Mitomycin injection
- Introduction
- Uses of Mitomycin Injection
- How Mitomycin Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Off-Label Uses of Mitomycin
- Composition
- Storage
- Interactions
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to the Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Overdosage
- Handling Precautions
Introduction
Throughout the history of medicine, there have been groundbreaking discoveries that have greatly influenced modern healthcare. One such discovery that stands out is the unearthing of Mitomycin. Discovered in the 1950s from the broth of Streptomyces caespitosus, Mitomycin has a historical background. It was initially isolated from a strain of soil bacterium and quickly gained attention from researchers worldwide due to its unique chemical structure and potential therapeutic properties. The journey of Mitomycin involved research, rigorous studies, clinical trials, and thorough validations before it reached its current status. In the 1970s, regulatory bodies approved Mitomycin for cancer therapy thanks to its anti-tumor activity. This milestone marked a turning point in the field of cancer treatment.
Uses of Mitomycin Injection
Over the years, Mitomycin has proven to be highly versatile in its applications. It is not limited to one area but can be used in various therapeutic situations. Its main uses are in the treatment of cancers and tumors. Mitomycin has shown effectiveness against different malignancies like gastric, pancreatic, and adenocarcinoma. The fact that it can be adapted to treatment plans highlights its crucial role in oncology. Moreover, Mitomycin also brings benefits when used alongside therapies. These combination treatments use the power of Mitomycin, enhancing its effects and offering a comprehensive approach to managing cancer.
How Mitomycin Works
The way Mitomycin works in the body is quite complex and fascinating. One must explore its intricacies and how it interacts with cells to understand its potential fully.
- In terms of its mechanism of action, Mitomycin acts as an alkylating agent. When exposed to oxygen conditions commonly found in tumor environments, Mitomycin undergoes a process of reductive activation. This triggers the creation of substances that bind DNA together, preventing its replication and ultimately inhibiting cell growth.
- Mitomycin has an affinity for rapidly dividing cells when interacting with cancer cells. This selectivity ensures that normal tissues are minimally affected while maximizing drug toxicity against cells. The resulting damage to DNA prompts apoptosis, leading to the demise of cells.
Dosage and Administration
The precise administration of Mitomycin is essential. While its therapeutic benefits are significant, it is crucial to understand the recommended dosage and administration techniques for optimal outcomes.
- Dosage guidelines: Following the prescribed dosage guidelines for Mitomycin is essential. These guidelines have been carefully determined through clinical trials and research efforts.
- Methods of administration: Mitomycin is commonly administered through intravenous infusion. This ensures absorption into the bloodstream; it is vital to prioritize aseptic techniques to prevent potential complications.
- Factors influencing dosage: Each patient has characteristics that require personalized dosage regimens. Factors such as body weight, the type of cancer being treated, and the patient's overall health status are crucial in determining the ideal dosage.
Side Effects
Like any medication, Mitomycin can cause side effects1. It is essential to distinguish between harmless side effects and those that require immediate medical attention.
- Here is an overview of the side effects of Mitomycin: Sometimes, the pharmacological potency of Mitomycin can lead to side effects, which can range from mild and temporary to severe and long-lasting.
- To differentiate between rare side effects, it is necessary to understand their frequency and severity. Common side effects are usually mild. Not a cause for concern, while the rarer ones, although uncommon, may require immediate medical attention.

