Pantoprazole
- I. Introduction to Pantoprazole
- II. Composition of Pantoprazole
- III. How Pantoprazole Works
- IV. Uses of Pantoprazole
- V. Dosage and Administration of Pantoprazole
- VI. Interaction of Pantoprazole with Other Drugs
- VII. Side Effects of Pantoprazole
- VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Special Considerations for Pantoprazole Administration
- X. Overdosage of Pantoprazole
- XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
- XII. Important Precautions While Using Pantoprazole
I. Introduction to Pantoprazole
A. Brief Description
The trustworthy and effective solution known as Pantoprazole, classified within the drug class proton pump inhibitors, effectively treats specific stomach and esophagus issues. This remedy effectively reduces the volume of acid produced in the stomach, relieving patients.
B. Origin and Discovery
The development of Pantoprazole dates back to the early 1990s when it was created as a new and potent proton pump inhibitor by the pharmaceutical company Byk Gulden. Through subsequent mergers with Altana Pharma and integration into the Takeda group, Pantoprazole has continued to make its mark in the medical industry.
C. Purpose of the Medication
Pantoprazole is primarily prescribed to relieve gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms and aid in the healing process of erosive esophagitis. Additionally, it is utilized to treat pathological hypersecretory conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
II. Composition of Pantoprazole
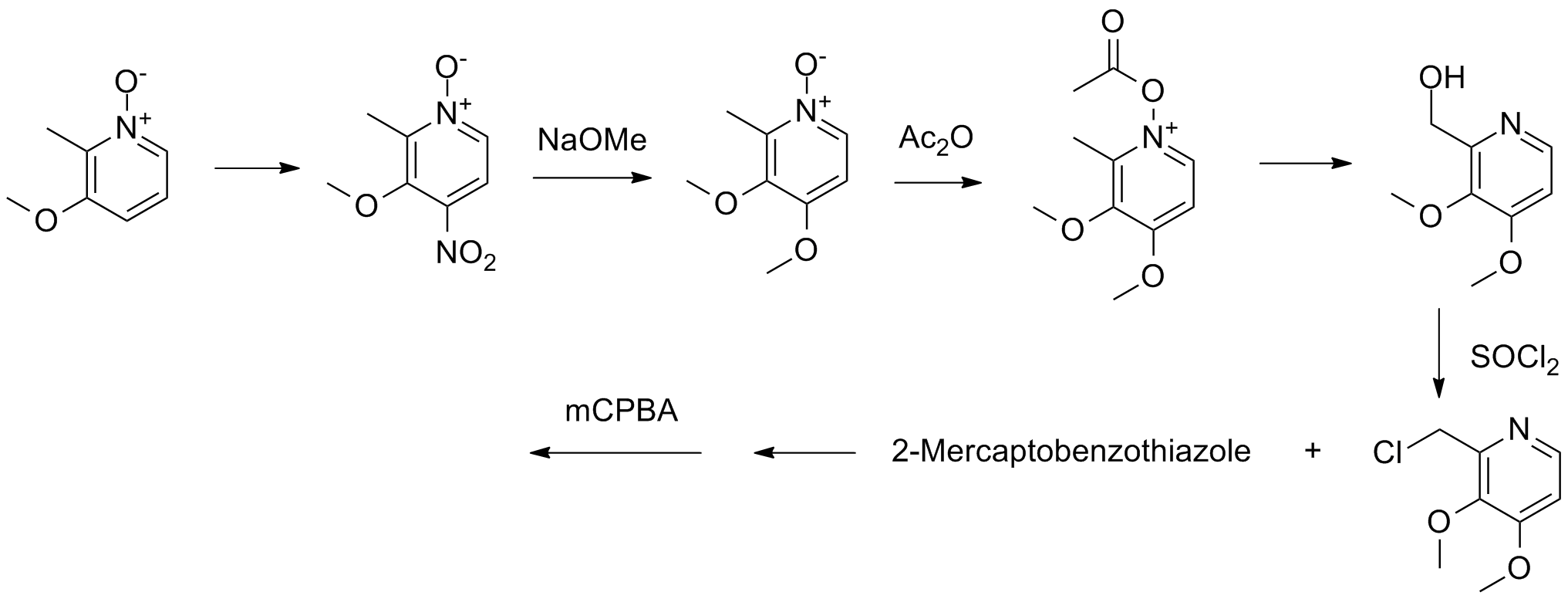
A. Active Ingredients
The main active component found in Pantoprazole is Pantoprazole sodium, a white to off-white crystalline powder. This substance falls under the category of substituted benzimidazole. It is important to note that this active ingredient provides Pantoprazole with its acid-reducing solid capabilities.
