Zinnat
Introduction
Origin and Development of Zinnat
Zinnats origins can be traced back to a group of medical researchers who sought to combat the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The unwavering commitment to its creation demonstrates the changing field of antibiotics and the constant pursuit of practical solutions against bacterial dangers.
Primary Purpose and Classification in the World of Medicine
First and foremost, the primary purpose of Zinnat is its capability to treat a wide range of bacterial infections effectively. It is categorized as a second-generation cephalosporin because of its broad spectrum effectiveness and antibacterial solid power.
Uses of Zinnat
Treating Bacterial Infections
Zinnat is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative susceptible organisms, including many beta-lactamase producing strains 1. It is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by sensitive bacteria 1. Zinnat is effective against the following organisms: Aerobic Gram-positive Microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes. Aerobic Gram-negative Microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains). Spirochetes: Borrelia burgdorferi 1.
Here are some references that provide more information about Zinnat:
Scope of its Antibacterial Properties
Zinnat goes beyond treating infections. Its remarkable effectiveness, against both gram gram-negative bacteria, including certain anaerobic strains demonstrates its wide-ranging antibacterial capabilities.
Ideal Situations for Prescription
It is most helpful for patients who frequently experience throat infections. It also benefits individuals who show signs of middle ear infections and those struggling with tract infections. However, it's essential to use it carefully to prevent antibiotic resistance.
How Zinnat Works
Mechanism of Action
Zinnat works by blocking the production of the cell wall, which is crucial, for the survival of bacteria. It achieves this by targeting penicillin-binding proteins leading to the breakdown of bacteria.
Impact on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis
The presence of Zinnat weakens the cell wall, which is a solid and protective layer. This antibiotic disrupts the production of peptidoglycan, a component that helps maintain the rigidity and strength of the bacterial wall.
The Spectrum of Susceptible Bacteria
Not all bacteria yield to the dominance of Zinnat. Zinnats effectiveness mainly focuses on Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, and Escherichia coli. When exposed to Zinnat, each strain experiences severe consequences that ultimately lead to its demise.
Off-Label Use
Emerging Uses Not Approved by Health Authorities
Like other pharmaceutical breakthroughs, Zinnat has been researched for uses beyond its intended label. Although these alternative applications haven't received endorsement, there are anecdotal accounts and early evidence indicating their potential effectiveness against specific nontraditional pathogens.
Clinical Studies Supporting Off-Label Uses
According to a systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Emerging Infectious Diseases journal, Lyme disease has been clinically diagnosed in 29 provinces in China. The study conducted a systematic literature review of Chinese- and English-language journal articles published during 2005‒2020. The summary estimate of Lyme disease seropositivity among persons across China was 9.1% 1.
However, Pfizer and Valneva are conducting a Phase 3 clinical trial to investigate the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an investigational Lyme disease vaccine candidate, VLA15 2.
Risks and Rewards of Unconventional Usage
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
Adjustments for Specific Infections
Considerations for Impaired Renal Function
Composition
Active Ingredient: Cefuroxime Axetil
The effectiveness of Zinnat primarily relies on a compound called Cefuroxime Axetil. It acts as a prodrug that transforms into its form, Cefuroxime after it is administered. This transformation ensures that the antibacterial activity is at its best.
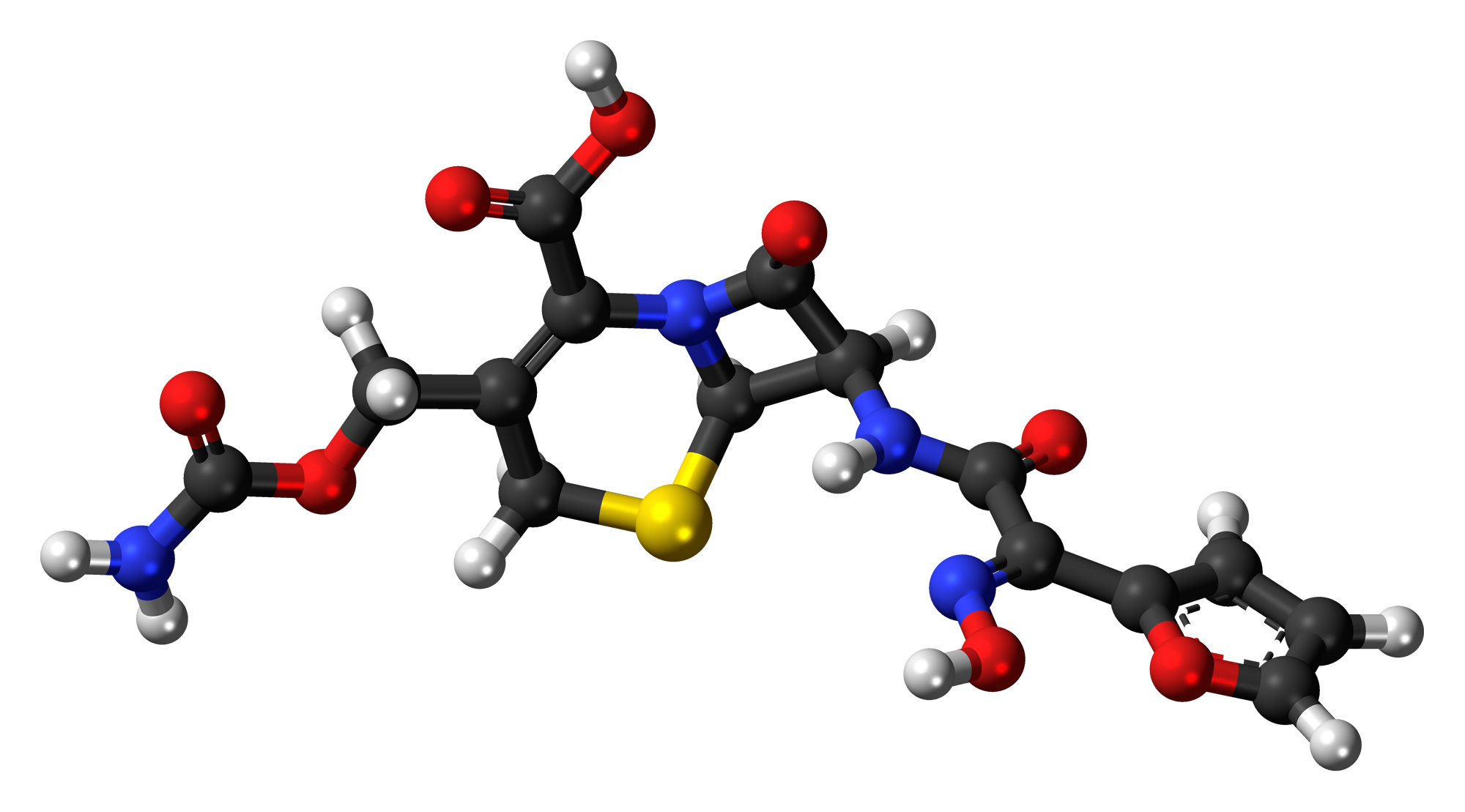
Excipients and Their Roles
Zinnat contains substances called excipients that help improve stability, absorption, and taste. These excipients include microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Each of these substances aims to ensure the drug works as effectively as possible.
