Vinorelbine. Injection
- I. Introduction to Vinorelbine Injection
- II. Composition of Vinorelbine Injection
- III. Mechanism of Action: How Vinorelbine Works
- IV. Approved Medical Uses of Vinorelbine Injection
- V. Off-Label Uses of Vinorelbine Injection
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Storage and Handling of Vinorelbine Injection
- VIII. Safe Handling and Preparation Precautions
- IX. Common and Serious Side Effects of Vinorelbine Injection
- X. Drug Interactions with Vinorelbine Injection
- XI. Contraindications for Vinorelbine Use
- XII. Warnings and Precautions Before Starting Therapy
- XIII. Precautions for Special Populations
- XIV. Careful Administration Guidelines
- XV. Overdose and Emergency Management
- XVI. Important Patient Information and Safety Advice
- XVII. Conclusion and Clinical Outlook
I. Introduction to Vinorelbine Injection
Overview of Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine, a synthetic vinca alkaloid used in cancer treatment, is known for its strong anti-cancer effects in oncology settings. It is extracted from the plant Catharanthus roseus and has demonstrated notable effectiveness against fast-growing cancer cells.

Classification and Pharmacological Category
Vinorelbine is categorized as an antimicrotubule agent within the vinca alkaloid subclass in terms of pharmacology; it acts as an inhibitor by interfering with the production of microtubules for cell replication.
Indications for Injection Form
The injectable form of vinorelbine is primarily indicated for:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), both as monotherapy and in combination protocols
- Advanced or metastatic breast cancer unresponsive to first-line treatments
Its parenteral route ensures rapid systemic absorption and precision dosing.
Regulatory Approval and Brand Names
Vinorelbine injection has received regulatory approval from major health authorities, including the FDA and EMA. Common brand names include:
II. Composition of Vinorelbine Injection
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
The main ingredient at work here is vinorelbine tartrate, an alkaloid known for its ability to stop cell division by affecting the process of mitosis.
List of Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Formulation may include:
- Water for injection
- Citrate buffer (as pH stabilizer)
- Polyethylene glycol or polysorbate (as solubilizers)
Available Concentrations and Formulations
Vinorelbine injection is commonly available in:
- 10 mg/mL in 1 mL and 5 mL vials
- Preservative-free formulations for single-dose use
III. Mechanism of Action: How Vinorelbine Works
Cellular Mechanism and Impact on Microtubule Formation
Vinorelbine binds to tubulin, inhibiting the polymerization required for mitotic spindle formation. This action halts cells in metaphase, leading to apoptosis.
