Amantrel, Amantadine
Introduction
Initially developed as an antiviral medication, the pharmaceutical agent Amantadine has burgeoned into a multifaceted therapeutic tool. Its inception dates back to the 1960s, when it was first synthesized as a potential treatment for influenza. Over the decades, its application has expanded to encompass a variety of neurological and psychiatric conditions, underscoring its continued relevance and adaptability in contemporary medical practices.

Overview of Amantadine
Amantadine stands out for its unique ability to affect dopamine levels in the nervous system, a key neurotransmitter. This unique feature makes it valuable for treating infections and alleviating symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Historical Context and Development
The medication was found by chance as scientists studied ways to treat the flu virus. It was noted for its capability to stop the virus from multiplying. Eventually, it was discovered that amantadine could provide relief for those with Parkinson's disease because it affects dopamine in the body.
Current Relevance and Usage in Medical Treatment
Over time, the use of amantadine has expanded to cover a range of conditions, such as managing side effects caused by drugs that affect the extrapyramidal system, multiple sclerosis-induced fatigue, and even certain neuropsychiatric conditions. This has established amantadine as a flexible and valuable component in pharmacology.
Composition and Properties
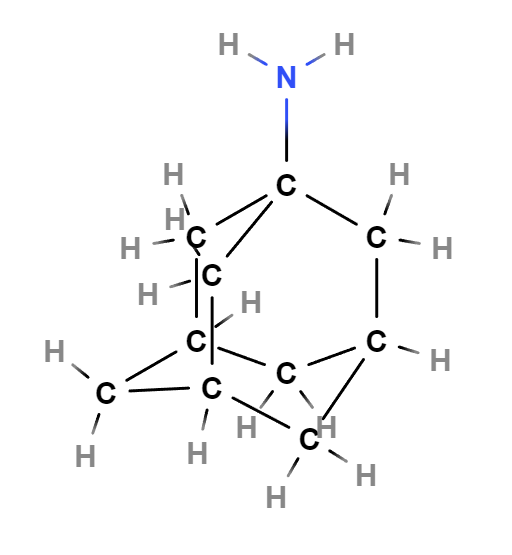
Chemical Structure and Formulation
Amantadine is known for its core structure, which consists of a cyclohexane ring with linked carbon atoms that play a role in its antiviral and dopaminergic properties. This unique structure enables it to pass through the blood-brain barrier effectively and boosts its efficacy in treating system conditions.
Active Ingredients and Excipients
- The main component of the medication is known as Amantadine hydrochloride.
- Additional substances known as excipients are sometimes added to medications to improve their effectiveness and make them easier for patients to take by providing stability and improving absorption in the body.
Amantadine for Depression
Used traditionally for treating depression symptoms and not responding to conventional treatments, a drug called amantadine may help by affecting the dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmitter systems in the brain.
Amantadine for ADHD
Amantadine has shown effectiveness in managing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) by adjusting dopamine pathways to enhance focus and impulse management abilities.
Amantadine for MS
Amantadine provides relief from fatigue for individuals dealing with Multiple Sclerosis (MS), helping improve their quality of life and daily functioning as a result.
Amantadine for Anxiety
The calming impact of this agent is a promising option for addressing anxiety when traditional treatments prove ineffective or are not suitable.
Amantadine vs Adderall
Adderall is usually prescribed for ADHD because of its effects; however, amantadine offers a gentler option with fewer side effects for individuals looking for a more subtle impact on dopamine levels.
Amantadine for Dogs
In medicine, amantadine is used to treat pain and hyperactivity conditions in dogs, demonstrating its effectiveness and safety in various animal species.