Forms Available: Tablets and Oral Suspension
Zinnat is available in two forms: convenient tablets for easy administration and an oral suspension designed for children and individuals with trouble swallowing.
Storage
Ideal Temperature and Conditions
Zinnat flourishes in a climate that's neither too hot nor too cold, with temperatures ranging from 15°C to 25°C. It's crucial to keep it from excessive moisture and sunlight to ensure it stays healthy for a long time.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
It's important to remember not to use Zinnat after it has expired. Generally, it is recommended to discard Zinnat after 24 months of its shelf life.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Liver and Kidney Function
Zinnat, although it is effective against bacteria, requires monitoring of liver and kidney functions. It is essential for patients on long-term treatment to undergo liver function tests and serum creatinine assessments twice a year.
Recognizing Early Signs of Adverse Reactions
Monitoring and being aware of any early signs of adverse reactions is crucial. If you experience symptoms such as jaundice, excessive fatigue, unexplained rashes, or itching, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent any worsening condition.
The Importance of Completing the Prescribed Course
Completing the course of antibiotics is crucial even if you start feeling better. Stopping early can lead to bacteria developing resistance, which means that Zinnat may become ineffective, against the very germs it was meant to eliminate.
Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly
The elderly population can sometimes pose challenges when determining the dosage of medications. It's essential to adjust the dosage considering the age-related changes in liver and kidney function to avoid any unintended overdosing. Additionally, due to their vulnerability, older individuals may be more sensitive to Zinnat, which increases the likelihood of experiencing side effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Pregnancy and breastfeeding have unique challenges regarding medication usage, so it's essential to be cautious. The available data shows that Zinnat is generally safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women as long as it is used judiciously. However, it's still crucial for doctors to exercise discretion. It is usually considered safe to prescribe Zinnat during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Extra care should be taken during the first trimester and immediately after giving birth. Doctors need to weigh the benefits against any risks for the baby in these cases.
Administration to Children
Children treated with Zinnat need to adjust their dosages based on their weight and age. The specific patient dosage depends on how old they are and how severe their condition is. It's essential to be aware of gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea or oral thrush, even though Zinnat is generally well tolerated by children.
Side Effects
Typical Bodily Reactions to Zinnat
When experiencing Zinnat, the human body may sometimes show signs of dissatisfaction through side effects. While most are harmless, a few might necessitate medical attention. These could include skin rashes or more serious gastrointestinal issues.
Monitoring and Reporting Side Effects to Healthcare Provider
It's crucial to maintain a line of communication with your healthcare provider. Make sure to report any symptoms no matter how minor they may seem. Taking this approach allows for early interventions, which can help prevent potential complications.
Common Side Effects
Most Frequently Reported Reactions
Experienced side effects of Zinnat may include nausea, diarrhea, and headaches. While these symptoms are usually temporary and resolve independently if they persist or worsen, it is advisable to seek advice.
Managing Mild Side Effects at Home
There are steps you can take at home to help alleviate mild side effects of Zinnat, such as drinking enough fluids for diarrhea or using cold compresses for mild rashes. However, it's important to remember that self-care should never replace the advice of a professional.
Overdosage
Symptoms of Zinnat Overdose
Excessive consumption of Zinnat may lead to symptoms, including abdominal cramps, neurological disruptions, and renal insufficiency. Sometimes, seeking immediate medical attention becomes imperative and should not be negotiated.
Immediate Steps and Remedial Measures
When dealing with a suspected overdose, it is crucial to prioritize hospitalization without delay. Typically, medical professionals employ lavage alongside other supportive measures, such as administering intravenous fluids to ensure effective treatment.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling and Disposal of Zinnat
Zinnat, similar to medications, requires careful handling. It is crucial to make sure that it is not accessible to individuals, particularly children. When disposing of unused medication it is essential to follow the local guidelines, for pharmaceutical waste disposal in order to protect the environment.
Preventing Contamination and Ensuring Potency
Storing Zinnat in an environment protected from extreme temperatures and humidity is crucial to maintaining its effectiveness. Following the manufacturer's instructions regarding storage and handling is also essential.