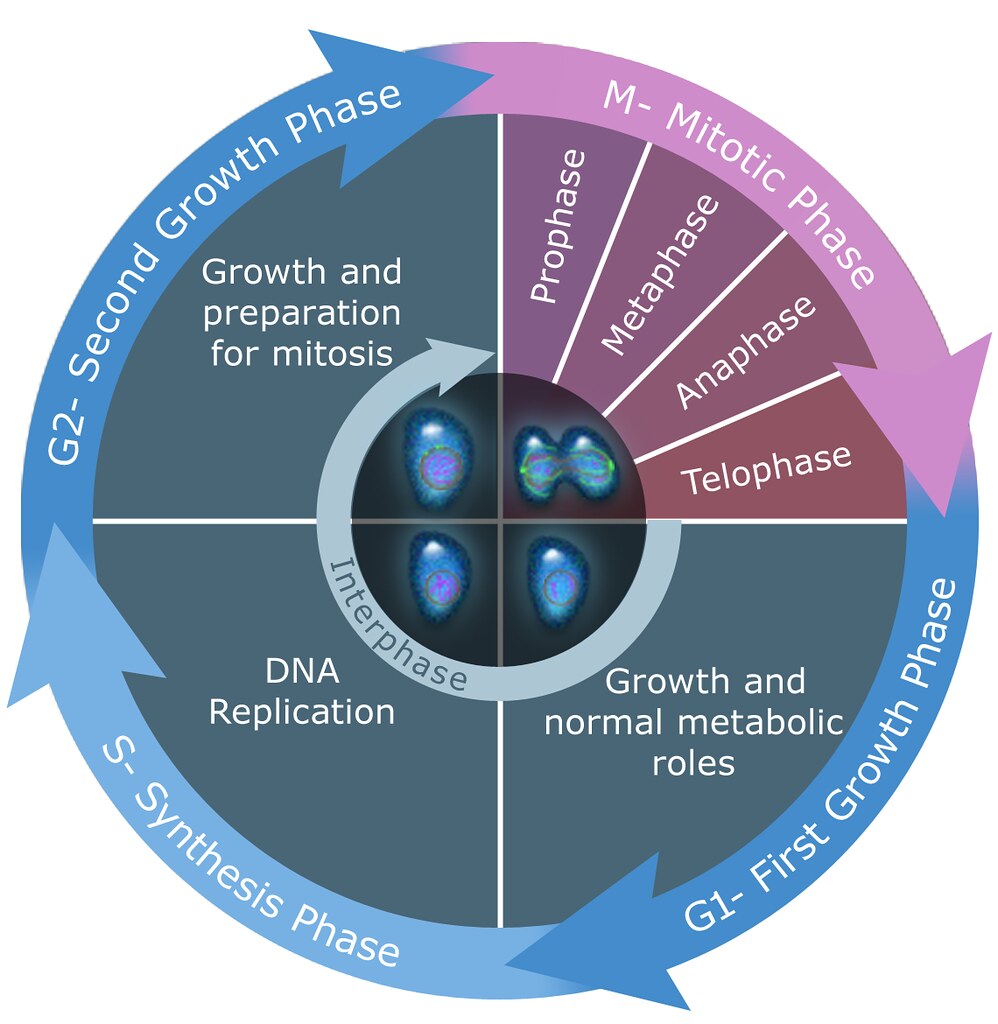
Effects on Cancer Cell Cycle and Apoptosis
By stopping cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, vinorelbine initiates programmed cell death, disrupts cell movement, and hinders crucial signaling pathways involved in tumor growth.
Comparison with Other Vinca Alkaloids
Compared to vincristine and vinblastine:
- Vinorelbine exhibits a more favorable neurotoxicity profile
- Higher selectivity for lung tissue and solid tumors
IV. Approved Medical Uses of Vinorelbine Injection
Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Vinorelbine is commonly utilized in the treatment of non small-cell lung cancer (NSCL). It is frequently prescribed for patients with metastatic conditions. It can be given either on its own or in combination with cisplatin.

Use in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Role in Advanced Ovarian Cancer
Vinorelbine as Part of Combination Chemotherapy Protocols
It is frequently combined with agents like:
Such regimens maximize tumor cytotoxicity while diversifying the mechanism of action.
V. Off-Label Uses of Vinorelbine Injection
Management of Mesothelioma
Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers
Use in Prostate Cancer Therapy
Investigational Applications in Pediatric Cancers
Various research studies have delved into how it functions in treating sarcomas and brain tumors and have seen levels of effectiveness and tolerance in patients.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage for Approved Indications
Typical dosages include:
- 25-30 mg/m² weekly as a single agent
- 20-25 mg/m² in combination regimens every 7-10 days
Dosing Schedules and Routes of Administration
Vinorelbine is administered intravenously:
- Over 6-10 minutes via a running IV line
- With weekly or bi-weekly intervals, depending on the protocol
Dosage Modifications for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
It's important to reduce doses in cases of liver dysfunction and be careful with kidney issues since vinorelbine is mostly metabolized in the liver.
Protocols for Intravenous Administration
- Use of central venous access preferred to avoid extravasation
- Flush line with saline pre- and post-infusion
Administration in Combination Regimens
In multidrug treatment plans it is crucial to schedule the timing and sequence of administration, with medications to reduce the risk of overlapping side effects.
VII. Storage and Handling of Vinorelbine Injection
Recommended Storage Conditions
- Store at 2°C-8°C (refrigerated)
- Do not freeze
Protection from Light and Temperature Stability
Vinorelbine can be affected by light. It's best to store it in its packaging to shield it from exposure to light, as changes in temperature could impact its effectiveness.