Common Side Effects
Understanding the side effects is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. With this knowledge, we can manage and alleviate these effects.
- Here are some experienced side effects: feeling nauseous, experiencing fatigue, having a reduced appetite, and developing skin rashes. While these symptoms can be bothersome, they are usually not severe or long-lasting.
- To effectively manage and reduce the impact of these side effects, it's essential to take an integrated approach that includes making lifestyle adjustments, providing symptomatic treatment, and regularly monitoring their progress. Consulting with healthcare professionals is vital to creating strategies for managing these side effects.
Off-Label Uses of Mitomycin
The medical field often explores therapeutic possibilities beyond the established norms. Mitomycin, a drug with known uses, has caught the attention of researchers due to its potential in off-label applications.
- Some documented off-label treatments for Mitomycin include its use in glaucoma surgeries and certain bladder conditions, highlighting its versatility in practice.
- Several research studies have played a role in substantiating these off-label uses. Through clinical trials and systematic reviews, empirical evidence has emerged, confirming the effectiveness and safety of Mitomycin in these unconventional areas.
Composition
Understanding the composition of Mitomycin involves an exploration of its various ingredients. Each active or inactive ingredient plays a role in how the drug works in the body. Let's take a look at these components and their functions:
- Mitomycin primarily contains an active ingredient called Mitomycin C, which is responsible for the drug's therapeutic effects. Alongside this are substances known as excipients that contribute to stability, solubility, and optimal delivery.
- When it comes to the inactive components of Mitomycin, we find that Mitomycin C takes center stage as the primary active substance. However, it is supported by inactive ingredients like mannitol and sodium chloride. These additional substances ensure that the drug remains soluble and stable within its formulation, ultimately making it practical and safe.
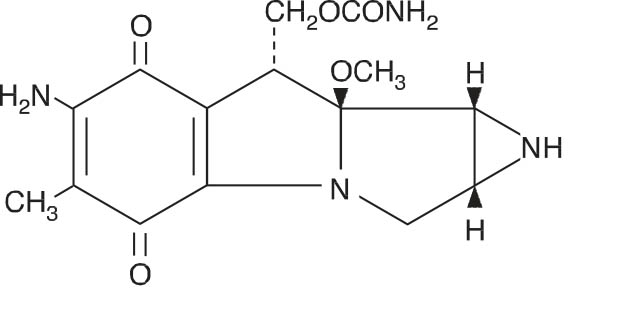
Storage
The effectiveness and lifespan of Mitomycin are closely tied to how it's stored. Holding the drug for optimal therapeutic outcomes and safety is crucial. Mitomycin should be kept in a cool and dry place to ensure storage, ideally at temperatures between 2°C and 8°C. It is essential to shield the drug from sunlight and excessive humidity. The packaging usually specifies the shelf life of Mitomycin. Following this timeframe is necessary to maintain its potency and safety. Any deviations from the recommended storage conditions could jeopardize the stability of the drug, so it's essential to use it cautiously.
Interactions
In the pharmacotherapy field, medication effectiveness can be influenced by interactions between drugs or between drugs and certain lifestyles. Mitomycin, known for its pharmacodynamic profile, is not exempt from this phenomenon. Some medications can either enhance or reduce the effects of Mitomycin when taken together. These medications include anticoagulants, live vaccines, and some antiviral drugs. It's important to note that such interactions might also worsen side effects, which may require careful adjustments in dosage or alternative treatment approaches.
Regarding lifestyle factors, explicit restrictions regarding food intake are uncommon. However, excessive consumption of alcohol or tobacco has the potential to affect the way Mitomycin is metabolized in the liver, potentially impacting its effectiveness. Furthermore, certain foods rich in antioxidants could theoretically interfere with how Mitomycin works. Considering these drug interactions and lifestyle factors is crucial when using Mitomycin as part of a treatment plan.
Warnings and Precautions
Considering the effects of Mitomycin2, healthcare professionals must approach its use with caution to ensure both its therapeutic benefits and patient safety. It is essential to exercise caution in patients with compromised hepatic functions, as dose adjustment may be necessary. Similarly, individuals with a history of diseases or compromised bone marrow function should be closely monitored. When undergoing Mitomycin therapy, regular monitoring and tests are crucial for managing the treatment. Blood tests, renal function assessments, and pulmonary function tests should be conducted periodically to identify any issues promptly and take appropriate action.
Contraindications
Mitomycin has a range of therapeutic benefits, but there are certain situations where its use is strongly discouraged. People with kidney problems, low platelet count, or those who have recently had a heart attack are generally advised not to take Mitomycin. This is because there is a risk of worsening these conditions or experiencing severe side effects. In addition, some medications should not be taken together with Mitomycin. Drugs that affect bone marrow function, antiviral medications, and specific cancer-fighting drugs may have harmful interactions, with Mitomycin making it not recommended to use them simultaneously.
Careful Administration
In the field of pharmacology, it is essential to approach the use of medication, taking advantage of its significant benefits while being cautious. When it comes to Mitomycin, this requires monitoring, especially for patients who have other health conditions. For patients with liver or heart problems, diabetes, or immune disorders, it is necessary to customize their treatment plans. This may involve adjusting the dosage of Mitomycin, administering it at times, or considering additional therapies to minimize potential risks. Regular health checkups and follow-ups are crucial to ensure that Mitomycin is working effectively and safely. These evaluations include examinations and diagnostic tests that provide essential insights into the drug's work and any potential side effects.
Important Precautions
Before starting treatment with Mitomycin, patients need to be informed about precautions. This ensures that they understand the possible challenges and know how to handle them effectively. Here are some things that patients should be aware of before beginning treatment:
- Side effects and interactions: Patients should have a clear understanding of the potential side effects of Mitomycin as well as any interactions it may have with other medications. It's also essential for them to know if any dietary or lifestyle modifications are necessary during treatment.
- Setting expectations: It's crucial for patients to clearly understand what therapeutic outcomes can be expected from Mitomycin and any potential challenges they may encounter along the way. This helps in creating an informed approach towards their treatment.
During Mitomycin treatment, patients are generally advised to avoid activities that could worsen the side effects. These activities include:
- Strenuous physical exertion: Engaging in physical activities might increase the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects from Mitomycin.
- Exposure to agents: Patients on Mitomycin should take precautions to minimize their risk of exposure to infectious agents, as their immune system may be compromised during treatment.
- Consumption of substances affecting metabolism: Certain substances can interfere with how Mitomycin is metabolized in the body, so patients should avoid consuming these substances while undergoing treatment. Patients can better navigate their therapeutic journey with Mitomycin by being aware of these precautions and making adjustments.
Administration to the Elderly
The elderly population, with their physical characteristics, requires a personalized approach to medication when using Mitomycin. It is important to administer this drug to maximize its benefits while minimizing any adverse effects associated with age-related changes.
- Specific considerations for adults: Due to the physiological changes that occur with aging, elderly patients may experience differences in how Mitomycin is processed and how it affects their bodies. Factors such as decreased kidney function and other medications being. Age-related vulnerabilities mean that careful adjustment of dosage and close monitoring are necessary.
- Adjusting dosage and monitoring: Older adults may need initial doses of Mitomycin, gradually increasing based on how well they respond to the treatment and their ability to tolerate it. Regular monitoring through evaluations and lab tests is crucial for ensuring the drug's effectiveness and safety in this population.

Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Managing medication during pregnancy or breastfeeding presents challenges and considerations. When it comes to Mitomycin, understanding the consequences is crucial to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
- Regarding known risks and possible effects, Initial studies have indicated that administering Mitomycin during pregnancy may carry risks. Additionally, concerns about whether the drug might be excreted in breast milk raise safety concerns for nursing infants.
- Recommendations and precautions: Due to these risks, pregnant women are generally not recommended to take Mitomycin unless the potential benefits outweigh those risks. Lactating mothers are usually advised to stop breastfeeding while undergoing Mitomycin treatment or explore alternative treatment options..

Administration to Children
It is essential to approach pharmacotherapy with care and attention when treating children due to their unique physiology. In the case of Mitomycin, understanding its profile and safety parameters in pediatric patients is crucial.
- When determining the dosage of Mitomycin for children, it is generally done based on their body surface area or weight, ensuring that the treatment plan is tailored to their physiological characteristics.
- Regarding safety, while Mitomycin has been used in oncology settings, it is essential to closely monitor young patients for potential side effects. Paying attention to hematological and gastrointestinal issues is particularly important to achieve the best possible therapeutic outcomes.

Overdosage
In the world of pharmacotherapy, accidental cases of taking too much Mitomycin can pose significant challenges. It is crucial to recognize and address such situations to ensure patient safety.
- Symptoms of an overdose of Mitomycin may include suppression of bone marrow function, mouth sores, and gastrointestinal problems like nausea and vomiting.
- It is essential to stop administering Mitomycin and provide supportive care when an overdose occurs. This may involve blood transfusions using growth factors to support recovery and providing treatments to alleviate the effects of the overdose.

Handling Precautions
Ensuring safety goes beyond administrative tasks. It involves handling and disposing of potent medications like Mitomycin, highlighting the importance of keeping patients and the environment safe.
- Safe administration of Mitomycin injections: Those who administer Mitomycin must take precautions, such as wearing gloves and protective clothing. These measures minimize the chance of exposure, ensuring the safety of both patients and caregivers.
- Disposal and environmental considerations: Unused mitomycin injections should be disposed of following local regulations to prevent any ecological harm. Incineration or disposal in biohazard containers is a recommended method emphasizing our responsibility towards environmental stewardship.


























