Metoprolol
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Metoprolol
- III. How Metoprolol Works
- IV. Uses of Metoprolol
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Special Considerations in Administration
- VII. Side Effects of Metoprolol
- VIII. Drug Interactions with Metoprolol
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications
- X. Overdose: Risks and Management
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Careful Administration: Maximizing Benefits and Minimizing Risks
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Metoprolol
Metoprolol is a medication prescribed by healthcare professionals. Falls under the category of beta blockers. Its primary purpose is to lower the heart rate and blood pressure and alleviate stress on the heart with its extensive usage. This medication offers beneficial effects for various cardiovascular conditions.
B. Brief History and Development of Metoprolol
Developed in the 1960s, Metoprolol became a product of exhaustive scientific investigation to discover safer and more efficient treatment alternatives for cardiovascular ailments. The advent of Metoprolol marked a substantial step forward in cardiovascular therapeutics offering enhanced precision in targeting receptors specifically within the heart.
C. Importance and Relevance in the Medical Field
Metoprolol plays a crucial role in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. It has shown remarkable potential in reducing heart damage following a heart attack and effectively controlling hypertension. This drug dramatically contributes to enhancing patient outcomes and overall quality of life.
II. Composition of Metoprolol
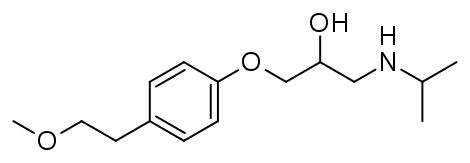
A. Key Active Ingredients and Their Roles
The main active ingredient in Metoprolol is either Metoprolol tartrate or Metoprolol succinate, depending on the specific formulation. This compound works to lessen the impact of adrenaline on the heart resulting in a lowering of heart rate, a decrease in blood pressure, and a reduction in the heart's need for oxygen.
B. Different Available Formulations (tartrate, succinate, etc.)
Metoprolol comes in two formulations: Metoprolol Tartrate and Metoprolol Succinate. The former necessitates multiple daily doses as it is an immediate-release formula. At the same time, the latter is designed explicitly for once-daily intake as an extended-release variant. Deciding between these alternatives hinges upon assessing each patient's requirements and understanding their medical condition accurately.
III. How Metoprolol Works
A. Understanding Beta-blockers: The Class of Drugs Metoprolol Belongs To
The pharmacological category known as beta blockers predominantly operate on pivotal sites within our circulatory system—the primary target being cardiac structures and their respective vasculature networks, impeding specific sites called beta-adrenergic receptors. These drugs effectively hinder the activity of catecholamines. Including adrenaline and noradrenaline. Consequently. This intricate disruption in biochemical signaling reduces heart rate, myocardial workload, and systemic blood pressure. Metoprolol exemplifies a selective beta1 blocker family member in a specific context, emphasizing its distinct propensity for targeting specific cardiac receptors. Within this framework, the true significance arises from its potential to actively enhance and fine-tune cardiovascular regulation with marked efficacy.
B. Mechanism of Action Within the Body
Metoprolol selectively inhibits beta1 adrenergic receptors found in the myocardium or heart muscle to achieve its effects. This mechanism of action effectively diminishes the stimulation these receptors receive from adrenaline and other related hormones. As a consequence, notable reductions are observed in terms of heart rate. Blood pressure level and overall demand for oxygen by the heart.
C. Influence on the Cardiovascular System
By reducing the burden on the heart, Metoprolol helps prevent angina and lowers the likelihood of heart complications. Additionally, it supports the management of hypertension. Furthermore, in situations where there is heart failure, it slows down the progression of the disease, decreases hospitalization rates, and enhances survival. Therefore Metoprolol plays a crucial role in modern cardiovascular therapeutics due to its extensive and diverse impact on the cardiovascular system.
IV. Uses of Metoprolol
A. Approved Indications
Metoprolol is a medication that has received official approval for multiple uses. One of its sanctioned indications is hypertension. Wherein Metoprolol serves as a potent beta blocker. By doing so, it contributes to the reduction of high blood pressure and helps mitigate the associated risks1. Another approved use of Metoprolol is for angina pectoris. This condition causes debilitating symptoms in individuals with coronary heart disease. However, Metoprolol can alleviate these symptoms by lessening the heart’s demand for oxygen. As a result, it reduces both the frequency and severity of angina attacks1. In cases of chronic heart failure, Metoprolol has proven to be effective in slowing down the progression of the disease. In addition to that, it also lowers hospitalization rates and improves survival rates2. Lastly, Metoprolol is valuable in managing various types of arrhythmias. It aids in restoring and maintaining a regular and stable heart rhythm. Its efficacy in combating irregular heartbeats is a crucial tool for healthcare professionals3.
