Adrenochrome Injection
- 1. Introduction to Adrenochrome
- 2. Composition of Adrenochrome Injection
- 3. Pharmacodynamics: How Adrenochrome Works
- 4. Therapeutic Uses of Adrenochrome
- 5. Off-Label Uses of Adrenochrome
- 6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 7. Adrenochrome in Special Populations
- 8. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- 9. Important Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- 10. Warnings and Precautions for Safe Use
- 11. Overdose Management and Emergency Response
1. Introduction to Adrenochrome
Definition and Overview
Adrenochrome is a substance formed through the oxidation of adrenaline, known for its molecular structure and mind altering effects. This compound has piqued the curiosity of both researchers and the general public because of its chemical makeup and medicinal qualities.
Historical Context and Discovery
Adrenochrome was first found in the 1900s when scientists noticed the oxidation of adrenaline. Since then researchers have studied this compound in scientific experiments to understand its effects and possible uses.
Current Relevance in Medical Science
Adrenochrome is currently being researched for its connections to mental health conditions and its effects on the heart. Its mysterious properties present both an opportunity and a puzzle for the medical field.
What does adrenochrome do?
Adrenochrome is a molecule that's not very stable and doesn't have many practical applications. On the other hand, its carbazochrome3 derivative is more stable and is believed to help with blood clotting, making it useful for treating bleeding issues.
2. Composition of Adrenochrome Injection
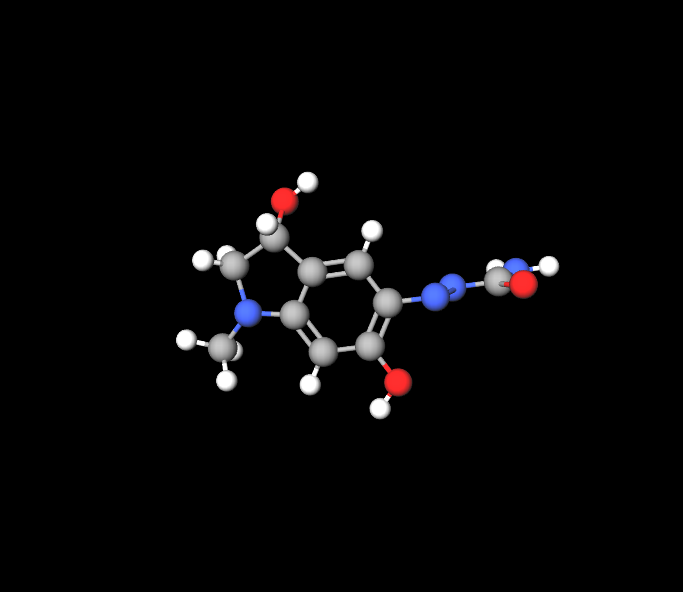
Chemical Structure and Properties
Adrenochrome is a substance derived from adrenaline, known for its properties due to its catecholamine structure and ability to undergo oxidation easily. This unique molecular composition plays a role, in its biological and pharmacological effects.
Active Ingredients and Excipients
The main component found in adrenochrome injections is monosemicarbazone, which is commonly combined with stabilizers such as sodium chloride and sterile water, for injection to guarantee effectiveness and safety during administration.
Formulation Variants and Their Applications
- Injectable solutions are typically employed in situations that require responses, while
- controlled-release formulations are created to provide long-lasting effects and reduce the need for frequent dosing.
How is adrenochrome produced?
Adrenochrome is a substance created through the oxidation of adrenaline (also known as epinephrine).
Epipen adrenochrome
Epinephrine solution degrades quickly when it comes into contact with air or light changing color to pink due to oxidation, into adrenochrome and turning brown because of formation.
3. Pharmacodynamics: How Adrenochrome Works
Mechanism of Action at the Cellular Level
Adrenochrome impacts receptors, influencing the release and absorption of neurotransmitters. Its effects on cells involve changes, in the status, which affect different metabolic processes.
Impact on the Cardiovascular System
Impact on the system involves adjusting heart rate and blood pressure which could be helpful in specific health conditions such, as shock or cardiac arrest.
Psychological Effects and Neurological Pathways
There have been suggestions that adrenochrome might have an impact, on brain activities, which could influence emotions and thinking. However these effects are a topic of debate. Are not completely clear.
4. Therapeutic Uses of Adrenochrome
Clinical Indications and Approved Uses
Role in Hemostasis and Wound Healing
In environments and emergency trauma treatment, its ability to encourage blood clotting and lessen bleeding is highly beneficial.