Shelf Life and Reconstitution Guidelines
Unopened vials maintain stability for up to 24 months. Once opened or diluted, use within 24 hours if stored at 2-8°C.
VIII. Safe Handling and Preparation Precautions
Cytotoxic Drug Handling Protocols for Healthcare Providers
Vinorelbine should be prepared in a certified biological safety cabinet. Staff must undergo hazardous drug handling training.
Personal Protective Equipment Requirements
Essential PPE includes:
- Chemotherapy gloves
- Protective gowns
- Face shields or goggles when splashing is possible
Spill Management and Disposal Guidelines
Spills must be contained using spill kits. Contaminated materials should be discarded in accordance with cytotoxic waste protocols. Incineration is preferred for final disposal.
IX. Common and Serious Side Effects of Vinorelbine Injection
Common Side Effects: Nausea, Fatigue, Injection Site Reactions
Vinorelbine frequently induces a spectrum of tolerable yet unpleasant effects. Common adverse reactions include:
- Nausea and vomiting: Often transient, manageable with prophylactic antiemetics
- Fatigue: A pervasive sense of lethargy that may affect daily functionality
- Injection site reactions: Pain, redness, and localized inflammation may occur, especially if extravasation happens
Hematologic Side Effects: Neutropenia, Anemia, Thrombocytopenia
Myelosuppression is a dose-limiting toxicity of vinorelbine:
- Neutropenia: The most prevalent hematologic effect, increasing susceptibility to infection
- Anemia: May manifest as pallor, dizziness, or shortness of breath
- Thrombocytopenia: Bruising and prolonged bleeding are potential indicators
Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Constipation, Vomiting
Gastrointestinal complications may compromise patient quality of life:
- Constipation: A frequent complaint, often requiring laxative support
- Vomiting: Less severe with antiemetic premedication but can be distressing
Serious Adverse Effects: Neurotoxicity, Pulmonary Toxicity
Though rare, serious adverse events demand vigilance:
- Neurotoxicity: Peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, and sensory loss may emerge over cumulative dosing
- Pulmonary toxicity: Dyspnea, interstitial pneumonitis, and pulmonary fibrosis have been documented
X. Drug Interactions with Vinorelbine Injection
Interactions with Other Chemotherapeutic Agents
Vinorelbine could enhance the effects of medications or be affected by them when taken together as part of treatment plans. It's crucial to coordinate treatments carefully to avoid any potential harmful interactions.
Impact of CYP3A4 Inhibitors and Inducers
As vinorelbine is metabolized by CYP3A4:
- Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, erythromycin) may elevate plasma levels, enhancing toxicity
- Inducers (e.g., rifampin, phenytoin) may reduce efficacy by accelerating metabolism
Risk of Additive Myelosuppression with Concurrent Medications
Drugs that suppress bone marrow (e.g., clozapine, zidovudine) heighten the risk of pancytopenia when used with vinorelbine.
Monitoring Recommendations for Known Interactions
- Baseline liver enzyme and hematologic evaluations
- Regular pharmacovigilance for unexpected side effects
- Patient education to avoid unapproved supplements or herbal medications
XI. Contraindications for Vinorelbine Use
Absolute Contraindications: Severe Neutropenia, Known Hypersensitivity
Use of vinorelbine is contraindicated in:
- Patients with severe baseline neutropenia (ANC < 1,500/mm³)
- Individuals with documented hypersensitivity to vinorelbine or related compounds
Relative Contraindications and Clinical Considerations
Caution is advised in cases of:
- Significant hepatic dysfunction
- Recent or ongoing infections
- Patients with compromised performance status
XII. Warnings and Precautions Before Starting Therapy
Risk of Extravasation and Tissue Necrosis
Vinorelbine is vesicant in nature. If extravasated, it may lead to:
- Severe localized pain
- Tissue necrosis requiring surgical intervention
Use of central lines is strongly recommended.

