is also used to treat herpes zoster (shingles) and helps alleviate pain while accelerating the healing process of skin lesions.
Here are some references for you:
1. Medline Plus
2. GoodRx
3. Mayo Clinic
4. Drugs.com
C. Prevention of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infections
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication for oral and genital herpes simplex virus infections. Healthcare professionals highly recommend it as it reduces outbreak duration and severity, leading to a more reasonable recovery period. Furthermore, Valaciclovir proves valuable as it helps prevent recurrent episodes among those suffering from chronic herpes. It also prevents cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high-risk cases. It is taken by mouth.
Here are some references for you:
1. Wikipedia
2. The Lancet
3. Europe PMC
V. Off-label Uses of Valaciclovir
A. Potential Uses in Other Viral Infections
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat oral and genital herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus infections. However, preliminary studies indicate that it may be helpful in addressing the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV 6). However, further scientific verification is needed.
Here are some references for you:
1. UpToDate
2. MDPI
B. Possible Benefits in Autoimmune Diseases
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat oral and genital herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus infections. However, recent evidence suggests that it may also be valuable in treating autoimmune diseases. Specifically, certain autoimmune conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, have been theorized to stem from viral causes. In these situations, Valaciclovir could potentially improve the course of the disease by managing and controlling the viral infection at its core.
Here are some references for you:
C. Research-Based Uses: What Studies Suggest
Valaciclovir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat oral and genital herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus infections. However, clinical studies have suggested its usefulness in treating conditions such as Bell's palsy and vestibular neuritis. Methylprednisolone significantly improves the recovery of peripheral vestibular function in patients with vestibular neuritis, whereas valacyclovir does not.
It is important to note that these uses are still being studied and require additional large-scale trials to support the initial findings.
Here are some references for you:
1. New England Journal of Medicine
2. Relias Media
3. Vestibular Disorders Association
VI. Dosage and Administration of Valaciclovir

A. Dosage Guidelines for Various Conditions
The dosage of valaciclovir varies depending on the specific condition being treated in the case of treating herpes zoster. Taking 1 gram three times daily for seven days is generally recommended. When it comes to genital herpes treatment, first-episode cases usually call for a dosage of 500 mg taken twice daily for up to ten days. A dosage of 500 mg taken twice daily for three days is typically sufficient for recurrent episodes. When it comes to preventing recurrent genital herpes, a lower daily dose of 500 mg may be prescribed in the context of preventing CMV infection in organ transplantation cases. The dosage can be as high as 2 grams, taken four times daily.
B. Administration Methods and Best Practices
To effectively manage outbreaks, Valaciclovir is typically ingested orally. Its efficacy is greatly enhanced as soon as symptoms manifest themselves, whether consumed alongside a meal or on an empty stomach. Ensuring sufficient hydration is crucial for preserving kidney well-being during treatment.
C. Adjustments for Specific Populations (Renal Impairment, Hepatic Impairment)
It is essential to make dose adjustments in patients with renal impairment to avoid the build-up of drugs. The specific reduction in dosage depends on the severity of the renal dysfunction. For patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. There is no requirement for adjusting the dosage. However, in cases of severe hepatic impairment, it is essential to carefully evaluate the patient's clinical condition to determine the appropriate dosage.
VII. Administration to Specific Populations
A. Administration to the Elderly: Precautions and Adjusted Dosages
Duly recognizing the frequently reduced renal capacity among older patients, particular care should be exercised while prescribing dosages. Modifying medication quantities as needed becomes imperative under such circumstances. Regular monitoring of renal function warrants utmost attention, particularly for those currently on high doses.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile and Recommendations
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution when using valacyclovir, as its potential benefits must outweigh any potential risks involved. As it is known for passing into breast milk, nursing mothers are advised to approach its use with care. To thoroughly evaluate the risk-to-benefit ratio. Consulting healthcare professionals becomes imperative for making informed decisions.
C. Administration to Children: Guidelines and Considerations
The use of Valaciclovir among pediatric patients holds an overall consensus on its safety profile when addressing cold sores among individuals aged 12 and above. Furthermore, its efficacy extends to treating chickenpox in those aged above two years. To maintain utmost caution and ensure proper dosing alignment with body weight, adjustments must be carefully made under expert supervision from healthcare providers during administration procedures.
VIII. Side Effects of Valaciclovir
A. Common Side Effects: Frequency and Management
Valaciclovir commonly causes mild side effects such as nausea, stomach pain, and headache. However, these side effects usually go away independently after some time. To minimize their impact, staying hydrated and taking the medication with food is recommended.
B. Serious Side Effects: Recognition and Immediate Actions
It should be noted that Valaciclovir rarely leads to more severe side effects; nonetheless, they might present as mental or mood changes, dizziness, or manifestations suggestive of kidney issues. If any such symptoms emerge, seeking medical attention promptly without delay is imperative. Acquiring a comprehensive understanding of these risks and taking prompt action upon observing these indicators is paramount.
C. Long-Term Side Effects: What to Monitor for
Long-term usage of Valaciclovir has the potential to cause renal dysfunction, especially in patients who already have kidney issues. Thus. It is advisable to regularly monitor renal function, especially in individuals undergoing prolonged therapy. Furthermore, it is essential to watch for neurological symptoms such as confusion, hallucinations, and seizures as they may manifest in specific individuals, particularly when there is renal impairment or other underlying factors.