Here are some references that you can check out:
- Metoprolol Tablets: Indications, Side Effects, Warnings - Drugs.com
- Metoprolol: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects - Drugs.com
- Metoprolol: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
- Metoprolol: MedlinePlus Drug Information - MedlinePlus
B. Off-Label Uses
Metoprolol has a variety of ‘off-label’ applications. One notable example is its utilization in the prophylactic treatment of migraines, where evidence suggests a significant reduction in both frequency and severity of episodes in susceptible individuals1. Additionally, Metoprolol’s anxiolytic properties make it a valuable adjunctive treatment for certain anxiety disorders, particularly those associated with physical symptoms2. Another application for Metoprolol is in managing hyperthyroidism, which can help alleviate symptoms like rapid heartbeat and tremors. It is providing relief while the primary condition is being addressed3.
Here are some references that you can check out:
- Metoprolol - Wikipedia
- Metoprolol: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Precautions - Verywell Health
- Metoprolol - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Beta-Blockers for Anxiety: Benefits, Side Effects, and Risks - Healthline
V. Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosages for Approved Uses
The exact amount of Metoprolol required is determined by the particular reason it is being prescribed for. The patient's overall health condition. And how they respond to the treatment. In the case of hypertension, the initial treatment usually consists of taking 50 100 mg of Metoprolol daily, either all at once or divided into multiple doses throughout the day. Their dosage may be increased depending on how the patient's body reacts. For angina and arrhythmias, similar dosing schedules are typically followed. On the other hand, when managing heart failure, lower doses are typically started and gradually increased under careful monitoring.
B. Dosage Modifications for Specific Populations
It is essential to take special considerations when prescribing Metoprolol to specific populations, such as older individuals or those with kidney problems. For example, the elderly may need lower initial doses because they have a higher chance of experiencing adverse reactions. On the other hand, people with renal impairment may require adjustments in their dosage to prevent the build-up of the drug and potential harm.
C. How to Administer Metoprolol Correctly
Metoprolol should be taken with or after meals to enhance absorption. It is crucial to swallow extended-release tablets whole without crushing or chewing them. Avoid stopping the treatment abruptly to prevent potential withdrawal symptoms and if needed reduce the dose gradually.
D. Frequency and Timing of Dosage
The administration of Metoprolol depends on the specific formulation used, which determines the timing and frequency. For immediate release Metoprolol. It is usually necessary to take it twice a day. At the same time, the extended-release version is intended for once-daily use. It is essential for patients to strictly follow their prescribed medication schedule to achieve the best therapeutic results.
VI. Special Considerations in Administration
A. Administration to the Elderly
In light of age-related decreases in hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and the presence of concurrent disease or other drug therapy amongst older individuals, they tend to experience heightened susceptibility toward the effects of Metoprolol. Consequently, adjusting their dosage or closely monitoring them throughout therapy becomes imperative to avoid undesirable outcomes and achieve optimal therapeutic results.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
For pregnant women to receive Metoprolol, healthcare professionals must determine whether its potential benefit surpasses any possible risks that could impact fetal health. Additionally, caution must be taken when giving this medication to nursing mothers due to its presence in breast milk. Considering and weighing both the adverse reaction risks associated with Metoprolol on infants and its advantages for maternal well-being are crucial aspects that need careful attention.
C. Administration to Children
While Metoprolol can be used in pediatric patients for specific indications like hypertension, it is essential to maintain careful supervision. It is vital to adapt the dosage according to the child's body weight and make necessary adjustments based on their clinical response and tolerance of the medication.
VII. Side Effects of Metoprolol
A. Overview of Potential Side Effects
Metoprolol, like any other medication, has the potential to cause side effects when used. These side effects can vary in their severity. They range from mild and temporary symptoms to more severe conditions that can potentially be life-threatening.
B. Common Side Effects
Some commonly experienced side effects of Metoprolol include tiredness or fatigue. Dizziness or lightheadedness. Depression, shortness of breath. And diarrhea or constipation.
C. Serious Side Effects and Warning Signs
While infrequent in occurrence, one must remain cautious regarding the possibility of experiencing severe side effects. Such outcomes encompass a decreased or erratic heartbeat and pronounced episodes of dizziness which could lead to fainting spells. Furthermore, manifestations such as swollen ankles or feet indicate potential heart failure symptoms in light of encountering any warning signs mentioned above. It is essential to contact medical professionals for appropriate intervention promptly.
D. Long-Term Side Effects
Long-term usage of Metoprolol may result in the emergence of specific conditions, including heart block, aggravation of angina symptoms upon sudden discontinuation, or the formation of an antinuclear antibody that can trigger certain autoimmune disorders. Therefore. It is imperative to conduct regular follow-ups and clinical assessments when undergoing long-term treatment.
VIII. Drug Interactions with Metoprolol
A. Common Drug-Drug Interactions
Certain medications have the potential to interact with Metoprolol and possibly modify its effects. These medications may include but are not restricted to, Antiarrhythmics, Antidepressants, Other beta blockers, and Antihypertensives.
B. Food-Drug Interactions
Although interactions between Metoprolol and food are limited. It is advisable to avoid consuming alcohol while undergoing treatment. This is because alcohol has the potential to amplify the blood pressure-lowering effect of the drug. Thereby increasing the likelihood of experiencing side effects like dizziness or fainting.