Pulmonary Complications and Monitoring
Rare but severe pulmonary events require:
- Baseline chest imaging for at-risk patients
- Monitoring for dyspnea or hypoxia during treatment
Risk of Treatment-Related Infections
Immunosuppression warrants:
- Prophylactic antimicrobials in high-risk patients
- Prompt treatment of febrile neutropenia
XIII. Precautions for Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Aging patients often require tailored approaches:
- Dose adjustments due to decreased metabolic clearance
- Monitoring for cumulative toxicity especially neurotoxicity and hematologic suppression
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Teratogenic Potential and Fetal Risk
Vinorelbine is classified as pregnancy category D. Risks include:
- Fetal growth restriction
- Congenital malformations

Recommendations for Contraception and Breastfeeding
- Effective contraception advised during and 3 months post-treatment
- Lactation should be discontinued during therapy
Pediatric Patients
Limited Data on Safety and Efficacy
Use in children remains investigational, with inconsistent clinical outcomes.
Dose Calculation Based on Body Surface Area
Pediatric dosing typically employs BSA (mg/m²), requiring individualized calculations and close toxicity monitoring.
XIV. Careful Administration Guidelines
Monitoring of Complete Blood Count Before Each Dose
CBC with differential must be assessed prior to administration to:
- Avoid critical neutropenia
- Guide dose modifications
Timing and Management of Dose Delays or Reductions
Criteria for delay or reduction include:
- ANC < 1,000/mm³
- Platelet count < 75,000/mm³
- Grade 2 non-hematologic toxicity
Preventing and Managing Infusion-Related Reactions
Prophylactic antihistamines are generally not required, but vigilance for:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Infusion-site discomfort
is critical during administration.
XV. Overdose and Emergency Management
Signs and Symptoms of Vinorelbine Overdose
Overdosage may result in:
- Profound bone marrow suppression
- Gastrointestinal ulceration
- Neurologic disturbances
Recommended Interventions and Supportive Care
No specific antidote exists. Management includes:
- Colony-stimulating factors
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Intravenous fluids and electrolyte balance
Reporting and Documentation Procedures
All overdose events should be documented and reported to pharmacovigilance authorities for analysis and tracking.
XVI. Important Patient Information and Safety Advice
Counseling on Expected Side Effects and Symptom Tracking
Patients should be advised to anticipate; Temporary hair loss. Variations, in the way ones bowel moves. Feeling tired. Changes, in how things taste. Keeping a journal of side effects could help in spotting any problems rather than later.
Guidelines for Infection Prevention During Treatment
Key strategies include:
- Avoiding crowds and sick contacts
- Daily temperature monitoring
- Strict hygiene and oral care routines
Importance of Adherence to Scheduled Dosing and Monitoring
Missing doses or delaying lab work can compromise treatment efficacy. Regular follow-ups are indispensable for:
- Evaluating treatment response
- Detecting early toxicity
XVII. Conclusion and Clinical Outlook
Vinorelbine injection remains a cornerstone in the management of specific malignancies. Its targeted mechanism, manageable toxicity profile, and compatibility with other agents support its sustained relevance.
Vinorelbine. Injection FAQ
- What type of chemotherapy is vinorelbine?
- What is vinorelbine used for?
- Is vinorelbine toxic to the liver?
- What is the mechanism of action of vinorelbine?
- Will I lose my hair on vinorelbine?
- What is the success rate of vinorelbine?
- How often is vinorelbine dosing?
- What are the precautions for vinorelbine?
- What is Vinorelbine Injection used for?
- How does Vinorelbine work?
- How is Vinorelbine administered?
- What are the common side effects of Vinorelbine?
- Can Vinorelbine cause low blood cell counts?
- Can Vinorelbine cause nerve damage (neuropathy)?
- How often is Vinorelbine administered?
- Can Vinorelbine be used during pregnancy?
- Can Vinorelbine be used during breastfeeding?
- What precautions should be taken before receiving Vinorelbine?
- What should patients report to their doctor while on Vinorelbine?
- Can Vinorelbine cause hair loss?
- Can Vinorelbine cause constipation?
- Can Vinorelbine cause nausea and vomiting?
- What are the long-term risks associated with Vinorelbine?
- How is Vinorelbine dosage determined?
- What blood tests are monitored during Vinorelbine treatment?
- Can Vinorelbine cause changes in liver or kidney function?
- Can Vinorelbine cause vein irritation or damage at the injection site?