IX. Interactions with Valaciclovir
A. Drug-drug Interactions: Combinations to Avoid
Valaciclovir has the potential to interact with specific medications, which may result in the occurrence of severe side effects. It is essential to take note of crucial interactions that include drugs affecting kidney function. When Valaciclovir is used together with medicines such as aminoglycosides, cyclosporine, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), there is an increased risk of encountering kidney problems. Additionally, it should be noted that probenecid and cimetidine can impact the elimination of Valaciclovir from the body, possibly leading to higher levels of the drug and subsequent side effects.
B. Drug-food Interactions: Dietary Considerations
Patients have the option to consume Valaciclovir with or without food. However, maintaining proper fluid intake while taking this medication is crucial for their overall well-being and preventing any kidney-related problems.
C. Drug-disease Interactions: Contraindications and Cautions
Valaciclovir should be used cautiously in individuals with a previous history of kidney disease, a weakened immune system, or those experiencing dehydration. It is imperative to thoroughly assess medical history before initiating therapy.
X. Contraindications and Warnings of Valaciclovir Use
A. Absolute Contraindications: When not to use Valaciclovir
Valaciclovir should not be used in patients who have experienced a clinically significant hypersensitive reaction (such as anaphylaxis) to Valaciclovir, acyclovir, or any ingredient in the formulation.
B. Relative Contraindications: When to use with Caution
Patients with renal impairment, elderly patients, and individuals with neurological disorders are considered to have relative contraindications for this drug. It is essential to exercise caution while administering the medication to these specific populations, as dosage adjustments may be required.
C. Important Warnings: What Patients Should Know
Patients should be informed and made aware of possible side effects in their central nervous system, such as confusion, hallucinations, and seizures. Additionally, it is essential to notify them about the potential risk of kidney damage while undergoing treatment and emphasize the importance of maintaining adequate hydration.
XI. Careful Administration of Valaciclovir
A. Steps for Safe and Effective Administration
Following the healthcare provider's instructions is essential when taking Valaciclovir. Its maximum effectiveness is achieved when started promptly at the initial indication of a viral outbreak. Ensuring sufficient hydration throughout the treatment duration is crucial for minimizing the likelihood of encountering kidney issues.
B. Importance of Adherence to Therapy
Maintaining a regular and consistent usage of Valaciclovir is of utmost importance to effectively manage viral infection symptoms and prevent future recurrences. Neglecting the prescribed doses can result in poor outcomes and may lead to the virus developing resistance towards treatment.
C. Management of Missed Doses and Overdosage
If a person forgets to take a dose, it is essential for them to take it as soon as they remember. However, if the time for the next dose is near it is advised to skip the missed dose and stick to the regular schedule. In the event of an overdose, seeking immediate medical assistance is crucial. Overdosing can result in severe symptoms such as kidney damage, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
XII. Overdosage of Valaciclovir
A. Recognizing Signs of Overdose
An excess amount of Valaciclovir can result in various manifestations. Primary indications may encompass feelings of nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, seizures, and alterations in urine output. In more severe occurrences. Individuals may experience loss of consciousness, renal complications, and neurological symptoms like hallucinations and confusion.
B. Immediate Actions and Treatment
If an overdose is suspected, it is crucial to seek prompt medical attention. The primary approach to treatment usually includes providing the necessary support and managing any emerging symptoms in situations with significant kidney impairment. The administration of hemodialysis might be necessary to eliminate the drug from the body.
C. Prevention of Future Overdosage
Promoting awareness amongst patients regarding the paramount importance of adhering diligently to their prescribed dose, frequency, and duration of therapy is essential for averting potential instances of overdose. Moreover, implementing regular monitoring protocols specifically tailored towards high-risk individuals can serve as an effective preventive measure against overdosage.
XIII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Valaciclovir
A. Proper Storage Conditions and Practices
To maintain the quality of Valaciclovir, It is vital to store it at a suitable room temperature and protect it from exposure to light and moisture. To avoid any unintentional ingestion. It is necessary to keep Valaciclovir out of the reach of children.
B. Handling Precautions: How to Maintain Drug Quality
To handle Valaciclovir tablets appropriately, it is advisable to employ clean and dry hands. Moreover, to preserve the medication's effectiveness and safeguard it against dampness, it is imperative to close the container after usage firmly.
C. Disposal of Expired or Unused Valaciclovir
It is imperative not to discard expired or unused Valaciclovir by pouring it into wastewater or mixing it with regular household trash. A more suitable course of action would be returning this medication to a local pharmacy or designated disposal facility capable of handling such pharmaceuticals safely and responsibly. By doing so, we contribute positively towards reducing environmental harm while protecting individuals against accidental consumption.
XIV. Conclusion
A. Recap of Valaciclovir's Properties, Uses, and Precautions
Valaciclovir, a highly effective antiviral medication, is vital in managing herpes viruses. However, it is crucial to carefully consider the administration of this drug as well as its side effects and potential interactions. Neglecting proper precautions can result in severe health consequences and should be avoided.
B. Emphasizing the Importance of Patient-Physician Communication
An essential component of achieving effective treatment with Valaciclovir is an open and transparent line of communication between the patient and their healthcare provider. It is crucial that patients feel empowered to express any concerns or adverse effects they may encounter while undergoing therapy.
C. Future Prospects of Valaciclovir in Medicine
Valaciclovir shows excellent promise for the future. Ongoing research might unveil its potential applications beyond just treating herpes viruses. However, using this medication cautiously while embracing its possibilities is crucial. Following established guidelines can help us maximize Valaciclovir's benefits while minimizing potential risks.