B. Inactive Components
Each Pantoprazole tablet or granule formulation also contains several inactive ingredients. These include Crospovidone, Sodium stearate, Propylene glycol, and Cellulose microcrystalline.
C. Formulations Available
Pantoprazole comes in two primary forms: a delayed-release tablet taken orally and granules used to create a suspension for oral administration. Both forms' purpose is slowly releasing the active ingredient into your body.
III. How Pantoprazole Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Pantoprazole functions by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme in the stomach wall responsible for acid production. This specific enzyme is referred to as the proton pump is obstructed, resulting in reduced gastric acid secretion and raising the stomach's pH level. The increased pH assists in relieving symptoms and promoting the healing process of the esophagus.
B. Impact on Gastric Acid Production
Pantoprazole successfully restricts the synthesis of gastric acid through its action on the proton pump. Consequently, a decrease in gastric acidity levels contributes significantly to managing conditions linked to excess acid secretion.
C. Time to Onset and Duration of Effect
After being taken orally, pantoprazole typically begins to suppress acid within an hour. Reaching its peak effect within two hours. This inhibitory effect lasts about 24 hours, so Pantoprazole is usually given daily.
IV. Uses of Pantoprazole
A. Approved Uses
With its formidable capacity to suppress acid, Pantoprazole finds significant usage in treating numerous stomach and esophageal health concerns. Its approved applications are primarily concentrated on:
References:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Pantoprazole is an effective treatment for GERD. By reducing gastric acid production, this medication can help alleviate GERD symptoms and facilitate the healing of erosive esophagitis.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information about Pantoprazole:
- Pantoprazole: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
2. Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers
Gastric and duodenal ulcers are lesions in the lining of the stomach or upper portion of the small intestine respectively. Pantoprazole is widely used for its therapeutic efficacy in healing these ulcers, especially those caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori when combined with appropriate antibiotics1.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Pantoprazole: 7 things you should know - Drugs.com
- Peptic ulcer - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
- Pantoprazole Oral Tablet: Side Effects, Uses, Dosage, and More - Healthline
3. Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome is an uncommon disorder characterized by tumors called gastrinomas. These tumors are often found in the pancreas and small intestine. A consequence of this syndrome is the increased secretion of gastrin hormone, which stimulates the excessive production of stomach acid. Pantoprazole is an effective treatment for this condition as it works by reducing gastric acid secretion12345.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Pantoprazole: medicine to lower stomach acid - NHS
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome | SpringerLink
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome - Cleveland Clinic
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome | Johns Hopkins Medicine
B. Off-Label Uses
Pantoprazole is prescribed for various 'off-label' purposes alongside its approved uses. While these specific applications lack formal approval from regulatory bodies, their efficacy is backed by significant clinical experience and research evidence. These encompass:
References:
- National Institutes of Health: Off-label use of proton pump inhibitors
- NEJM Journal Watch: Proton-Pump Inhibitors May Be Useful in Some Patients with Dyspepsia
- NEJM Journal Watch: Which Patients in the ICU Need Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis?
1. Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis
Pantoprazole is frequently employed as a preventive measure in individuals who are critically ill or have to undergo major surgical procedures. Its main purpose is to inhibit the production of gastric acid thereby reducing the chances of stress ulcer formation and consequent gastrointestinal bleeding12345.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis | McGovern Medical School
- Different Antiulcer Activities of Pantoprazole in Stress, Alcohol and …
- Indikasi dan Dosis Pantoprazole - Alomedika
- PulmCrit- SUP-ICU: Is pantoprazole the elixir of life? Should it be?
- Stress ulcers in the intensive care unit: Diagnosis … - UpToDate
2. Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia, also known as indigestion, frequently presents with symptoms such as heartburn, bloating, and discomfort in the upper abdomen. The causes of this condition are multifaceted. Pantoprazole is recommended for the management of dyspepsia symptoms when there is reason to suspect excessive gastric acid production or when a diagnosis of GERD is under consideration .