- Is Vinorelbine always used alone?
What type of chemotherapy is vinorelbine?
Vinorelbine and cisplatin are often prescribed as a chemotherapy regimen for small cell lung cancer (NSCL). In some cases, this treatment may also be recommended for certain types of cancer. It is commonly referred to as VP or NP chemotherapy.
What is vinorelbine used for?
Vinorelbine is commonly prescribed for patients with breast cancer and nonsmall cell lung cancer to hinder the replication of material (DNA), thereby impeding the proliferation and spread of cells.
Is vinorelbine toxic to the liver?
Liver toxicity may occur in individuals who are undergoing vinorelbine treatment, leading to liver damage, as a side effect of this chemotherapy medication.
What is the mechanism of action of vinorelbine?
It works by attaching to proteins in the spindle of cells and stopping division during metaphase.
Will I lose my hair on vinorelbine?
When vinorelbine is used independently, it may lead to slight and temporary hair thinning. In rare instances, it could result in a loss of hair.
What is the success rate of vinorelbine?
80.8%
How often is vinorelbine dosing?
The standard dosage plan for taking vinorelbine involves taking 60 mg/m² per week for the 3 weeks (cycle 1), followed by a weekly dose of 80 mg/m² thereafter.
What are the precautions for vinorelbine?
Make sure to consult your healthcare provider if you experience stomach cramps or pain, sticky stools, diarrhea, fever, or intense vomiting that may contain blood.
What is Vinorelbine Injection used for?
It is utilized for addressing forms of lung cancer (small cell lung cancer) as well as breast cancer.
How does Vinorelbine work?
It interferes with the growth of cancer cells by stopping cell division.
How is Vinorelbine administered?
It is typically given through an IV by a healthcare provider.
What are the common side effects of Vinorelbine?
Typical adverse reactions may consist of reduced blood cell levels (neutropenia), decreased blood cell counts (anemia), diminished platelet counts (thrombocytopenia), feelings of sickness and vomiting, hair loss, and constipation.
Can Vinorelbine cause low blood cell counts?
It often results in myelosuppression that can result in decreased blood cell counts and raise susceptibility to infections and bleeding.
Can Vinorelbine cause nerve damage (neuropathy)?
Yes, it can result in neuropathy, which can cause sensations of numbness and tingling or even pain in the hands and feet.
How often is Vinorelbine administered?
The amount and timing of medication vary based on the cancer and how the individual patient is reacting to treatment.
Can Vinorelbine be used during pregnancy?
No
Can Vinorelbine be used during breastfeeding?
It advised against breastfeeding because it could pose a threat to the baby.
What precautions should be taken before receiving Vinorelbine?
Before commencing treatment, it is important for patients to undergo blood tests and other essential assessments to establish a baseline for their health status.
What should patients report to their doctor while on Vinorelbine?
Patients need to notify any indications of infection or numbness and tingling in their limbs, as well as chest discomfort or unusual breathing difficulties, along with any unexpected bleeding or bruising occurrences.
Can Vinorelbine cause hair loss?
Losing hair (alopecia ) is a common side effect.
Can Vinorelbine cause constipation?
Yes
Can Vinorelbine cause nausea and vomiting?
Indeed, feeling queasy and throwing up are reactions resulting in the recommendation of anti-nausea drugs.
What are the long-term risks associated with Vinorelbine?
Potential long-term consequences involve nerve injury and the risk of developing cancers.
How is Vinorelbine dosage determined?
The dosage is calculated meticulously, taking into account the patient's body surface area and various other factors.
What blood tests are monitored during Vinorelbine treatment?
Regular blood tests, known as blood counts (CBC), are conducted to check for bone marrow issues and evaluate the likelihood of infections or bleeding complications.
Can Vinorelbine cause changes in liver or kidney function?
Liver and kidney function can be impacted by it, and regular monitoring is crucial for patients with existing health issues.
Can Vinorelbine cause vein irritation or damage at the injection site?
Yes, it may lead to irritation of the vein or phlebitis at the spot where the injection is administered.
Is Vinorelbine always used alone?
It is commonly utilized alongside chemotherapy medications.