Effects on Mental Health Disorders
5. Off-Label Uses of Adrenochrome
Unconventional Applications in Medical Practice
Controversial Uses and Community Perspectives
In culture, there are many myths and misunderstandings surrounding the compound, often depicted with a mystical or dangerous aura.
Review of Studies and Clinical Trials on Off-Label Benefits
Studies and experiments conducted recently have started to unveil the applications of adrenochrome with the goal of scientifically validating its potential for wider therapeutic benefits.
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing Recommendations
Adrenochrome is administered carefully and strictly following guidelines in medical environments.
Administration Techniques: Intravenous, Intramuscular
The medication is usually given through intramuscular injections depending on the medical need and how quickly it needs to take effect.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Making sure to adjust the dosage is very important for groups like people, kids, and those with kidney or liver issues.
7. Adrenochrome in Special Populations
Elderly Patients: Considerations and Cautions
Doctors tend to be more careful when prescribing adrenochrome to patients because they are more likely to experience negative side effects and possible interactions with other drugs.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile
Pregnant women and nursing mothers are advised to avoid using it unless necessary, as there is insufficient data on its safety for these groups.
Pediatric Use: Efficacy and Safety Assessment
Adrenochrome is seldom used in children, only in severe cases when other treatments have not been effective and always under careful medical supervision.
8. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common and Minor Side Effects
Adrenochrome injection, similar to medications, may lead to some minor side effects that can cause different levels of discomfort. These may include:
- Headaches and slight dizziness
- Feelings of unease or restlessness
- Heart palpitations or a rapid heartbeat
- Nausea and other digestive issues
- Although these effects are usually temporary, it is advisable to consult a professional if they continue or worsen.
Serious Adverse Effects and Risk Factors
Serious side effects are uncommon. This can happen, particularly when the medication is misused or taken in excessive amounts. Immediate medical attention is needed for the following reactions:
- Extreme low or high blood pressure
- Heart rhythm irregularities
- Psychological symptoms, like hallucinations and intense restlessness
- Factors that can worsen these reactions include pre-existing heart issues, mental health conditions, or a past of substance misuse.
Long-term Health Implications
There is an amount of research on adrenochrome over time, and the lasting effects of using it are not well documented. People are worried about the impact of oxidative stress and how it could affect aging organ function and mental well-being.
9. Important Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Interaction with Common Medications and Supplements
Adrenochrome may react with medications like:
- Blood thinners (for example warfarin) may have their impacts increased.
- MAO inhibitors and some antidepressants could raise the chances of negative cardiovascular incidents.
- Supplements, like St. Johns Wort could enhance its mind altering effects.
Contraindications: Conditions and Risk Factors
There are situations where the use of adrenochrome is not recommended:
- Individuals with severe heart conditions like unstable angina or arrhythmias.
- People, with mental health disorders especially those related to psychosis.
- Those who have a known allergy or sensitivity to adrenochrome or any of its components.
Managing Drug-Drug Interactions
To manage interactions effectively, it's important to:
- Review the patient's history and medications thoroughly before giving any treatment.
- Monitor the patient closely for reactions when using drugs together.
- Adjust medication dosages as needed to minimize the risks of interactions.
10. Warnings and Precautions for Safe Use
Handling and Storage Precautions
Adrenochrome injections should be kept in a controlled room temperature environment shielded from light and moisture to preserve their stability and efficacy.
Warning Signs of Adverse Reactions
Healthcare professionals and individuals should stay alert for symptoms like high blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, or mental changes, as these could signal negative responses.
Emergency Procedures and Antidote Information
In situations where there is a suspicion of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical assistance. There is no antidote for an adrenochrome overdose so the approach to treatment involves addressing symptoms and providing supportive care with an emphasis, on maintaining vital signs and ensuring the patients comfort.
11. Overdose Management and Emergency Response
Symptoms and Immediate Actions
Signs of taking too much adrenochrome can lead to significant alterations in heart function, intense mental disruptions, and breathing difficulties. It is crucial to:
- Contact emergency services,
- Offer necessary care like oxygen and IV fluids
- Keep a close watch on heart and lung health for stability
Medical Treatments and Interventions
When dealing with an adrenochrome overdose, the main approach centers on care which includes:
- Using beta blockers to address heart-related symptoms
- Providing sedatives for intense restlessness or mental disturbances
- Restoring electrolyte balance and correcting any acid-base issues
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring Strategies
After an emergency, it's important to keep a close eye on patients for any lingering issues. This includes
- Checking their heart health
- Providing mental health checkups and assistance
- Watch out for any recurring symptoms over the long term.