Here are some references that you can use:
- Pantoprazole: medicine to lower stomach acid - NHS
- Dyspepsia - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic
- Dyspepsia - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia) | NIDDK
V. Dosage and Administration of Pantoprazole
A. Standard Dosage Recommendations
In general, it is recommended that adults take 40 mg of Pantoprazole per day. This dosage is usually prescribed for conditions like GERD and erosive esophagitis. It is taken once a day for up to 8 weeks. However, if the patient has Zollinger-Ellison syndrome or requires long-term treatment, the dosage may be adjusted according to their response and tolerance.
B. Dosage Adjustments
Dosage adjustments might be needed in specific situations, like for individuals experiencing severe liver impairment. Moreover, elderly patients or those with specific health conditions may necessitate careful dosage management. It is always advisable to consult your healthcare provider for personalized dosage advice.
C. Instructions for Use
D. Importance of Adherence to Dosage Instructions
It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage regimen in order to achieve the best therapeutic results and prevent any potential adverse effects. If doses are skipped or the medication is stopped too soon its effectiveness may decrease, and the condition being treated could potentially worsen.
VI. Interaction of Pantoprazole with Other Drugs
A. Common Drug Interactions
Pantoprazole may influence its efficacy or result in adverse effects due to potential drug interactions. Notable examples of such medications encompass Warfarin, Methotrexate as well, as Atazanavir, and other HIV medications.
B. How to Manage Potential Interactions
Effective management of potential drug interactions necessitates open communication with your healthcare provider regarding all medications and supplements and over-the-counter products you are currently using. By sharing this information, you provide your doctor with the necessary details to adjust your treatment plan appropriately and minimize the risk of drug interactions.
C. Importance of Sharing Complete Medication List with Healthcare Provider
It is vital to provide your healthcare provider with a complete list of your current medications. By doing so, they can thoroughly assess possible interactions and implement preventive measures, guaranteeing your treatment regimen's safety and effectiveness.
VII. Side Effects of Pantoprazole
A. Most Common Side Effects
Although Pantoprazole is generally well tolerated, specific individuals may encounter some common side effects. These may include symptoms such as headaches, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
B. Potential Serious Side Effects
In rare instances, individuals may encounter more severe side effects, such as severe allergic reactions, bone fractures resulting from long-term usage, low levels of magnesium, and lupus erythematosus. It is essential to promptly seek medical attention if you observe any unusual symptoms or experience severe side effects.
C. Management of Side Effects
If you experience any side effects from using Pantoprazole, kindly inform your healthcare provider immediately. They will be able to offer you valuable advice on how to manage these symptoms effectively. Furthermore, they may consider adjusting your dosage or recommending alternative treatments if necessary. It is vital to always bear in mind that you should never stop taking the medication without first consulting with your healthcare provider.
VIII. Warnings and Contraindications
A. Individuals at Risk
It is essential to acknowledge that particular groups of people may be subject to a heightened risk while using Pantoprazole. This includes individuals grappling with severe liver disease, those who may have previously encountered allergic reactions in response to medication, and people who have been officially diagnosed with osteoporosis or osteopenia. These individuals' prolonged utilization of Pantoprazole may inadvertently amplify their susceptibility to experiencing bone fractures.
B. Conditions Potentially Aggravated by Pantoprazole
Even though Pantoprazole is generally considered safe for consumption, it is essential to highlight that there are situations where it may exacerbate specific health conditions like Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) or Vitamin B12 deficiency. Henceforth individuals suffering from these particular ailments should responsibly initiate a conversation with their healthcare provider to thoroughly comprehend and evaluate the potential risks before embarking on treatment involving Pantoprazole.
C. Importance of Discussing Medical History with Healthcare Provider
Establishing a detailed understanding of your complete medical background is paramount before embarking on Pantoprazole therapy; it necessitates open communication with the expertise of your chosen healthcare professional. Engaging in comprehensive discussions will encompass pertinent aspects such as prevailing health conditions demanding attention, prescribed medications that require consideration alongside historical ailments faced previously, and allergic manifestations observed over time for managing these concerns effectively. In addition or a variation thereof will be needed around aspects involving family inclinations or trends towards particular health disorders amongst immediate relatives – crucial pieces that shall help enable prescribing safe yet efficacious therapies specifically tailored for your unique needs and circumstances.