C. How to Avoid Harmful Interactions
It is essential to effectively manage drug interactions by being knowledgeable about potential interactions and communicating with healthcare providers about medications, including those prescribed over the counter and herbal products. It is also advised to maintain a consistent and well-balanced diet while undergoing medication therapy to avoid harmful food-drug interactions.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Conditions that May Prevent the Use of Metoprolol
There are particular situations where the use of Metoprolol is not recommended. These consist of but are not restricted to, severe bradycardia, second or third-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock decompensated heart failure, and severe pulmonary hypertension. It is also essential for patients with a known hypersensitivity to Metoprolol or any of its components to refrain from using it.
B. Potential Dangers and Complications
Utilizing Metoprolol comes with inherent risks and possible complications. Incredibly in cases where consumption is unsupervised or adherence to prescribed dosages is disregarded. Stopping the drug abruptly may exacerbate angina symptoms or precipitate myocardial infarction. Individuals with diabetes ought to exercise caution since Metoprolol may mask indications of hypoglycemia, potentially leading to additional complications. It should be noted that although rare severe hepatic injury can occur due to using this medication.
C. Important Precautions Before and During Treatment
Providing an in-depth account of one's medical background becomes imperative before initiating treatment, mainly if previous encounters with hepatic, nephritic, or cardiac impairments are involved. Consistently monitoring blood pressure and heart rate throughout therapy is tantamount to its success. Promptly informing healthcare providers about any atypical symptoms or detrimental consequences is strongly advised. Furthermore, to maximize treatment efficiency, it is highly recommended that individuals make lifestyle modifications encompassing a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, and abstinence from the consumption of alcohol as well as tobacco.
X. Overdose: Risks and Management
A. Symptoms of Metoprolol Overdose
The symptoms of Metoprolol overdose can vary and might include bradycardia, hypotension, heart failure, and cardiogenic shock. In more severe cases, individuals may also exhibit signs such as bronchospasm, unconsciousness, or even cardiac arrest.
B. What to Do in Case of Overdose
If suspected of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Dealing with an overdose primarily involves providing support and focusing on interventions that maintain essential bodily functions and address symptoms. Suppose the patient comes in within 1 or 2 hours of ingestion. Considering gastric lavage or administering activated charcoal is an option.
C. Possible Outcomes and Complications
An array of variables play a role in determining how intense complications can be following an overdose of Metoprolol; factors include the quantity consumed and the general health condition of the individual involved. Outcomes encompass a wide range - starting with successful recovery due to appropriate medical intervention and extending to more severe ramifications like cardiac arrest; this latter scenario is more likely when considerable excess consumption exists. Ergo, strict adherence to prescribed dosage is essential for averting potential life-threatening circumstances.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
It is advisable to store Metoprolol at room temperature, specifically within the range of 20°C to 25°C. Ensure it is placed away from direct light, moisture, and heat to maintain its quality. Additionally, it is recommended to keep the medication in its original container until the designated time of consumption to preserve its effectiveness.
B. Handling Precautions to Maintain Potency
When dealing with Metoprolol, you must ensure that your hands are clean and dry. It is crucial to avoid any unnecessary contact with the medication, particularly when it comes to crushed or broken tablets. As this can potentially impact its potency, unless explicitly advised by a healthcare provider, it is important not to split or crush the medication.
C. Procedures for Safe Disposal
In order to prioritize safety and avoid any undesirable outcomes, it is advised against flushing or pouring unused or expired Metoprolol down the toilet or drains unless specifically instructed otherwise. To guarantee proper disposal. It is strongly recommended that individuals return this medication to a pharmacy or utilize a community take-back disposal program. This responsible approach will help prevent unintentional ingestion and potential environmental harm.
XII. Careful Administration: Maximizing Benefits and Minimizing Risks
A. Lifestyle Modifications Alongside Metoprolol Administration
It is essential to incorporate lifestyle modifications alongside Metoprolol to improve treatment outcomes. These can encompass following a well-balanced diet and engaging in consistent physical activity. And refrain from using tobacco or alcohol. Moreover, implementing stress management techniques like yoga or meditation can significantly enhance cardiovascular health.
B. Monitoring Patient Responses
It is essential to regularly monitor blood pressure, heart rate, and other clinical indicators when undergoing Metoprolol therapy. Patients should be encouraged to promptly report any side effects or unusual symptoms they may experience. Regular healthcare visits provide an opportunity to adjust the dosage as needed, contributing significantly to a successful treatment plan.
C. Adherence to Treatment Plans
Following the treatment plan diligently plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of Metoprolol therapy. This entails taking the medication as prescribed, scheduling and attending regular follow-up visits with your healthcare provider and promptly notifying them of any side effects or concerns you might encounter. Neglecting to adhere to this plan diminishes the treatment's effectiveness and poses potential complications. You are potentially elevating your chances of experiencing cardiovascular events.