Amantadine for Cats
Amantadine is generally utilized to help alleviate pain in cats and felines. It can also be beneficial in dealing with issues such as arthritis, showcasing its wide range of medical applications and benefits.
Uses of Amantadine
Approved Indications for Amantadine
Amantadine is approved for use in fighting viruses and treating conditions like Parkinson's disease by easing symptoms such as tremors and rigidity. It is also prescribed for movement disorders due to its ability to regulate dopamine levels effectively.
Mechanisms of Action in Various Diseases
- Influenza A works by blocking the virus from entering host cells.
- Parkinson's disease boosts dopaminergic signaling, which is essential for regulating movement.
- Neurological conditions may show benefits that could help slow down the advancement of the disease.
Comparative Effectiveness with Other Similar Medications
Amantadine is frequently compared to drugs such as Rimantidine for treating influenza or Levodopa for managing Parkinson's disease. Studies indicate that although it may not be as potent as medications on the market, it provides a more favorable side effect profile and remains beneficial for many patients, especially those who cannot tolerate stronger treatments.
Off-Label Uses of Amantadine
Exploring Non-Approved Applications in Clinical Practice
Amantadine uses go beyond their approved purposes as it is often recommended for off-label conditions, like addressing fatigue in sclerosis and supporting the treatment of depression cases. Demonstrating vast-ranging therapeutic possibilities.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Current studies highlight the advantages of using amantadine in situations.
- An investigation revealed its effectiveness in lessening signs of brain damage, such as thinking and irritability.
- A different study found that amantadine can help improve abilities in individuals with Alzheimer's disease.
Legal and Ethical Considerations of Off-Label Prescribing
The use of amantadine for purposes not officially approved is quite common; however, it requires assessment and the consent of patients, who must be informed about the treatment's off-label nature while weighing its potential benefits against safety considerations and regulatory standards.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms Available
Amantadine is available in forms to accommodate preferences and clinical needs.
- Prescription capsules are often recommended for their dosing method.
- Tablets are more popular because they provide flexibility in dosage and make it easier for patients to follow instructions.
- Liquid is recommended for individuals who struggle with swallowing tablets or capsules.
Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions and Patient Groups
The way amantadine is prescribed differs greatly depending on the condition being treated.
- Treat Influenza A by taking 100 mg a day for adults.
- Managing Parkinson's disease involves increasing the dosage from 100 mg per day to 300, adjusting as needed for tolerance levels.
- For patients, it is advisable to begin with doses as their renal function may be reduced.
Amantadine Dose for Dogs
In medicine, the dosage of amantadine for dogs in need of treatment is typically determined by their weight and the seriousness of their condition. The range is usually 3 to 5 mg per kilogram of body weight once a day.
Amantadine Dose for Tardive Dyskinesia
Effective treatment of dyskinesia requires a high initial dose, typically 100 mg daily, which can be adjusted according to how well the treatment is working and how well it is being tolerated.
Administration Techniques and Best Practices
Using caution when giving Amantadine is essential to achieve the treatment results and reduce side effects.
- Consistency is key to timing your doses every day to keep your blood levels stable and balanced.
- Maintaining hydration is essential to help the body eliminate waste and reduce the risk of toxins building up.
How Amantadine Works
Pharmacodynamics: Action at the Molecular and Cellular Levels
Amantadine alters the functioning of dopamine and glutamate in the brain to achieve its benefits by inhibiting NMDA receptors that help ease symptoms related to Parkinson's disease and various neuropsychiatric conditions.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The way amantadine behaves in the body is described by its profile.
- The medication is quickly absorbed from the stomach and reaches its levels in the bloodstream within 1 to 3 hours.
- It is found all over the body and can even reach the brain because it can pass through the blood-brain barrier.
- Metabolism occurs minimally in the body as most of the drug is eliminated unchanged through urine excretion.
- The elimination process mainly occurs through the kidneys, and adjustments to the dosage might be needed for individuals with reduced kidney function.
Bioavailability and Half-Life Details
Amantadine has an absorption rate of around 86%. It stays in the body for 10 to 31 hours, depending on how well the patient's kidneys are working. This consistent behavior in the body allows for twice-daily dosages for most patients.
Side Effects of Amantadine
Common Side Effects: Symptoms and Management Strategies
Amantadine is usually well received by people; however, as with any medication, there may be some side effects experienced by individuals taking it regularly. The side effects commonly reported include:
- Feeling queasy and lightheaded? It's usually better when you have your medicine with a meal and drink plenty of water.
- Having trouble sleeping and feeling anxious? Try cutting back on caffeine and changing when you take it. It could make a difference!
- Having a mouth can be eased by taking sips of water or indulging in sugar-free candies for comfort.
Severe Reactions and Rare Complications
Severe but uncommon adverse reactions may involve experiencing hallucinations or drastic shifts, in mood and rare cases of heart failure. Intervention is vital in such situations.
Amantadine for Dogs Side Effects
In dogs, some side effects, such as stomach disturbances and agitation, may be noticed. Vets might modify doses and suggest adjustments to address these problems.
Amantadine Side Effects Parkinson's
Individuals diagnosed with Parkinson's disease might notice increased tremors or unexpected alterations in skin condition, highlighting the necessity of monitoring and regular visits to healthcare professionals to manage these symptoms.
Long-term Side Effect Profile
Prolonged use of amantadine may result in skin discoloration, known as a livedoid net pattern, and swelling in the extremities called edema. It is recommended that you regularly undergo physical checkups and make dosage adjustments according to how your body responds to the medication over time.
Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug-Drug Interactions and Their Consequences
Amantadine could potentially have interactions with the following substances:
- Anticholinergic medications may heighten the chances of experiencing retention and constipation.
- The use of CNS stimulants can potentially boost the side effects associated with CNS stimulation.
- Certain live vaccines might not work effectively as expected.
Interaction with Food, Alcohol, and Dietary Supplements
Amantadine absorption may be influenced by elements.
- Alcohol consumption may worsen feelings of dizziness or sleepiness.
- Some dietary supplements can potentially impact the excretion and effectiveness of medications that influence urinary pH levels.
Recommendations for Managing Interactions
It's essential for patients to stick to a medication routine and keep track of what they eat while also talking to their healthcare provider about any medications they're taking to avoid any possible issues with interactions.
Special Precautions and Warnings
Contraindications for Use of Amantadine
Patients who are allergic to amantadine or its ingredients should avoid this medication at all costs due to the reactions it might cause in them. Moreover, individuals with kidney problems are advised against using this drug unless the dosage is modified accordingly.
Populations at Risk: Elderly, Pregnant Women, and Nursing Mothers
Extra care is recommended when prescribing amantadine to individuals or pregnant and nursing women as it may pose a risk of adverse effects or harm to the developing baby or newborn child.
Important Safety Information and Black Box Warnings
The FDA has cautioned about dangers related to skin reactions and neuropsychiatric issues linked with amantadine use, emphasizing the importance of informing patients about signs of significant skin rashes and mood or behavior alterations for timely medical attention and assistance.
Handling and Storage
Proper Storage Conditions to Maintain Efficacy
To maintain its effectiveness and extend its lifespan, store Amantadine at room temperature in a dry place away from light. Properly store it in its container and keep it tightly closed when you're not using it.

Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
When using amantadine medication, both healthcare providers and patients need to make sure it doesn't accidentally touch the skin or eyes. If it happens, the affected area should be washed well with water. It's crucial to be careful to prevent breathing in any dust from the tablets or capsules when handling them.
Disposal Recommendations
Properly getting rid of unused amantadine is important to avoid harming the environment, so it's best to follow instructions on how to dispose of it safely, such as returning it through take-back programs or following local rules for throwing away medications securely.
Specific Populations
Administration in Elderly Patients: Adjustments and Considerations
As people age, their medication doses might need to be adjusted because their kidney function could decrease over time. It's important to monitor their kidney function and change the dosage as needed to avoid any harm from taking too much medication.

Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Guidelines
During pregnancy, it is recommended to use Amantadine only if the advantages outweigh the risks to the child. If you are a nursing mother, it is advised to weigh the option of either stopping the medication or breastfeeding, as there might be risks of adverse effects to your breastfeeding baby.

Pediatric Use: Dosage Adjustments and Safety Data
The use of amantadine in children has not been fully proven safe and effective for all purposes. The dosage should be adjusted according to the child's weight, and any reactions should be closely monitored when it is prescribed.

Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Amantadine Overdose
Experiencing an overdose of amantadine could result in feelings of nausea and dizziness as well as hallucinations and irregular heartbeats known as cardiac arrhythmias; in severe instances, it may even lead to a coma or death.
Immediate First Aid and Treatment Procedures
If an overdose situation arises, direct medical care is necessary without delay! Quick actions entail confirming the airway's openness, providing help with breathing if there are challenges, and giving activated charcoal within a two-hour window post-ingestion to reduce absorption levels.

Preventive Measures and Monitoring
To avoid overdosing incidents and ensure safety when taking medication,it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosages and schedules as recommended by healthcare providers. Patients and their caregivers should receive education regarding the significance of dosage management and the potential risks associated with overdosing. Additionally, monitoring of drug levels can play a role in preventing unintended overdoses.