IX. Special Considerations for Pantoprazole Administration

A. Administration to the Elderly
Although elderly patients can receive treatment involving Pantoprazole, it's essential to exercise caution due to the higher susceptibility towards bone fractures that arises from its long-term use. This risk is especially pronounced in individuals already suffering from osteoporosis. Therefore. Close monitoring and appropriate adjustments regarding dosage may need implementation as a precautionary measure.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Suppose there is a justifiable potential benefit. Pantoprazole may be considered for use during pregnancy. It is essential to exercise caution when administering Pantoprazole to a nursing mother as it is uncertain whether it can be excreted in human milk.
C. Administration to Children
It is important to note that the safety and effectiveness of Pantoprazole have not been proven for children aged below 5, as a result. It is imperative to administer this medication to children and adolescents under the supervision of a pediatrician. It ensures vigilant monitoring for any potential side effects.
D. Careful Administration and Monitoring
Administering Pantoprazole with care and maintaining regular monitoring is crucial irrespective of the patient's demographic. Routine follow-ups and health check-ups are indispensable to gauge their response to this medication accurately and flexibly adjust their treatment plan if required.
X. Overdosage of Pantoprazole
A. Symptoms of Overdosage
Although a rare occurrence, it is possible for overdosage of Pantoprazole to happen. This can potentially result in symptoms such as confusion, drowsiness, blurred vision, and nausea or vomiting.
B. Immediate Actions and Treatment
If someone experiences an overdose, it is crucial to seek prompt medical assistance. The necessary treatment for this situation varies depending on the severity of the symptoms. It may consist of supportive measures aimed at managing these symptoms effectively. In some cases, if the overdose has occurred recently, Gastric lavage might be considered as part of the treatment approach.
C. Prevention Measures
To prevent an excessive dosage, patients must diligently follow their prescribed dosage schedule and abstain from surpassing the recommended amount. Moreover, it is crucial that Pantoprazole and all other medications are stored in a manner inaccessible to children as a precaution against accidental ingestion.
XI. Storage and Handling Precautions
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
To maintain the quality of pantoprazole, it is advisable to store it at room temperature, specifically between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). The medication is suggested to remain in its original packaging until it is ready for use, as this helps safeguard it against moisture and light. It is important to avoid storing pantoprazole in areas with excessive humidity, such as bathrooms or near kitchen sinks.
B. Expiry and Disposal
Before utilizing Pantoprazole, you must double-check its expiration date as a precautionary measure. The usage of outdated medication can be both ineffective and potentially detrimental. To properly dispose of any unused or expired medicine, kindly adhere to the guidelines presented by the FDA or kindly consult with your local pharmacy or waste disposal service for appropriate procedures.
C. Safety Measures in Handling
Despite not requiring any particular safety precautions during its handling, washing hands before and after administering Pantoprazole is always considered the best practice. Moreover, maintaining airtight control over access to this medication to protect it from children or pets must never be overlooked.
XII. Important Precautions While Using Pantoprazole
A. Precautions Regarding Prolonged Usage
Using Pantoprazole for an extended period, particularly beyond one year, can heighten the likelihood of experiencing specific side effects such as bone fractures, deficiency in vitamin B12, and particular gastrointestinal infections. Consequently, it is imperative to ensure that Pantoprazole is solely taken as prescribed by a healthcare professional and that patients undergoing long-term treatment receive ongoing check-ups.
B. Monitoring Health during Treatment
While receiving Pantoprazole treatment, engaging in regular health monitoring is crucial. This involves regularly attending medical appointments for assessments and potentially undergoing laboratory tests. This vigilant monitoring aims to promptly identify any potential side effects and make appropriate adaptations to the treatment regimen.
C. Communicating Concerns and Side Effects to Healthcare Provider
Promptly communicate your concerns about the medication, its side effects, or your underlying condition to your healthcare provider. This includes informing them of new or worsening symptoms and any unexpected side effects. Ensuring open and regular communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for safe and effective treatment.